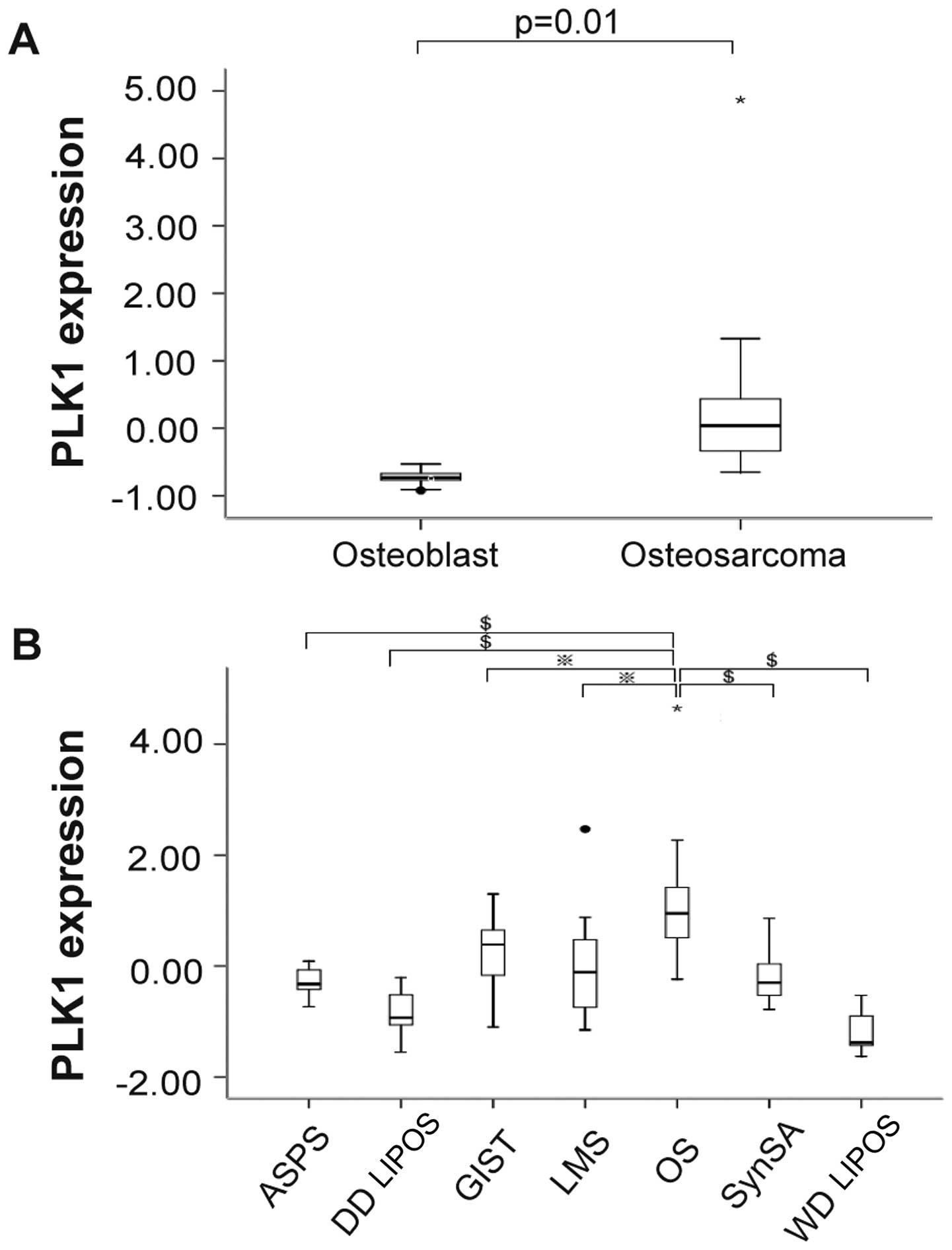
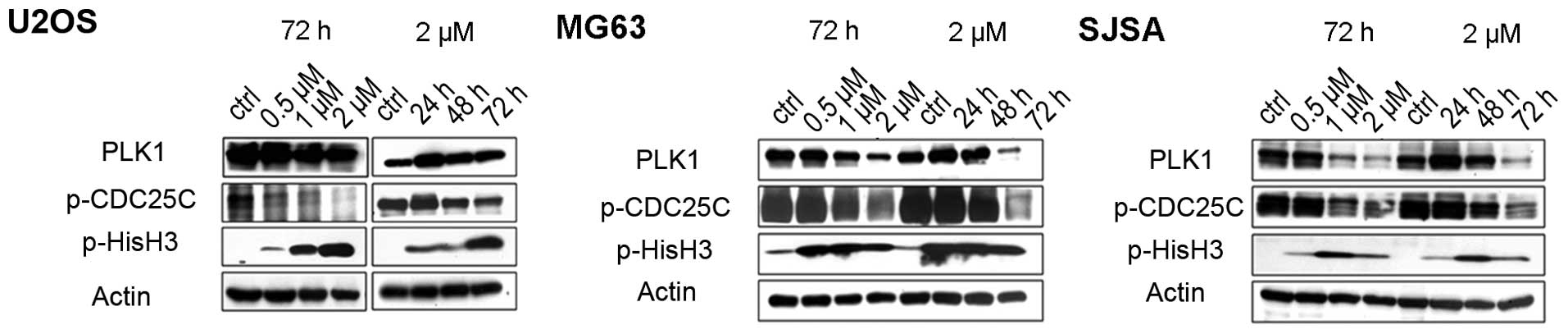
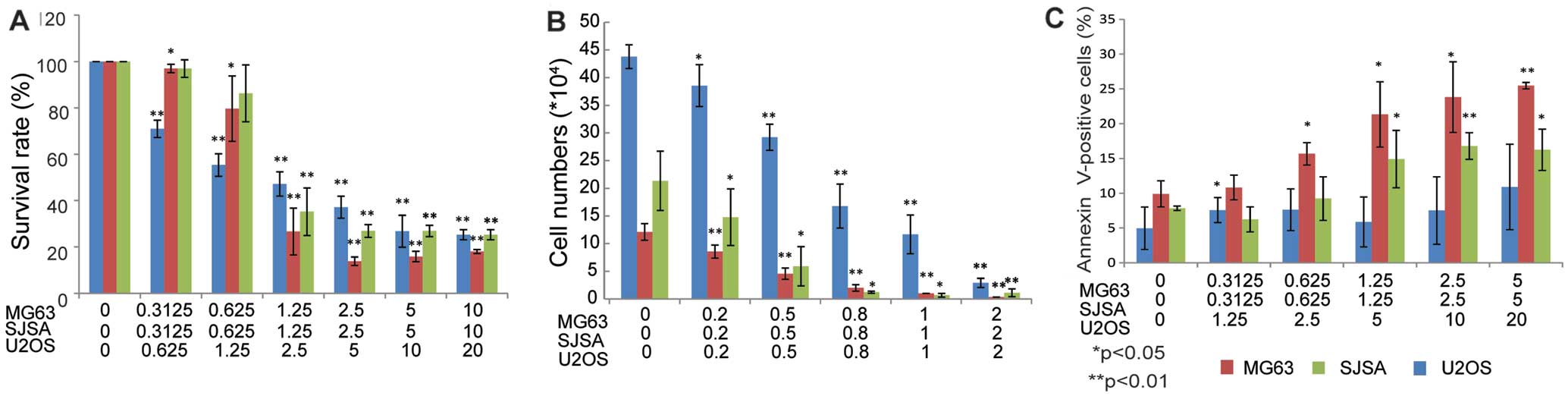
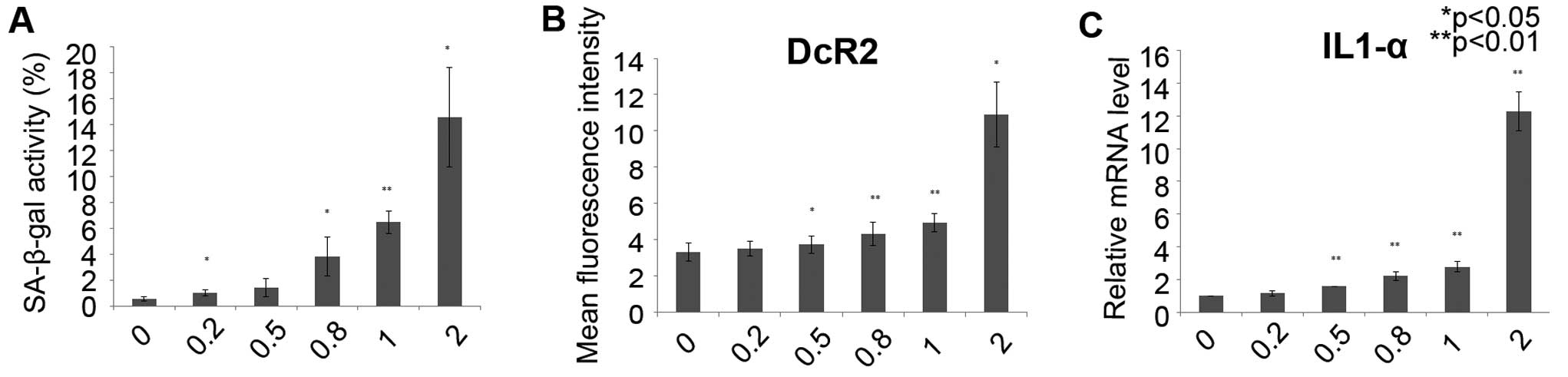
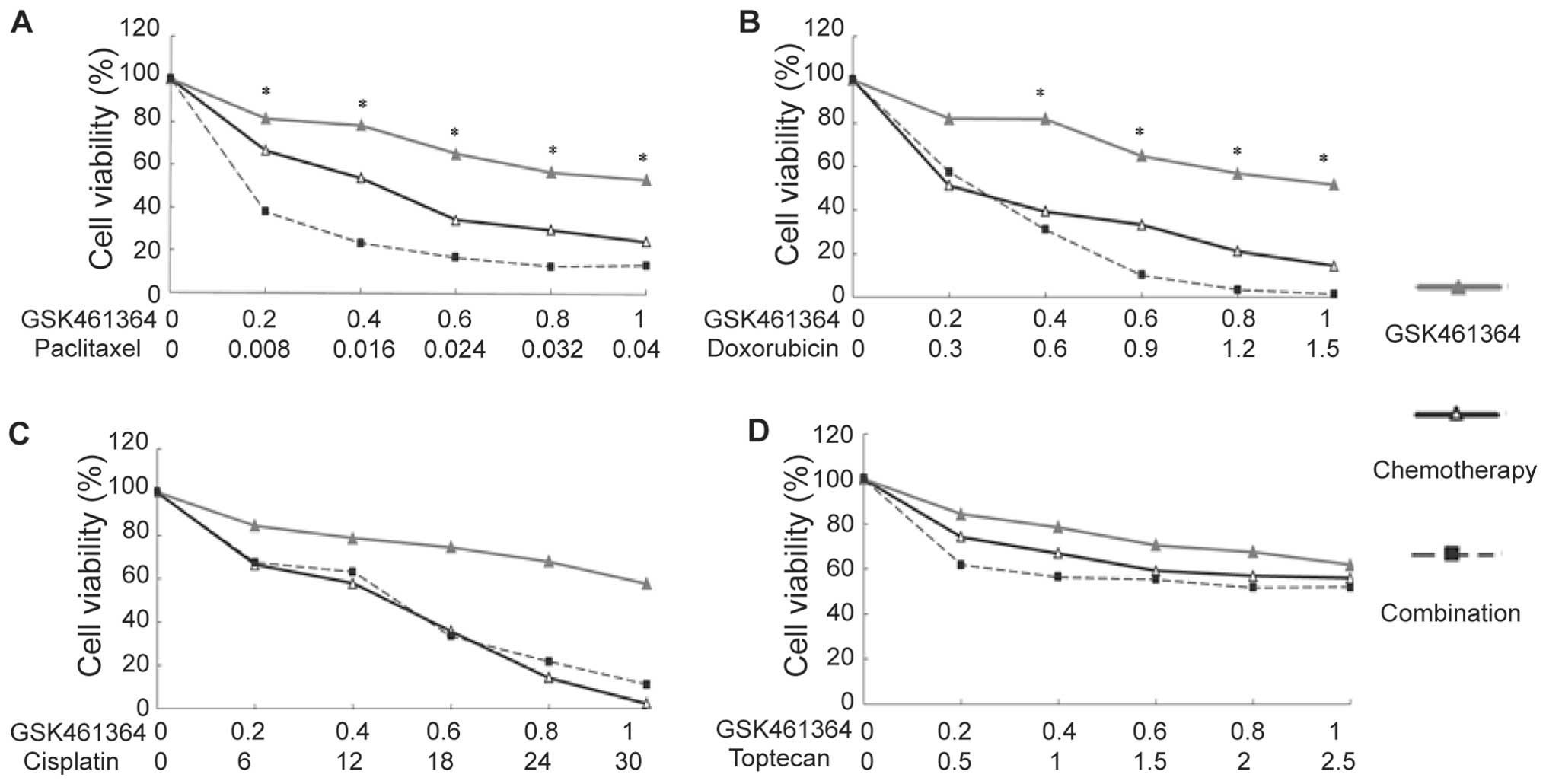
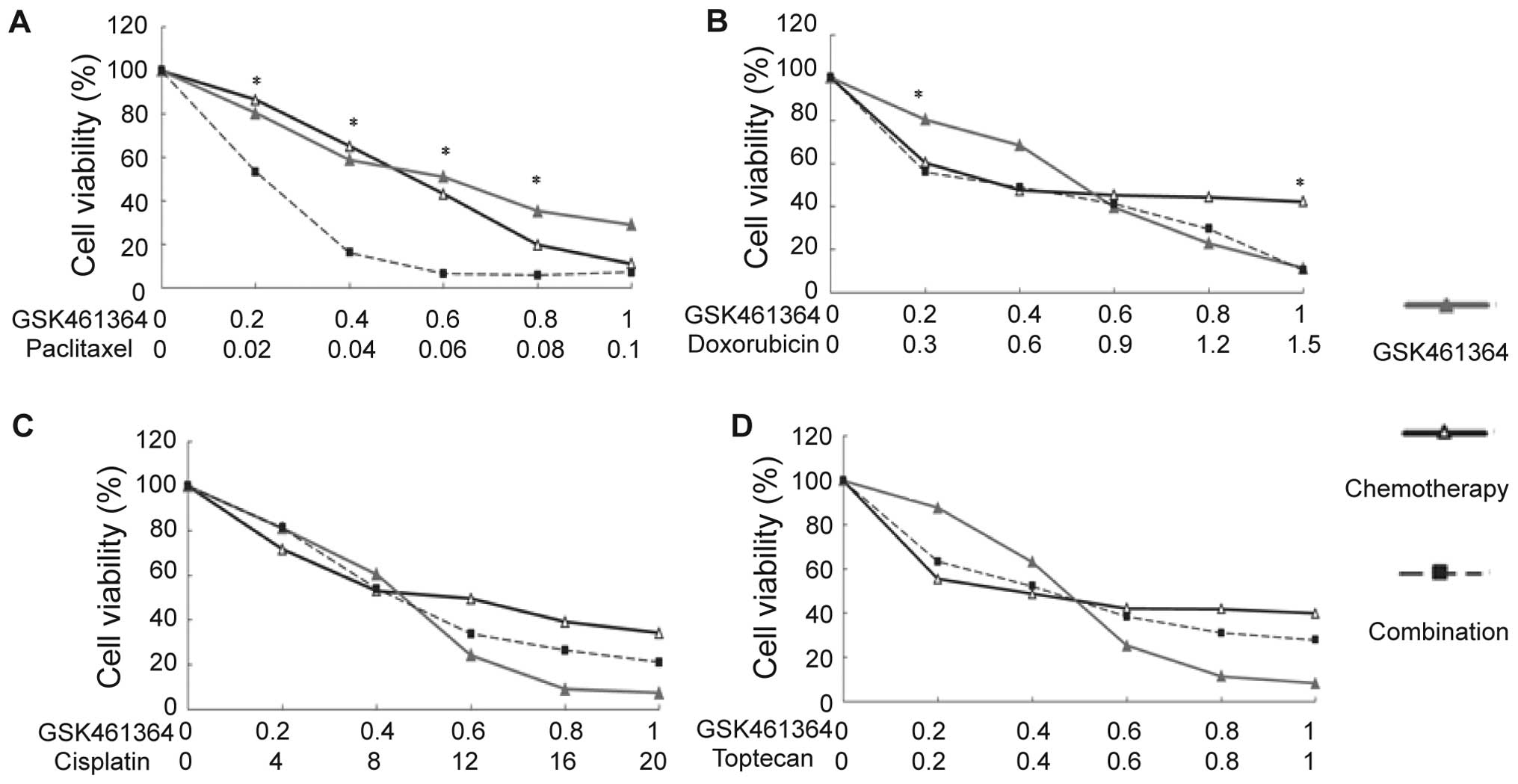
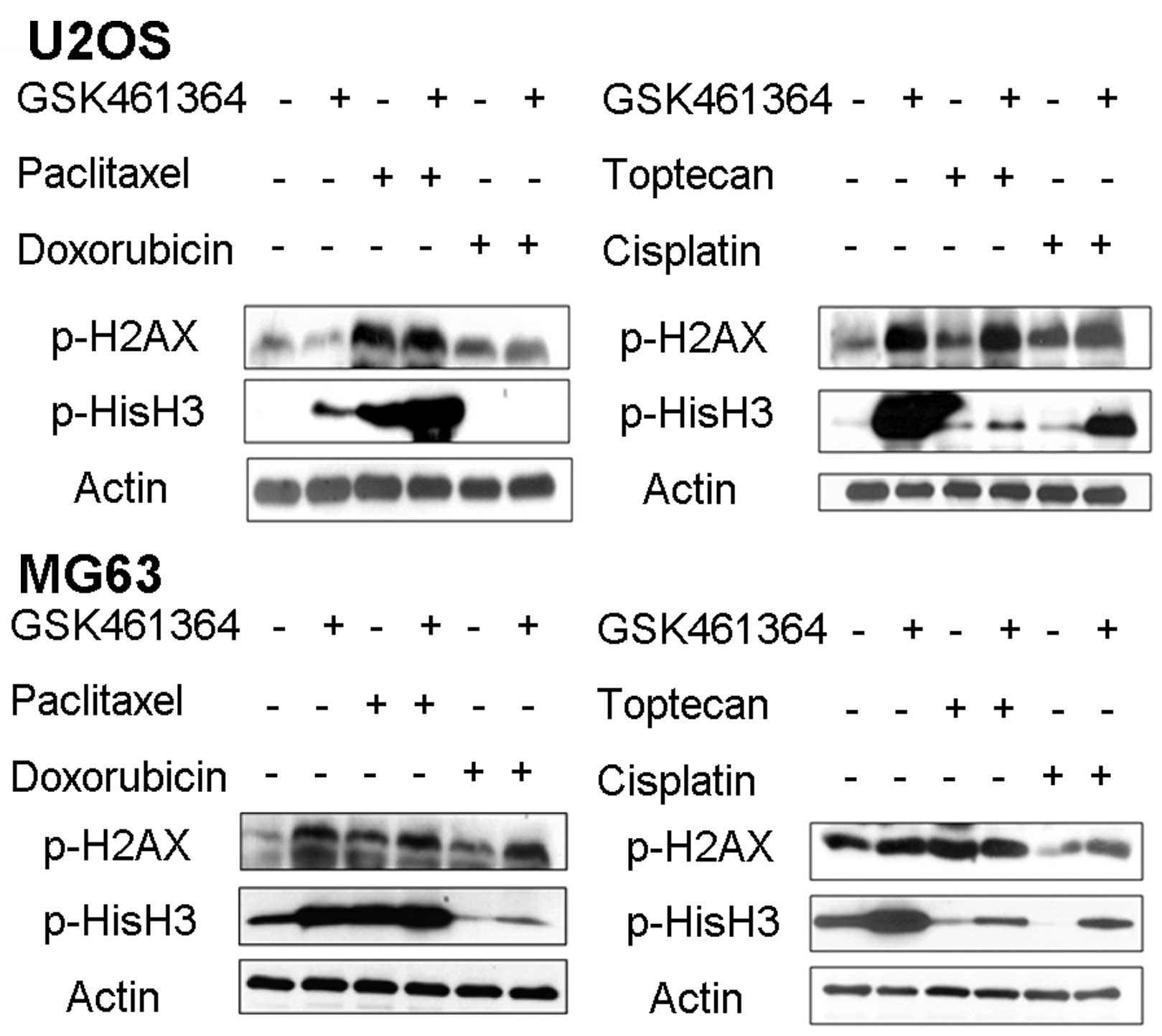
|
1
|
Hung GY, Horng JL, Yen HJ, Yen CC, Chen
WM, Chen PC, Wu HT and Chiou HJ: Incidence patterns of primary bone
cancer in Taiwan (2003–2010): A population-based study. Ann Surg
Oncol. 21:2490–2498. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hung GY, Yen HJ, Yen CC, Chen WM, Chen PC,
Wu HT, Chiou HJ, Chang WH and Hsu HE: Experience of pediatric
osteosarcoma of the extremity at a single institution in Taiwan:
Prognostic factors and impact on survival. Ann Surg Oncol.
22:1080–1087. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ferrari S, Smeland S, Mercuri M, Bertoni
F, Longhi A, Ruggieri P, Alvegard TA, Picci P, Capanna R, Bernini
G, et al; Italian and Scandinavian Sarcoma Groups. Neoadjuvant
chemotherapy with high-dose Ifosfamide, high-dose methotrexate,
cisplatin, and doxorubicin for patients with localized osteosarcoma
of the extremity: A joint study by the Italian and Scandinavian
Sarcoma Groups. J Clin Oncol. 23:8845–8852. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iwamoto Y, Tanaka K, Isu K, Kawai A,
Tatezaki S, Ishii T, Kushida K, Beppu Y, Usui M, Tateishi A, et al:
Multiinstitutional phase II study of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for
osteosarcoma (NECO study) in Japan: NECO-93J and NECO-95J. J Orthop
Sci. 14:397–404. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Harting MT, Lally KP, Andrassy RJ,
Vaporciyan AA, Cox CS Jr, Hayes-Jordan A and Blakely ML: Age as a
prognostic factor for patients with osteosarcoma: An analysis of
438 patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:561–570. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Joo MW, Shin SH, Kang YK, Kawai A, Kim HS,
Asavamongkolkul A, Jeon DG, Kim JD, Niu X, Tsuchiya H, et al:
Osteosarcoma in Asian populations over the age of 40 years: A
Multicenter study. Ann Surg Oncol. 22:3557–3564. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Janeway KA, Barkauskas DA, Krailo MD,
Meyers PA, Schwartz CL, Ebb DH, Seibel NL, Grier HE, Gorlick R and
Marina N: Outcome for adolescent and young adult patients with
osteosarcoma: A report from the Children's Oncology Group. Cancer.
118:4597–4605. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Whelan JS, Jinks RC, McTiernan A, Sydes
MR, Hook JM, Trani L, Uscinska B, Bramwell V, Lewis IJ, Nooij MA,
et al: Survival from high-grade localised extremity osteosarcoma:
Combined results and prognostic factors from three European
Osteosarcoma Intergroup randomised controlled trials. Ann Oncol.
23:1607–1616. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Mejia-Guerrero S, Quejada M, Gokgoz N,
Gill M, Parkes RK, Wunder JS and Andrulis IL: Characterization of
the 12q15 MDM2 and 12q13-14 CDK4 amplicons and clinical
correlations in osteosarcoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 49:518–525.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Crago AM, Socci ND, DeCarolis P, O'Connor
R, Taylor BS, Qin LX, Antonescu CR and Singer S: Copy number losses
define subgroups of dedifferentiated liposarcoma with poor
prognosis and genomic instability. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1334–1340.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wunder JS, Nielsen TO, Maki RG, O'Sullivan
B and Alman BA: Opportunities for improving the therapeutic ratio
for patients with sarcoma. Lancet Oncol. 8:513–524. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ladanyi M, Cha C, Lewis R, Jhanwar SC,
Huvos AG and Healey JH: MDM2 gene amplification in metastatic
osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 53:16–18. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Koshkina NV, Kleinerman ES, Li G, Zhao CC,
Wei Q and Sturgis EM: Exploratory analysis of Fas gene
polymorphisms in pediatric osteosarcoma patients. J Pediatr Hematol
Oncol. 29:815–821. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choy E, Hornicek F, MacConaill L, Harmon
D, Tariq Z, Garraway L and Duan Z: High-throughput genotyping in
osteosarcoma identifies multiple mutations in
phosphoinositide-3-kinase and other oncogenes. Cancer.
118:2905–2914. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Perry JA, Kiezun A, Tonzi P, Van Allen EM,
Carter SL, Baca SC, Cowley GS, Bhatt AS, Rheinbay E, Pedamallu CS,
et al: Complementary genomic approaches highlight the PI3K/mTOR
pathway as a common vulnerability in osteosarcoma. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 111:E5564–E5573. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Scheel C, Schaefer KL, Jauch A, Keller M,
Wai D, Brinkschmidt C, van Valen F, Boecker W, Dockhorn-Dworniczak
B and Poremba C: Alternative lengthening of telomeres is associated
with chromosomal instability in osteosarcomas. Oncogene.
20:3835–3844. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wan X, Mendoza A, Khanna C and Helman LJ:
Rapamycin inhibits ezrin-mediated metastatic behavior in a murine
model of osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 65:2406–2411. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yen CC, Chen WM, Chen TH, Chen WY, Chen
PC, Chiou HJ, Hung GY, Wu HT, Wei CJ, Shiau CY, et al:
Identification of chromosomal aberrations associated with disease
progression and a novel 3q13.31 deletion involving LSAMP gene in
osteosarcoma. Int J Oncol. 35:775–788. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pasic I, Shlien A, Durbin AD, Stavropoulos
DJ, Baskin B, Ray PN, Novokmet A and Malkin D: Recurrent focal
copy-number changes and loss of heterozygosity implicate two
noncoding RNAs and one tumor suppressor gene at chromosome 3q13.31
in osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 70:160–171. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Grignani G, Palmerini E, Ferraresi V,
D'Ambrosio L, Bertulli R, Asaftei SD, Tamburini A, Pignochino Y,
Sangiolo D, Marchesi E, et al; Italian Sarcoma Group. Sorafenib and
everolimus for patients with unresectable high-grade osteosarcoma
progressing after standard treatment: A non-randomised phase 2
clinical trial. Lancet Oncol. 16:98–107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Strebhardt K and Ullrich A: Targeting
polo-like kinase 1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:321–330.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Duan Z, Ji D, Weinstein EJ, Liu X, Susa M,
Choy E, Yang C, Mankin H and Hornicek FJ: Lentiviral shRNA screen
of human kinases identifies PLK1 as a potential therapeutic target
for osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett. 293:220–229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yamaguchi U, Honda K, Satow R, Kobayashi
E, Nakayama R, Ichikawa H, Shoji A, Shitashige M, Masuda M, Kawai
A, et al: Functional genome screen for therapeutic targets of
osteosarcoma. Cancer Sci. 100:2268–2274. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sero V, Tavanti E, Vella S, Hattinger CM,
Fanelli M, Michelacci F, Versteeg R, Valsasina B, Gudeman B, Picci
P, et al: Targeting polo-like kinase 1 by NMS-P937 in osteosarcoma
cell lines inhibits tumor cell growth and partially overcomes drug
resistance. Invest New Drugs. 32:1167–1180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yen CC, Hsiao CD, Chen WM, Wen YS, Lin YC,
Chang TW, Yao FY, Hung SC, Wang JY, Chiu JH, et al: Cytotoxic
effects of 15d-PGJ2 against osteosarcoma through ROS-mediated AKT
and cell cycle inhibition. Oncotarget. 5:716–725. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gilmartin AG, Bleam MR, Richter MC,
Erskine SG, Kruger RG, Madden L, Hassler DF, Smith GK, Gontarek RR,
Courtney MP, et al: Distinct concentration-dependent effects of the
polo-like kinase 1-specific inhibitor GSK461364A, including
differential effect on apoptosis. Cancer Res. 69:6969–6977. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li C and Hung Wong W: Model-based analysis
of oligonucleotide arrays: model validation, design issues and
standard error application. Genome Biol. 2:Research0032.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li C and Wong WH: Model-based analysis of
oligonucleotide arrays: Expression index computation and outlier
detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:31–36. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Quantitative
analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of
multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 22:27–55.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schmit TL, Nihal M, Ndiaye M, Setaluri V,
Spiegelman VS and Ahmad N: Numb regulates stability and
localization of the mitotic kinase PLK1 and is required for transit
through mitosis. Cancer Res. 72:3864–3872. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tuveson DA, Willis NA, Jacks T, Griffin
JD, Singer S, Fletcher CD, Fletcher JA and Demetri GD: STI571
inactivation of the gastrointestinal stromal tumor c-KIT
oncoprotein: Biological and clinical implications. Oncogene.
20:5054–5058. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu Y, Xu L, Zhang J, Hu X, Liu Y, Yin H,
Lv T, Zhang H, Liu L, An H, et al: Sunitinib induces cellular
senescence via p53/Dec1 activation in renal cell carcinoma cells.
Cancer Sci. 104:1052–1061. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Müller-Tidow C, Metzger R, Kügler K,
Diederichs S, Idos G, Thomas M, Dockhorn-Dworniczak B, Schneider
PM, Koeffler HP, Berdel WE, et al: Cyclin E is the only
cyclin-dependent kinase 2-associated cyclin that predicts
metastasis and survival in early stage non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Res. 61:647–653. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ewald JA, Desotelle JA, Wilding G and
Jarrard DF: Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 102:1536–1546. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chibon F, Lagarde P, Salas S, Pérot G,
Brouste V, Tirode F, Lucchesi C, de Reynies A, Kauffmann A, Bui B,
et al: Validated prediction of clinical outcome in sarcomas and
multiple types of cancer on the basis of a gene expression
signature related to genome complexity. Nat Med. 16:781–787. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yen CC, Yeh CN, Cheng CT, Jung SM, Huang
SC, Chang TW, Jan YY, Tzeng CH, Chao TC, Chen YY, et al:
Integrating bioinformatics and clinicopathological research of
gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Identification of aurora kinase A
as a poor risk marker. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:3491–3499. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yeh CN, Yen CC, Chen YY, Cheng CT, Huang
SC, Chang TW, Yao FY, Lin YC, Wen YS, Chiang KC, et al:
Identification of aurora kinase A as an unfavorable prognostic
factor and potential treatment target for metastatic
gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncotarget. 5:4071–4086. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Morales AG, Brassesco MS, Pezuk JA,
Oliveira JC, Montaldi AP, Sakamoto-Hojo ET, Scrideli CA and Tone
LG: BI 2536-mediated PLK1 inhibition suppresses HOS and MG-63
osteosarcoma cell line growth and clonogenicity. Anticancer Drugs.
22:995–1001. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu X, Choy E, Harmon D, Yang S, Yang C,
Mankin H, Hornicek FJ and Duan Z: Inhibition of polo-like kinase 1
leads to the suppression of osteosarcoma cell growth in vitro and
in vivo. Anticancer Drugs. 22:444–453. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bogado RF, Pezuk JA, de Oliveira HF, Tone
LG and Brassesco MS: BI 6727 and GSK461364 suppress growth and
radiosensitize osteosarcoma cells, but show limited cytotoxic
effects when combined with conventional treatments. Anticancer
Drugs. 26:56–63. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Spankuch B, Heim S, Kurunci-Csacsko E,
Lindenau C, Yuan J, Kaufmann M and Strebhardt K: Down-regulation of
Polo-like kinase 1 elevates drug sensitivity of breast cancer cells
in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 66:5836–5846. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|