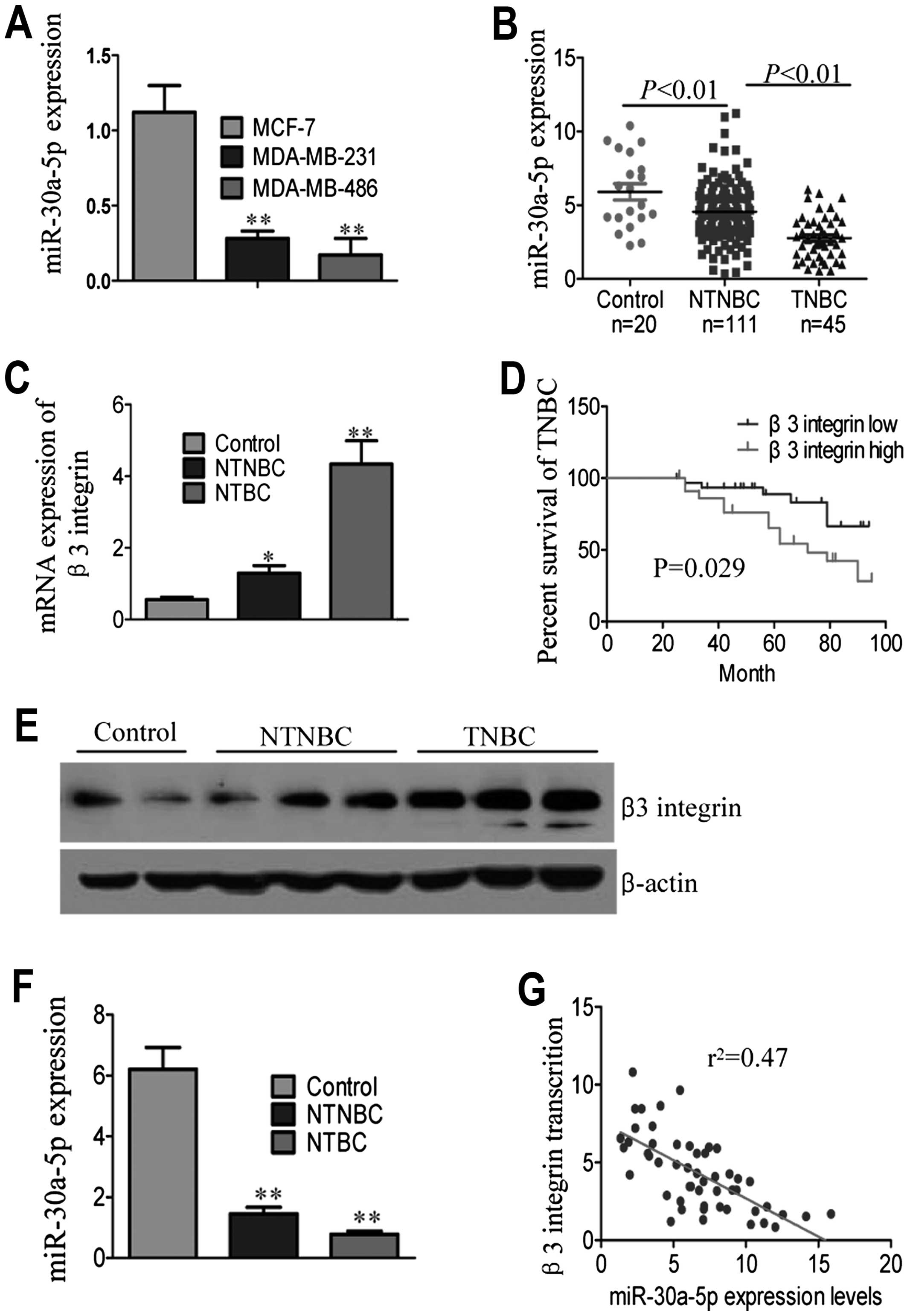
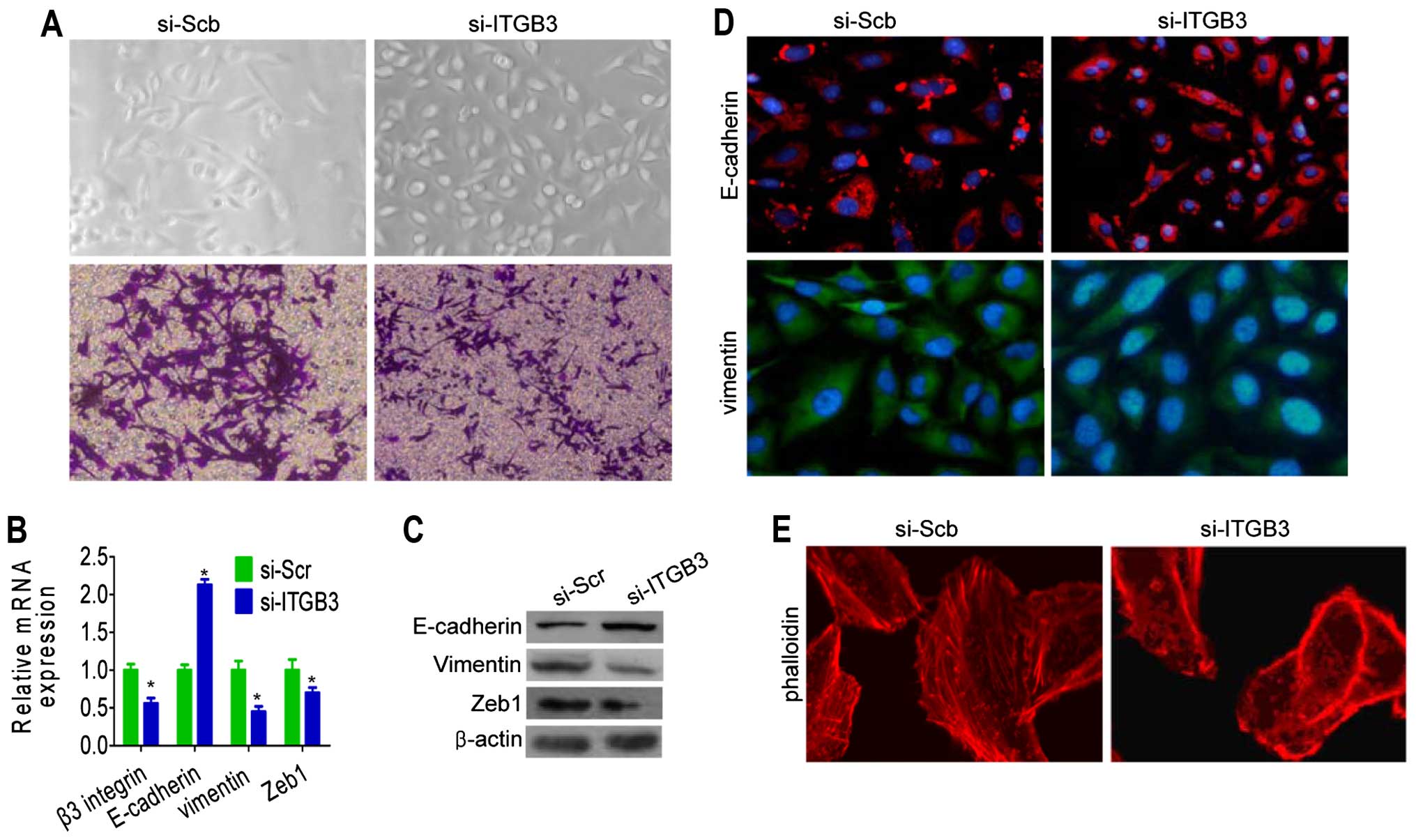
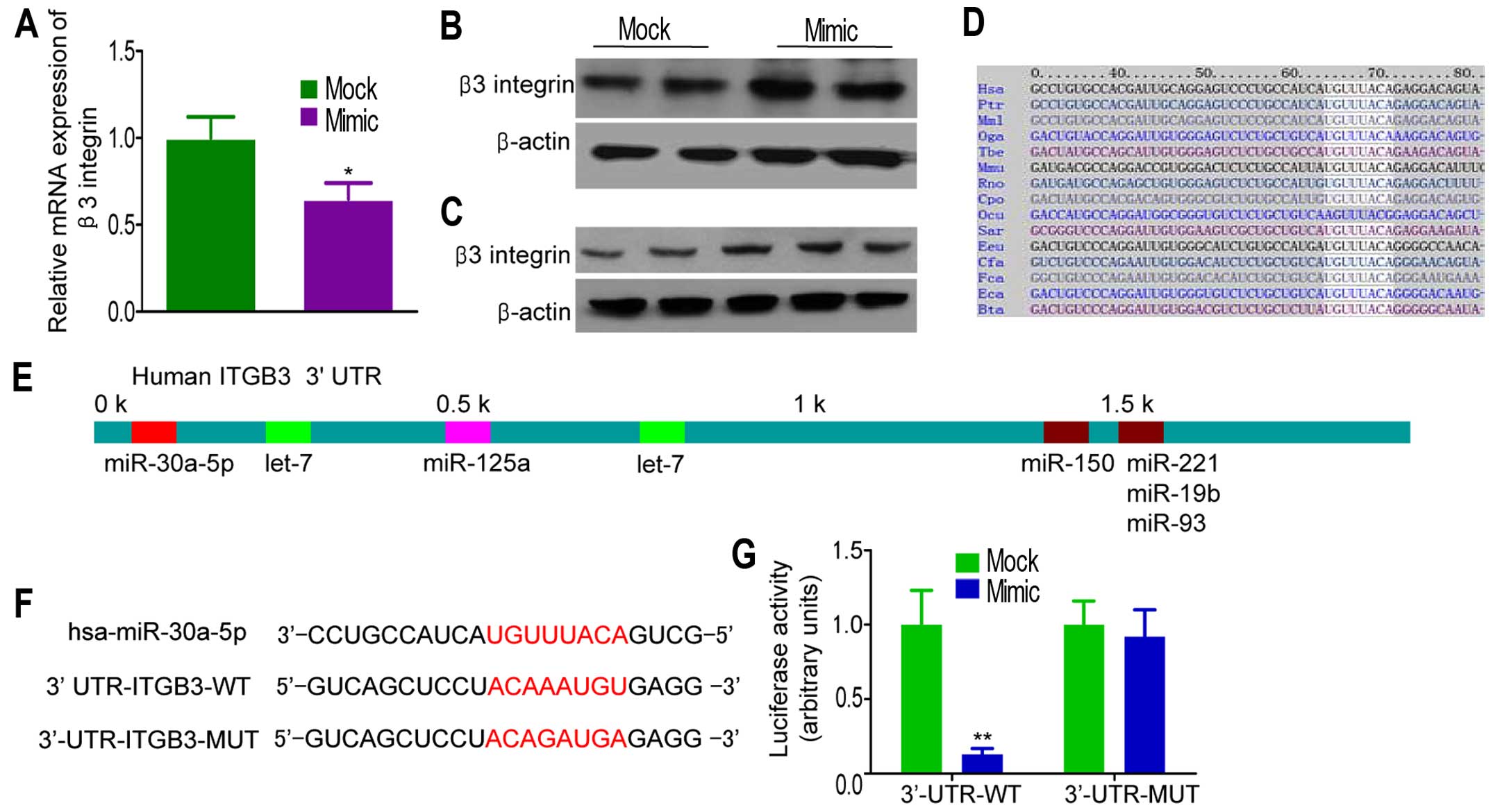
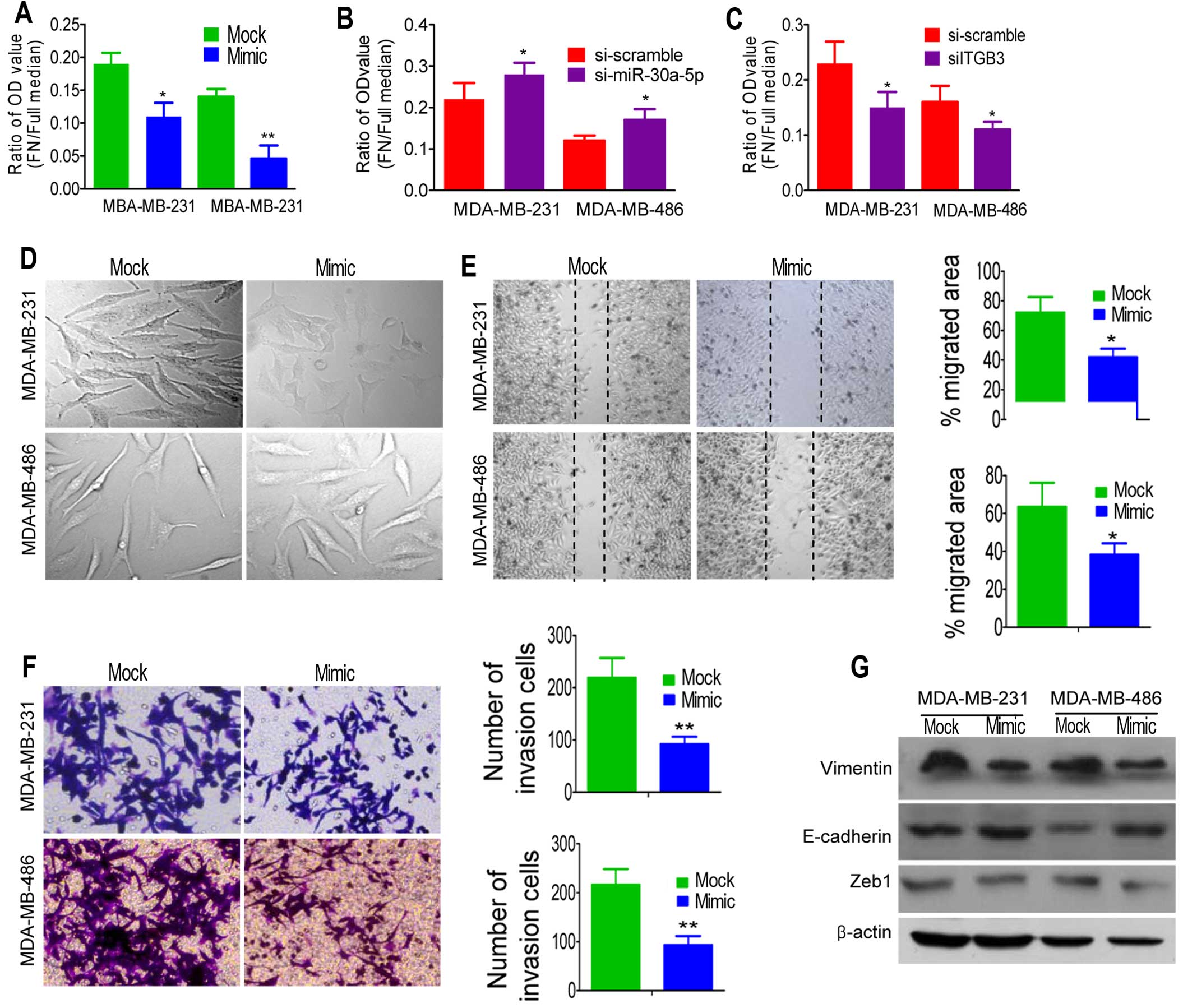
|
1
|
Taylor MA, Davuluri G, Parvani JG,
Schiemann BJ, Wendt MK, Plow EF, Schiemann WP and Sossey-Alaoui K:
Upregulated WAVE3 expression is essential for TGF-β-mediated EMT
and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 142:341–353. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Barcus CE, Keely PJ, Eliceiri KW and
Schuler LA: Stiff collagen matrices increase tumorigenic prolactin
signaling in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 288:12722–12732.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang Y, Shenouda S, Baranwal S, Rathinam
R, Jain P, Bao L, Hazari S, Dash S and Alahari SK: Integrin
subunits alpha5 and alpha6 regulate cell cycle by modulating the
chk1 and Rb/E2F pathways to affect breast cancer metastasis. Mol
Cancer. 10:842011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Felding-Habermann B, O'Toole TE, Smith JW,
Fransvea E, Ruggeri ZM, Ginsberg MH, Hughes PE, Pampori N, Shattil
SJ, Saven A, et al: Integrin activation controls metastasis in
human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:1853–1858. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Salvo E, Garasa S, Dotor J, Morales X,
Peláez R, Altevogt P and Rouzaut A: Combined targeting of TGF-β1
and integrin β3 impairs lymph node metastasis in a mouse model of
non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 13:1122014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li N, Zhang JP, Guo S, Min J, Liu LL, Su
HC, Feng YM and Zhang HL: Down-regulation of β3-integrin inhibits
bone metastasis of small cell lung cancer. Mol Biol Rep.
39:3029–3035. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Parvani JG, Gujrati MD, Mack MA, Schiemann
WP and Lu ZR: Silencing β3 integrin by targeted ECO/siRNA
nanoparticles inhibits EMT and metastasis of triple-negative breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 75:2316–2325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huveneers S and Danen EH: Adhesion
signaling - crosstalk between integrins, Src and Rho. J Cell Sci.
122:1059–1069. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Raymond K, Faraldo MM, Deugnier MA and
Glukhova MA: Integrins in mammary development. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
23:599–605. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Harquail J, Benzina S and Robichaud GA:
MicroRNAs and breast cancer malignancy: an overview of
miRNA-regulated cancer processes leading to metastasis. Cancer
biomarkers: section. Dis Markers. 11:269–280. 2012.
|
|
11
|
de Krijger I, Mekenkamp LJ, Punt CJ and
Nagtegaal ID: MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer metastasis. J Pathol.
224:438–447. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shi M and Guo N: MicroRNA expression and
its implications for the diagnosis and therapeutic strategies of
breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 35:328–334. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang N, Wang X, Huo Q, Sun M, Cai C, Liu
Z, Hu G and Yang Q: MicroRNA-30a suppresses breast tumor growth and
metastasis by targeting metadherin. Oncogene. 33:3119–3128. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kao CJ, Martiniez A, Shi XB, Yang J, Evans
CP, Dobi A, deVere White RW and Kung HJ: miR-30 as a tumor
suppressor connects EGF/Src signal to ERG and EMT. Oncogene.
33:2495–2503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Baraniskin A, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K,
Maghnouj A, Zöllner H, Munding J, Klein-Scory S, Reinacher-Schick
A, Schwarte-Waldhoff I, Schmiegel W and Hahn SA: MiR-30a-5p
suppresses tumor growth in colon carcinoma by targeting DTL.
Carcinogenesis. 33:732–739. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu G, Chong RA, Yang Q, Wei Y, Blanco MA,
Li F, Reiss M, Au JL, Haffty BG and Kang Y: MTDH activation by 8q22
genomic gain promotes chemoresistance and metastasis of
poor-prognosis breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 15:9–20. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Heckman KL and Pease LR: Gene splicing and
mutagenesis by PCR-driven overlap extension. Nat Protoc. 2:924–932.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Knowles LM, Gurski LA, Engel C, Gnarra JR,
Maranchie JK and Pilch J: Integrin αvβ3 and fibronectin upregulate
Slug in cancer cells to promote clot invasion and metastasis.
Cancer Res. 73:6175–6184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hynes RO: Integrins: Bidirectional,
allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 110:673–687. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hynes RO: Targeted mutations in cell
adhesion genes: What have we learned from them? Dev Biol.
180:402–412. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morgan MR, Humphries MJ and Bass MD:
Synergistic control of cell adhesion by integrins and syndecans.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:957–969. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gehler S, Ponik SM, Riching KM and Keely
PJ: Bi-directional signaling: Extracellular matrix and integrin
regulation of breast tumor progression. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene
Expr. 23:139–157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Truong HH, Xiong J, Ghotra VP, Nirmala E,
Haazen L, Le Dévédec SE, Balcioğlu HE, He S, Snaar-Jagalska BE,
Vreugdenhil E, et al: β1 integrin inhibition elicits a
prometastatic switch through the TGFβ-miR-200-ZEB network in
E-cadherin-positive triple-negative breast cancer. Sci Signal.
7:ra152014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sumimoto S, Muramatsu R, Fujii S and
Yamashita T: Vascular endothelial cells promote cortical neurite
outgrowth via an integrin β3-dependent mechanism. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 450:593–597. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nasulewicz-Goldeman A, Uszczyńska B,
Szczaurska-Nowak K and Wietrzyk J: siRNA-mediated silencing of
integrin β3 expression inhibits the metastatic potential of B16
melanoma cells. Oncol Rep. 28:1567–1573. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li A, Guo Q, Kim C, Hu W and Ye F:
Integrin alphaII b tail distal of GFFKR participates in inside-out
alphaII b beta3 activation. J Thromb Haemost. 12:1145–1155. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Beauvais DM and Rapraeger AC:
Syndecan-1-mediated cell spreading requires signaling by
alphavbeta3 integrins in human breast carcinoma cells. Exp Cell
Res. 286:219–232. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kudo-Saito C, Shirako H, Takeuchi T and
Kawakami Y: Cancer metastasis is accelerated through
immunosuppression during Snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer
Cell. 15:195–206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Hlubek F, Berx
G, Eger A, Merkel S, Jung A, Kirchner T and Brabletz T: A
transient, EMT-linked loss of basement membranes indicates
metastasis and poor survival in colorectal cancer.
Gastroenterology. 131:830–840. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Augoff K, Das M, Bialkowska K, McCue B,
Plow EF and Sossey-Alaoui K: miR-31 is a broad regulator of
β1-integrin expression and function in cancer cells. Mol Cancer
Res. 9:1500–1508. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Frijns E, Sachs N, Kreft M, Wilhelmsen K
and Sonnenberg A: EGF-induced MAPK signaling inhibits hemidesmosome
formation through phosphorylation of the integrin {beta}4. J Biol
Chem. 285:37650–37662. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wei Y, Tang CH, Kim Y, Robillard L, Zhang
F, Kugler MC and Chapman HA: Urokinase receptors are required for
alpha 5 beta 1 integrin-mediated signaling in tumor cells. J Biol
Chem. 282:3929–3939. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sato T and Miwa A: Ets-1 and integrin
beta3 for lung metastasis from colorectal cancer. APMIS.
110:347–353. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rothhammer T, Hahne JC, Florin A, Poser I,
Soncin F, Wernert N and Bosserhoff AK: The Ets-1 transcription
factor is involved in the development and invasion of malignant
melanoma. Cell Mol Life Sci. 61:118–128. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|