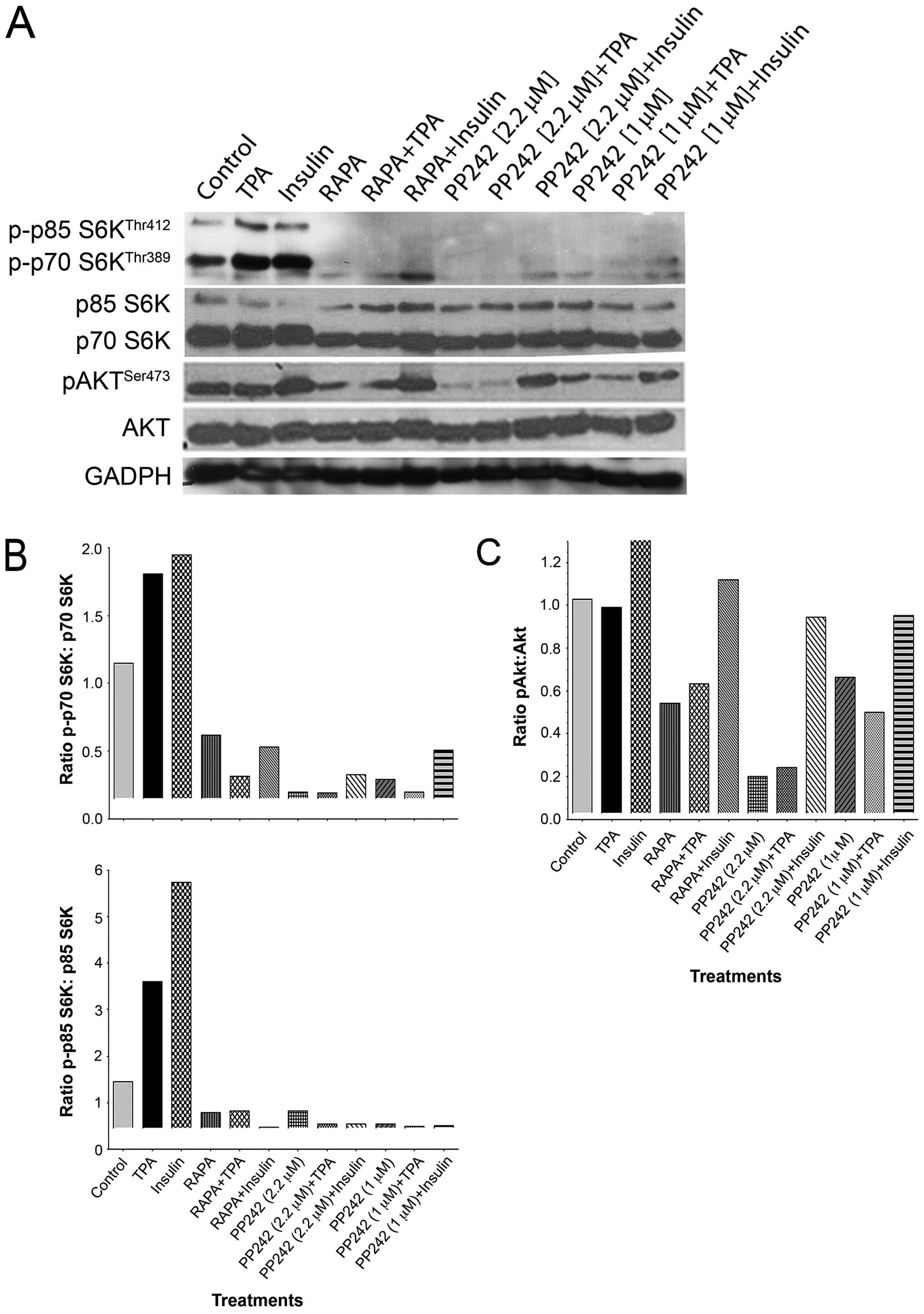
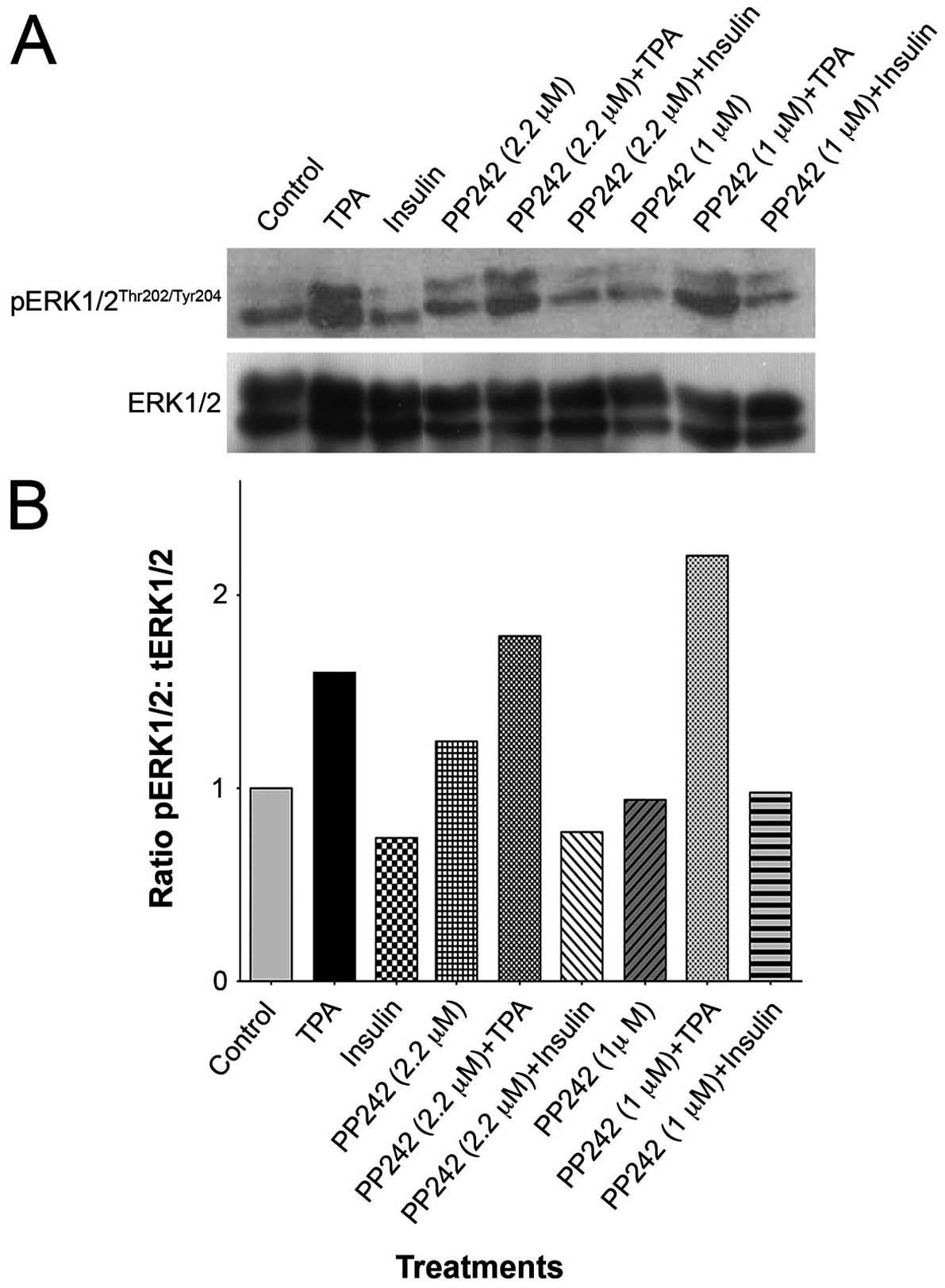
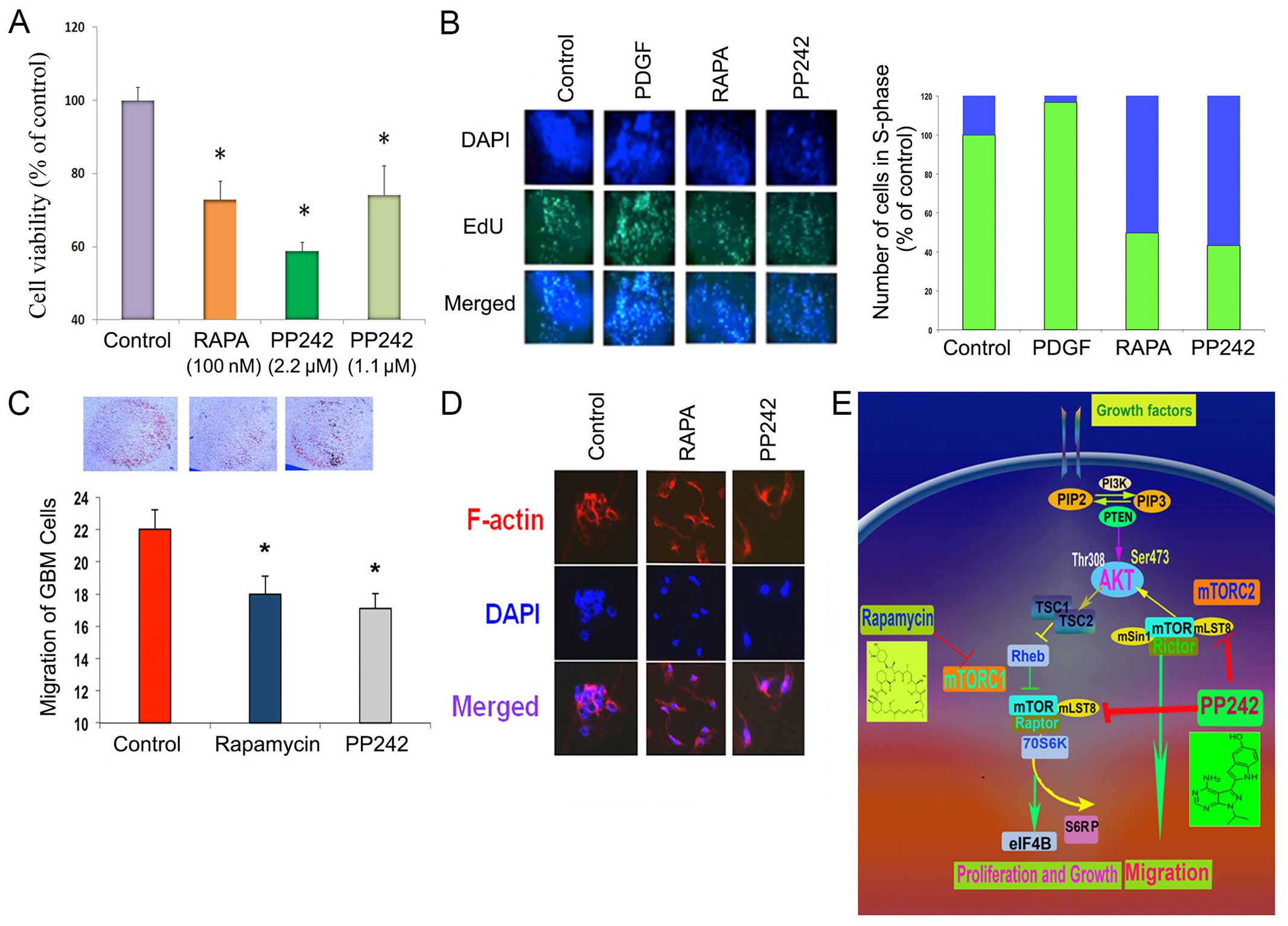
|
1
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of
Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer
Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Radiotherapy plus
concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J
Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Genetic pathways
to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am J Pathol. 170:1445–1453.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V,
Qi Y, Wilkerson MD, Miller CR, Ding L, Golub T, Mesirov JP, et al;
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic analysis
identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma
characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1.
Cancer Cell. 17:98–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Phillips HS, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Forrest
WF, Soriano RH, Wu TD, Misra A, Nigro JM, Colman H, Soroceanu L, et
al: Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis,
delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in
neurogenesis. Cancer Cell. 9:157–173. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu X, Pandolfi PP, Li Y, Koutcher JA,
Rosenblum M and Holland EC: mTOR promotes survival and astrocytic
characteristics induced by Pten/AKT signaling in glioblastoma.
Neoplasia. 7:356–368. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nutt C and Louis D: Cancer of the Nervous
System. 2nd edition. McGraw-Hill; New York: 2005
|
|
7
|
Berger AH and Pandolfi PP:
Haplo-insufficiency: A driving force in cancer. J Pathol.
223:137–146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Di Cristofano A, Pesce B, Cordon-Cardo C
and Pandolfi PP: Pten is essential for embryonic development and
tumour suppression. Nat Genet. 19:348–355. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Carracedo A and Pandolfi PP: The PTEN-PI3K
pathway: Of feedbacks and cross-talks. Oncogene. 27:5527–5541.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Groszer M, Erickson R, Scripture-Adams DD,
Dougherty JD, Le Belle J, Zack JA, Geschwind DH, Liu X, Kornblum HI
and Wu H: PTEN negatively regulates neural stem cell self-renewal
by modulating G0–G1 cell cycle entry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:111–116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hay N and Sonenberg N: Upstream and
downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 18:1926–1945. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Holland EC: Gliomagenesis: Genetic
alterations and mouse models. Nat Rev Genet. 2:120–129. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guertin DA and Sabatini DM: Defining the
role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell. 12:9–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jacinto E and Hall MN: Tor signalling in
bugs, brain and brawn. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:117–126. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sabatini DM: mTOR and cancer: Insights
into a complex relationship. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:729–734. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ruggero D, Montanaro L, Ma L, Xu W, Londei
P, Cordon-Cardo C and Pandolfi PP: The translation factor eIF-4E
promotes tumor formation and cooperates with c-Myc in
lymphomagenesis. Nat Med. 10:484–486. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hara K, Maruki Y, Long X, Yoshino K,
Oshiro N, Hidayat S, Tokunaga C, Avruch J and Yonezawa K: Raptor, a
binding partner of target of rapamycin (TOR), mediates TOR action.
Cell. 110:177–189. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jacinto E, Loewith R, Schmidt A, Lin S,
Rüegg MA, Hall A and Hall MN: Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the
actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive. Nat Cell Biol.
6:1122–1128. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim DH, Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, King JE,
Latek RR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P and Sabatini DM: mTOR
interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that
signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell. 110:163–175. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Kim DH, Guertin DA,
Latek RR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P and Sabatini DM: Rictor, a
novel binding partner of mTOR, defines a rapamycin-insensitive and
raptor-independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton. Curr
Biol. 14:1296–1302. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brown EJ, Beal PA, Keith CT, Chen J, Shin
TB and Schreiber SL: Control of p70 s6 kinase by kinase activity of
FRAP in vivo. Nature. 377:441–446. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gingras AC, Kennedy SG, O'Leary MA,
Sonenberg N and Hay N: 4E-BP1, a repressor of mRNA translation, is
phosphorylated and inactivated by the Akt(PKB) signaling pathway.
Genes Dev. 12:502–513. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ruvinsky I and Meyuhas O: Ribosomal
protein S6 phosphorylation: From protein synthesis to cell size.
Trends Biochem Sci. 31:342–348. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
García-Martínez JM and Alessi DR: mTOR
complex 2 (mTORC2) controls hydrophobic motif phosphorylation and
activation of serum- and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase 1
(SGK1). Biochem J. 416:375–385. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM and
Sabatini DM: Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the
rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 307:1098–1101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han EK, Leverson JD, McGonigal T, Shah OJ,
Woods KW, Hunter T, Giranda VL and Luo Y: Akt inhibitor A-443654
induces rapid Akt Ser-473 phosphorylation independent of mTORC1
inhibition. Oncogene. 26:5655–5661. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cloughesy TF, Yoshimoto K, Nghiemphu P,
Brown K, Dang J, Zhu S, Hsueh T, Chen Y, Wang W, Youngkin D, et al:
Antitumor activity of rapamycin in a Phase I trial for patients
with recurrent PTEN-deficient glioblastoma. PLoS Med. 5:e82008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Albert L, Karsy M, Murali R and
Jhanwar-Uniyal M: Inhibition of mTOR activates the MAPK pathway in
glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 6:255–261.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guertin DA, Stevens DM, Thoreen CC, Burds
AA, Kalaany NY, Moffat J, Brown M, Fitzgerald KJ and Sabatini DM:
Ablation in mice of the mTORC components raptor, rictor, or mLST8
reveals that mTORC2 is required for signaling to Akt-FOXO and
PKCalpha, but not S6K1. Dev Cell. 11:859–871. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gulati N, Karsy M, Albert L, Murali R and
Jhanwar-Uniyal M: Involvement of mTORC1 and mTORC2 in regulation of
glioblastoma multiforme growth and motility. Int J Oncol.
35:731–740. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jacinto E, Facchinetti V, Liu D, Soto N,
Wei S, Jung SY, Huang Q, Qin J and Su B: SIN1/MIP1 maintains
rictor-mTOR complex integrity and regulates Akt phosphorylation and
substrate specificity. Cell. 127:125–137. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Sengupta S, Sheen
JH, Hsu PP, Bagley AF, Markhard AL and Sabatini DM: Prolonged
rapamycin treatment inhibits mTORC2 assembly and Akt/PKB. Mol Cell.
22:159–168. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Feldman ME, Apsel B, Uotila A, Loewith R,
Knight ZA, Ruggero D and Shokat KM: Active-site inhibitors of mTOR
target rapamycin-resistant outputs of mTORC1 and mTORC2. PLoS Biol.
7:e382009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chang SM, Wen P, Cloughesy T, Greenberg H,
Schiff D, Conrad C, Fink K, Robins HI, De Angelis L, Raizer J, et
al; North American Brain Tumor Consortium and the National Cancer
Institute. Phase II study of CCI-779 in patients with recurrent
glioblastoma multiforme. Invest New Drugs. 23:357–361. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Eshleman JS, Carlson BL, Mladek AC,
Kastner BD, Shide KL and Sarkaria JN: Inhibition of the mammalian
target of rapamycin sensitizes U87 xenografts to fractionated
radiation therapy. Cancer Res. 62:7291–7297. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gulati P and Thomas G: Nutrient sensing in
the mTOR/S6K1 signalling pathway. Biochem Soc Trans. 35:236–238.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network.
Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma
genes and core pathways. Nature. 455:1061–1068. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, Lin JC,
Leary RJ, Angenendt P, Mankoo P, Carter H, Siu IM, Gallia GL, et
al: An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma
multiforme. Science. 321:1807–1812. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim DH, Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Latek RR,
Guntur KV, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P and Sabatini DM: GbetaL, a
positive regulator of the rapamycin-sensitive pathway required for
the nutrient-sensitive interaction between raptor and mTOR. Mol
Cell. 11:895–904. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zeng Z, Sarbassov D, Samudio IJ, Yee KW,
Munsell MF, Ellen Jackson C, Giles FJ, Sabatini DM, Andreeff M and
Konopleva M: Rapamycin derivatives reduce mTORC2 signaling and
inhibit AKT activation in AML. Blood. 109:3509–3512. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Knight ZA, Gonzalez B, Feldman ME, Zunder
ER, Goldenberg DD, Williams O, Loewith R, Stokoe D, Balla A, Toth
B, et al: A pharmacological map of the PI3-K family defines a role
for p110alpha in insulin signaling. Cell. 125:733–747. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jhanwar-Uniyal M, Albert L, McKenna E,
Karsy M, Rajdev P, Braun A and Murali R: Deciphering the signaling
pathways of cancer stem cells of glioblastoma multiforme: Role of
Akt/mTOR and MAPK pathways. Adv Enzyme Regul. 51:164–170. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Jhanwar-Uniyal M, Jeevan D, Neil J,
Shannon C, Albert L and Murali R: Deconstructing mTOR complexes in
regulation of Glioblastoma Multiforme and its stem cells. Adv Biol
Regul. 53:202–210. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Jhanwar-Uniyal M, Labagnara M, Friedman M,
Kwasnicki A and Murali R: Glioblastoma: Molecular pathways, stem
cells and therapeutic targets. Cancers (Basel). 7:538–555. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Jhanwar-Uniyal M, Gillick JL, Neil J,
Tobias M, Thwing ZE and Murali R: Distinct signaling mechanisms of
mTORC1 and mTORC2 in glioblastoma multiforme: A tale of two
complexes. Adv Biol Regul. 57:64–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
McCubrey JA, Abrams SL, Fitzgerald TL,
Cocco L, Martelli AM, Montalto G, Cervello M, Scalisi A, Candido S,
Libra M, et al: Roles of signaling pathways in drug resistance,
cancer initiating cells and cancer progression and metastasis. Adv
Biol Regul. 57:75–101. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|