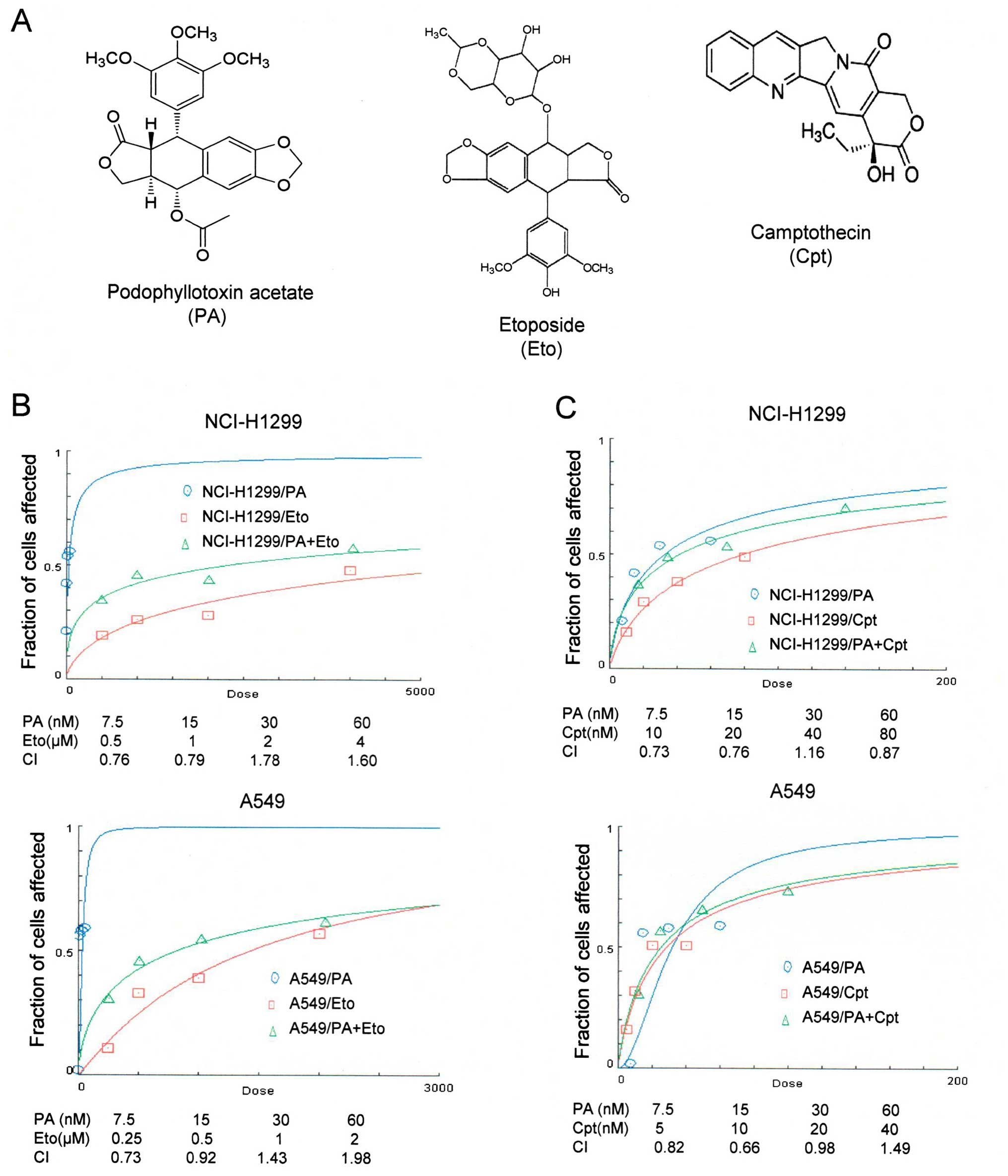
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mitsudomi T, Suda K and Yatabe Y: Surgery
for NSCLC in the era of personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
10:235–244. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ismael GF, Rosa DD, Mano MS and Awada A:
Novel cytotoxic drugs: Old challenges, new solutions. Cancer Treat
Rev. 34:81–91. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Choi JY, Cho HJ, Hwang SG, Kim WJ, Kim JI,
Um HD and Park JK: Podophyllotoxin acetate enhances γ-ionizing
radiation-induced apoptotic cell death by stimulating the
ROS/p38/caspase pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 70:111–118. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gordaliza M, García PA, del Corral JM,
Castro MA and Gómez-Zurita MA: Podophyllotoxin: Distribution,
sources, applications and new cytotoxic derivatives. Toxicon.
44:441–459. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guerram M, Jiang Z-Z and Zhang L-Y:
Podophyllotoxin, a medicinal agent of plant origin: Past, present
and future. Chin J Nat Med. 10:161–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wall ME, Wani MC, Cooke CE, Palmer KH,
McPhail AT and Sim GA: Plant antitumor agents. I. The isolation and
structure of camptothecin, a novel alkaloidal leukemia and tumor
nhibitor from Camptotheca acuminata. J Am Chem Soc. 88:3888–3890.
1966. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hsiang Y-H, Hertzberg R, Hecht S and Liu
LF: Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian
DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 260:14873–14878. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gabr A, Kuin A, Aalders M, El-Gawly H and
Smets LA: Cellular pharmacokinetics and cytotoxicity of
camptothecin and topotecan at normal and acidic pH. Cancer Res.
57:4811–4816. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Venditto VJ and Simanek EE: Cancer
therapies utilizing the camptothecins: A review of the in vivo
literature. Mol Pharm. 7:307–349. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Choi JY, Hong WG, Cho JH, Kim EM, Kim J,
Jung CH, Hwang SG, Um HD and Park JK: Podophyllotoxin acetate
triggers anticancer effects against non-small cell lung cancer
cells by promoting cell death via cell cycle arrest, ER stress and
autophagy. Int J Oncol. 47:1257–1265. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park JK, Jung HY, Park SH, Kang SY, Yi MR,
Um HD and Hong SH: Combination of PTEN and gamma-ionizing radiation
enhances cell death and G(2)/M arrest through regulation of AKT
activity and p21 induction in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Int
J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 70:1552–1560. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Park JK, Park SH, So K, Bae IH, Yoo YD and
Um HD: ICAM-3 enhances the migratory and invasive potential of
human non-small cell lung cancer cells by inducing MMP-2 and MMP-9
via Akt and CREB. Int J Oncol. 36:181–192. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Piva R, Belardo G and Santoro MG:
NF-kappaB: A stress-regulated switch for cell survival. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 8:478–486. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shabbits JA, Hu Y and Mayer LD: Tumor
chemosensitization strategies based on apoptosis manipulations. Mol
Cancer Ther. 2:805–813. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reed JC: Regulation of apoptosis by bcl-2
family proteins and its role in cancer and chemoresistance. Curr
Opin Oncol. 7:541–546. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
LaCasse EC, Baird S, Korneluk RG and
MacKenzie AE: The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) and their emerging
role in cancer. Oncogene. 17:3247–3259. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Turrini E, Ferruzzi L and Fimognari C:
Natural compounds to overcome cancer chemoresistance: Toxicological
and clinical issues. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 10:1677–1690.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rudolf E and Cervinka M: Topoisomerases
and tubulin inhibitors: A promising combination for cancer
treatment. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 3:421–429. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Houghton PJ, Cheshire PJ, Hallman JD II,
Lutz L, Friedman HS, Danks MK and Houghton JA: Efficacy of
topoisomerase I inhibitors, topotecan and irinotecan, administered
at low dose levels in protracted schedules to mice bearing
xenografts of human tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 36:393–403.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bunn PA Jr and Kelly K: New
chemotherapeutic agents prolong survival and improve quality of
life in non-small cell lung cancer: A review of the literature and
future directions. Clin Cancer Res. 4:1087–1100. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lawenda BD, Kelly KM, Ladas EJ, Sagar SM,
Vickers A and Blumberg JB: Should supplemental antioxidant
administration be avoided during chemotherapy and radiation
therapy? J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:773–783. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Van Laethem A, Nys K, Van Kelst S,
Claerhout S, Ichijo H, Vandenheede JR, Garmyn M and Agostinis P:
Apoptosis signal regulating kinase-1 connects reactive oxygen
species to p38 MAPK-induced mitochondrial apoptosis in
UVB-irradiated human keratinocytes. Free Radic Biol Med.
41:1361–1371. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pang H, Cai L, Yang Y, Chen X, Sui G and
Zhao C: Knockdown of osteopontin chemosensitizes MDA-MB-231 cells
to cyclophosphamide by enhancing apoptosis through activating p38
MAPK pathway. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 26:165–173. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shin DY, Lee WS, Lu JN, Kang MH, Ryu CH,
Kim GY, Kang HS, Shin SC and Choi YH: Induction of apoptosis in
human colon cancer HCT-116 cells by anthocyanins through
suppression of Akt and activation of p38-MAPK. Int J Oncol.
35:1499–1504. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chiu SJ, Chao JI, Lee YJ and Hsu TS:
Regulation of gamma-H2AX and securin contribute to apoptosis by
oxaliplatin via a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent
pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. Toxicol Lett. 179:63–70.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lou X, Zhou Q, Yin Y, Zhou C and Shen Y:
Inhibition of the met receptor tyrosine kinase signaling enhances
the chemosensitivity of glioma cell lines to CDDP through
activation of p38 MAPK pathway. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:1126–1136. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Crans HN and Sakamoto KM: Transcription
factors and translocations in lymphoid and myeloid leukemia.
Leukemia. 15:313–331. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pigazzi M, Ricotti E, Germano G, Faggian
D, Aricò M and Basso G: cAMP response element binding protein
(CREB) over-expression CREB has been described as critical for
leukemia progression. Haematologica. 92:1435–1437. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shankar DB, Cheng JC, Kinjo K, Federman N,
Moore TB, Gill A, Rao NP, Landaw EM and Sakamoto KM: The role of
CREB as a proto-oncogene in hematopoiesis and in acute myeloid
leukemia. Cancer Cell. 7:351–362. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Seo H-S, Liu DD, Bekele BN, Kim MK,
Pisters K, Lippman SM, Wistuba II and Koo JS: Cyclic AMP response
element-binding protein overexpression: A feature associated with
negative prognosis in never smokers with non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Res. 68:6065–6073. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shaywitz AJ and Greenberg ME: CREB: A
stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array
of extracellular signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 68:821–861. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mayr B and Montminy M: Transcriptional
regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 2:599–609. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mayr BM, Canettieri G and Montminy MR:
Distinct effects of cAMP and mitogenic signals on CREB-binding
protein recruitment impart specificity to target gene activation
via CREB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:10936–10941. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Amorino GP, Hamilton VM, Valerie K, Dent
P, Lammering G and Schmidt-Ullrich RK: Epidermal growth factor
receptor dependence of radiation-induced transcription factor
activation in human breast carcinoma cells. Mol Biol Cell.
13:2233–2244. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Matsumoto K, Yamamoto T, Kurachi H, Nishio
Y, Takeda T, Homma H, Morishige K, Miyake A and Murata Y: Human
chorionic gonadotropin-alpha gene is transcriptionally activated by
epidermal growth factor through cAMP response element in
trophoblast cells. J Biol Chem. 273:7800–7806. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Swarthout JT, Tyson DR, Jefcoat SC Jr and
Partridge NC: Induction of transcriptional activity of the cyclic
adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein by
parathyroid hormone and epidermal growth factor in osteoblastic
cells. J Bone Miner Res. 17:1401–1407. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|