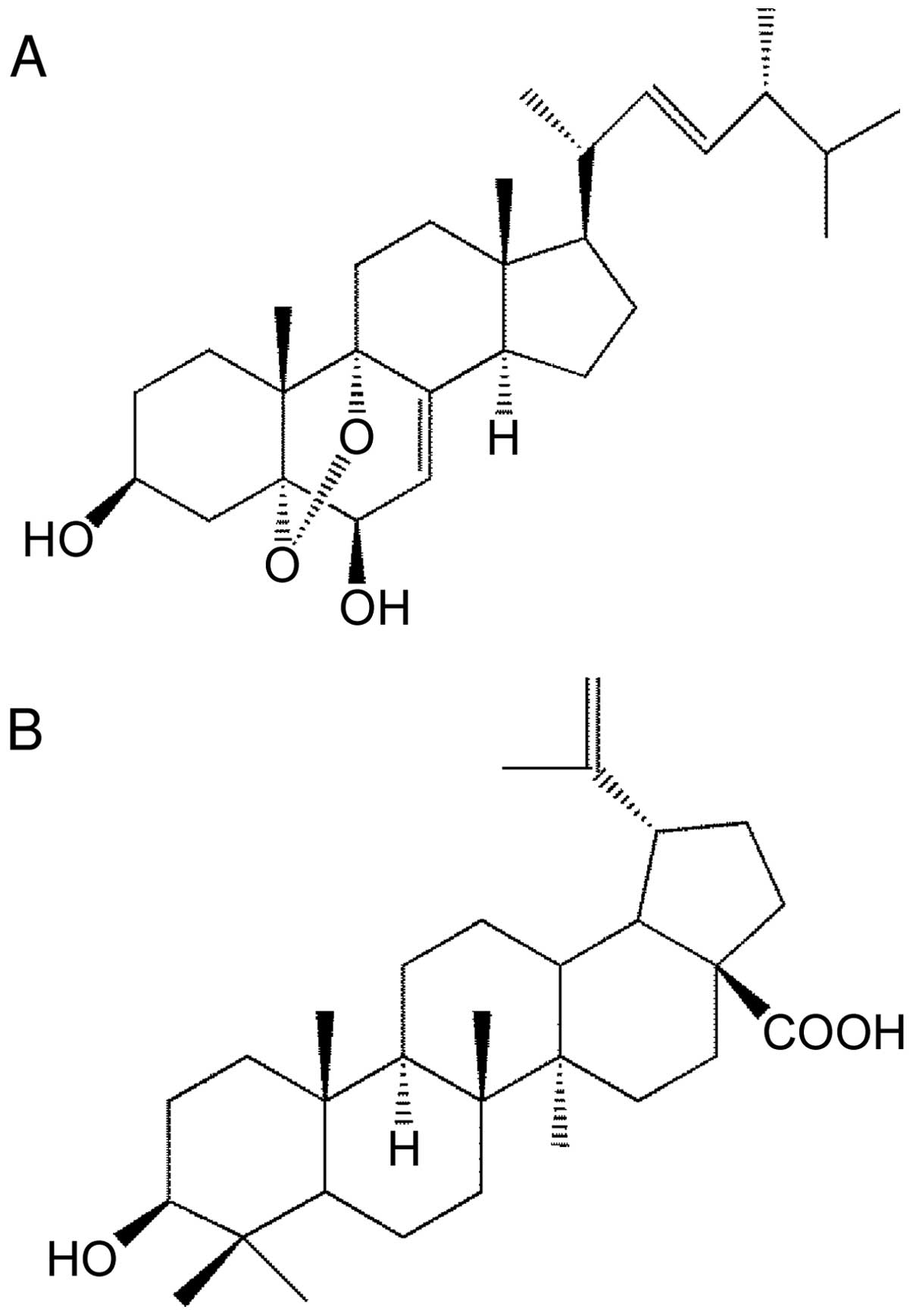
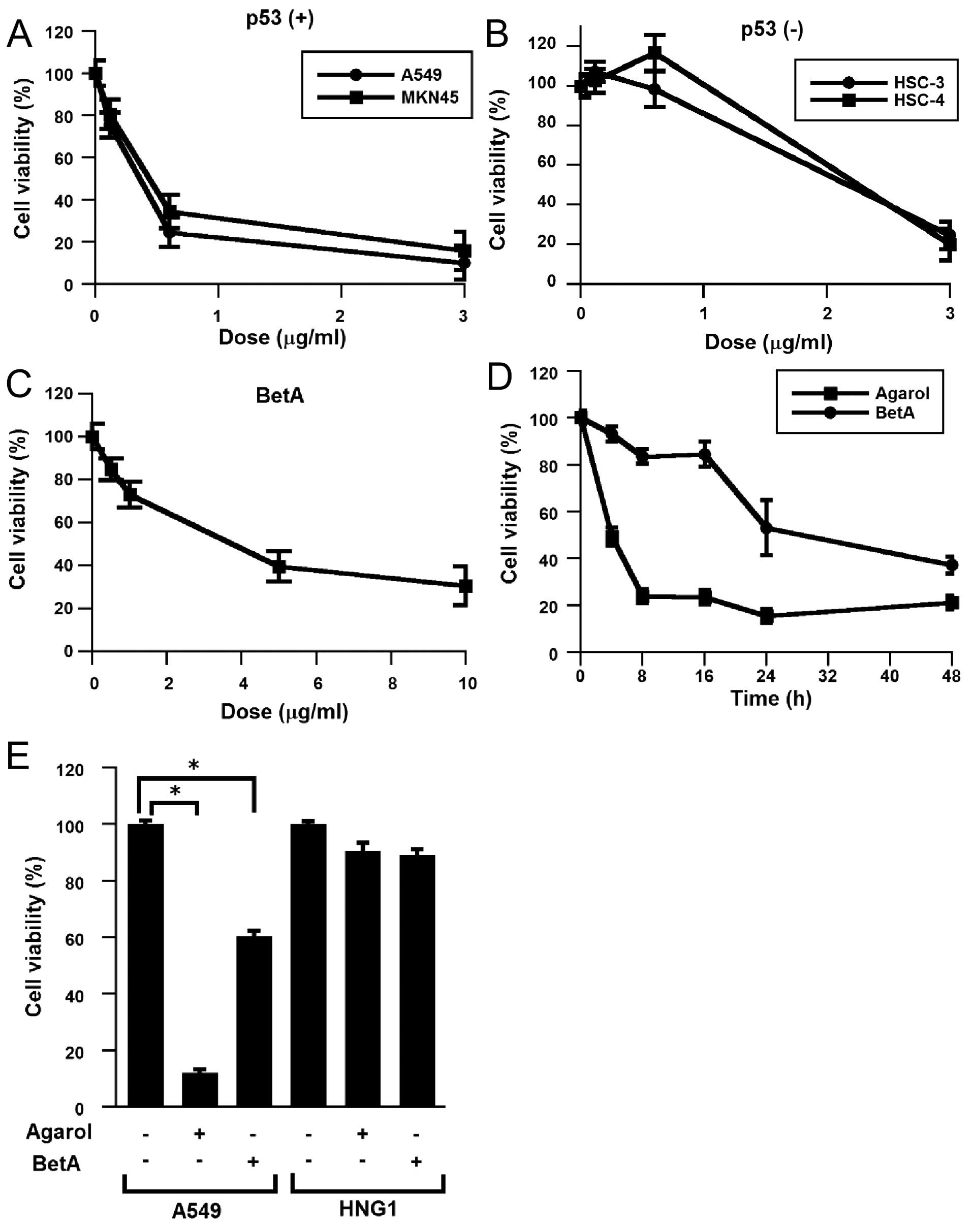
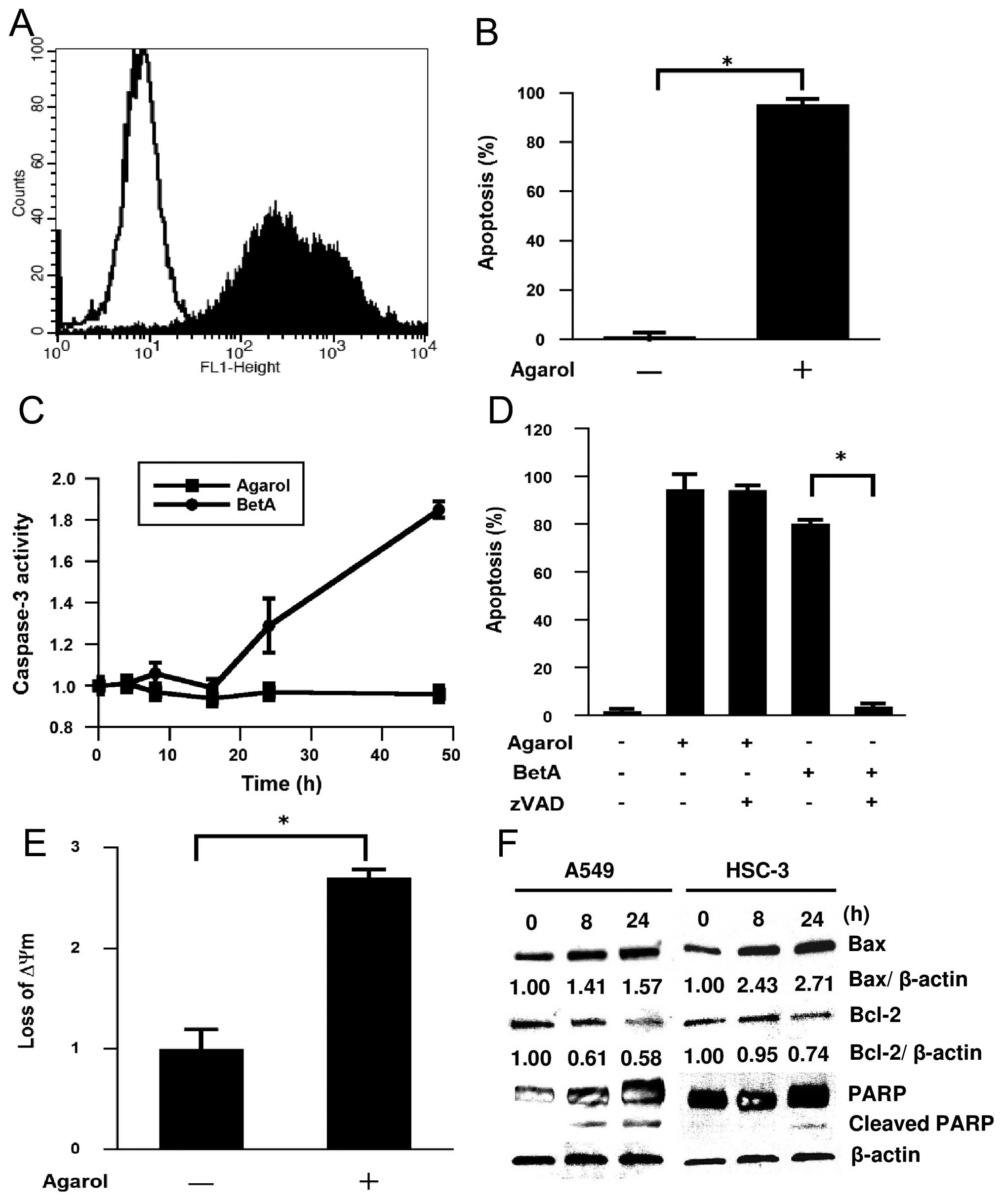
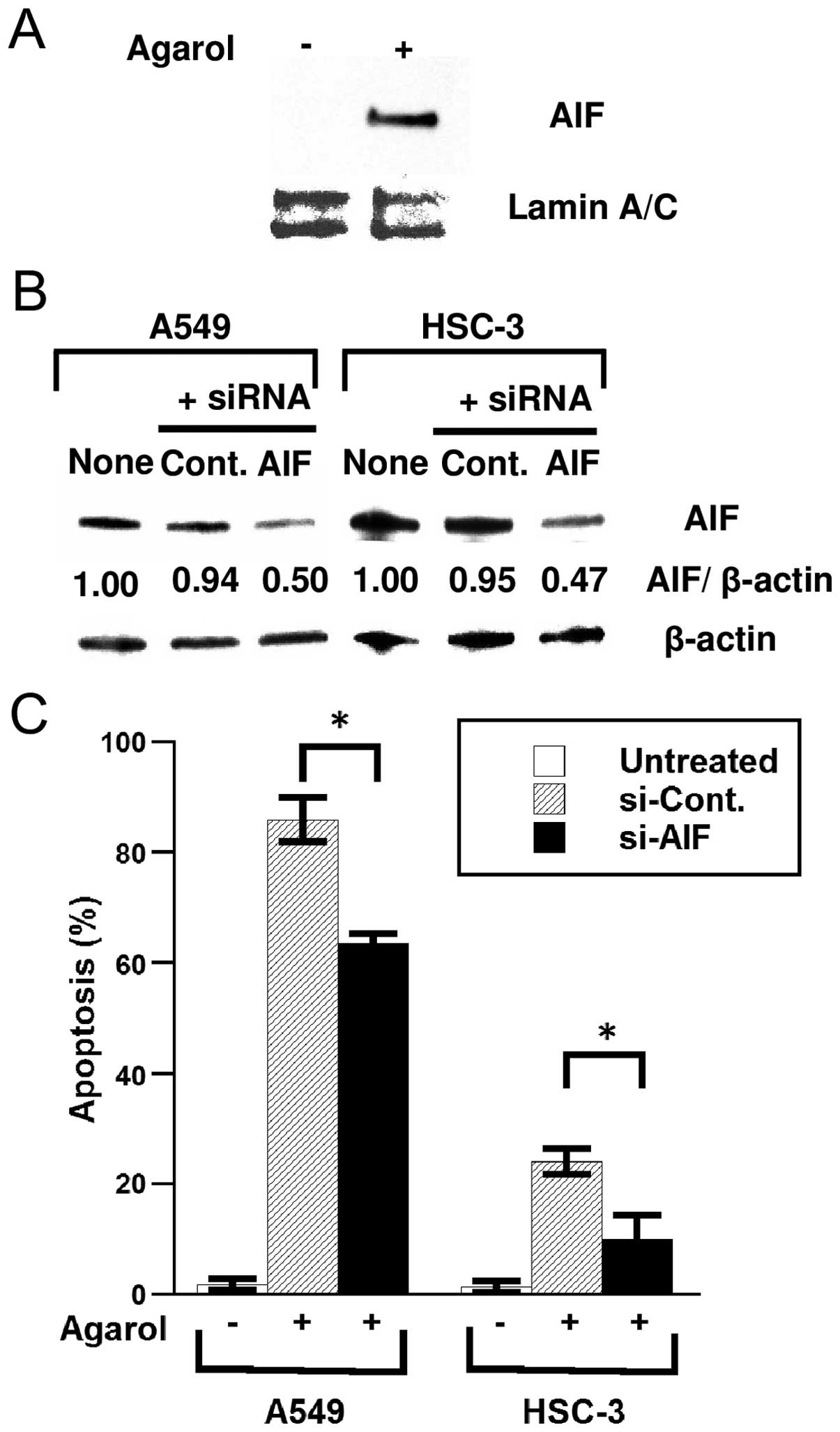
|
1
|
Xu T, Beelman RB and Lambert JD: The
cancer preventive effects of edible mushrooms. Anticancer Agents
Med Chem. 12:1255–1263. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kidd PM: The use of mushroom glucans and
proteoglycans in cancer treatment. Altern Med Rev. 5:4–27.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ohno N, Furukawa M, Miura NN, Adachi Y,
Motoi M and Yadomae T: Antitumor beta glucan from the cultured
fruit body of Agaricus blazei. Biol Pharm Bull. 24:820–828. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takaku T, Kimura Y and Okuda H: Isolation
of an antitumor compound from Agaricus blazei Murill and its
mechanism of action. J Nutr. 131:1409–1413. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Su Z-Y, Tung Y-C, Hwang LS and Sheen L-Y:
Blazeispirol A from Agaricus blazei fermentation product induces
cell death in human hepatoma Hep 3B cells through caspase-dependent
and caspase-independent pathways. J Agric Food Chem. 59:5109–5116.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ziliotto L, Pinheiro F, Barbisan LF and
Rodrigues MAM: Screening for in vitro and in vivo antitumor
activities of the mushroom Agaricus blazei. Nutr Cancer.
61:245–250. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Suzuki M, Endo M, Shinohara F, Echigo S
and Rikiishi H: Differential apoptotic response of human cancer
cells to organoselenium compounds. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
66:475–484. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kroemer G and Martin SJ:
Caspase-independent cell death. Nat Med. 11:725–730. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hirose T and Horvitz HR: An Sp1
transcription factor coordinates caspase-dependent and -independent
apoptotic pathways. Nature. 500:354–358. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim E-A, Jang J-H, Lee Y-H, Sung EG, Song
IH, Kim JY, Kim S, Sohn HY and Lee TJ: Dioscin induces
caspase-independent apoptosis through activation of
apoptosis-inducing factor in breast cancer cells. Apoptosis.
19:1165–1175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yogeeswari P and Sriram D: Betulinic acid
and its derivatives: A review on their biological properties. Curr
Med Chem. 12:657–666. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Y and Luo W: Betulinic acid induces
Bax/Bak-independent cytochrome c release in human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells. Mol Cells. 33:517–524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hetland G, Johnson E, Lyberg T and
Kvalheim G: The mushroom Agaricus blazei murill elicits medicinal
effects on tumor, infection, allergy, and inflammation through its
modulation of innate immunity and amelioration of Th1/Th2 imbalance
and inflammation. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2011:1570152011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ooi VE and Liu F: Immunomodulation and
anti-cancer activity of polysaccharide-protein complexes. Curr Med
Chem. 7:715–729. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu C-H, Kan S-F, Shu C-H, Lu T-J,
Sun-Hwang L and Wang PS: Inhibitory mechanisms of Agaricus blazei
Murill on the growth of prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo. J
Nutr Biochem. 20:753–764. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kobayashi H, Yoshida R, Kanada Y, Fukuda
Y, Yagyu T, Inagaki K, Kondo T, Kurita N, Suzuki M, Kanayama N, et
al: Suppressing effects of daily oral supplementation of
beta-glucan extracted from Agaricus blazei Murill on spontaneous
and peritoneal disseminated metastasis in mouse model. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 131:527–538. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jin C-Y, Choi YH, Moon D-O, Park C, Park
YM, Jeong SC, Heo MS, Lee TH, Lee JD and Kim GY: Induction of G2/M
arrest and apoptosis in human gastric epithelial AGS cells by
aqueous extract of Agaricus blazei. Oncol Rep. 16:1349–1355.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rieber M and Rieber MS: Signalling
responses linked to betulinic acid-induced apoptosis are
antagonized by MEK inhibitor U0126 in adherent or 3D spheroid
melanoma irrespective of p53 status. Int J Cancer. 118:1135–1143.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Green DR and Kroemer G: Cytoplasmic
functions of the tumour suppressor p53. Nature. 458:1127–1130.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tung Y-C, Su Z-Y, Kuo M-L and Sheen L-Y:
Ethanolic extract of Agaricus blazei fermentation product inhibits
the growth and invasion of human hepatoma HA22T/VGH and SK-Hep-1
cells. J Tradit Complement Med. 2:145–153. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hajnóczky G, Davies E and Madesh M:
Calcium signaling and apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
304:445–454. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Holley AK, Dhar SK and St Clair DK:
Manganese superoxide dismutase versus p53: The mitochondrial
center. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1201:72–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maillet A and Pervaiz S: Redox regulation
of p53, redox effectors regulated by p53: A subtle balance.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:1285–1294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim M-O, Moon D-O, Jung JM, Lee WS, Choi
YH and Kim G-Y: Agaricus blazei extract induces apoptosis through
ROS-dependent JNK activation involving the mitochondrial pathway
and suppression of constitutive NF-κB in THP-1 cells. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2011:8381722011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chintharlapalli S, Papineni S, Lei P,
Pathi S and Safe S: Betulinic acid inhibits colon cancer cell and
tumor growth and induces proteasome-dependent and -independent
downregulation of specificity proteins (Sp) transcription factors.
BMC Cancer. 11:3712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li X, Zhao X, Wang H, Han J and Liu L: A
polysaccharide from the fruiting bodies of Agaricus blazei Murill
induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells.
Tumour Biol. 35:8963–8968. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xie J, Xu Y, Huang X, Chen Y, Fu J, Xi M
and Wang L: Berberine-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer
cells is mediated by reactive oxygen species generation and
mitochondrial-related apoptotic pathway. Tumour Biol. 36:1279–1288.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Su J, Cheng H, Zhang D, Wang M, Xie C, Hu
Y, Chang HC and Li Q: Synergistic effects of 5-fluorouracil and
gambogenic acid on A549 cells: Activation of cell death caused by
apoptotic and necroptotic mechanisms via the ROS-mitochondria
pathway. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:1259–1268. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu M-F, Chen Y-L, Lee M-H, Shih YL, Hsu
YM, Tang MC, Lu HF, Tang NY, Yang ST, Chueh FS, et al: Effect of
Agaricus blazei Murrill extract on HT-29 human colon cancer cells
in SCID mice in vivo. In Vivo. 25:673–677. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wasser SP: Medicinal mushrooms as a source
of antitumor and immunomodulating polysaccharides. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 60:258–274. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nozaki H, Itonori S, Sugita M, Nakamura K,
Ohba K, Suzuki A and Kushi Y: Mushroom acidic glycosphingolipid
induction of cytokine secretion from murine T cells and
proliferation of NK1.1 α/β TCR-double positive cells in vitro.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 373:435–439. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee JS and Hong EK: Agaricus blazei Murill
enhances doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by NFκB-mediated increase of intracellular
doxorubicin accumulation. Int J Oncol. 38:401–408. 2011.
|