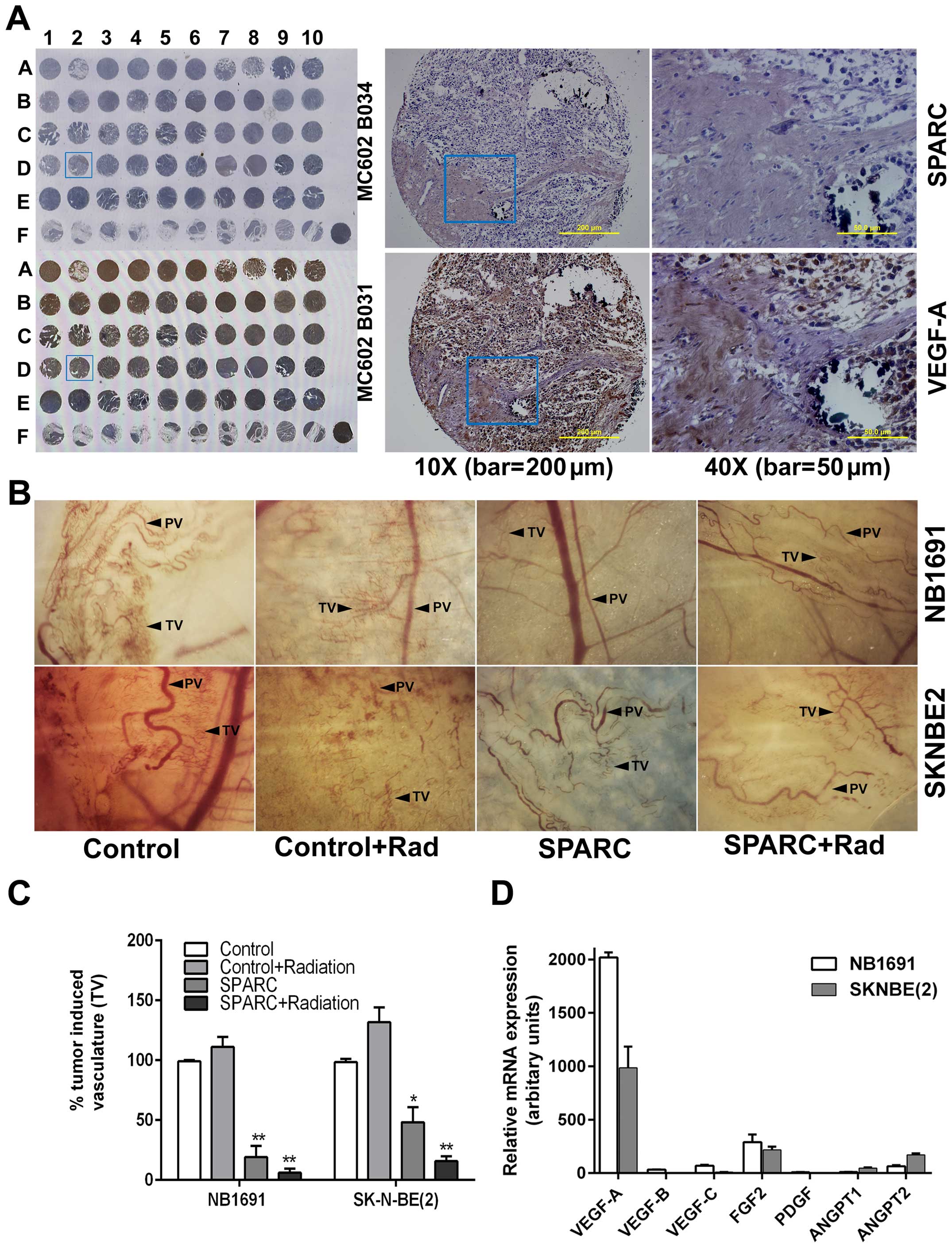
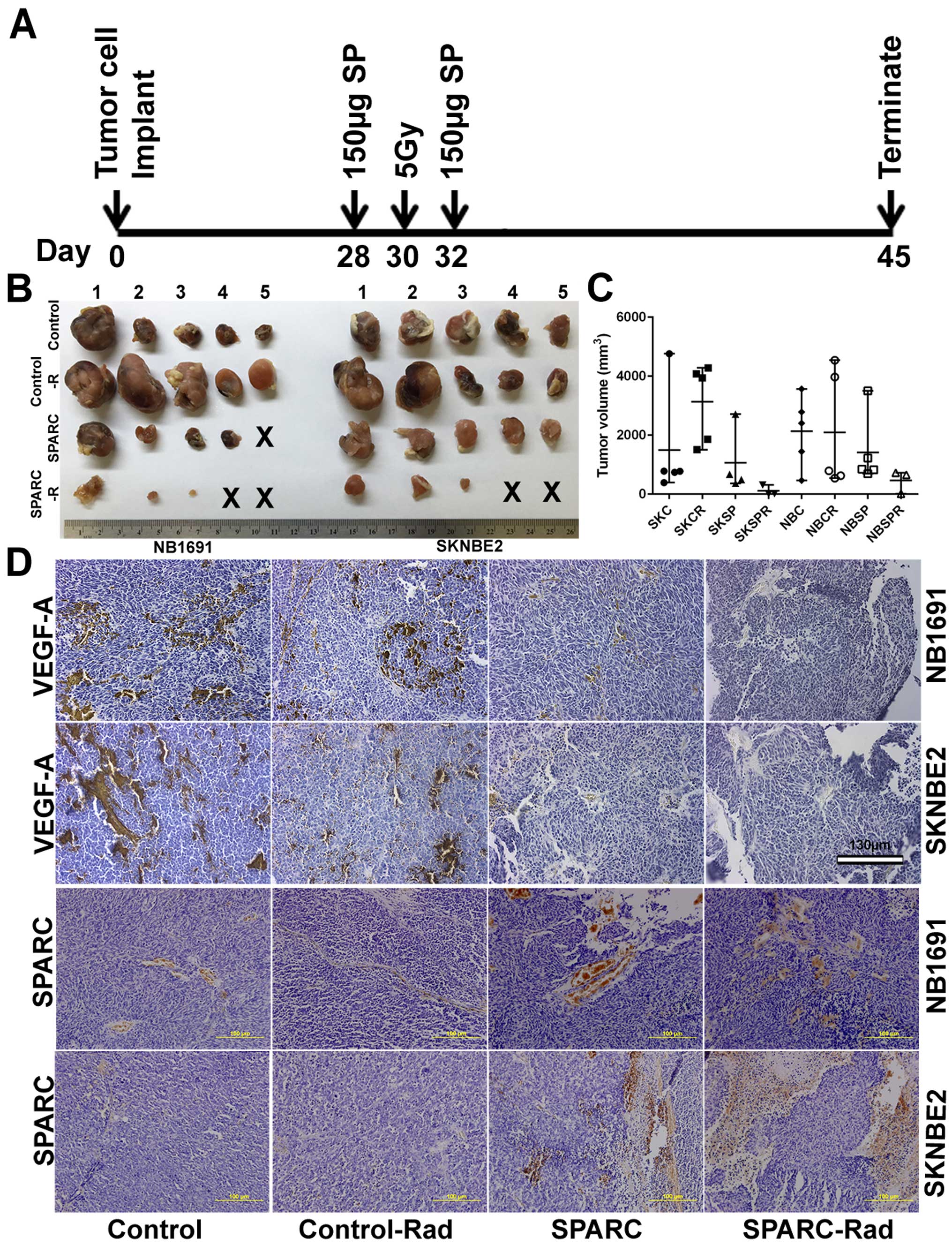
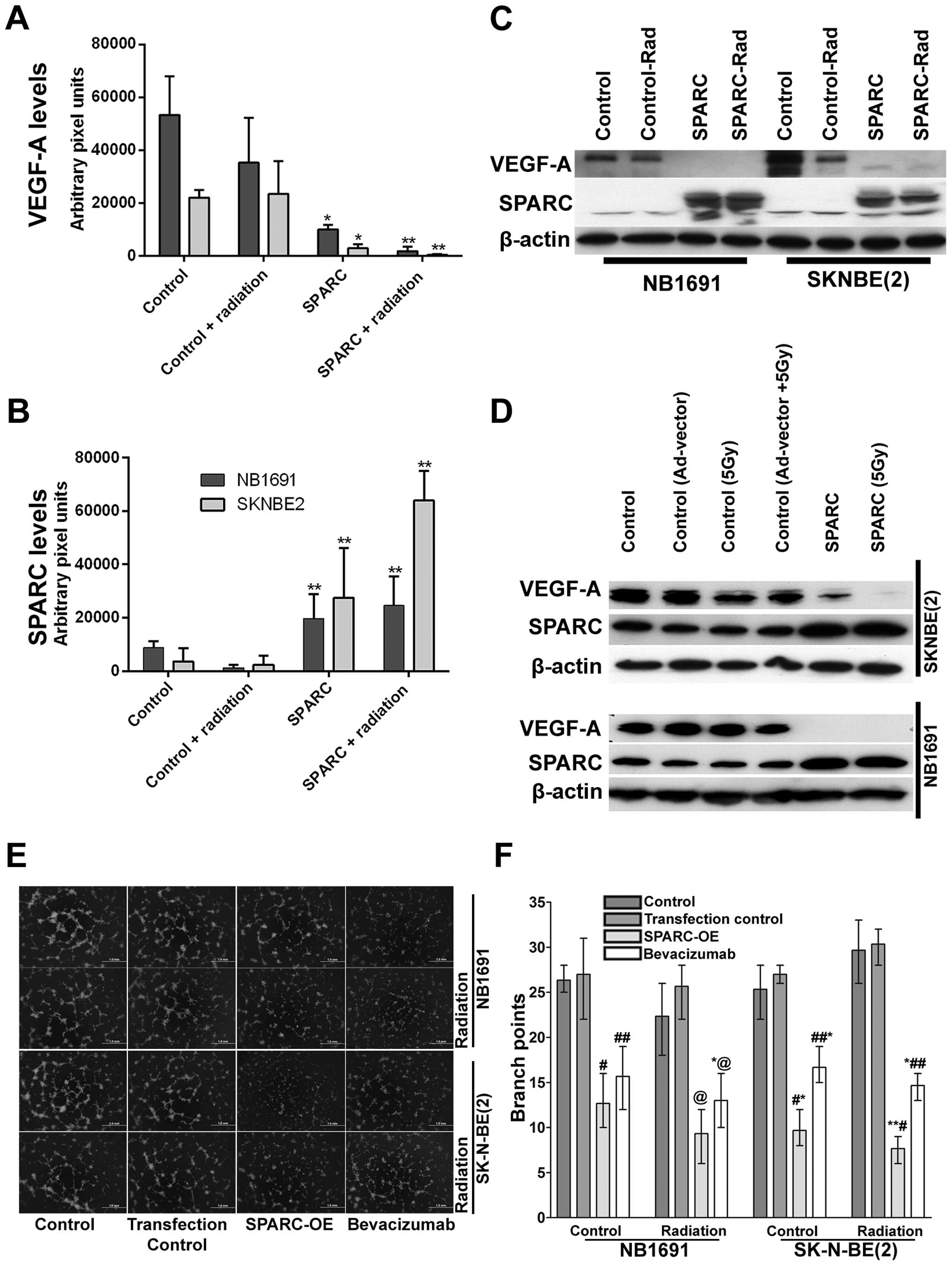
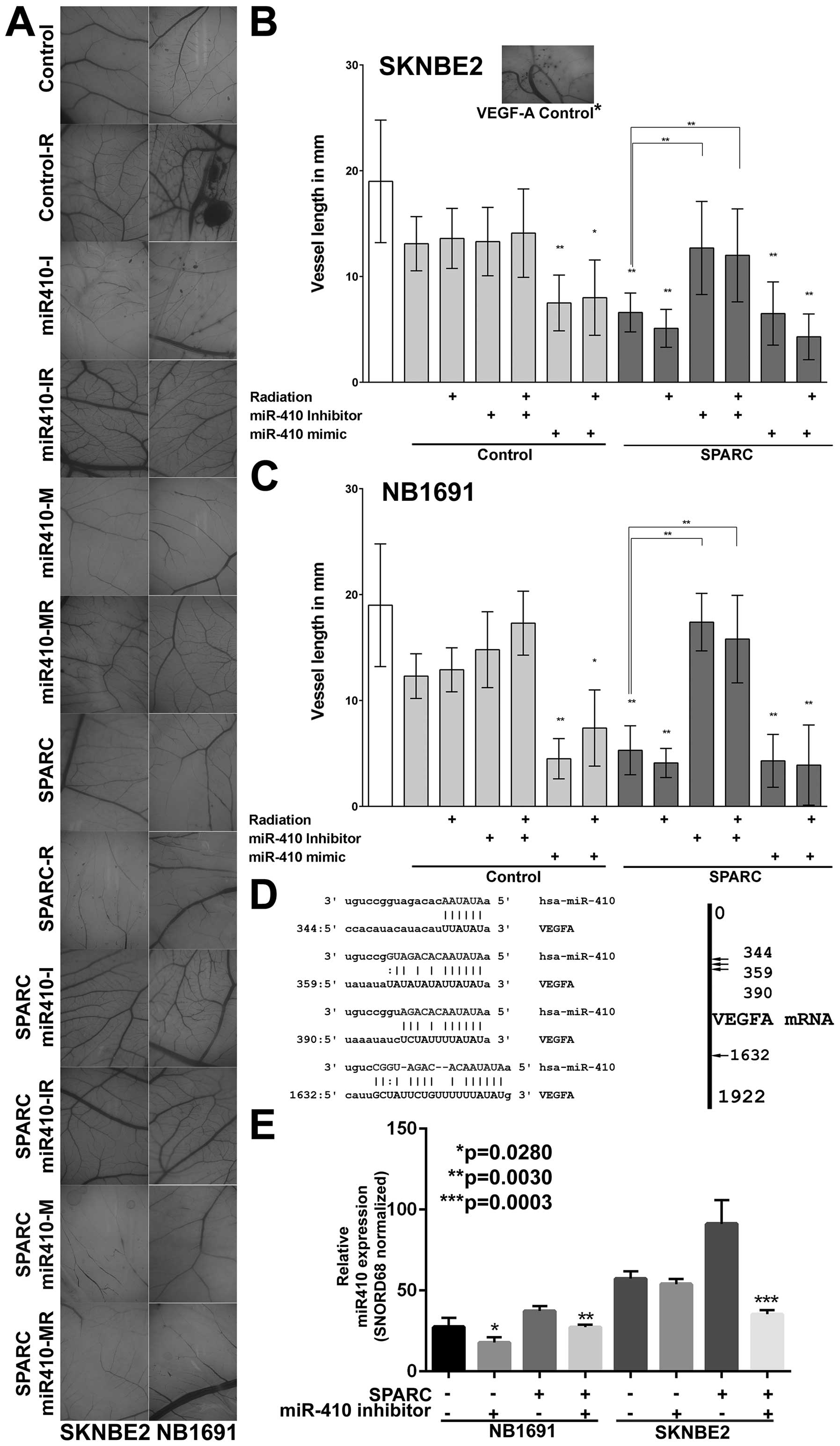
|
1
|
Maris JM, Hogarty MD, Bagatell R and Cohn
SL: Neuroblastoma. Lancet. 369:2106–2120. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pinto NR, Applebaum MA, Volchenboum SL,
Matthay KK, London WB, Ambros PF, Nakagawara A, Berthold F,
Schleiermacher G, Park JR, et al: Advances in risk classification
and treatment strategies for neuroblastoma. J Clin Oncol.
33:3008–3017. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yu DM, Huynh T, Truong AM, Haber M and
Norris MD: ABC transporters and neuroblastoma. Adv Cancer Res.
125:139–170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scaldaferri F, Vetrano S, Sans M, Arena V,
Straface G, Stigliano E, Repici A, Sturm A, Malesci A, Panes J, et
al: VEGF-A links angiogenesis and inflammation in inflammatory
bowel disease pathogenesis. Gastroenterology. 136:585–95. e52009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kowshik J, Giri H, Kishore TK, Kesavan R,
Vankudavath RN, Reddy GB, Dixit M and Nagini S: Ellagic acid
inhibits VEGF/VEGFR2, PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling cascades in the
hamster cheek pouch carcinogenesis model. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 14:1249–1260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maris JM: Recent advances in
neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. 362:2202–2211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kushner BH, LaQuaglia MP, Bonilla MA,
Lindsley K, Rosenfield N, Yeh S, Eddy J, Gerald WL, Heller G and
Cheung NK: Highly effective induction therapy for stage 4
neuroblastoma in children over 1 year of age. J Clin Oncol.
12:2607–2613. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
De Ioris MA, Crocoli A, Contoli B,
Garganese MC, Natali G, Tomà P, Jenkner A, Boldrini R, De Pasquale
MD, Milano GM, et al: Local control in metastatic neuroblastoma in
children over 1 year of age. BMC Cancer. 15:792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu AL, Gilman AL, Ozkaynak MF, London WB,
Kreissman SG, Chen HX, Smith M, Anderson B, Villablanca JG, Matthay
KK, et al; Children's Oncology Group. Anti-GD2 antibody with
GM-CSF, interleukin-2, and isotretinoin for neuroblastoma. N Engl J
Med. 363:1324–1334. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jones C, Mackay A, Grigoriadis A, Cossu A,
Reis-Filho JS, Fulford L, Dexter T, Davies S, Bulmer K, Ford E, et
al: Expression profiling of purified normal human luminal and
myoepithelial breast cells: Identification of novel prognostic
markers for breast cancer. Cancer Res. 64:3037–3045. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lien HC, Hsiao YH, Lin YS, Yao YT, Juan
HF, Kuo WH, Hung MC, Chang KJ and Hsieh FJ: Molecular signatures of
metaplastic carcinoma of the breast by large-scale transcriptional
profiling: Identification of genes potentially related to
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene. 26:7859–7871. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen J, Wang M, Xi B, Xue J, He D, Zhang J
and Zhao Y: SPARC is a key regulator of proliferation, apoptosis
and invasion in human ovarian cancer. PLoS One. 7:e424132012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sato T, Oshima T, Yamamoto N, Yamada T,
Hasegawa S, Yukawa N, Numata K, Kunisaki C, Tanaka K, Shiozawa M,
et al: Clinical significance of SPARC gene expression in patients
with gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 108:364–368. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shin M, Mizokami A, Kim J, Ofude M, Konaka
H, Kadono Y, Kitagawa Y, Miwa S, Kumaki M, Keller ET, et al:
Exogenous SPARC suppresses proliferation and migration of prostate
cancer by interacting with integrin β1. Prostate. 73:1159–1170.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
DiMartino JF, Lacayo NJ, Varadi M, Li L,
Saraiya C, Ravindranath Y, Yu R, Sikic BI, Raimondi SC and Dahl GV:
Low or absent SPARC expression in acute myeloid leukemia with MLL
rearrangements is associated with sensitivity to growth inhibition
by exogenous SPARC protein. Leukemia. 20:426–432. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bhoopathi P, Gorantla B, Sailaja GS, Gondi
CS, Gujrati M, Klopfenstein JD and Rao JS: SPARC overexpression
inhibits cell proliferation in neuroblastoma and is partly mediated
by tumor suppressor protein PTEN and AKT. PLoS One. 7:e360932012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chlenski A, Liu S, Guerrero LJ, Yang Q,
Tian Y, Salwen HR, Zage P and Cohn SL: SPARC expression is
associated with impaired tumor growth, inhibited angiogenesis and
changes in the extracellular matrix. Int J Cancer. 118:310–316.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chlenski A, Liu S, Crawford SE, Volpert
OV, DeVries GH, Evangelista A, Yang Q, Salwen HR, Farrer R, Bray J,
et al: SPARC is a key Schwannian-derived inhibitor controlling
neuroblastoma tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 62:7357–7363.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Feng J and Tang L: SPARC in tumor
pathophysiology and as a potential therapeutic target. Curr Pharm
Des. 20:6182–6190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gorantla B, Asuthkar S, Rao JS, Patel J
and Gondi CS: Suppression of the uPAR-uPA system retards
angiogenesis, invasion, and in vivo tumor development in pancreatic
cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 9:377–389. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gondi CS, Lakka SS, Yanamandra N, Siddique
K, Dinh DH, Olivero WC, Gujrati M and Rao JS: Expression of
antisense uPAR and antisense uPA from a bicistronic adenoviral
construct inhibits glioma cell invasion, tumor growth, and
angiogenesis. Oncogene. 22:5967–5975. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gorantla B, Bhoopathi P, Chetty C,
Gogineni VR, Sailaja GS, Gondi CS and Rao JS: Notch signaling
regulates tumor-induced angiogenesis in SPARC-overexpressed
neuroblastoma. Angiogenesis. 16:85–100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chlenski A, Guerrero LJ, Peddinti R, Spitz
JA, Leonhardt PT, Yang Q, Tian Y, Salwen HR and Cohn SL:
Anti-angiogenic SPARC peptides inhibit progression of neuroblastoma
tumors. Mol Cancer. 9:1382010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liao D and Johnson RS: Hypoxia: A key
regulator of angiogenesis in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:281–290. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mabjeesh NJ and Amir S: Hypoxia-inducible
factor (HIF) in human tumorigenesis. Histol Histopathol.
22:559–572. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu Y, Kudo K, Abe Y, Aoki M, Hu DL,
Kijima H and Nakane A: Hypoxia expression in radiation-induced late
rectal injury. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 49:261–268. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Simons M: Integrative signaling in
angiogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem. 264:99–102. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang W, Ran S, Sambade M, Huang X and
Thorpe PE: A monoclonal antibody that blocks VEGF binding to VEGFR2
(KDR/Flk-1) inhibits vascular expression of Flk-1 and tumor growth
in an orthotopic human breast cancer model. Angiogenesis. 5:35–44.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hong DS, Garrido-Laguna I, Ekmekcioglu S,
Falchook GS, Naing A, Wheler JJ, Fu S, Moulder SL, Piha-Paul S,
Tsimberidou AM, et al: Dual inhibition of the vascular endothelial
growth factor pathway: A phase 1 trial evaluating bevacizumab and
AZD2171 (cediranib) in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer.
120:2164–2173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Waldner MJ and Neurath MF: Targeting the
VEGF signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
16:5–13. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Staton CA, Reed MW and Brown NJ: A
critical analysis of current in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis
assays. Int J Exp Pathol. 90:195–221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
2:e3632004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ribatti D: Anti-angiogenesis in
neuroblastoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 86:212–221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Roy CS, Karmakar S, Banik NL and Ray SK:
Targeting angiogenesis for controlling neuroblastoma. J Oncol.
2012:Article ID 782020. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chlenski A, Liu S and Cohn SL: The
regulation of angiogenesis in neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett.
197:47–52. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ribatti D, Marimpietri D, Pastorino F,
Brignole C, Nico B, Vacca A and Ponzoni M: Angiogenesis in
neuroblastoma. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1028:133–142. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Gorski DH1, Beckett MA, Jaskowiak NT,
Calvin DP, Mauceri HJ, Salloum RM, Seetharam S, Koons A, Hari DM,
Kufe DW, et al: Blockage of the vascular endothelial growth factor
stress response increases the antitumor effects of ionizing
radiation. Cancer Res. 59:3374–3378. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sofia Vala I1, Martins LR, Imaizumi N,
Nunes RJ, Rino J, Kuonen F, Carvalho LM, Rüegg C, Grillo IM, Barata
JT, et al: Low doses of ionizing radiation promote tumor growth and
metastasis by enhancing angiogenesis. PLoS One. 5:e112222010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
El Ghazi F, Desfeux A, Brasse-Lagnel C,
Roux C, Lesueur C, Mazur D, Remy-Jouet I, Richard V, Jégou S,
Laudenbach V, et al: NO-dependent protective effect of VEGF against
excitotoxicity on layer VI of the developing cerebral cortex.
Neurobiol Dis. 45:871–886. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang JL, Chen GW, Liu YC, Wang PY, Wang
X, Wan YL, Zhu J, Gao HQ, Yin J, Wang W, et al: Secreted protein
acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) suppresses angiogenesis by
down-regulating the expression of VEGF and MMP-7 in gastric cancer.
PLoS One. 7:e446182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen N, Wang J, Hu Y, Cui B, Li W, Xu G,
Liu L and Liu S: MicroRNA-410 reduces the expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor and inhibits oxygen-induced retinal
neovascularization. PLoS One. 9:e956652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guo R, Gu J, Zhang Z, Wang Y and Gu C:
MicroRNA-410 functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting
angiotensin II type 1 receptor in pancreatic cancer. IUBMB Life.
67:42–53. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao D, Jia P, Wang W and Zhang G:
VEGF-mediated suppression of cell proliferation and invasion by
miR-410 in osteosarcoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 400:87–95. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Hanada R, Hanada T, Sigl V, Schramek D and
Penninger JM: RANKL/RANK-beyond bones. J Mol Med (Berl).
89:647–656. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Morandi F, Corrias MV and Pistoia V:
Evaluation of bone marrow as a metastatic site of human
neuroblastoma. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1335:23–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Xu W, Ying Y, Shan L, Feng J, Zhang S, Gao
Y, Xu X, Yao Y, Zhu C and Mao W: Enhanced expression of cohesin
loading factor NIPBL confers poor prognosis and chemotherapy
resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med. 13:1532015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Farhang Ghahremani M, Goossens S, Nittner
D, Bisteau X, Bartunkova S, Zwolinska A, Hulpiau P, Haigh K,
Haenebalcke L, Drogat B, et al: p53 promotes VEGF expression and
angiogenesis in the absence of an intact p21-Rb pathway. Cell Death
Differ. 20:888–897. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Grinberg S, Teiblum G, Rahav G and
Bakhanashvili M: p53 in cytoplasm exerts 3′→5′ exonuclease activity
with dsRNA. Cell Cycle. 9:2442–2455. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zheng ZM, Tang S and Tao M: Development of
resistance to RNAi in mammalian cells. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1058:105–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wang W, Ren F, Wu Q, Jiang D, Li H and Shi
H: MicroRNA-497 suppresses angiogenesis by targeting vascular
endothelial growth factor A through the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK
pathways in ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:2127–2133.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhou B, Ma R, Si W, Li S, Xu Y, Tu X and
Wang Q: MicroRNA-503 targets FGF2 and VEGFA and inhibits tumor
angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Lett. 333:159–169. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang Y, Wang X, Xu B, Wang B, Wang Z,
Liang Y, Zhou J, Hu J and Jiang B: Epigenetic silencing of miR-126
contributes to tumor invasion and angiogenesis in colorectal
cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:1976–1984. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen L, Li ZY, Xu SY, Zhang XJ, Zhang Y,
Luo K and Li WP: Upregulation of miR-107 inhibits glioma
angiogenesis and VEGF expression. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 36:113–120.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|