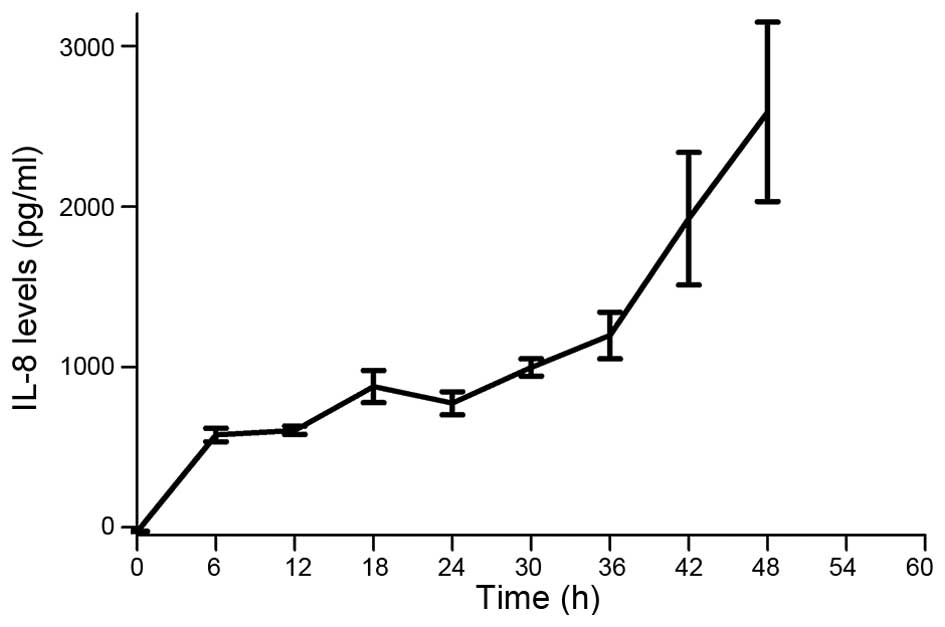
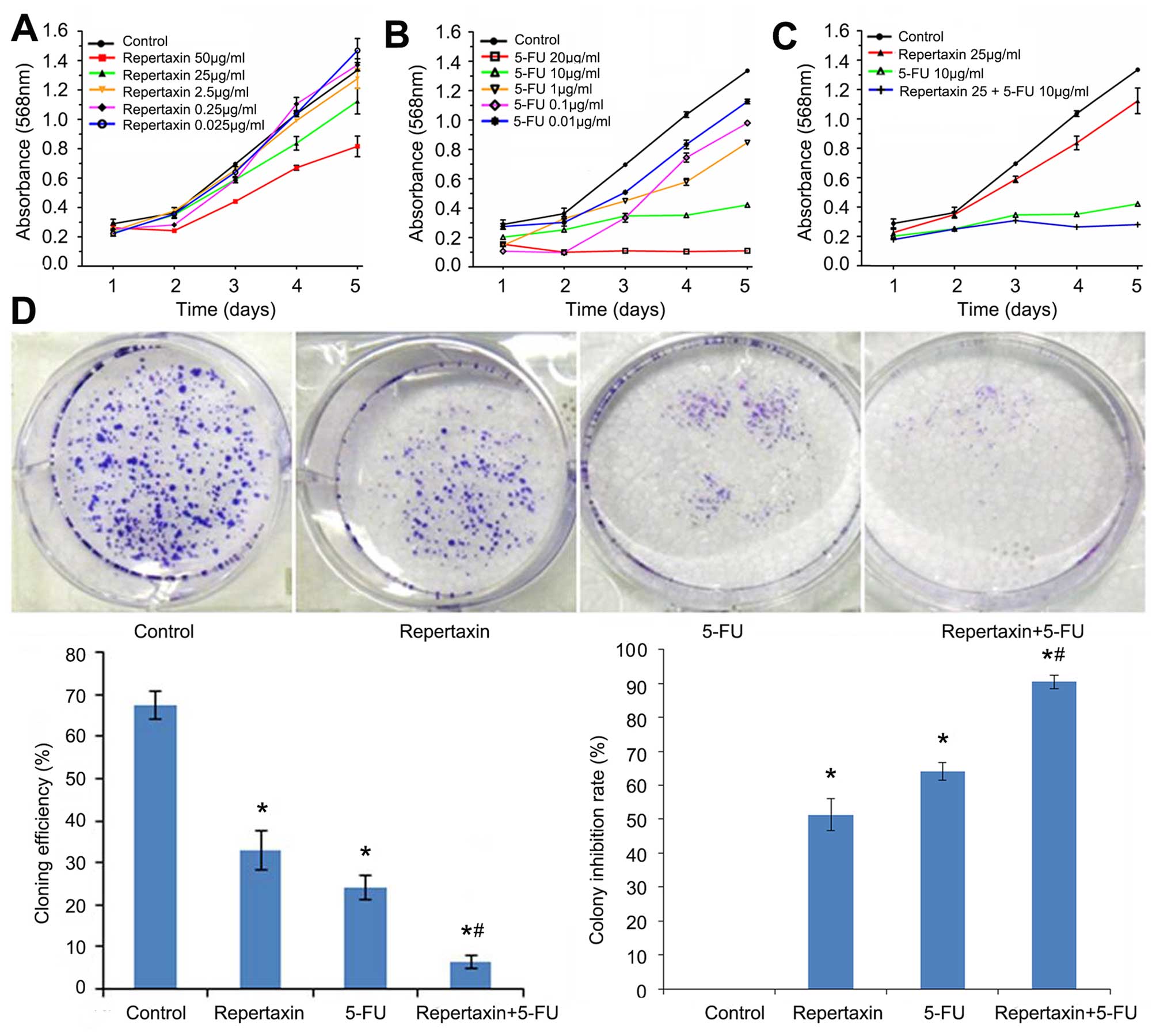
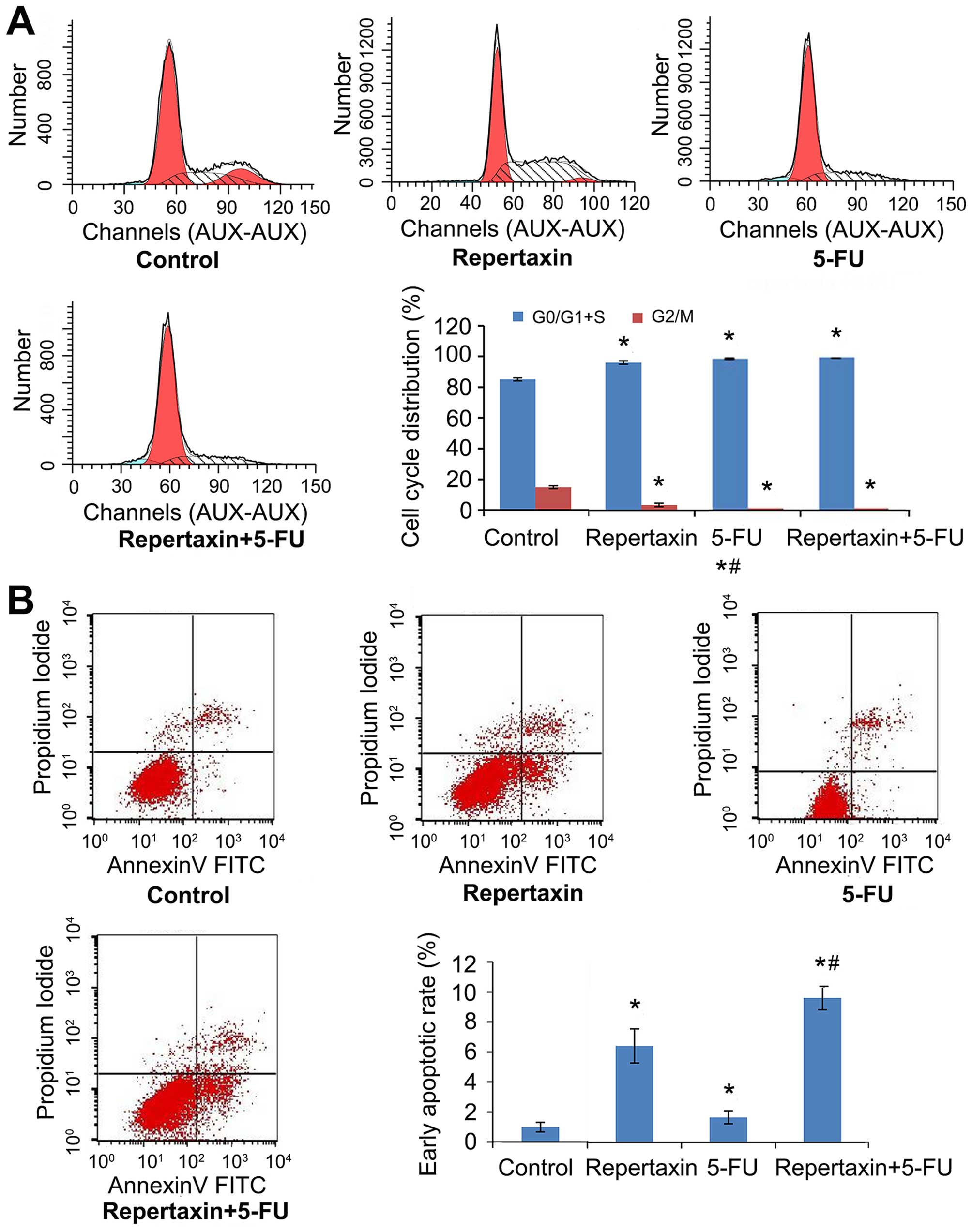
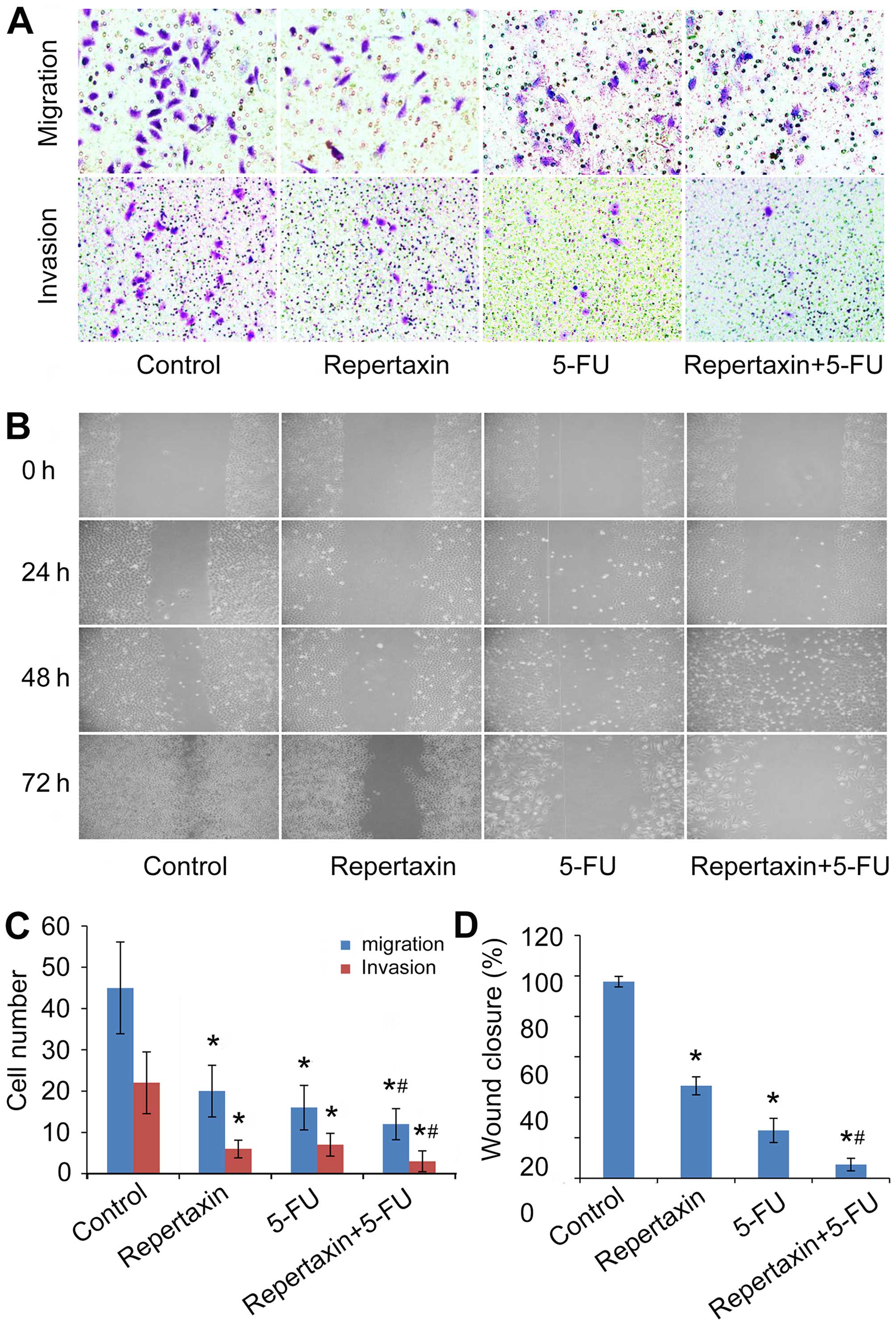
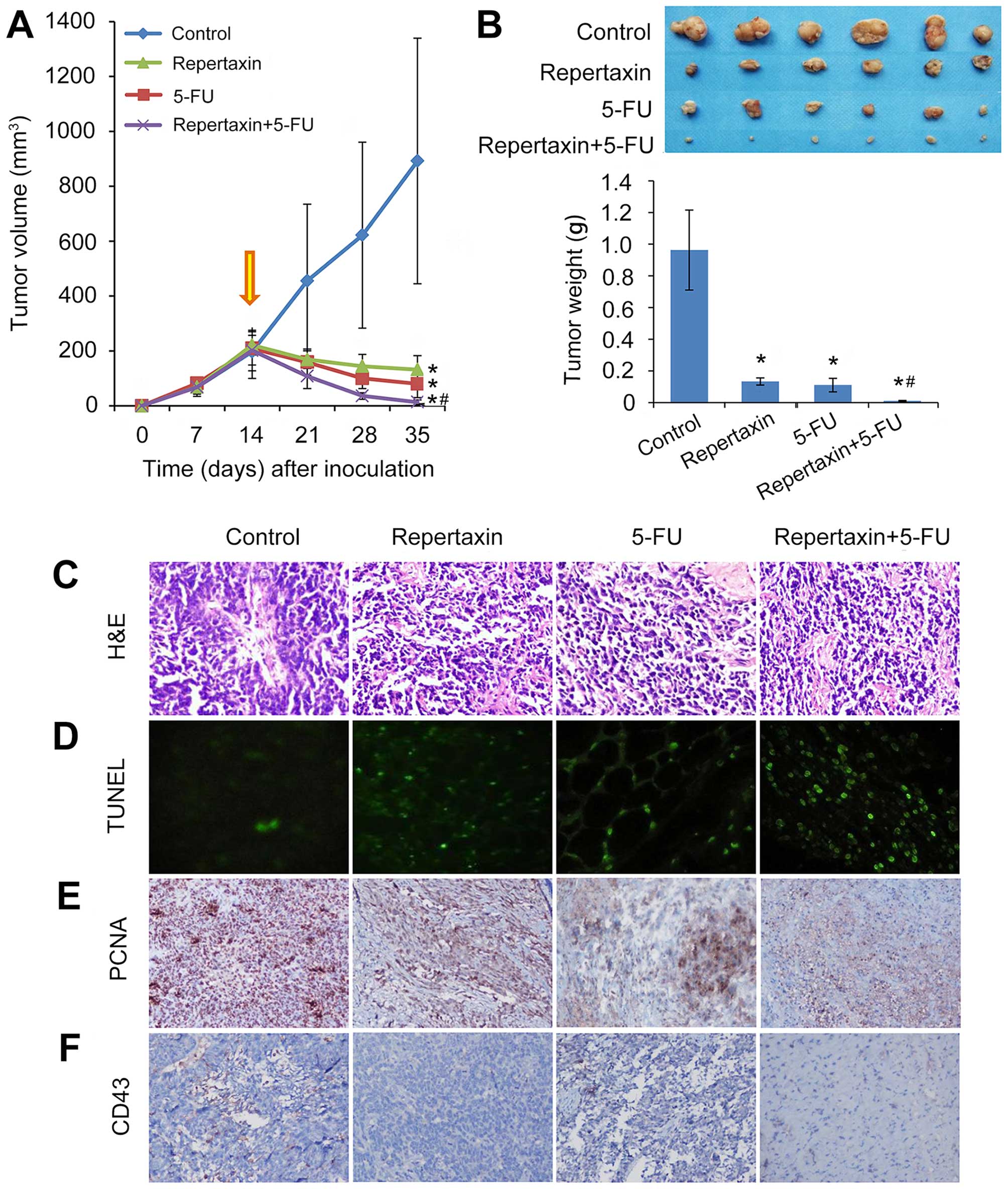
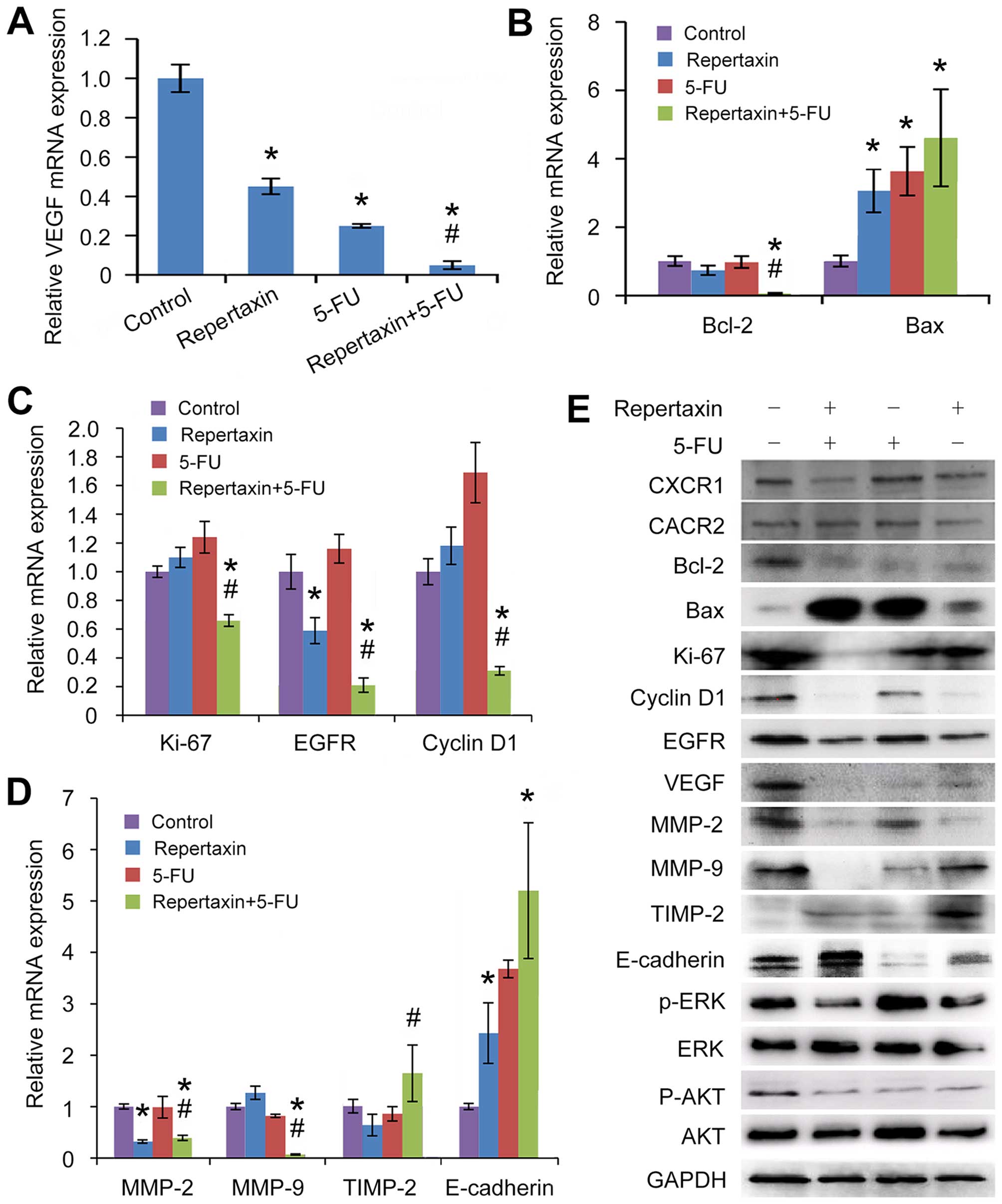
|
1
|
Alberts SR, Cervantes A and van de Velde
CJ: Gastric cancer: Epidemiology, pathology and treatment. Ann
Oncol. 14(Suppl 2): ii31–ii36. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
|
|
3
|
Yang L: Incidence and mortality of gastric
cancer in China. World J Gastroenterol. 12:17–20. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shah MA and Kelsen DP: Gastric cancer: A
primer on the epidemiology and biology of the disease and an
overview of the medical management of advanced disease. J Natl
Compr Canc Netw. 8:437–447. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hyung WJ, Noh SH, Yoo CH, Huh JH, Shin DW,
Lah KH, Lee JH, Choi SH and Min JS: Prognostic significance of
meta-static lymph node ratio in T3 gastric cancer. World J Surg.
26:323–329. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nathan C and Ding A: Nonresolving
inflammation. Cell. 140:871–882. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mantovani A: Cancer: Inflaming metastasis.
Nature. 457:36–37. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Righi E, Kashiwagi S, Yuan J, Santosuosso
M, Leblanc P, Ingraham R, Forbes B, Edelblute B, Collette B, Xing
D, et al: CXCL12/CXCR4 blockade induces multimodal antitumor
effects that prolong survival in an immunocompetent mouse model of
ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 71:5522–5534. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wendel C, Hemping-Bovenkerk A, Krasnyanska
J, Mees ST, Kochetkova M, Stoeppeler S and Haier J: CXCR4/CXCL12
participate in extravasation of metastasizing breast cancer cells
within the liver in a rat model. PLoS One. 7:e300462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Balkwill FR: The chemokine system and
cancer. J Pathol. 226:148–157. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lazennec G and Richmond A: Chemokines and
chemokine receptors: New insights into cancer-related inflammation.
Trends Mol Med. 16:133–144. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Raman D, Baugher PJ, Thu YM and Richmond
A: Role of chemokines in tumor growth. Cancer Lett. 256:137–165.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ali S and Lazennec G: Chemokines: Novel
targets for breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:401–420. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vindrieux D, Escobar P and Lazennec G:
Emerging roles of chemokines in prostate cancer. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 16:663–673. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC,
Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, Carey VJ, Richardson AL
and Weinberg RA: Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human
breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through
elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell. 121:335–348. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Colmone A, Amorim M, Pontier AL, Wang S,
Jablonski E and Sipkins DA: Leukemic cells create bone marrow
niches that disrupt the behavior of normal hematopoietic progenitor
cells. Science. 322:1861–1865. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singh S, Varney M and Singh RK: Host
CXCR2-dependent regulation of melanoma growth, angiogenesis, and
experimental lung metastasis. Cancer Res. 69:411–415. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kitamura T, Kometani K, Hashida H,
Matsunaga A, Miyoshi H, Hosogi H, Aoki M, Oshima M, Hattori M,
Takabayashi A, et al: SMAD4-deficient intestinal tumors recruit
CCR1+ myeloid cells that promote invasion. Nat Genet.
39:467–475. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Buonamici S, Trimarchi T, Ruocco MG,
Reavie L, Cathelin S, Mar BG, Klinakis A, Lukyanov Y, Tseng JC, Sen
F, et al: CCR7 signalling as an essential regulator of CNS
infiltration in T-cell leukaemia. Nature. 459:1000–1004. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Murphy PM: The molecular biology of
leukocyte chemoattractant receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 12:593–633.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin BR, Chang CC, Chen LR, Wu MH, Wang MY,
Kuo IH, Chu CY, Chang KJ, Lee PH, Chen WJ, et al: Cysteine-rich 61
(CCN1) enhances chemotactic migration, transendothelial cell
migration, and intravasation by concomitantly up-regulating
chemokine receptor 1 and 2. Mol Cancer Res. 5:1111–1123. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kitadai Y, Haruma K, Mukaida N, Ohmoto Y,
Matsutani N, Yasui W, Yamamoto S, Sumii K, Kajiyama G, Fidler IJ,
et al: Regulation of disease-progression genes in human gastric
carcinoma cells by interleukin 8. Clin Cancer Res. 6:2735–2740.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Waugh DJ and Wilson C: The interleukin-8
pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6735–6741. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Y, Wang L, Zhang M, Jin M, Bai C and
Wang X: Potential mechanism of interleukin-8 production from lung
cancer cells: An involvement of EGF-EGFR-PI3K-Akt-Erk pathway. J
Cell Physiol. 227:35–43. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ginestier C, Liu S, Diebel ME, Korkaya H,
Luo M, Brown M, Wicinski J, Cabaud O, Charafe-Jauffret E, Birnbaum
D, et al: CXCR1 blockade selectively targets human breast cancer
stem cells in vitro and in xenografts. J Clin Invest. 120:485–497.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Singh S, Nannuru KC, Sadanandam A, Varney
ML and Singh RK: CXCR1 and CXCR2 enhances human melanoma
tumourigenesis, growth and invasion. Br J Cancer. 100:1638–1646.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Varney ML, Singh S, Li A, Mayer-Ezell R,
Bond R and Singh RK: Small molecule antagonists for CXCR2 and CXCR1
inhibit human colon cancer liver metastases. Cancer Lett.
300:180–188. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Eck M, Schmausser B, Scheller K, Brändlein
S and Müller-Hermelink HK: Pleiotropic effects of CXC chemokines in
gastric carcinoma: Differences in CXCL8 and CXCL1 expression
between diffuse and intestinal types of gastric carcinoma. Clin Exp
Immunol. 134:508–515. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Singh JK, Farnie G, Bundred NJ, Simões BM,
Shergill A, Landberg G, Howell SJ and Clarke RB: Targeting CXCR1/2
significantly reduces breast cancer stem cell activity and
increases the efficacy of inhibiting HER2 via HER2-dependent and
-independent mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res. 19:643–656. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ning Y, Labonte MJ, Zhang W, Bohanes PO,
Gerger A, Yang D, Benhaim L, Paez D, Rosenberg DO, Nagulapalli
Venkata KC, et al: The CXCR2 antagonist, SCH-527123, shows
antitumor activity and sensitizes cells to oxaliplatin in
preclinical colon cancer models. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:1353–1364.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Singh S, Sadanandam A, Nannuru KC, Varney
ML, Mayer-Ezell R, Bond R and Singh RK: Small-molecule antagonists
for CXCR2 and CXCR1 inhibit human melanoma growth by decreasing
tumor cell proliferation, survival, and angiogenesis. Clin Cancer
Res. 15:2380–2386. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Casilli F, Bianchini A, Gloaguen I, Biordi
L, Alesse E, Festuccia C, Cavalieri B, Strippoli R, Cervellera MN,
Di Bitondo R, et al: Inhibition of interleukin-8 (CXCL8/IL-8)
responses by repertaxin, a new inhibitor of the chemokine receptors
CXCR1 and CXCR2. Biochem Pharmacol. 69:385–394. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bertini R, Allegretti M, Bizzarri C,
Moriconi A, Locati M, Zampella G, Cervellera MN, Di Cioccio V,
Cesta MC, Galliera E, et al: Noncompetitive allosteric inhibitors
of the inflammatory chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2: Prevention
of reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:11791–11796.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Clarke C, Kuboki S, Sakai N, Kasten KR,
Tevar AD, Schuster R, Blanchard J, Caldwell CC, Edwards MJ and
Lentsch AB: CXC chemokine receptor-1 is expressed by hepatocytes
and regulates liver recovery after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Hepatology. 53:261–271. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang JP, Hu WM, Wang KS, Luo BH, Wu C,
Chen ZH, Luo GQ, Liu YW, Liu QL, Yu J, et al: Upregulation of C-X-C
chemokine receptor type 1 expression is associated with late-stage
gastric adenocarcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 4:55–60. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang JP, Hu WM, Wang KS, Yu J, Luo BH, Wu
C, Chen ZH, Luo GQ, Liu YW, Liu QL, et al: Expression of C-X-C
chemokine receptor types 1/2 in patients with gastric carcinoma:
Clinicopathological correlations and significance. Oncol Lett.
5:574–582. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim JG, Kang MJ, Yoon YK, Kim HP, Park J,
Song SH, Han SW, Park JW, Kang GH, Kang KW, et al:
Heterodimerization of glycosylated insulin-like growth factor-1
receptors and insulin receptors in cancer cells sensitive to
anti-IGF1R antibody. PLoS One. 7:e333222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lecomte N, Njardarson JT, Nagorny P, Yang
G, Downey R, Ouerfelli O, Moore MA and Danishefsky SJ: Emergence of
potent inhibitors of metastasis in lung cancer via syntheses based
on migrastatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:15074–15078. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Matsuo Y, Ochi N, Sawai H, Yasuda A,
Takahashi H, Funahashi H, Takeyama H, Tong Z and Guha S: CXCL8/IL-8
and CXCL12/SDF-1alpha co-operatively promote invasiveness and
angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 124:853–861. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Singh S, Sadanandam A, Varney ML, Nannuru
KC and Singh RK: Small interfering RNA-mediated CXCR1 or CXCR2
knock-down inhibits melanoma tumor growth and invasion. Int J
Cancer. 126:328–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hall PA, Levison DA, Woods AL, Yu CC,
Kellock DB, Watkins JA, Barnes DM, Gillett CE, Camplejohn R, Dover
R, et al: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)
immunolocalization in paraffin sections: An index of cell
proliferation with evidence of deregulated expression in some
neoplasms. J Pathol. 162:285–294. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Che X, Hokita S, Natsugoe S, Tanabe G,
Baba M, Takao S and Aikou T: Tumor angiogenesis related to growth
pattern and lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer. Chin Med
J (Engl). 111:1090–1093. 1998.
|
|
44
|
Kitadai Y: Angiogenesis and
lymphangiogenesis of gastric cancer. J Oncol. 2010:4687252010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Singh S, Sadanandam A and Singh RK:
Chemokines in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 26:453–467. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Smalley KS: A pivotal role for ERK in the
oncogenic behaviour of malignant melanoma? Int J Cancer.
104:527–532. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cheng GZ, Park S, Shu S, He L, Kong W,
Zhang W, Yuan Z, Wang LH and Cheng JQ: Advances of AKT pathway in
human oncogenesis and as a target for anti-cancer drug discovery.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:2–6. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xue M, Ge Y, Zhang J, Wang Q, Hou L, Liu
Y, Sun L and Li Q: Anticancer properties and mechanisms of fucoidan
on mouse breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.
7:e434832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Verbeke H, Geboes K, Van Damme J and
Struyf S: The role of CXC chemokines in the transition of chronic
inflammation to esophageal and gastric cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1825.117–129. 2012.
|
|
50
|
Lane HC, Anand AR and Ganju RK: Cbl and
Akt regulate CXCL8-induced and CXCR1- and CXCR2-mediated
chemo-taxis. Int Immunol. 18:1315–1325. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Venkatakrishnan G, Salgia R and Groopman
JE: Chemokine receptors CXCR-1/2 activate mitogen-activated protein
kinase via the epidermal growth factor receptor in ovarian cancer
cells. J Biol Chem. 275:6868–6875. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
MacManus CF, Pettigrew J, Seaton A, Wilson
C, Maxwell PJ, Berlingeri S, Purcell C, McGurk M, Johnston PG and
Waugh DJ: Interleukin-8 signaling promotes translational regulation
of cyclin D in androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Res. 5:737–748. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Luppi F, Longo AM, de Boer WI, Rabe KF and
Hiemstra PS: Interleukin-8 stimulates cell proliferation in
non-small cell lung cancer through epidermal growth factor receptor
transactivation. Lung Cancer. 56:25–33. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|