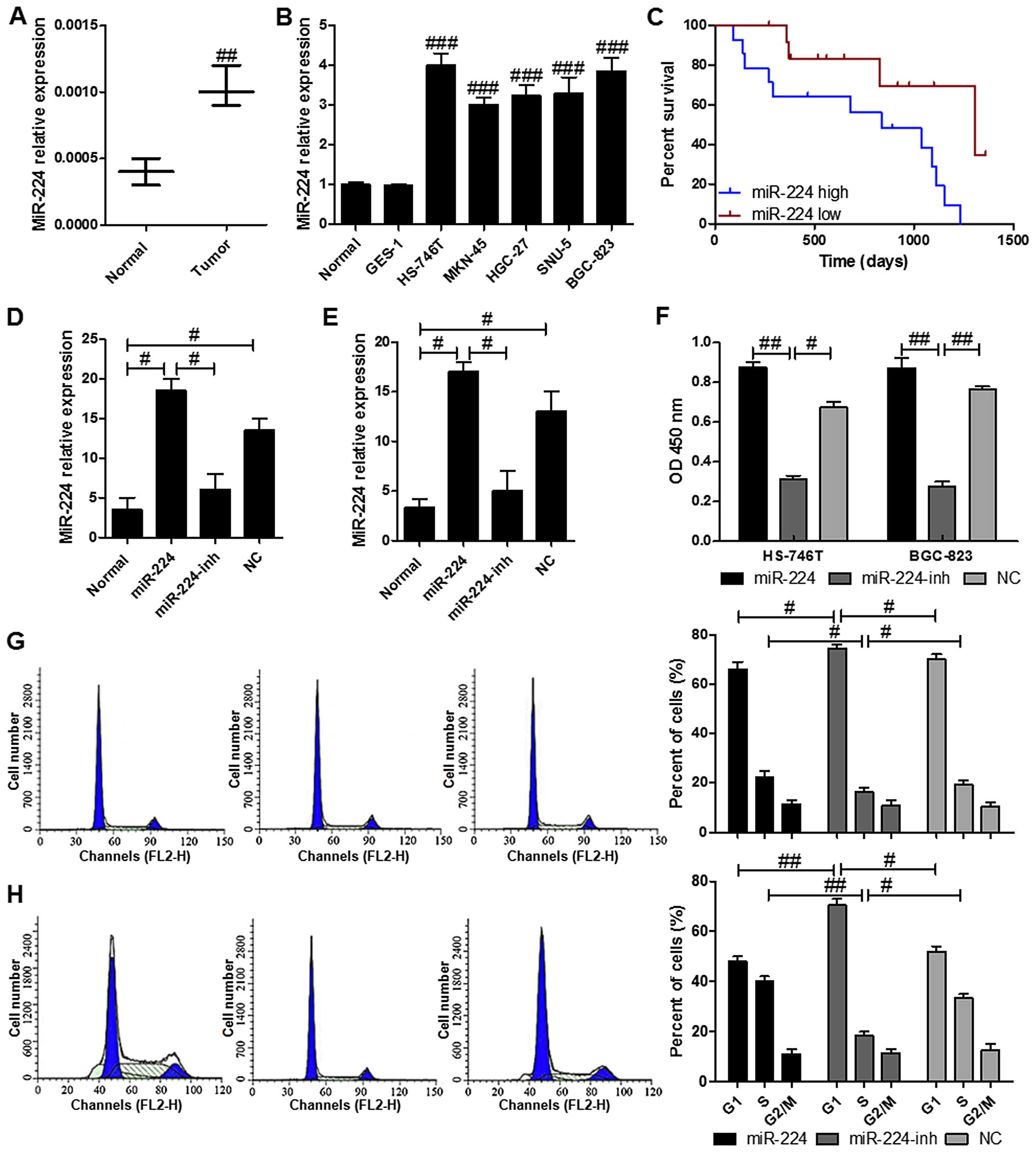
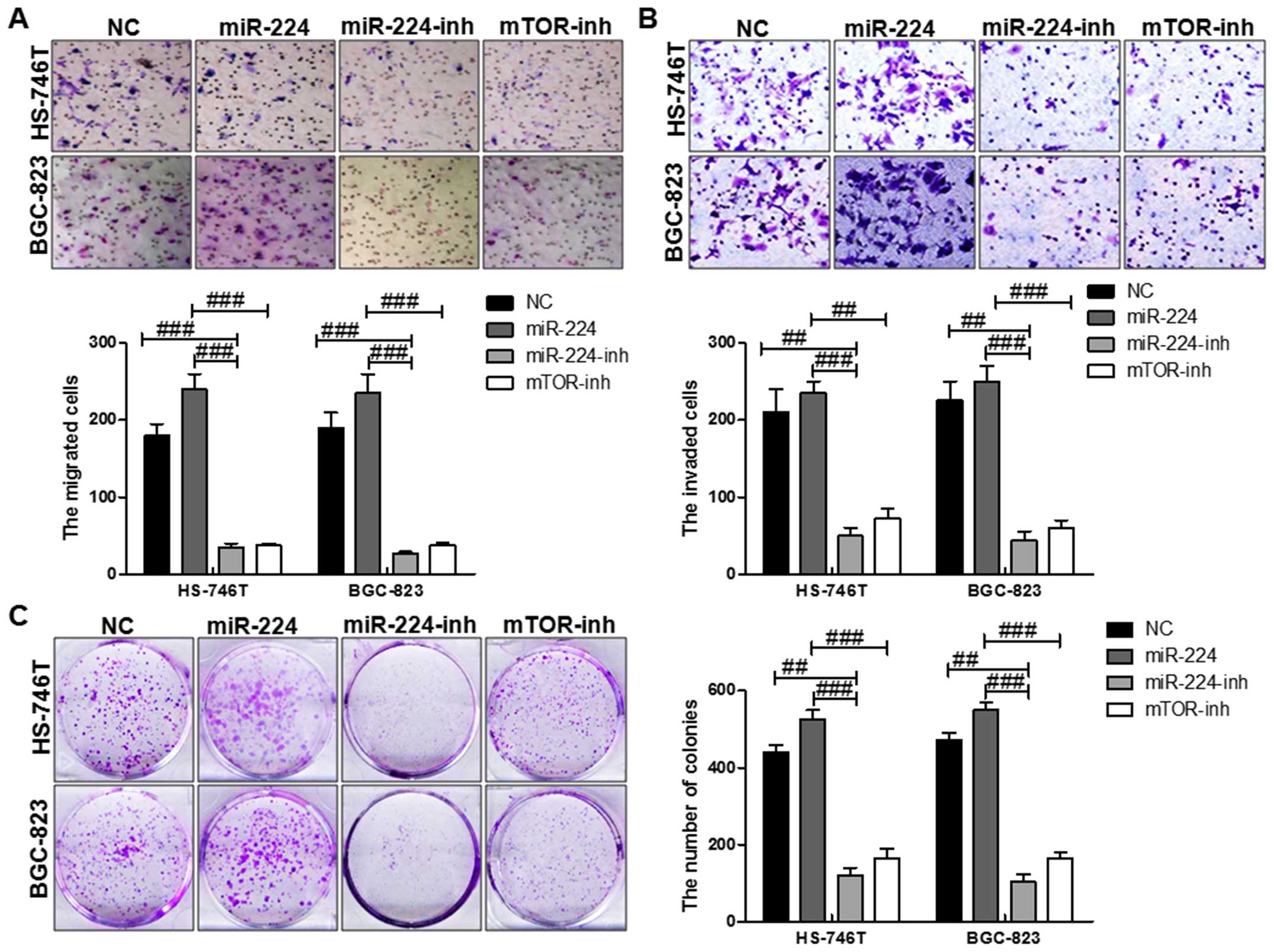
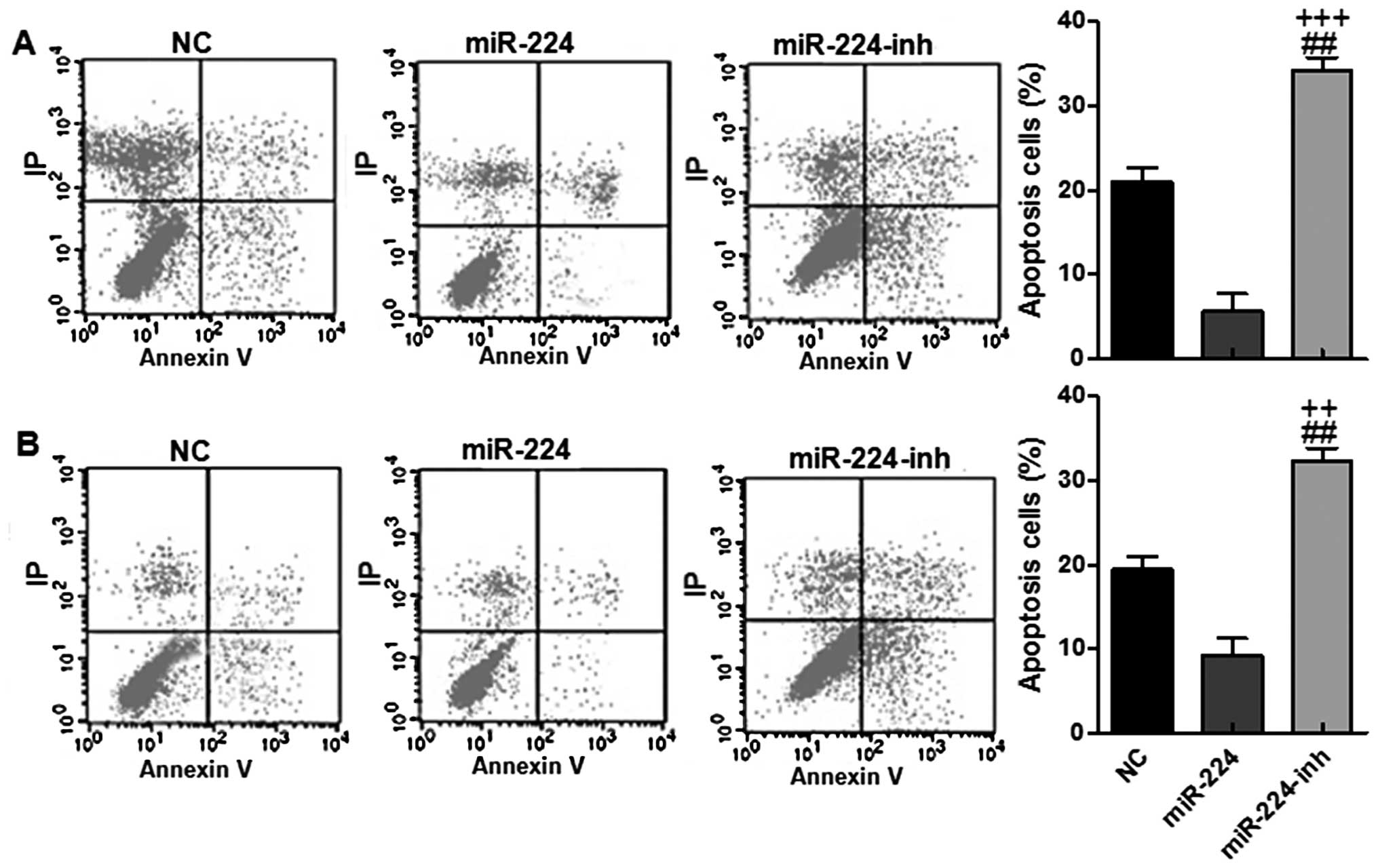
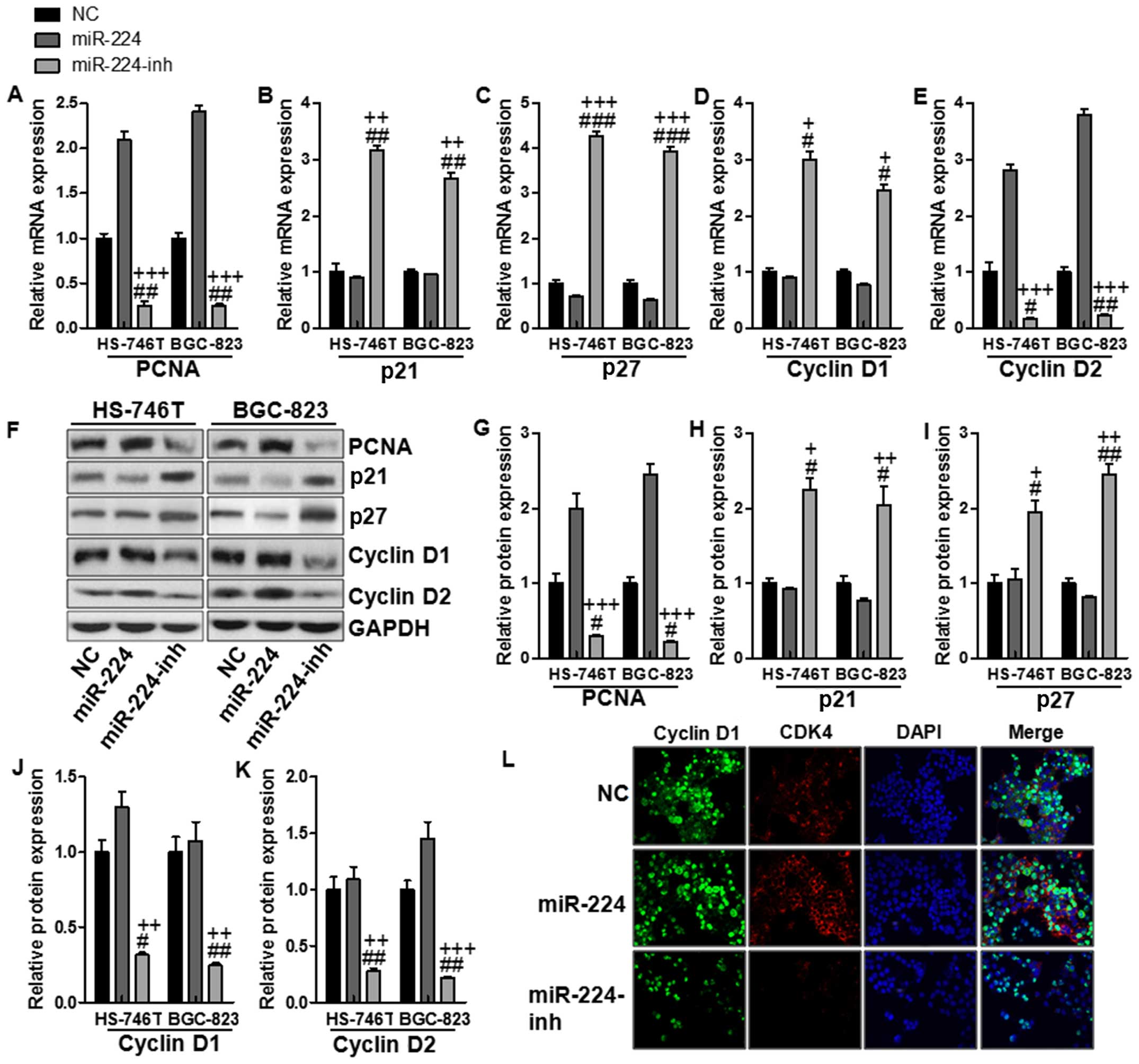
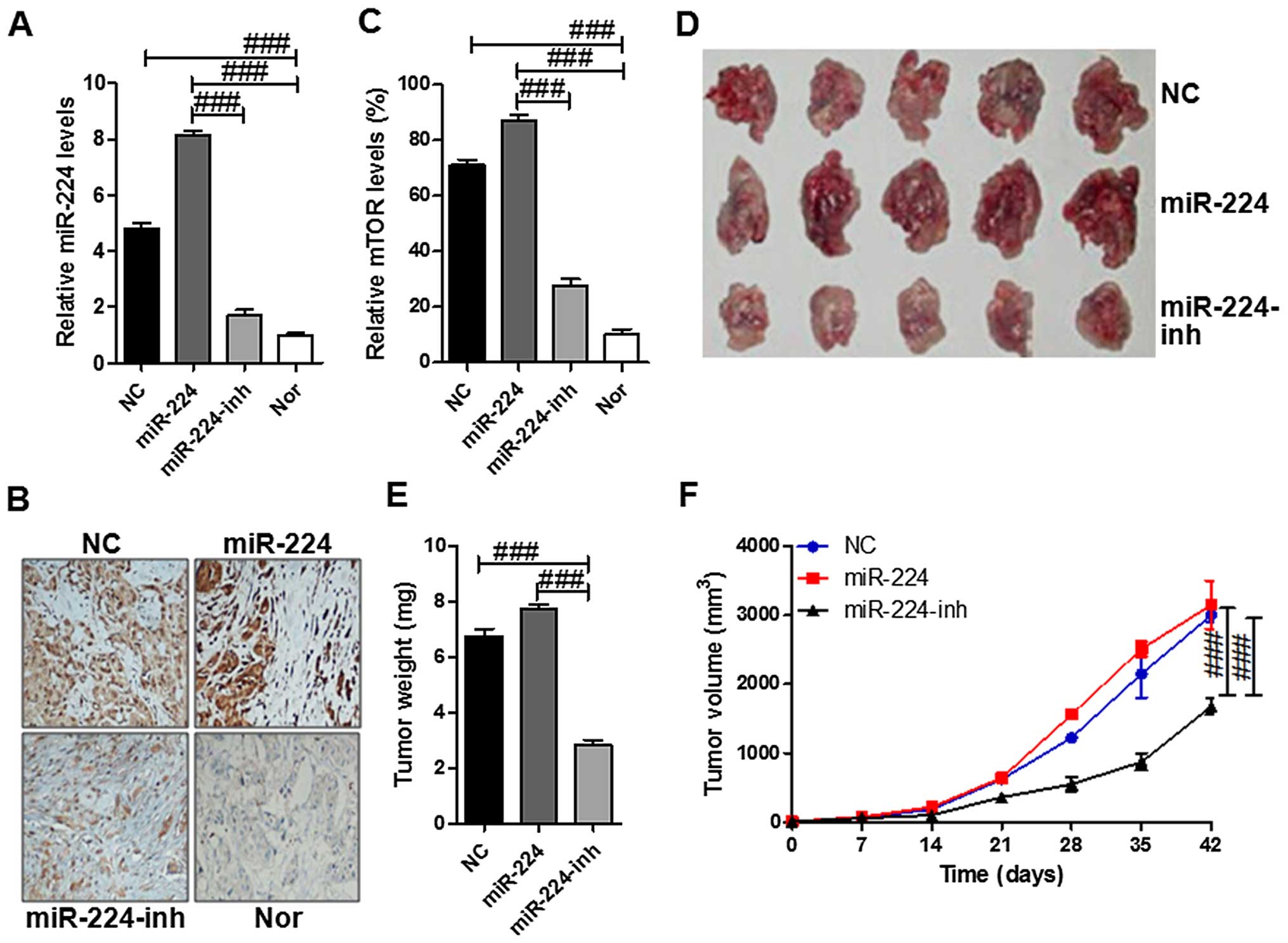
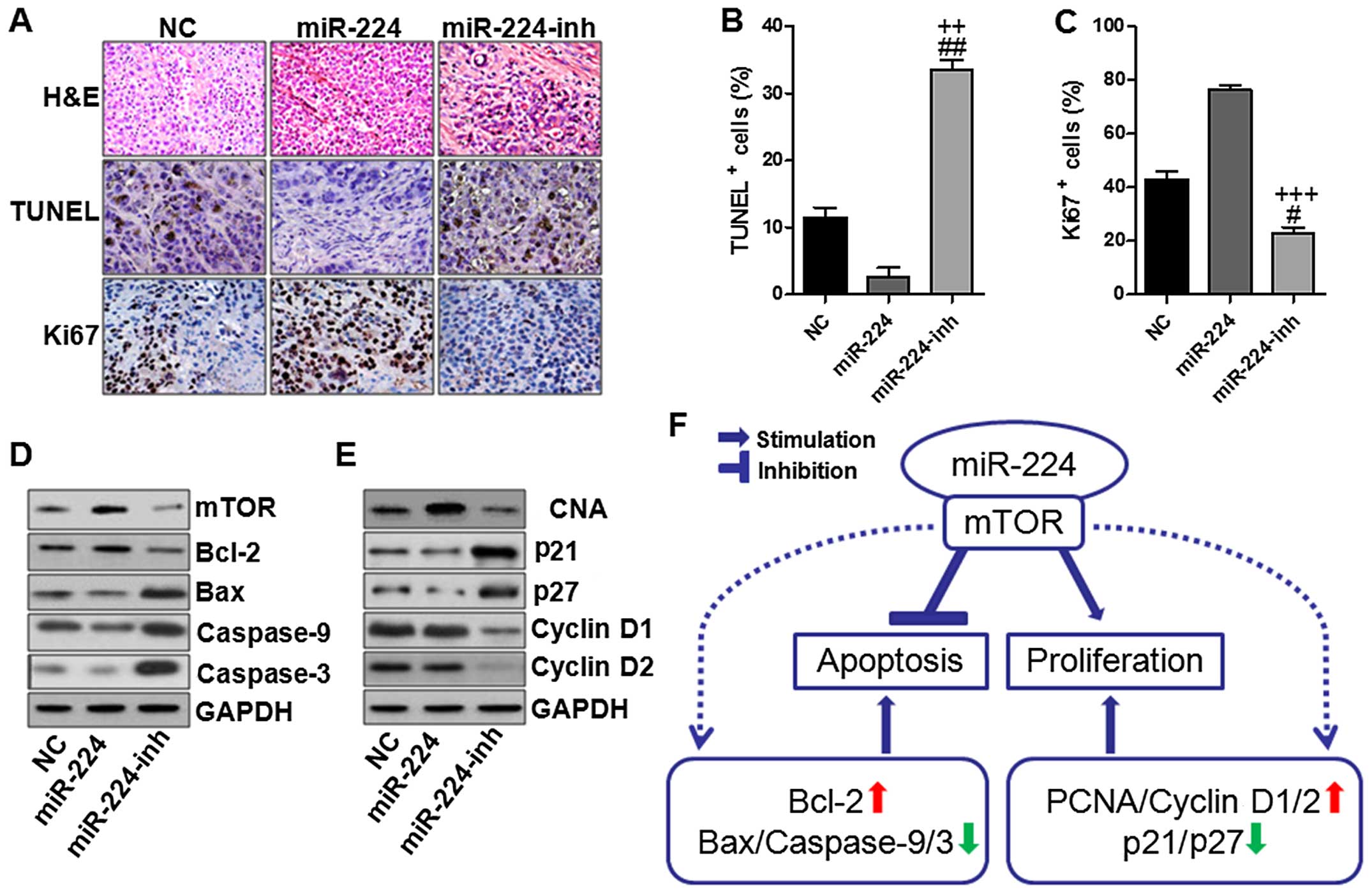
|
1
|
JeJemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J,
Ward E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Verdecchia A, Santaquilani M and Sant M:
Survival for cancer patients in Europe. Ann Ist Super Sanita.
45:315–324. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Deng N, Goh LK, Wang H, Das K, Tao J, Tan
IB, Zhang S, Lee M, Wu J, Lim KH, et al: A comprehensive survey of
genomic alterations in gastric cancer reveals systematic patterns
of molecular exclusivity and co-occurrence among distinct
therapeutic targets. Gut. 61:673–684. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A,
Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T,
et al; ToGA Trial Investigators. Trastuzumab in combination with
chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of
HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction
cancer (ToGA): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial.
Lancet. 376:687–697. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee J, Seo JW, Jun HJ, Ki CS, Park SH,
Park YS, Lim HY, Choi MG, Bae JM, Sohn TS, et al: Impact of MET
amplification on gastric cancer: Possible roles as a novel
prognostic marker and a potential therapeutic target. Oncol Rep.
25:1517–1524. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sasaki T, Kuniyasu H, Luo Y, Kitayoshi M,
Tanabe E, Kato D, Shinya S, Fujii K, Ohmori H and Yamashita Y: AKT
activation and telomerase reverse transcriptase expression are
concurrently associated with prognosis of gastric cancer.
Pathobiology. 81:36–41. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jiang YW and Chen LA: microRNAs as tumor
inhibitors, oncogenes, biomarkers for drug efficacy and outcome
predictors in lung cancer (Review). Mol Med Rep. 5:890–894.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou C, Li G, Zhou J, Han N, Liu Z and Yin
J: miR-107 activates ATR/Chk1 pathway and suppress cervical cancer
invasion by targeting MCL1. PLoS One. 9:e1118602014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Roldo C, Missiaglia E, Hagan JP, Falconi
M, Capelli P, Bersani S, Calin GA, Volinia S, Liu CG, Scarpa A, et
al: MicroRNA expression abnormalities in pancreatic endocrine and
acinar tumors are associated with distinctive pathologic features
and clinical behavior. J Clin Oncol. 24:4677–4684. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takahashi Y, Forrest AR, Maeno E,
Hashimoto T, Daub CO and Yasuda J: MiR-107 and MiR-185 can induce
cell cycle arrest in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.
PLoS One. 4:e66772009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zeng L, He X, Wang Y, Tang Y, Zheng C, Cai
H, Liu J, Wang Y, Fu Y and Yang GY: MicroRNA-210 overexpression
induces angiogenesis and neurogenesis in the normal adult mouse
brain. Gene Ther. 21:37–43. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang L, Chang L, Li Z, Gao Q, Cai D, Tian
Y, Zeng L and Li M: miR-99a and -99b inhibit cervical cancer cell
proliferation and invasion by targeting mTOR signaling pathway. Med
Oncol. 31:9342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Marcucci G, Maharry KS, Metzeler KH,
Volinia S, Wu YZ, Mrózek K, Nicolet D, Kohlschmidt J, Whitman SP,
Mendler JH, et al: Clinical role of microRNAs in cytogenetically
normal acute myeloid leukemia: miR-155 upregulation independently
identifies high-risk patients. J Clin Oncol. 31:2086–2093. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang X, Taeb S, Jahangiri S, Emmenegger
U, Tran E, Bruce J, Mesci A, Korpela E, Vesprini D, Wong CS, et al:
miRNA-95 mediates radioresistance in tumors by targeting the
sphingolipid phosphatase SGPP1. Cancer Res. 73:6972–6986. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mees ST, Mardin WA, Sielker S, Willscher
E, Senninger N, Schleicher C, Colombo-Benkmann M and Haier J:
Involvement of CD40 targeting miR-224 and miR-486 on the
progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol.
16:2339–2350. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang L, Dai T, Lin X, Zhao X, Chen X,
Wang C, Li X, Shen H and Wang X: MicroRNA-224 targets RKIP to
control cell invasion and expression of metastasis genes in human
breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 425:127–133. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee DF and Hung MC: All roads lead to
mTOR: Integrating inflammation and tumor angiogenesis. Cell Cycle.
6:3011–3014. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gridelli C, Maione P and Rossi A: The
potential role of mTOR inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncologist. 13:139–147. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li T, Lai Q, Wang S, Cai J, Xiao Z, Deng
D, He L, Jiao H, Ye Y, Liang L, et al: MicroRNA-224 sustains
Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promotes aggressive phenotype of
colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:21–27. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sasaki T, Kuniyasu H, Luo Y, Kitayoshi M,
Tanabe E, Kato D, Shinya S, Fujii K, Ohmori H and Yamashita Y:
Increased phosphorylation of AKT in high-risk gastric mucosa.
Anticancer Res. 33:3295–3300. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sukawa Y, Yamamoto H, Nosho K, Kunimoto H,
Suzuki H, Adachi Y, Nakazawa M, Nobuoka T, Kawayama M, Mikami M, et
al: Alterations in the human epidermal growth factor receptor
2-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-v-Akt pathway in gastric cancer.
World J Gastroenterol. 18:6577–6586. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Poplawski T, Tomaszewska K, Galicki M,
Morawiec Z and Blasiak J: Promoter methylation of cancer-related
genes in gastric carcinoma. Exp Oncol. 30:112–116. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oue N, Motoshita J, Yokozaki H, Hayashi K,
Tahara E, Taniyama K, Matsusaki K and Yasui W: Distinct promoter
hyper-methylation of p16INK4a, CDH1, and RAR-beta in intestinal,
diffuse-adherent, and diffuse-scattered type gastric carcinomas. J
Pathol. 198:55–59. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi XB, Xue L, Ma AH, Tepper CG, Kung HJ
and White RW: miR-125b promotes growth of prostate cancer xenograft
tumor through targeting pro-apoptotic genes. Prostate. 71:538–549.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Szabó DR, Luconi M, Szabó PM, Tóth M,
Szücs N, Horányi J, Nagy Z, Mannelli M, Patócs A, Rácz K, et al:
Analysis of circulating microRNAs in adrenocortical tumors. Lab
Invest. 94:331–339. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo H, Liu H, Mitchelson K, Rao H, Luo M,
Xie L, Sun Y, Zhang L, Lu Y, Liu R, et al: MicroRNAs-372/373
promote the expression of hepatitis B virus through the targeting
of nuclear factor I/B. Hepatology. 54:808–819. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Prueitt RL, Yi M, Hudson RS, Wallace TA,
Howe TM, Yfantis HG, Lee DH, Stephens RM, Liu CG, Calin GA, et al:
Expression of microRNAs and protein-coding genes associated with
perineural invasion in prostate cancer. Prostate. 68:1152–1164.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Q, Wang G, Shan J-L, Yang ZX, Wang HZ,
Feng J, Zhen JJ, Chen C, Zhang ZM, Xu W, et al: MicroRNA-224 is
upregulated in HepG2 cells and involved in cellular migration and
invasion. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:164–171. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bhaskar PT and Hay N: The two TORCs and
Akt. Dev Cell. 12:487–502. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tokunaga C, Yoshino K and Yonezawa K: mTOR
integrates amino acid- and energy-sensing pathways. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 313:443–446. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Betz C and Hall MN: Where is mTOR and what
is it doing there? J Cell Biol. 203:563–574. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Frias MA, Thoreen CC, Jaffe JD, Schroder
W, Sculley T, Carr SA and Sabatini DM: mSin1 is necessary for
Akt/PKB phosphorylation, and its isoforms define three distinct
mTORC2s. Curr Biol. 16:1865–1870. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Betz C, Stracka D, Prescianotto-Baschong
C, Frieden M, Demaurex N and Hall MN: Feature Article: mTOR complex
2-Akt signaling at mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum
membranes (MAM) regulates mitochondrial physiology. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 110:12526–12534. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chang HY and Yang X: Proteases for cell
suicide: Functions and regulation of caspases. Microbiol Mol Biol
Rev. 64:821–846. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Beurel E and Jope RS: The paradoxical pro-
and anti-apoptotic actions of GSK3 in the intrinsic and extrinsic
apoptosis signaling pathways. Prog Neurobiol. 79:173–189. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yo YT, Shieh GS, Hsu KF, Wu CL and Shiau
AL: Licorice and licochalcone-A induce autophagy in LNCaP prostate
cancer cells by suppression of Bcl-2 expression and the mTOR
pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 57:8266–8273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lapenna S and Giordano A: Cell cycle
kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
8:547–566. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen Y, Robles AI, Martinez LA, Liu F,
Gimenez-Conti IB and Conti CJ: Expression of G1 cyclins,
cyclin-dependent kinases, and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in
androgen-induced prostate proliferation in castrated rats. Cell
Growth Differ. 7:1571–1578. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kastan MB and Bartek J: Cell-cycle
checkpoints and cancer. Nature. 432:316–323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhong W, Peng J, He H, Wu D, Han Z, Bi X
and Dai Q: Ki-67 and PCNA expression in prostate cancer and benign
prostatic hyperplasia. Clin Invest Med. 31:E8–E15. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|