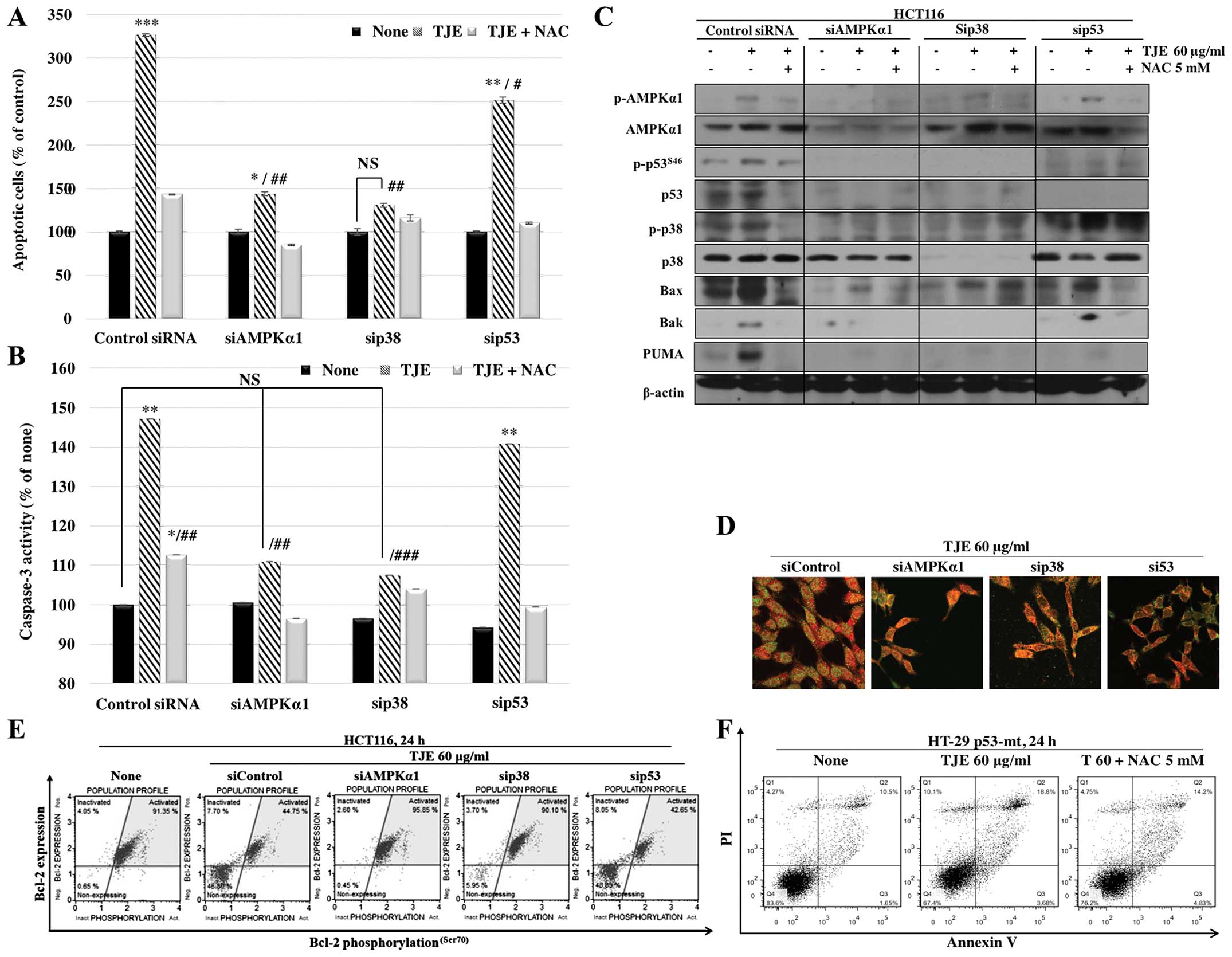
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Center MM, Jemal A and Ward E:
International trends in colorectal cancer incidence rates. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:1688–1694. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Parkin DM, Whelan SL, Ferlay J and Storm
H: Cancer Incidence in Five Continents. I to VIII. Cancer Base 7.
IARC Press; Lyon: 2005
|
|
5
|
Ito Y, Ioka A, Tanaka M, Nakayama T and
Tsukuma H: Trends in cancer incidence and mortality in Osaka,
Japan: Evaluation of cancer control activities. Cancer Sci.
100:2390–2395. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Giovannucci E: Modifiable risk factors for
colon cancer. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 31:925–943. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kushi LH, Byers T, Doyle C, Bandera EV,
McCullough M, McTiernan A, Gansler T, Andrews KS and Thun MJ;
American Cancer Society 2006 Nutrition and Physical Activity
Guidelines Advisory Committee: American Cancer Society Guidelines
on Nutrition and Physical Activity for cancer prevention. Reducing
the risk of cancer with healthy food choices and physical activity.
CA Cancer J Clin. 56:254–281; quiz 313–314. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Colditz GA, Sellers TA and Trapido E:
Epidemiology - identifying the causes and preventability of cancer?
Nat Rev Cancer. 6:75–83. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pan SY, Zhou SF, Gao SH, Yu ZL, Zhang SF,
Tang MK, Sun JN, Ma DL, Han YF, Fong WF, et al: New perspectives on
how to discover drugs from Herbal medicines: CAM’s outstanding
contribution to modern therapeutics. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2013:6273752013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Prindull G: Apoptosis in the embryo and
tumorigenesis. Eur J Cancer. 31A:116–123. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meier P, Finch A and Evan G: Apoptosis in
development. Nature. 407:796–801. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee YK, Park SY, Kim YM, Kim DC, Lee WS,
Surh YJ and Park OJ: Suppression of mTOR via Akt-dependent and
-independent mechanisms in selenium-treated colon cancer cells:
Involvement of AMPKalpha1. Carcinogenesis. 31:1092–1099. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chien SY, Wu YC, Chung JG, Yang JS, Lu HF,
Tsou MF, Wood WG, Kuo SJ and Chen DR: Quercetin-induced apoptosis
acts through mitochondrial- and caspase-3-dependent pathways in
human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Hum Exp Toxicol. 28:493–503.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Adams JM and Cory S: Life-or-death
decisions by the Bcl-2 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci.
26:61–66. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Harris MH and Thompson CB: The role of the
Bcl-2 family in the regulation of outer mitochondrial membrane
permeability. Cell Death Differ. 7:1182–1191. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Martinou JC and Green DR: Breaking the
mitochondrial barrier. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:63–67. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jia L, Macey MG, Yin Y, Newland AC and
Kelsey SM: Subcellular distribution and redistribution of Bcl-2
family proteins in human leukemia cells undergoing apoptosis.
Blood. 93:2353–2359. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Griffin DE and Hardwick JM: Regulators of
apoptosis on the road to persistent alphavirus infection. Annu Rev
Microbiol. 51:565–592. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hsu YT, Wolter KG and Youle RJ:
Cytosol-to-membrane redistribution of Bax and Bcl-X(L) during
apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3668–3672. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C
and Wang X: Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c
release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface
death receptors. Cell. 94:481–490. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ and Yuan J: Cleavage of
BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas
pathway of apoptosis. Cell. 94:491–501. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mikhailov V, Mikhailova M, Pulkrabek DJ,
Dong Z, Venkatachalam MA and Saikumar P: Bcl-2 prevents Bax
oligomerization in the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Biol Chem.
276:18361–18374. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Antonsson B, Montessuit S, Lauper S, Eskes
R and Martinou JC: Bax oligomerization is required for
channel-forming activity in liposomes and to trigger cytochrome c
release from mitochondria. Biochem J. 345:271–278. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Antonsson B, Montessuit S, Sanchez B and
Martinou JC: Bax is present as a high molecular weight
oligomer/complex in the mitochondrial membrane of apoptotic cells.
J Biol Chem. 276:11615–11623. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sundararajan R and White E: E1B 19K blocks
Bax oligomerization and tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated
apoptosis. J Virol. 75:7506–7516. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Degterev A, Boyce M and Yuan J: A decade
of caspases. Oncogene. 22:8543–8567. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim GT, Lee SH and Kim YM: Torilis
japonica extract, a new potential EMT suppressor agent by
regulation of EGFR signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 45:1673–1679.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim GT, Lee SH, Kim JI and Kim YM:
Quercetin regulates the sestrin 2-AMPK-p38 MAPK signaling pathway
and induces apoptosis by increasing the generation of intracellular
ROS in a p53-independent manner. Int J Mol Med. 33:863–869.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee YK, Park SY, Kim YM, Lee WS and Park
OJ: AMP kinase/cyclooxygenase-2 pathway regulates proliferation and
apoptosis of cancer cells treated with quercetin. Exp Mol Med.
41:201–207. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gibellini L, Pinti M, Nasi M, Montagna JP,
De Biasi S, Roat E, Bertoncelli L, Cooper EL and Cossarizza A:
Quercetin and cancer chemoprevention. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2011:5913562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weidner C, Rousseau M, Micikas RJ, Fischer
C, Plauth A, Wowro SJ, Siems K, Hetterling G, Kliem M, Schroeder
FC, et al: Amorfrutin C induced apoptosis and inhibits
proliferation in colon cancer cells through targeting mitochondria.
J Nat Prod. 79:2–12. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang X, Chen M, Zou P, Kanchana K, Weng
Q, Chen W, Zhong P, Ji J, Zhou H, He L, et al: Curcumin analog WZ35
induced cell death via ROS-dependent ER stress and G2/M cell cycle
arrest in human prostate cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 15:8662015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
He G, He G, Zhou R, Pi Z, Zhu T, Jiang L
and Xie Y: Enhancement of cisplatin-induced colon cancer cells
apoptosis by shikonin, a natural inducer of ROS in vitro and in
vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 469:1075–1082. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tanigawa S, Fujii M and Hou DX:
Stabilization of p53 is involved in quercetin-induced cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
72:797–804. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee YK, Hwang JT, Kwon DY, Surh YJ and
Park OJ: Induction of apoptosis by quercetin is mediated through
AMPKalpha1/ASK1/p38 pathway. Cancer Lett. 292:228–236. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bouchet BP, Caron de Fromentel C, Puisieux
A and Galmarini CM: p53 as a target for anticancer drug
development. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 58:190–207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Moll UM, Marchenko N and Zhang XK: p53 and
Nur77/TR3 - transcription factors that directly target mitochondria
for cell death induction. Oncogene. 25:4725–4743. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gorgoulis VG, Vassiliou LV, Karakaidos P,
Zacharatos P, Kotsinas A, Liloglou T, Venere M, Ditullio RA Jr,
Kastrinakis NG, Levy B, et al: Activation of the DNA damage
checkpoint and genomic instability in human precancerous lesions.
Nature. 434:907–913. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oren M: Decision making by p53: Life,
death and cancer. Cell Death Differ. 10:431–442. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Olivier M, Hollstein M and Hainaut P: TP53
mutations in human cancers: Origins, consequences, and clinical
use. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2:a0010082010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cuadrado A, Lafarga V, Cheung PC, Dolado
I, Llanos S, Cohen P and Nebreda AR: A new p38 MAP kinase-regulated
transcriptional coactivator that stimulates p53-dependent
apoptosis. EMBO J. 26:2115–2126. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sanchez-Prieto R, Rojas JM, Taya Y and
Gutkind JS: A role for the p38 mitogen-acitvated protein kinase
pathway in the transcriptional activation of p53 on genotoxic
stress by chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Res. 60:2464–2472.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|