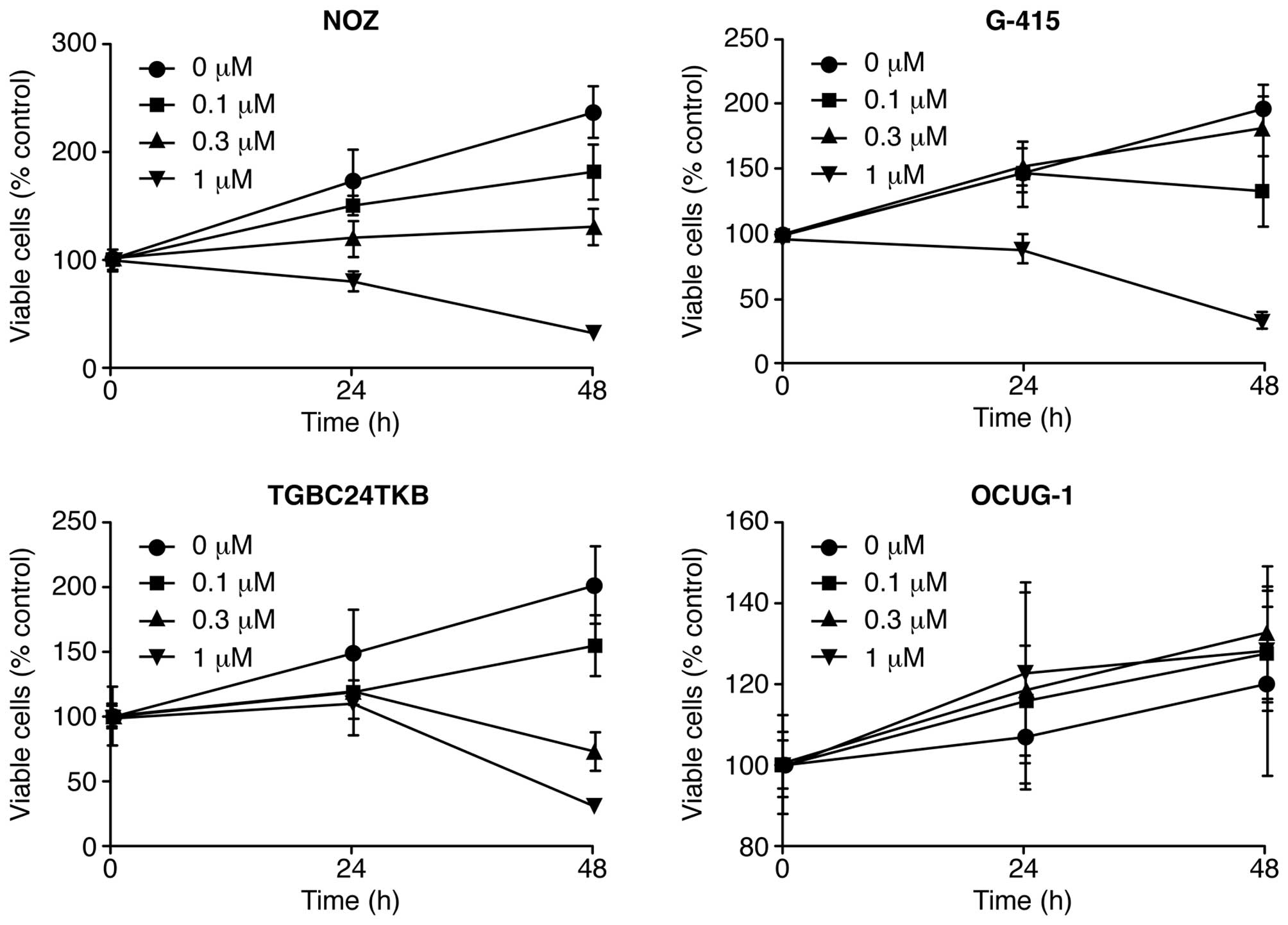
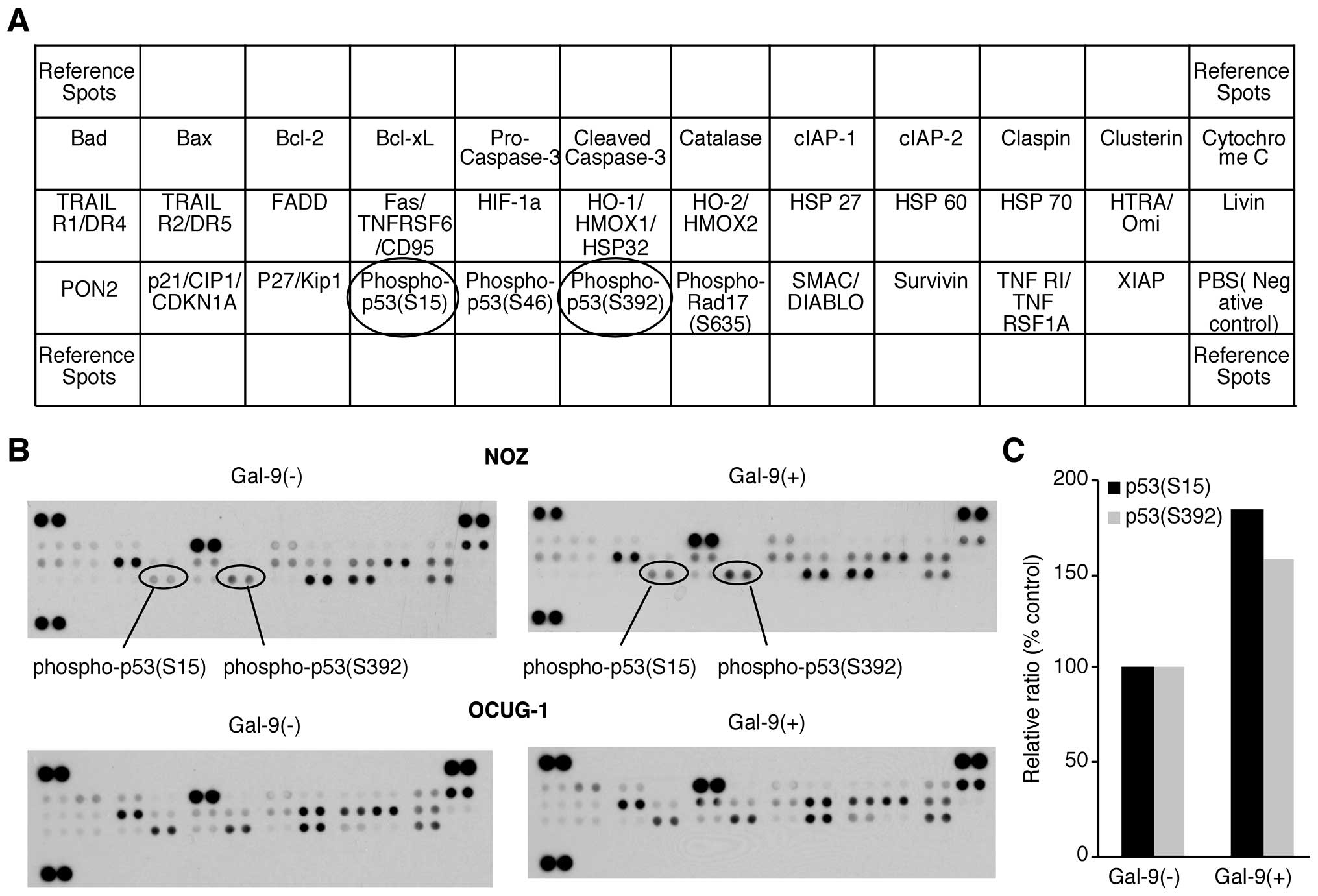
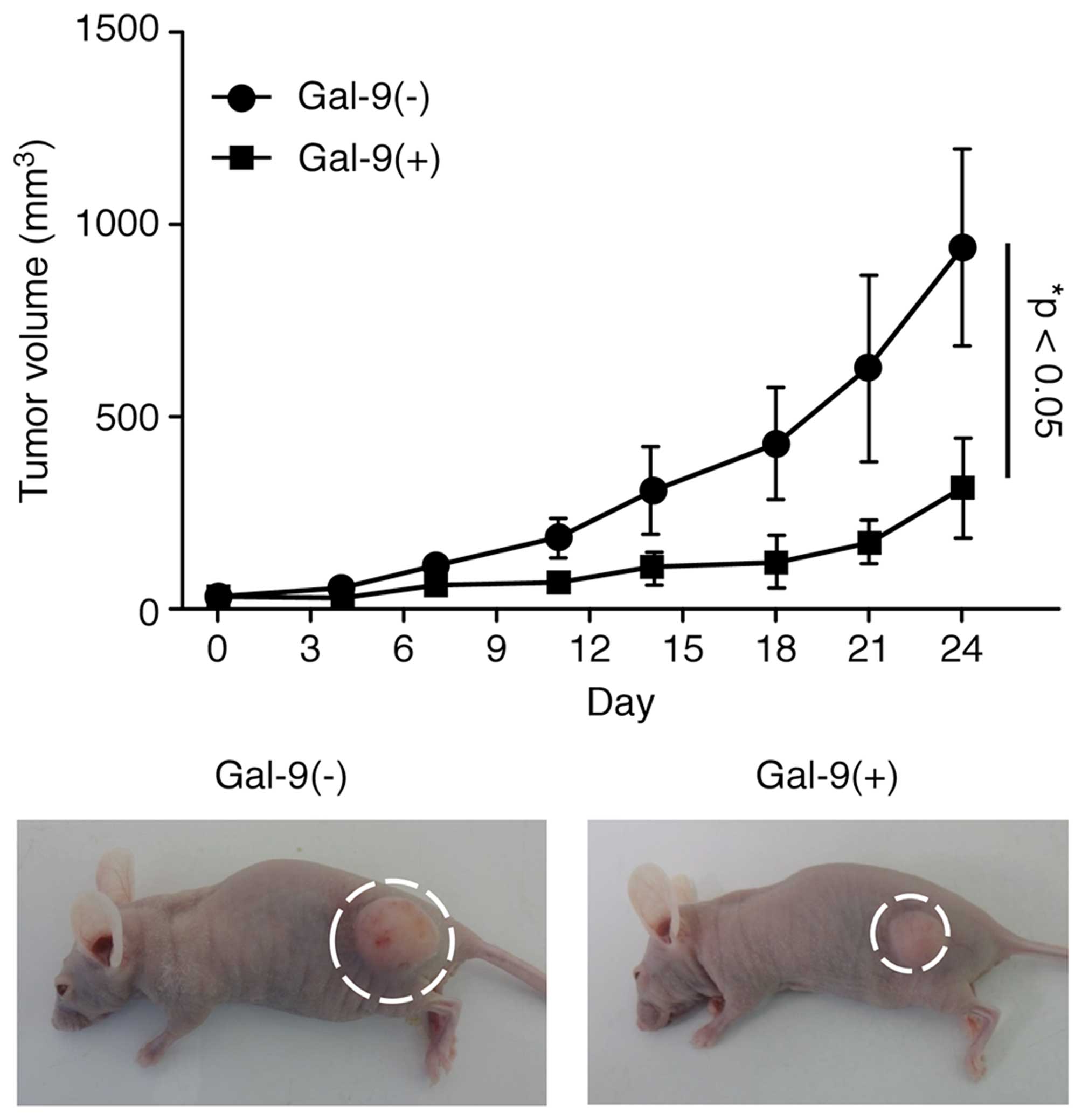
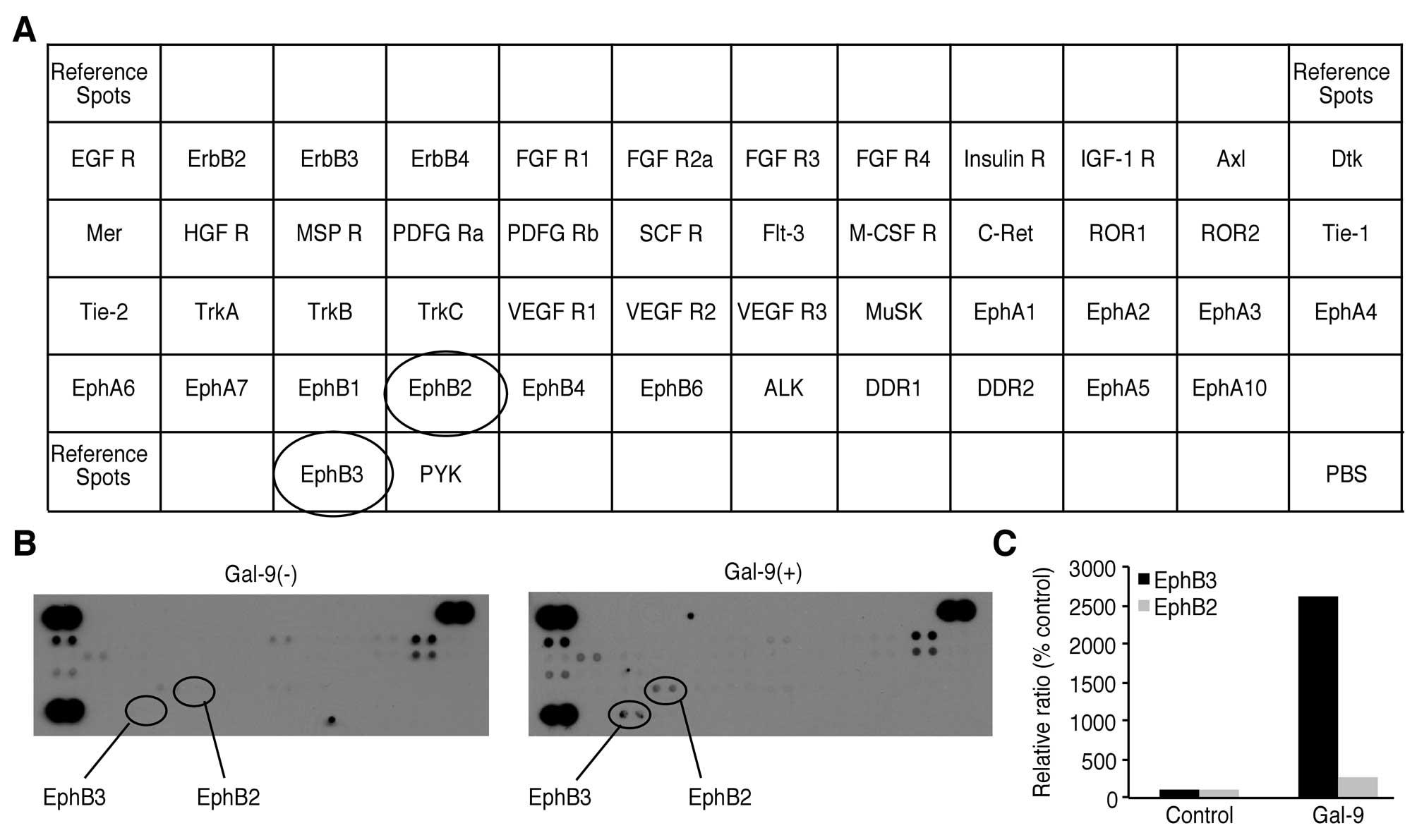
|
1
|
Bal MM, Ramadwar M, Deodhar K and
Shrikhande S: Pathology of gallbladder carcinoma: Current
understanding and new perspectives. Pathol Oncol Res. 21:509–525.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Randi G, Franceschi S and La Vecchia C:
Gallbladder cancer worldwide: Geographical distribution and risk
factors. Int J Cancer. 118:1591–1602. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dwivedi AN, Jain S and Dixit R: Gall
bladder carcinoma: Aggressive malignancy with protean loco-regional
and distant spread. World J Clin Cases. 3:231–244. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hirashima M, Kashio Y, Nishi N, Yamauchi
A, Imaizumi TA, Kageshita T, Saita N and Nakamura T: Galectin-9 in
physiological and pathological conditions. Glycoconj J. 19:593–600.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu C, Anderson AC, Schubart A, Xiong H,
Imitola J, Khoury SJ, Zheng XX, Strom TB and Kuchroo VK: The Tim-3
ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates T helper type 1 immunity.
Nat Immunol. 6:1245–1252. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oomizu S, Arikawa T, Niki T, Kadowaki T,
Ueno M, Nishi N, Yamauchi A and Hirashima M: Galectin-9 suppresses
Th17 cell development in an IL-2-dependent but Tim-3-independent
manner. Clin Immunol. 143:51–58. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Seki M, Oomizu S, Sakata KM, Sakata A,
Arikawa T, Watanabe K, Ito K, Takeshita K, Niki T, Saita N, et al:
Galectin-9 suppresses the generation of Th17, promotes the
induction of regulatory T cells, and regulates experimental
autoimmune arthritis. Clin Immunol. 127:78–88. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Niki T, Tsutsui S, Hirose S, Aradono S,
Sugimoto Y, Takeshita K, Nishi N and Hirashima M: Galectin-9 is a
high affinity IgE-binding lectin with anti-allergic effect by
blocking IgE-antigen complex formation. J Biol Chem.
284:32344–32352. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wiersma VR, de Bruyn M, Helfrich W and
Bremer E: Therapeutic potential of Galectin-9 in human disease. Med
Res Rev. 33(Suppl 1): E102–E126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fujihara S, Mori H, Kobara H, Rafiq K,
Niki T, Hirashima M and Masaki T: Galectin-9 in cancer therapy.
Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 7:130–137. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kageshita T, Kashio Y, Yamauchi A, Seki M,
Abedin MJ, Nishi N, Shoji H, Nakamura T, Ono T and Hirashima M:
Possible role of galectin-9 in cell aggregation and apoptosis of
human melanoma cell lines and its clinical significance. Int J
Cancer. 99:809–816. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuroda J, Yamamoto M, Nagoshi H, Kobayashi
T, Sasaki N, Shimura Y, Horiike S, Kimura S, Yamauchi A, Hirashima
M, et al: Targeting activating transcription factor 3 by Galectin-9
induces apoptosis and overcomes various types of treatment
resistance in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Mol Cancer Res.
8:994–1001. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fujita K, Iwama H, Sakamoto T, Okura R,
Kobayashi K, Takano J, Katsura A, Tatsuta M, Maeda E, Mimura S, et
al: Galectin-9 suppresses the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma
via apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol. 46:2419–2430.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kobayashi K, Morishita A, Iwama H, Fujita
K, Okura R, Fujihara S, Yamashita T, Fujimori T, Kato K, Kamada H,
et al: Galectin-9 suppresses cholangiocarcinoma cell proliferation
by inducing apoptosis but not cell cycle arrest. Oncol Rep.
34:1761–1770. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zamore PD and Haley B: Ribo-gnome: The big
world of small RNAs. Science. 309:1519–1524. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Morishita A and Masaki T: miRNA in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 45:128–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nishi N, Itoh A, Fujiyama A, Yoshida N,
Araya S, Hirashima M, Shoji H and Nakamura T: Development of highly
stable galectins: Truncation of the linker peptide confers
protease-resistance on tandem-repeat type galectins. FEBS Lett.
579:2058–2064. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schutte B, Henfling M, Kölgen W, Bouman M,
Meex S, Leers MP, Nap M, Björklund V, Björklund P, Björklund B, et
al: Keratin 8/18 breakdown and reorganization during apoptosis. Exp
Cell Res. 297:11–26. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Workman P, Aboagye EO, Balkwill F, Balmain
A, Bruder G, Chaplin DJ, Double JA, Everitt J, Farningham DA,
Glennie MJ, et al; Committee of the National Cancer Research
Institute. Guidelines for the welfare and use of animals in cancer
research. Br J Cancer. 102:1555–1577. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
D'Incalci M, Colombo T, Ubezio P,
Nicoletti I, Giavazzi R, Erba E, Ferrarese L, Meco D, Riccardi R,
Sessa C, et al: The combination of yondelis and cisplatin is
synergistic against human tumor xenografts. Eur J Cancer.
39:1920–1926. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kapoor VK: Gallbladder cancer: A global
perspective. J Surg Oncol. 93:607–609. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamada N, Chung Y, Ohtani H, Ikeda T,
Onoda N, Sawada T, Nishiguchi Y, Hasuma T and Sowa M: Establishment
and characterization of a new human gallbladder carcinoma cell line
(OCUG-1) producing TA-4. Int J Oncol. 10:1251–1255. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim WS, Jang KT, Choi DW, Choi SH, Heo JS,
You DD and Lee HG: Clinicopathologic analysis of
adenosquamous/squamous cell carcinoma of the gallbladder. J Surg
Oncol. 103:239–242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hamdani NH, Qadri SK, Aggarwalla R,
Bhartia VK, Chaudhuri S, Debakshi S, Baig SJ and Pal NK:
Clinicopathological study of gall bladder carcinoma with special
reference to gallstones: Our 8-year experience from eastern India.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:5613–5617. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chan KM, Yu MC, Lee WC, Jan YY and Chen
MF: Adeno-squamous/squamous cell carcinoma of the gallbladder. J
Surg Oncol. 95:129–134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mingoli A, Brachini G, Petroni R,
Antoniozzi A, Cavaliere F, Simonelli L, Chirletti P and Modini C:
Squamous and adeno-squamous cell carcinomas of the gallbladder. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 24:143–150. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Miyanishi N, Nishi N, Abe H, Kashio Y,
Shinonaga R, Nakakita S, Sumiyoshi W, Yamauchi A, Nakamura T,
Hirashima M, et al: Carbohydrate-recognition domains of galectin-9
are involved in intermolecular interaction with galectin-9 itself
and other members of the galectin family. Glycobiology. 17:423–432.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matsumoto R, Matsumoto H, Seki M, Hata M,
Asano Y, Kanegasaki S, Stevens RL and Hirashima M: Human ecalectin,
a variant of human galectin-9, is a novel eosinophil
chemoattractant produced by T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem.
273:16976–16984. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kobayashi T, Kuroda J, Ashihara E, Oomizu
S, Terui Y, Taniyama A, Adachi S, Takagi T, Yamamoto M, Sasaki N,
et al: Galectin-9 exhibits anti-myeloma activity through JNK and
p38 MAP kinase pathways. Leukemia. 24:843–850. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Leers MP, Kölgen W, Björklund V, Bergman
T, Tribbick G, Persson B, Björklund P, Ramaekers FC, Björklund B,
Nap M, et al: Immunocytochemical detection and mapping of a
cytokeratin 18 neo-epitope exposed during early apoptosis. J
Pathol. 187:567–572. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
el-Deiry WS: Regulation of p53 downstream
genes. Semin Cancer Biol. 8:345–357. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Batlle E, Bacani J, Begthel H, Jonkheer S,
Gregorieff A, van de Born M, Malats N, Sancho E, Boon E, Pawson T,
et al: EphB receptor activity suppresses colorectal cancer
progression. Nature. 435:1126–1130. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jägle S, Rönsch K, Timme S, Andrlová H,
Bertrand M, Jäger M, Proske A, Schrempp M, Yousaf A, Michoel T, et
al: Silencing of the EPHB3 tumor-suppressor gene in human
colorectal cancer through decommissioning of a transcriptional
enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:4886–4891. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yuan Y, Yang ZL, Miao XY, Liu ZR, Li DQ,
Zou Q, Li JH, Liang LF, Zeng GX and Chen SL: EphB1 and Ephrin-B,
new potential biomarkers for squamous cell/adenosquamous carcinomas
and adenocarcinomas of the gallbladder. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:1441–1446. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Lin C, Yamaguchi
H, Ohtsuka T, Sato N, Toma H, Nakamura M, Nagai E, Hashizume M, et
al: MicroRNA-10a is overexpressed in human pancreatic cancer and
involved in its invasiveness partially via suppression of the HOXA1
gene. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:2394–2402. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu T, Liu L, Li J, Yan M, Lin H, Liu Y,
Chu D, Tu H, Gu A and Yao M: MiRNA-10a is upregulated in NSCLC and
may promote cancer by targeting PTEN. Oncotarget. 6:30239–30250.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cui R, Kim T, Fassan M, Meng W, Sun HL,
Jeon YJ, Vicentini C, Tili E, Peng Y, Scarpa A, et al: MicroRNA-224
is implicated in lung cancer pathogenesis through targeting
caspase-3 and caspase-7. Oncotarget. 6:21802–21815. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang C, Xu M, Shen HJ, Zhu HY, Li F, He M,
Chen T, Wang J, Shi WJ and Ji F: Potential biomarkers for
sensitivity of gall-bladder cancer cells to gemcitabine. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:521–528. 2014.
|
|
39
|
Plunkett W, Huang P, Searcy CE and Gandhi
V: Gemcitabine: Preclinical pharmacology and mechanisms of action.
Semin Oncol. 23(Suppl 10): 3–15. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Toyota Y, Iwama H, Kato K, Tani J, Katsura
A, Miyata M, Fujiwara S, Fujita K, Sakamoto T, Fujimori T, et al:
Mechanism of gemcitabine-induced suppression of human
cholangiocellular carcinoma cell growth. Int J Oncol. 47:1293–1302.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|