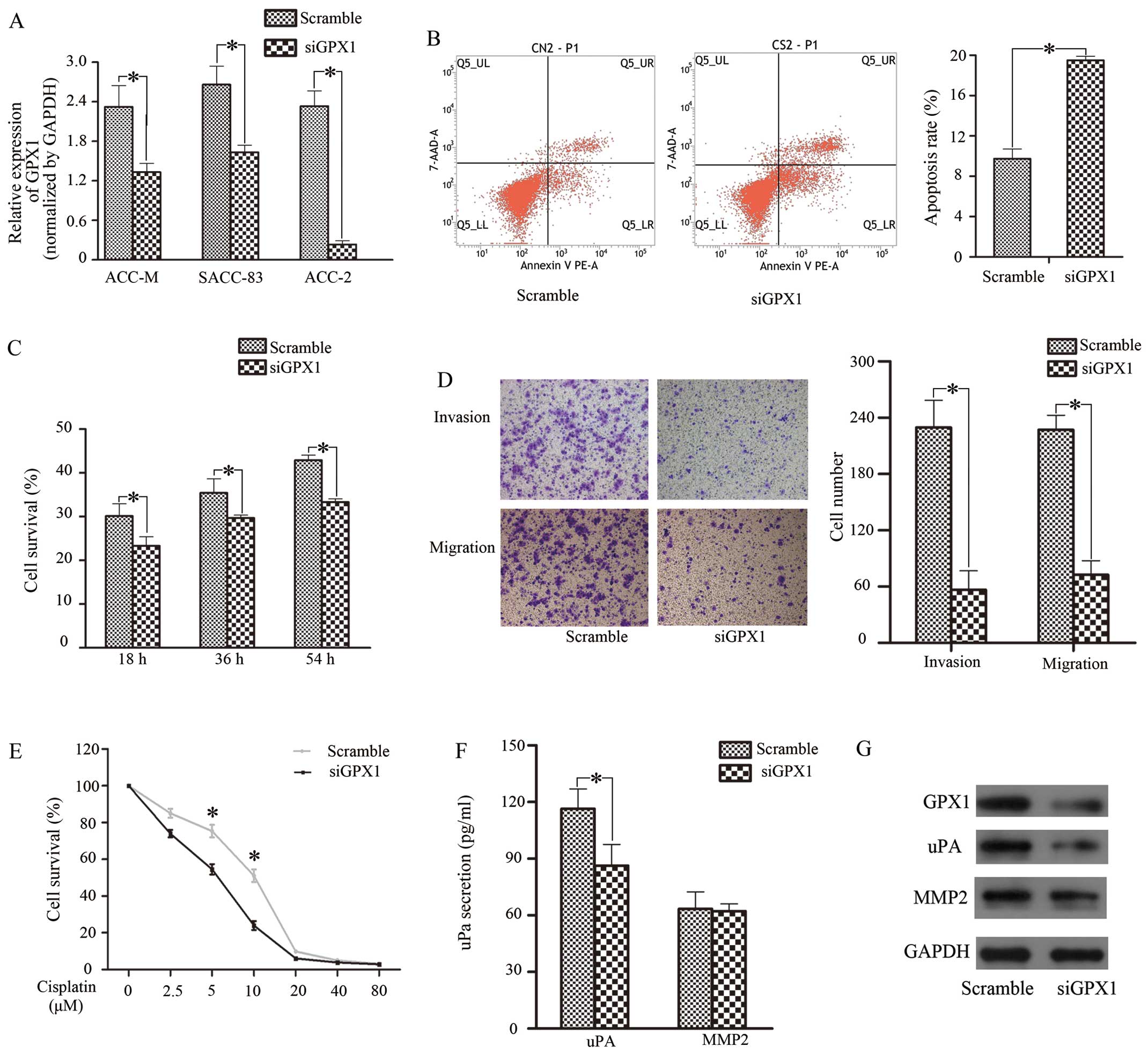
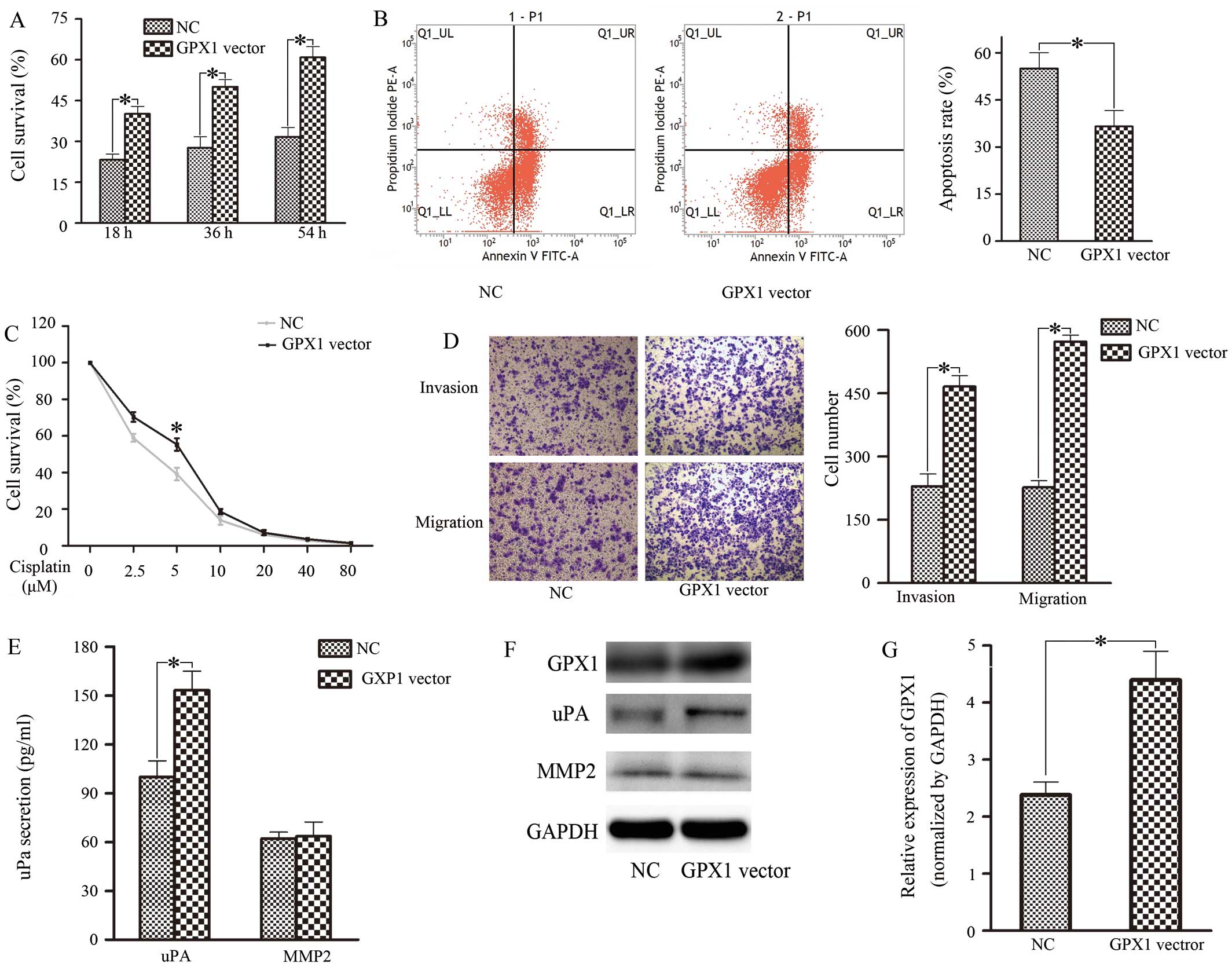
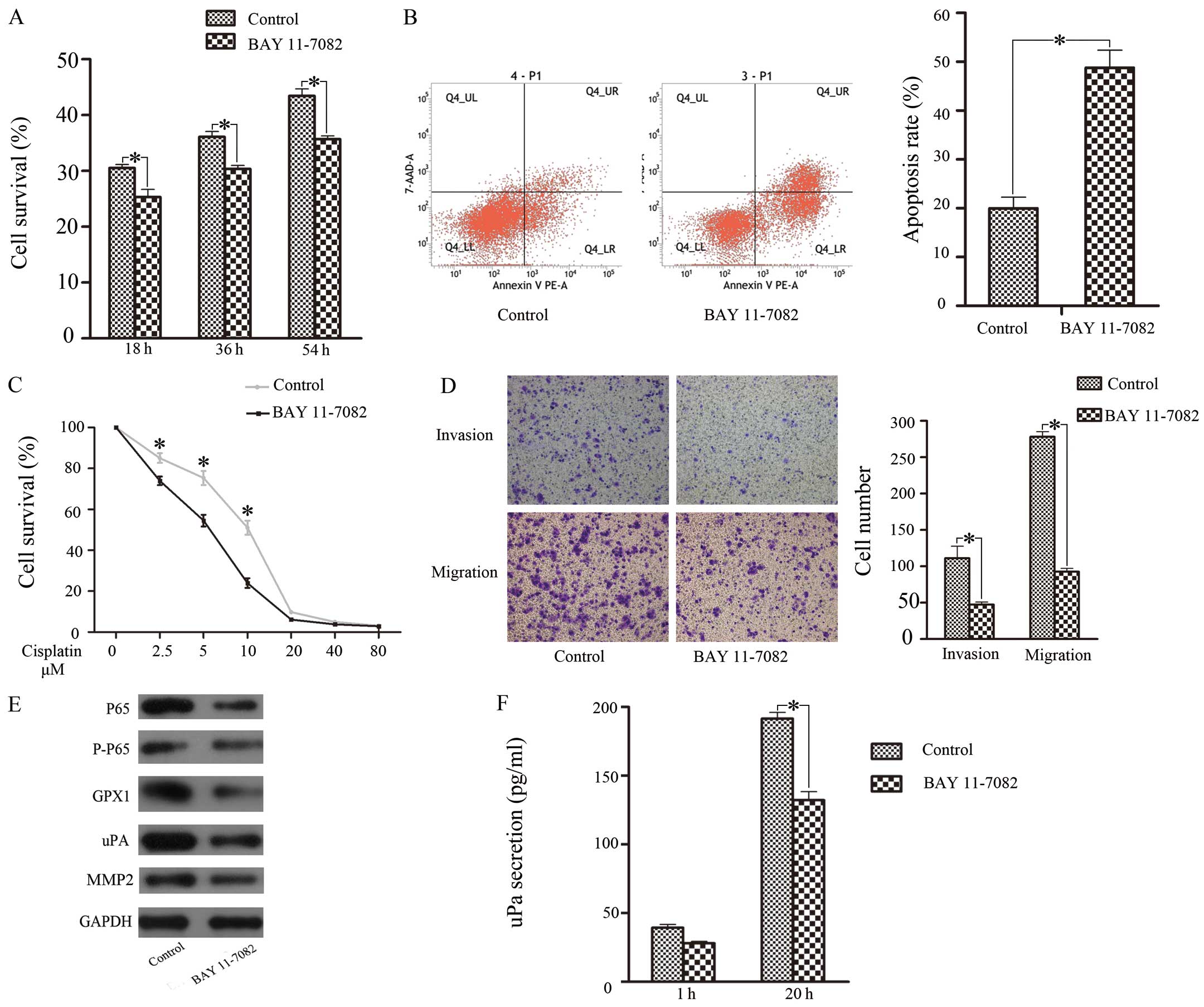
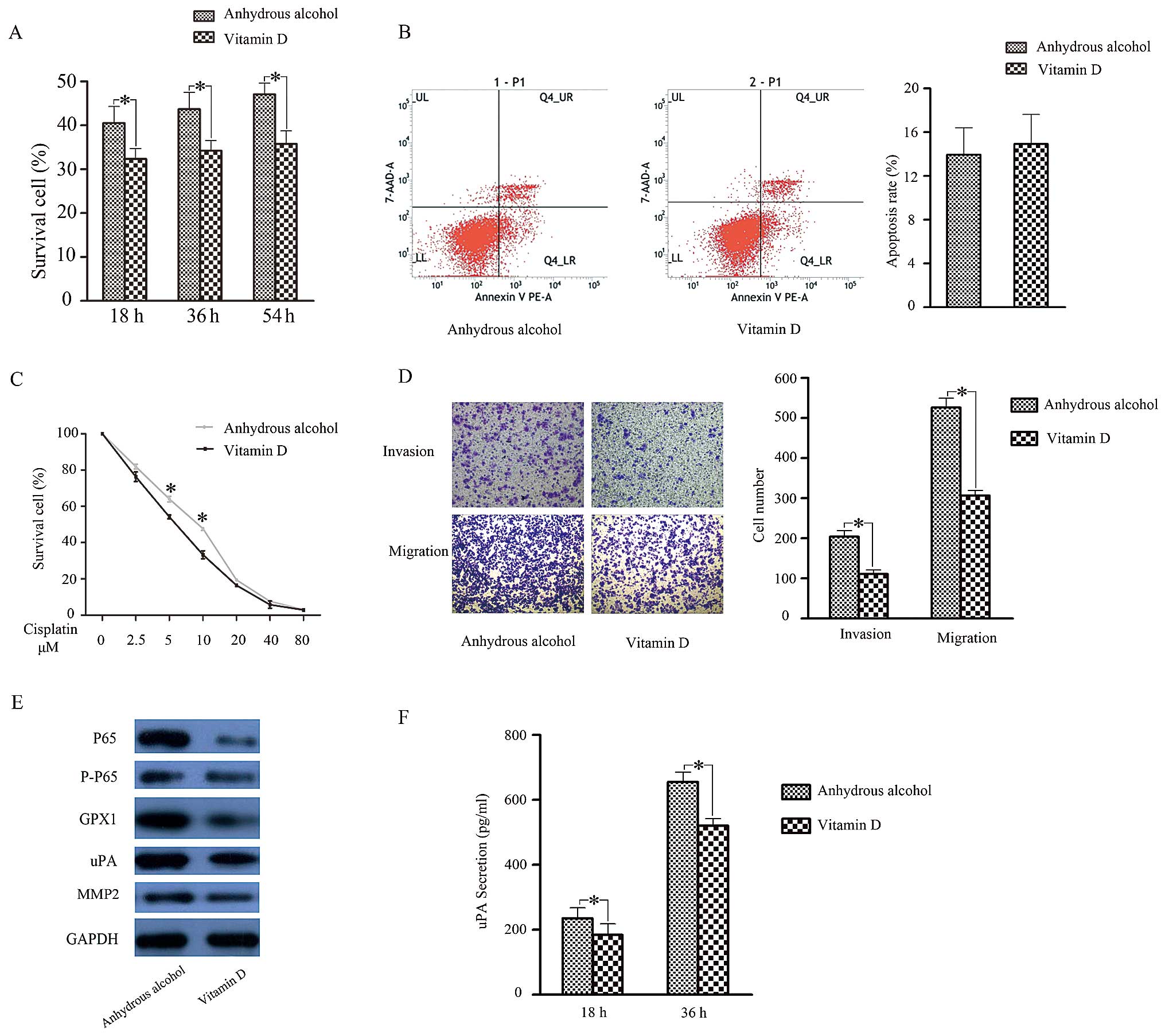
|
1
|
Thompson L: World Health Organization
classification of tumours: Pathology and genetics of head and neck
tumours. Ear Nose Throat J. 85:742006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fordice J, Kershaw C, El-Naggar A and
Goepfert H: Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck:
Predictors of morbidity and mortality. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck
Surg. 125:149–152. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Colevas AD: Chemotherapy options for
patients with metastatic or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of
the head and neck. J Clin Oncol. 24:2644–2652. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brigelius-Flohé R: Tissue-specific
functions of individual glutathione peroxidases. Free Radic Biol
Med. 27:951–965. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lubos E, Loscalzo J and Handy DE:
Glutathione peroxidase-1 in health and disease: From molecular
mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal.
15:1957–1997. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Fu TY, Hou YY, Chu ST, Liu CF, Huang CH,
Chen HC, Hsiao M, Lu PJ, Wang JS and Ger LP: Manganese superoxide
dismutase and glutathione peroxidase as prognostic markers in
patients with buccal mucosal squamous cell carcinomas. Head Neck.
33:1606–1615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schumacker PT: Reactive oxygen species in
cancer cells: Live by the sword, die by the sword. Cancer Cell.
10:175–176. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gong G, Méplan C, Gautrey H, Hall J and
Hesketh JE: Differential effects of selenium and knock-down of
glutathione peroxidases on TNFα and flagellin inflammatory
responses in gut epithelial cells. Genes Nutr. 7:167–178. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Schreck R, Albermann K and Baeuerle PA:
Nuclear factor kappa B: An oxidative stress-responsive
transcription factor of eukaryotic cells (Review). Free Radic Res
Commun. 17:221–237. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vibet S, Goupille C, Bougnoux P, Steghens
JP, Goré J and Mahéo K: Sensitization by docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
of breast cancer cells to anthracyclines through loss of
glutathione peroxidase (GPx1) response. Free Radic Biol Med.
44:1483–1491. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Feldman D, Krishnan AV, Swami S,
Giovannucci E and Feldman BJ: The role of vitamin D in reducing
cancer risk and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:342–357. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ting HJ, Messing J, Yasmin-Karim S and Lee
YF: Identification of microRNA-98 as a therapeutic target
inhibiting prostate cancer growth and a biomarker induced by
vitamin D. J Biol Chem. 288:1–9. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Krishnan AV, Swami S and Feldman D: The
potential therapeutic benefits of vitamin D in the treatment of
estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. Steroids. 77:1107–1112.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bao BY, Yao J and Lee YF: 1alpha,
25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses interleukin-8-mediated prostate
cancer cell angiogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 27:1883–1893. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tse AK, Zhu GY, Wan CK, Shen XL, Yu ZL and
Fong WF: 1alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits transcriptional
potential of nuclear factor kappa B in breast cancer cells. Mol
Immunol. 47:1728–1738. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rosli SN, Shintani T, Hayashido Y,
Toratani S, Usui E and Okamoto T: 1α,25OH2D3 down-regulates
HBp17/FGFBP-1 expression via NF-κB pathway. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 136:98–101. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Janjetovic Z, Brozyna AA, Tuckey RC, Kim
TK, Nguyen MN, Jozwicki W, Pfeffer SR, Pfeffer LM and Slominski AT:
High basal NF-κB activity in nonpigmented melanoma cells is
associated with an enhanced sensitivity to vitamin D3 derivatives.
Br J Cancer. 105:1874–1884. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang Z, Huang H, Li H, Chen W and Pan C:
EMMPRIN expression in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol
Med. 38:518–523. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang Z, Tan N, Guo W, Wang L, Li H, Zhang
T, Liu X, Xu Q, Li J and Guo Z: Overexpression of EMMPRIN isoform 2
is associated with head and neck cancer metastasis. PLoS One.
9:e915962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ghashghaeinia M, Toulany M, Saki M,
Bobbala D, Fehrenbacher B, Rupec R, Rodemann HP, Ghoreschi K,
Röcken M, Schaller M, et al: The NFκB pathway inhibitors Bay
11-7082 and parthenolide induce programmed cell death in anucleated
erythrocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 27:45–54. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kim KH, Sung MW, Chung PS, Rhee CS, Park
CI and Kim WH: Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck. Arch
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 120:721–726. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Matsuba HM, Spector GJ, Thawley SE,
Simpson JR, Mauney M and Pikul FJ: Adenoid cystic salivary gland
carcinoma. A histopathologic review of treatment failure patterns.
Cancer. 57:519–524. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sung MW, Kim KH, Kim JW, Min YG, Seong WJ,
Roh JL, Lee SJ, Kwon TK and Park SW: Clinicopathologic predictors
and impact of distant metastasis from adenoid cystic carcinoma of
the head and neck. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 129:1193–1197.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Takata Y, Kristal AR, Santella RM, King
IB, Duggan DJ, Lampe JW, Rayman MP, Blount PL, Reid BJ, Vaughan TL,
et al: Selenium, selenoenzymes, oxidative stress and risk of
neoplastic progression from Barrett's esophagus: Results from
biomarkers and genetic variants. PLoS One. 7:e386122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cao M, Mu X, Jiang C, Yang G, Chen H and
Xue W: Single-nucleotide polymorphisms of GPX1 and MnSOD and
susceptibility to bladder cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 35:759–764. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Dibra D, Mishra L and Li S: Molecular
mechanisms of oncogene-induced inflammation and
inflammation-sustained oncogene activation in gastrointestinal
tumors: An under-appreciated symbiotic relationship. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1846:152–160. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Harte MT, Gorski JJ, Savage KI, Purcell
JW, Barros EM, Burn PM, McFarlane C, Mullan PB, Kennedy RD, Perkins
ND, et al: NF-κB is a critical mediator of BRCA1-induced
chemoresistance. Oncogene. 33:713–723. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Wang H, Khor TO, Yang Q, Huang Y, Wu TY,
Saw CL, Lin W, Androulakis IP and Kong AN: Pharmacokinetics and
pharmacodynamics of phase II drug metabolizing/antioxidant enzymes
gene response by anticancer agent sulforaphane in rat lymphocytes.
Mol Pharm. 9:2819–2827. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Murphy AB, Nyame Y, Martin IK, Catalona
WJ, Hollowell CM, Nadler RB, Kozlowski JM, Perry KT, Kajdacsy-Balla
A and Kittles R: Vitamin D deficiency predicts prostate biopsy
outcomes. Clin Cancer Res. 20:2289–2299. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Grant WB: Vitamin D status: Ready for
guiding prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment? Clin Cancer Res.
20:2241–2243. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gilmore TD: The Rel/NF-kappaB signal
transduction pathway: Introduction. Oncogene. 18:6842–6844. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Thota C, Laknaur A, Farmer T, Ladson G,
Al-Hendy A and Ismail N: Vitamin D regulates contractile profile in
human uterine myometrial cells via NF-κB pathway. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 210:347.e1–347.e10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|