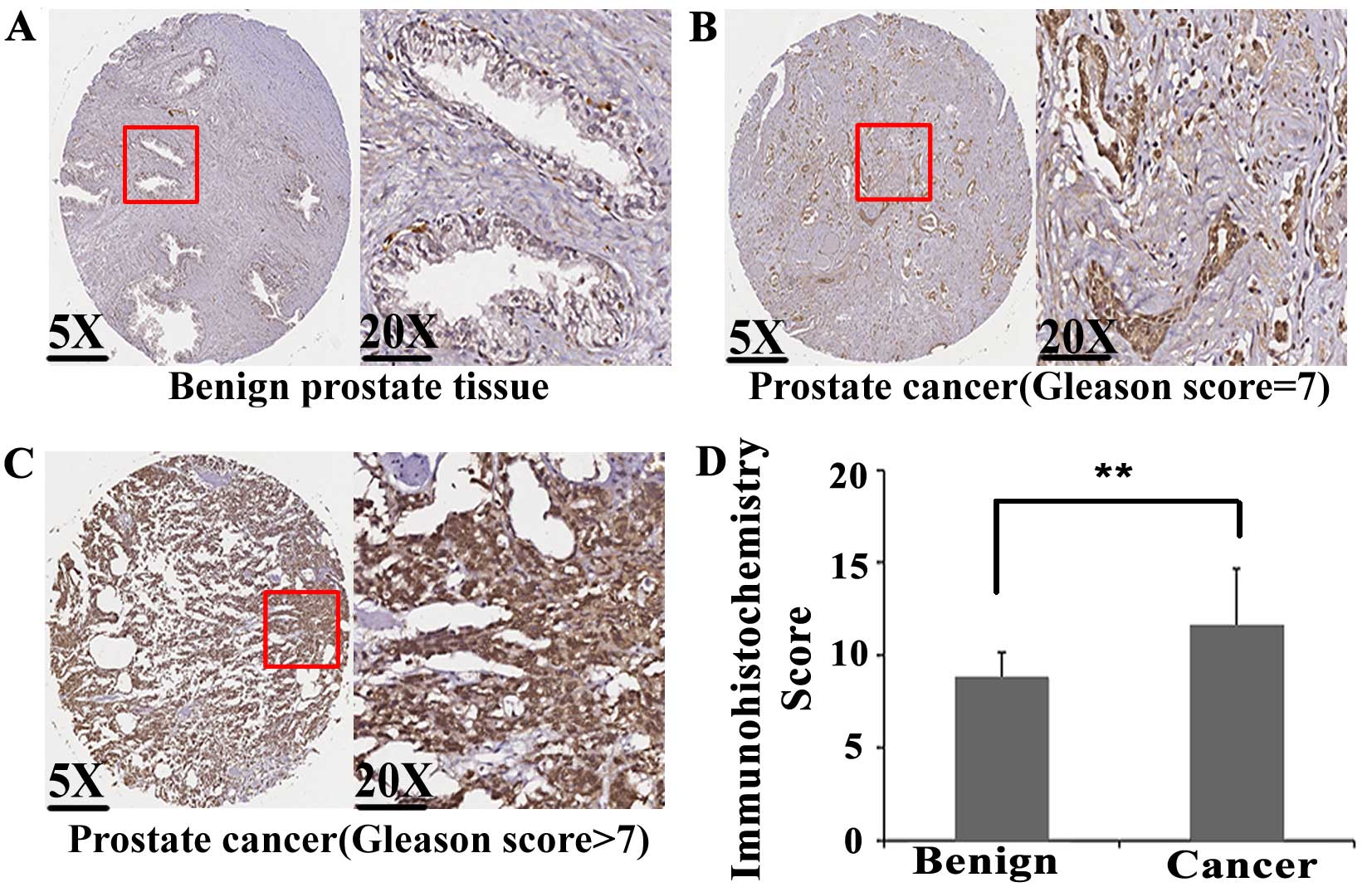
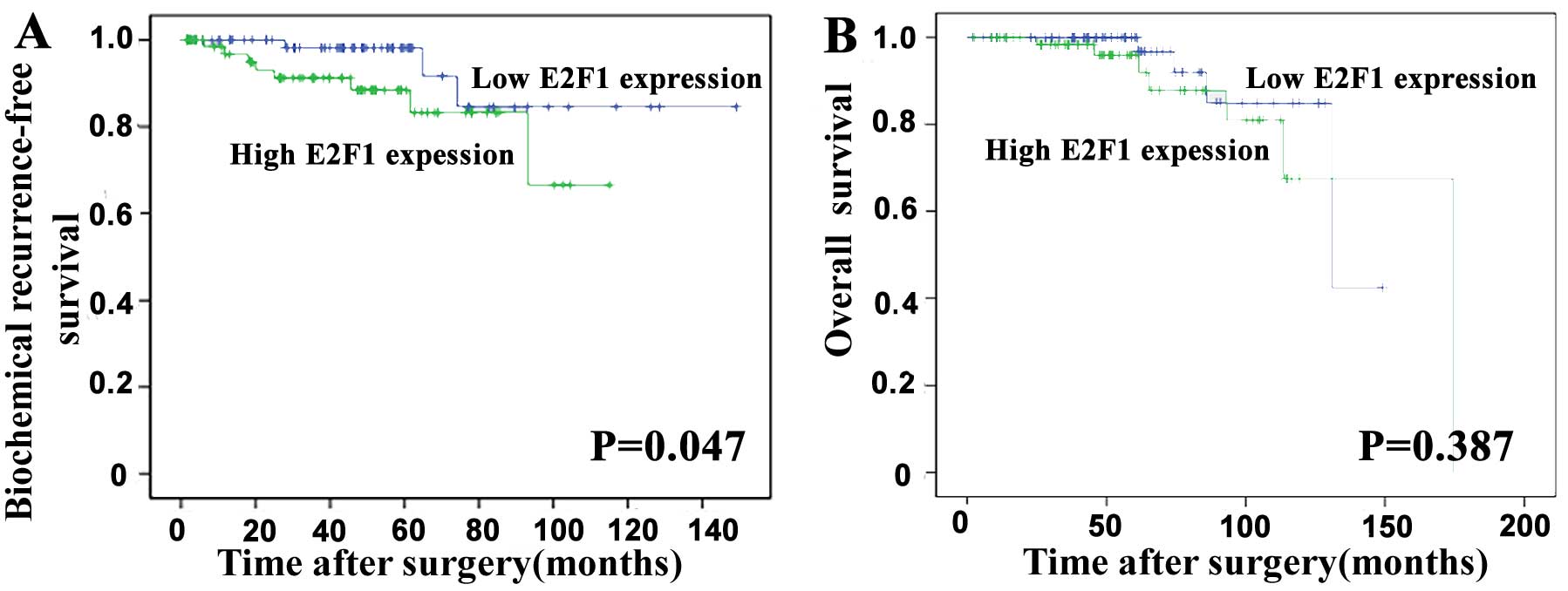
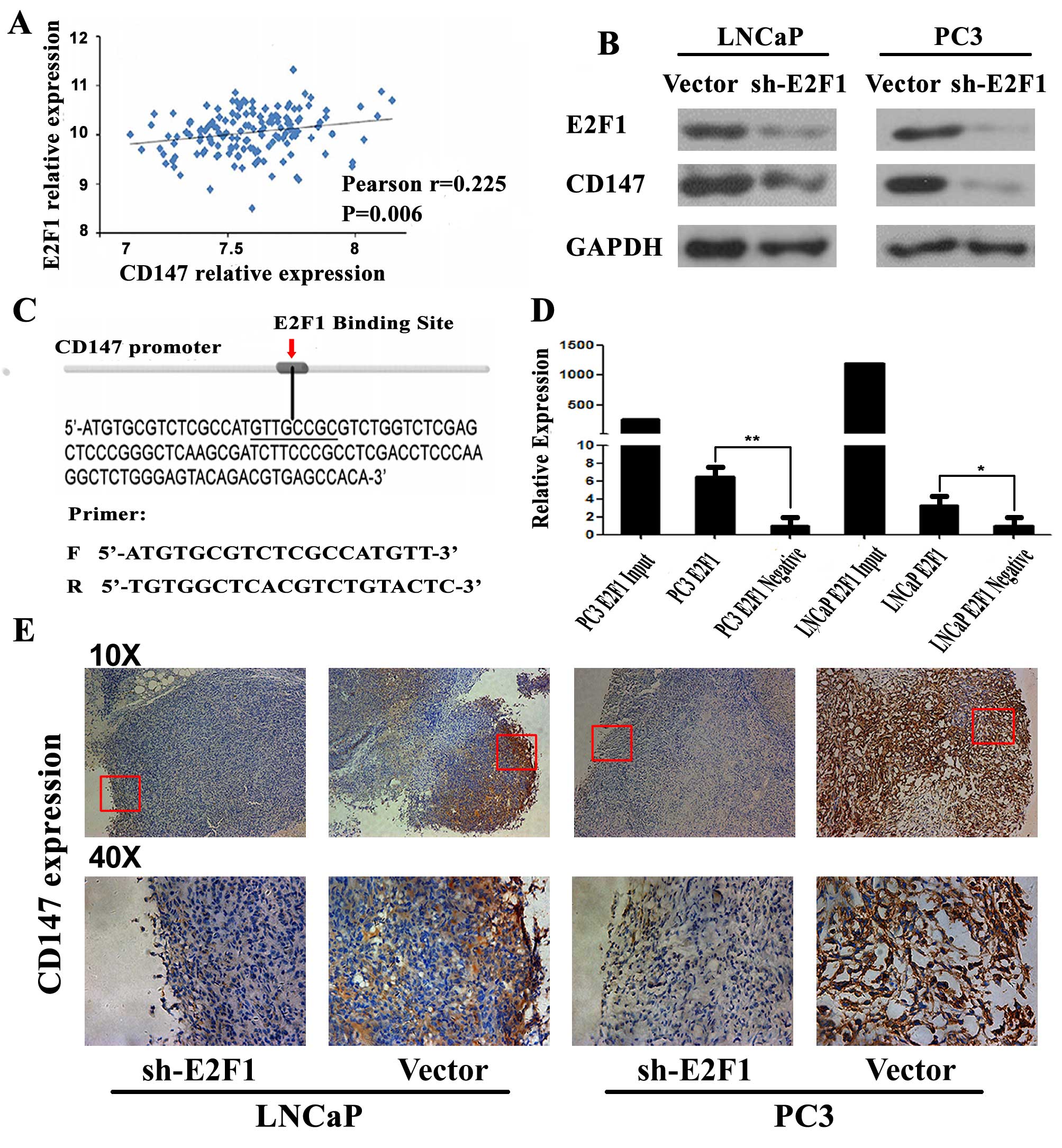
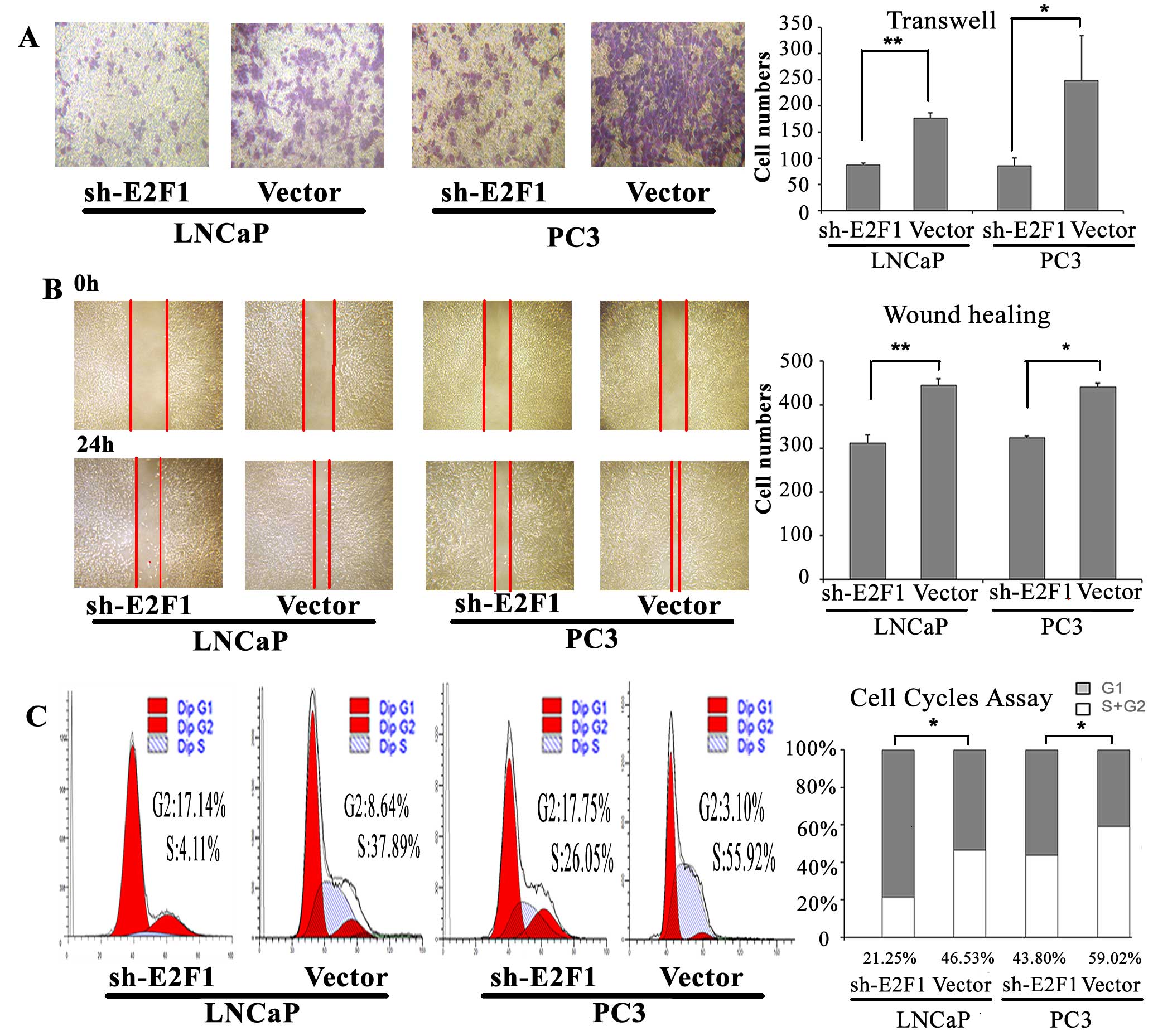
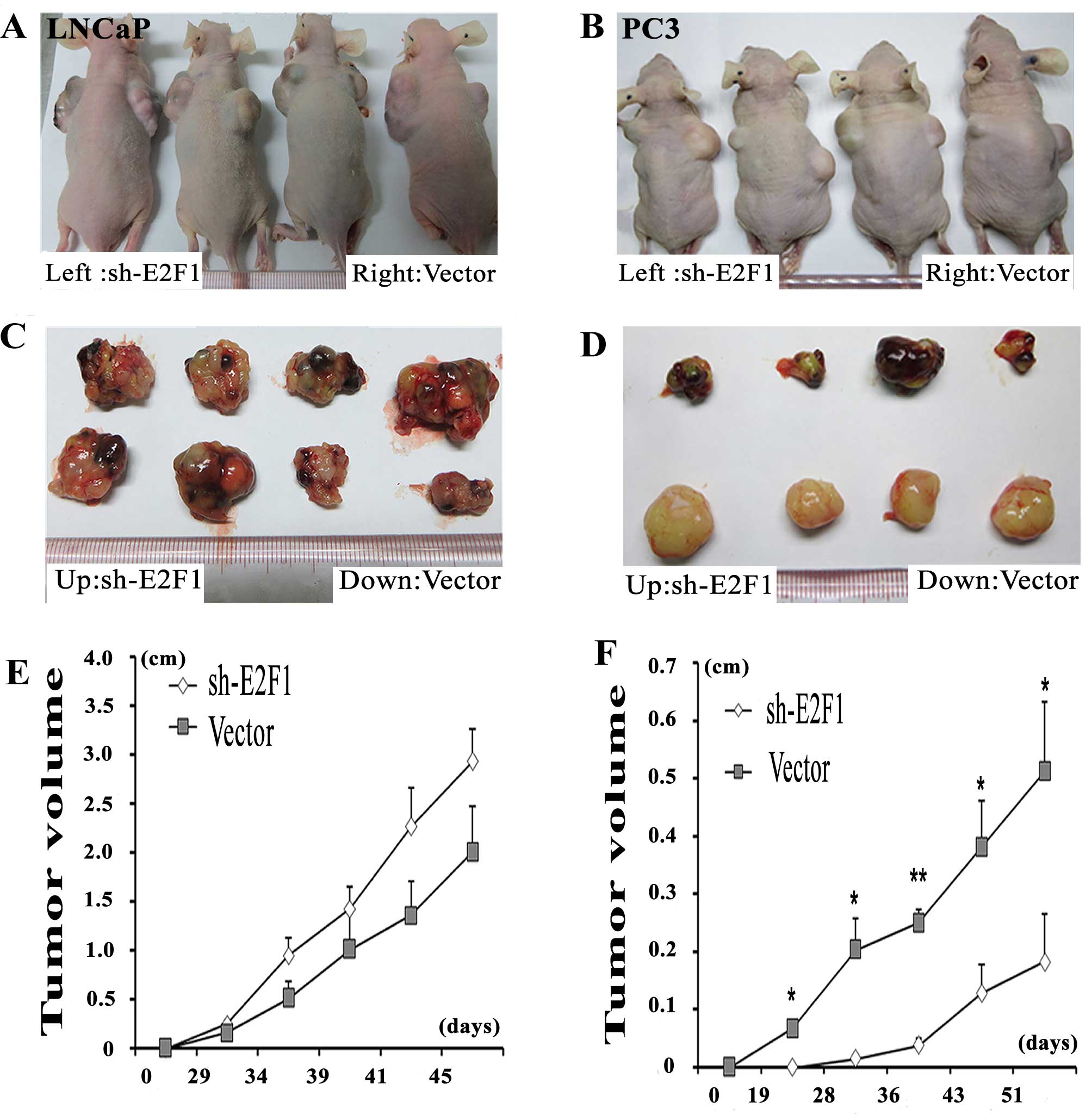
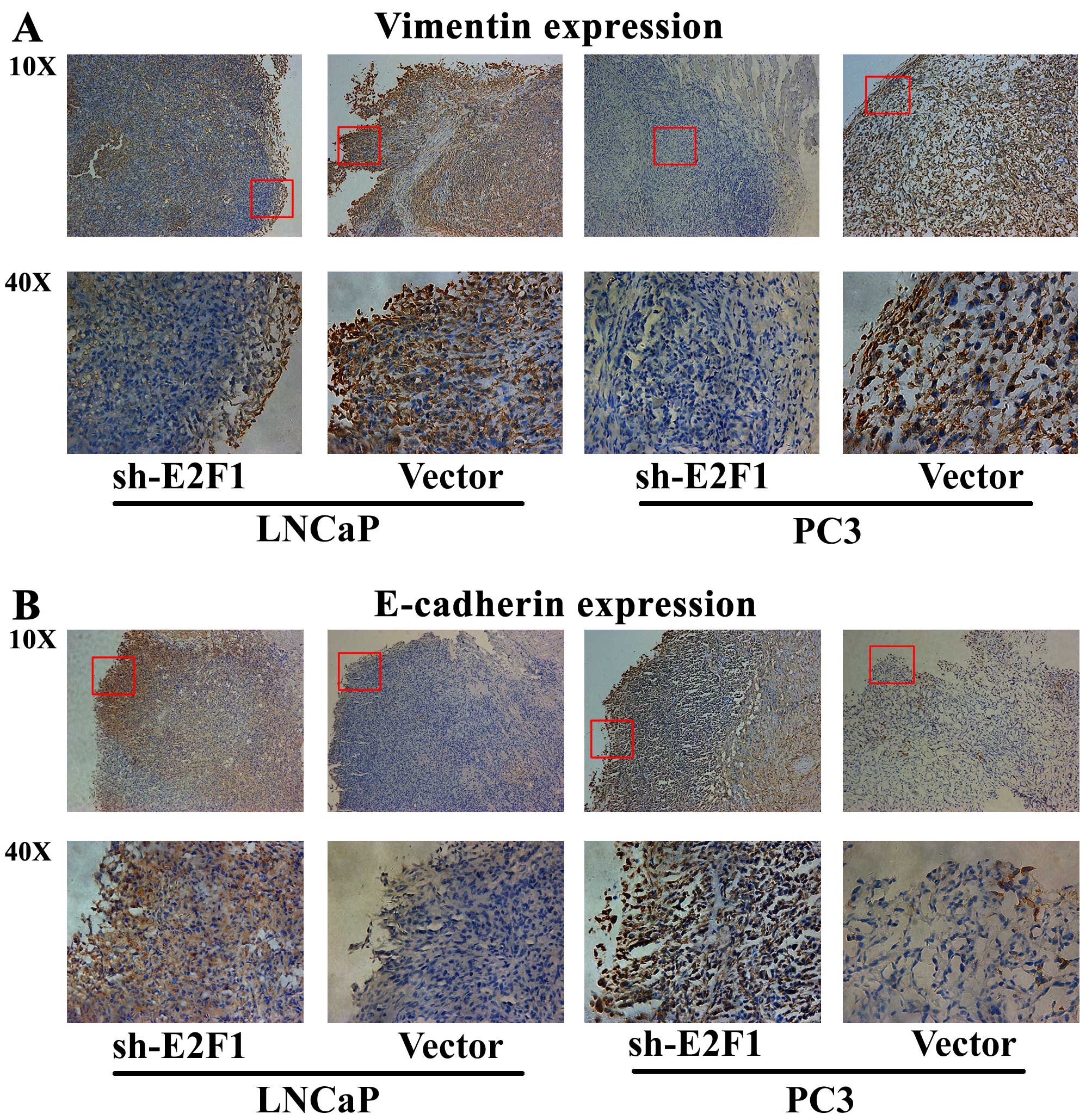
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nandana S and Chung LW: Prostate cancer
progression and metastasis: Potential regulatory pathways for
therapeutic targeting. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2:92–101.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Han M, Partin AW, Zahurak M, Piantadosi S,
Epstein JI and Walsh PC: Biochemical (prostate specific antigen)
recurrence probability following radical prostatectomy for
clinically localized prostate cancer. J Urol. 169:517–523. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lapointe J, Li C, Higgins JP, van de Rijn
M, Bair E, Montgomery K, Ferrari M, Egevad L, Rayford W, Bergerheim
U, et al: Gene expression profiling identifies clinically relevant
subtypes of prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:811–816.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
D'Amico AV, Moul J, Carroll PR, Sun L,
Lubeck D and Chen MH: Cancer-specific mortality after surgery or
radiation for patients with clinically localized prostate cancer
managed during the prostate-specific antigen era. J Clin Oncol.
21:2163–2172. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ogawa H, Ishiguro K, Gaubatz S, Livingston
DM and Nakatani Y: A complex with chromatin modifiers that occupies
E2F- and Myc-responsive genes in G0 cells. Science. 296:1132–1136.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ishida S, Huang E, Zuzan H, Spang R, Leone
G, West M and Nevins JR: Role for E2F in control of both DNA
replication and mitotic functions as revealed from DNA microarray
analysis. Mol Cell Biol. 21:4684–4699. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ginsberg D: E2F1 pathways to apoptosis.
FEBS Lett. 529:122–125. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Johnson DG: The paradox of E2F1: Oncogene
and tumor suppressor gene. Mol Carcinog. 27:151–157. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Saito M, Helin K, Valentine MB, Griffith
BB, Willman CL, Harlow E and Look AT: Amplification of the E2F1
transcription factor gene in the HEL erythroleukemia cell line.
Genomics. 25:130–138. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Montenegro MF, Collado-González MM,
Fernández-Pérez MP, Hammouda MB, Tolordava L, Gamkrelidze M and
Rodríguez-López JN: Promoting E2F1-mediated apoptosis in oestrogen
receptor-α-negative breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 14:5392014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lu M, Liu Z, Yu H, Wang LE, Li G, Sturgis
EM, Johnson DG and Wei Q: Combined effects of E2F1 and E2F2
polymorphisms on risk and early onset of squamous cell carcinoma of
the head and neck. Mol Carcinog. 51(Suppl 1): E132–E141. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rizwani W, Schaal C, Kunigal S, Coppola D
and Chellappan S: Mammalian lysine histone demethylase KDM2A
regulates E2F1-mediated gene transcription in breast cancer cells.
PLoS One. 9:e1008882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hung JJ, Hsueh CT, Chen KH, Hsu WH and Wu
YC: Clinical significance of E2F1 protein expression in non-small
cell lung cancer. Exp Hematol Oncol. 1:182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren Z, Kang W, Wang L, Sun B, Ma J, Zheng
C, Sun J, Tian Z, Yang X and Xiao W: E2F1 renders prostate cancer
cell resistant to ICAM-1 mediated antitumor immunity by NF-κB
modulation. Mol Cancer. 13:842014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Davis JN, Wojno KJ, Daignault S, Hofer MD,
Kuefer R, Rubin MA and Day ML: Elevated E2F1 inhibits transcription
of the androgen receptor in metastatic hormone-resistant prostate
cancer. Cancer Res. 66:11897–11906. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng C, Ren Z, Wang H, Zhang W,
Kalvakolanu DV, Tian Z and Xiao W: E2F1 Induces tumor cell survival
via nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent induction of EGR1 transcription
in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 69:2324–2331. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Libertini SJ, Tepper CG, Guadalupe M, Lu
Y, Asmuth DM and Mudryj M: E2F1 expression in LNCaP prostate cancer
cells deregulates androgen dependent growth, suppresses
differentiation, and enhances apoptosis. Prostate. 66:70–81. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lin ZY, Huang YQ, Zhang YQ, Han ZD, He HC,
Ling XH, Fu X, Dai QS, Cai C, Chen JH, et al: MicroRNA-224 inhibits
progression of human prostate cancer by downregulating TRIB1. Int J
Cancer. 135:541–550. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen G, Liang YX, Zhu JG, Fu X, Chen YF,
Mo RJ, Zhou L, Fu H, Bi XC, He HC, et al: CC chemokine ligand 18
correlates with malignant progression of prostate cancer. Biomed
Res Int. 2014:2301832014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kwon AT, Arenillas DJ, Worsley Hunt R and
Wasserman WW: oPOSSUM-3: Advanced analysis of regulatory motif
over-representation across genes or ChIP-Seq datasets. G3
(Bethesda). 2:987–1002. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Farré D, Roset R, Huerta M, Adsuara JE,
Roselló L, Albà MM and Messeguer X: Identification of patterns in
biological sequences at the ALGGEN server: PROMO and MALGEN.
Nucleic Acids Res. 31:3651–3653. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhong WD, Liang YX, Lin SX, Li L, He HC,
Bi XC, Han ZD, Dai QS, Ye YK, Chen QB, et al: Expression of CD147
is associated with prostate cancer progression. Int J Cancer.
130:300–308. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li Z, Guo Y, Jiang H, Zhang T, Jin C,
Young CY and Yuan H: Differential regulation of MMPs by E2F1, Sp1
and NF-kappa B controls the small cell lung cancer invasive
phenotype. BMC Cancer. 14:2762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma X, Gao Y, Fan Y, Ni D, Zhang Y, Chen W,
Zhang P, Song E, Huang Q, Ai Q, et al: Overexpression of E2F1
promotes tumor malignancy and correlates with TNM stages in clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e734362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Engelmann D, Mayoli-Nüssle D, Mayrhofer C,
Fürst K, Alla V, Stoll A, Spitschak A, Abshagen K, Vollmar B, Ran
S, et al: E2F1 promotes angiogenesis through the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3
axis in a feedback loop for cooperative induction of PDGF-B. J Mol
Cell Biol. 5:391–403. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee J, Park CK, Park JO, Lim T, Park YS,
Lim HY, Lee I, Sohn TS, Noh JH, Heo JS, et al: Impact of E2F-1
expression on clinical outcome of gastric adenocarcinoma patients
with adjuvant chemoradiation therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 14:82–88.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Grupp K, Höhne TS, Prien K, Hube-Magg C,
Tsourlakis MC, Sirma H, Pham T, Heinzer H, Graefen M, Michl U, et
al: Reduced CD147 expression is linked to ERG fusion-positive
prostate cancers but lacks substantial impact on PSA recurrence in
patients treated by radical prostatectomy. Exp Mol Pathol.
95:227–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pértega-Gomes N, Vizcaíno JR,
Miranda-Gonçalves V, Pinheiro C, Silva J, Pereira H, Monteiro P,
Henrique RM, Reis RM, Lopes C, et al: Monocarboxylate transporter 4
(MCT4) and CD147 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis
in prostate cancer. BMC Cancer. 11:3122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhong WD, Han ZD, He HC, Bi XC, Dai QS,
Zhu G, Ye YK, Liang YX, Qin WJ, Zhang Z, et al: CD147, MMP-1, MMP-2
and MMP-9 protein expression as significant prognostic factors in
human prostate cancer. Oncology. 75:230–236. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han ZD, Bi XC, Qin WJ, He HC, Dai QS, Zou
J, Ye YK, Liang YX, Zeng GH, Chen ZN, et al: CD147 expression
indicates unfavourable prognosis in prostate cancer. Pathol Oncol
Res. 15:369–374. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|