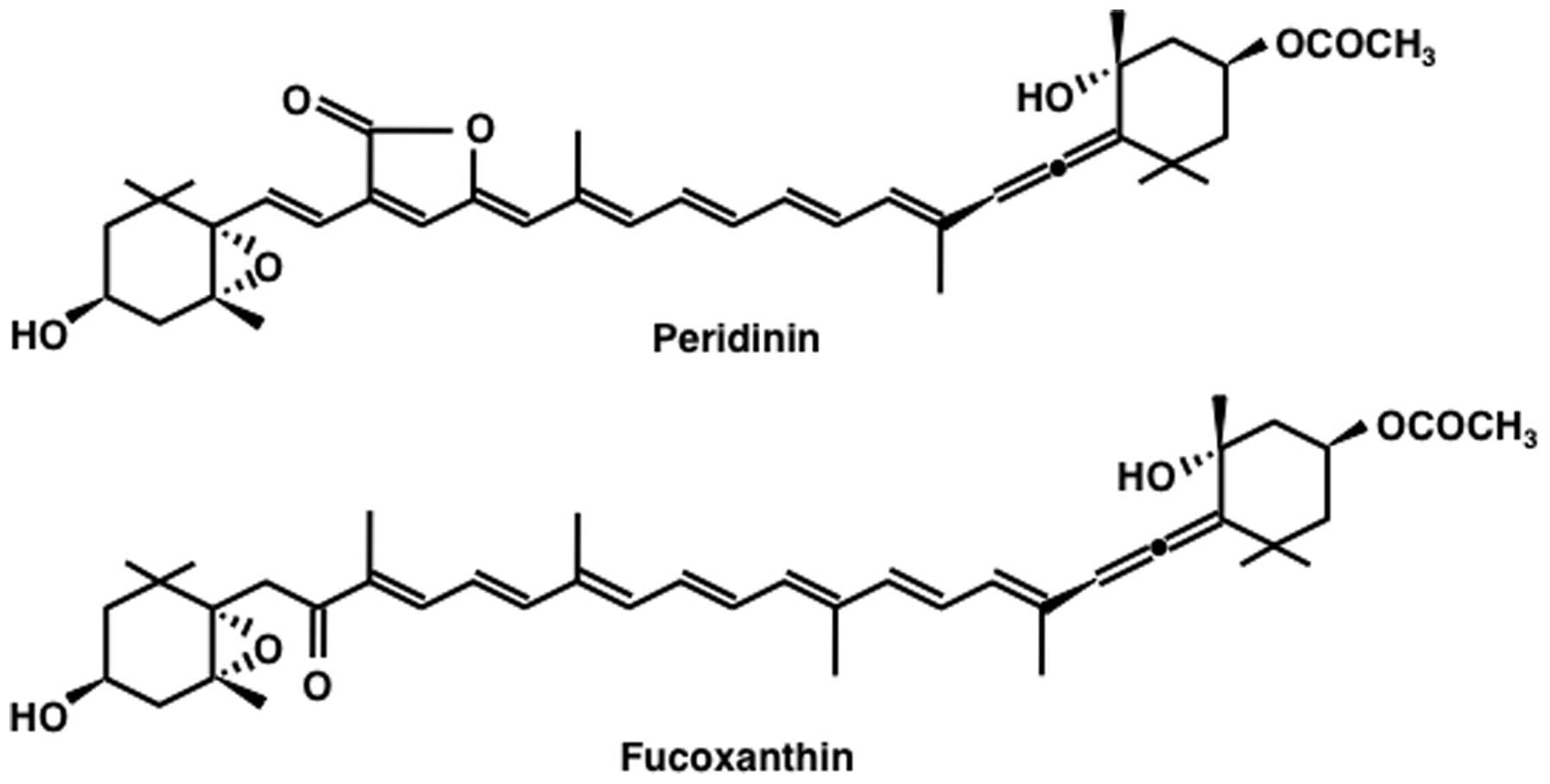
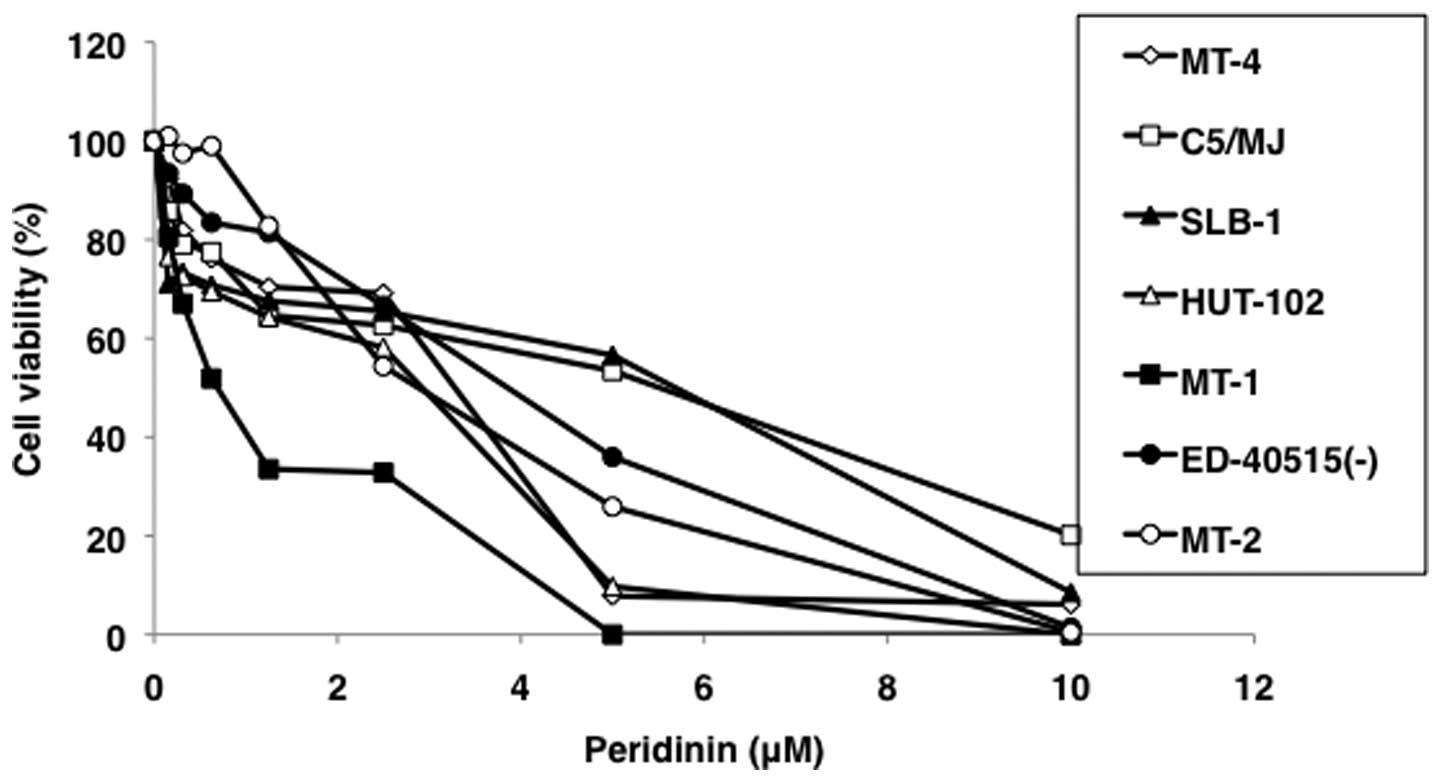
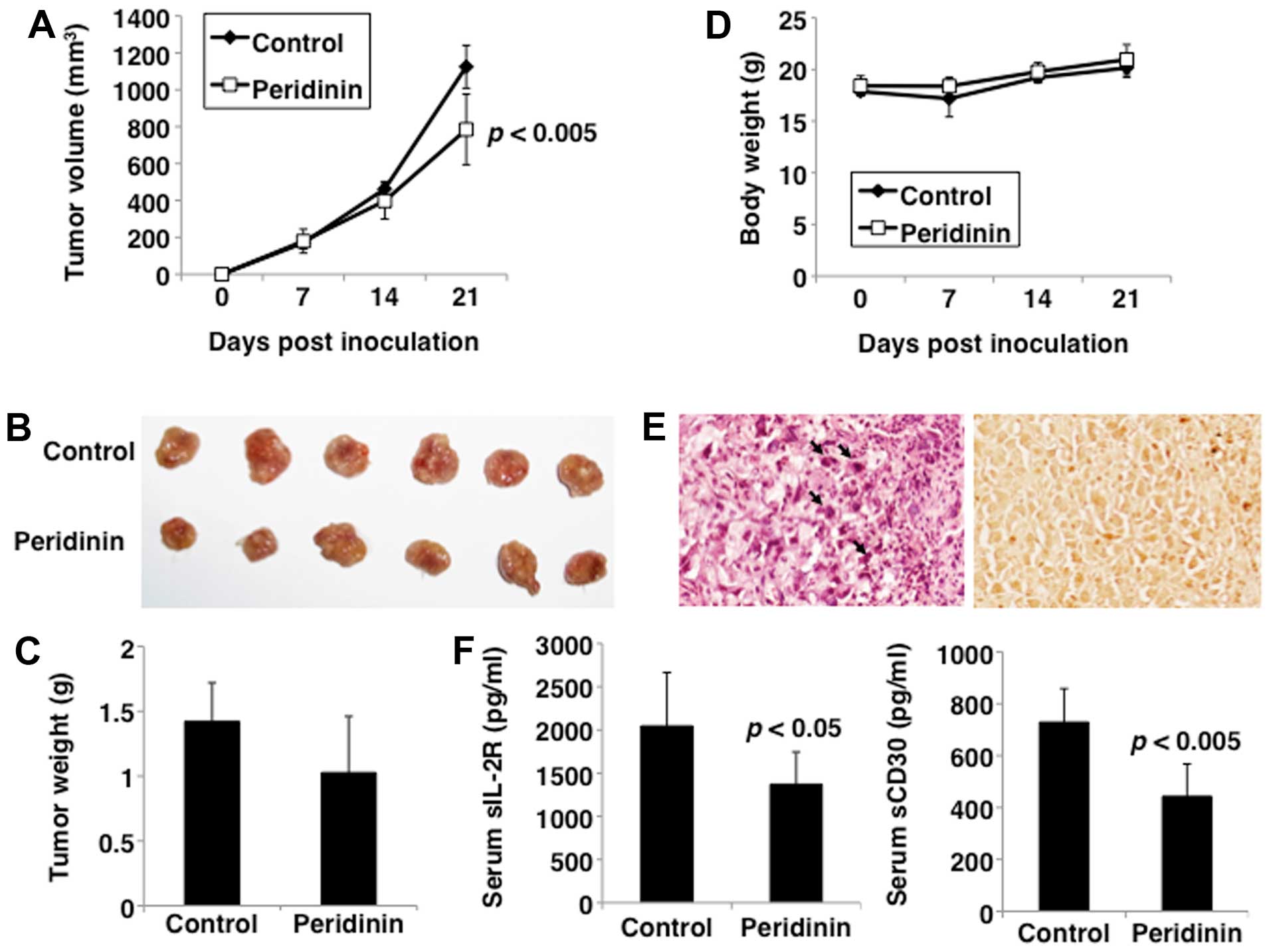
|
1
|
Kannian P and Green PL: Human T
lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1): Molecular biology and
oncogenesis. Viruses. 2:2037–2077. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rokkaku T, Kimura R, Ishikawa C, Yasumoto
T, Senba M, Kanaya F and Mori N: Anticancer effects of marine
carotenoids, fucoxanthin and its deacetylated product,
fucoxanthinol, on osteosarcoma. Int J Oncol. 43:1176–1186.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tafuku S, Ishikawa C, Yasumoto T and Mori
N: Anti-neoplastic effects of fucoxanthin and its deacetylated
product, fucoxanthinol, on Burkitt’s and Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells.
Oncol Rep. 28:1512–1518. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yamamoto K, Ishikawa C, Katano H, Yasumoto
T and Mori N: Fucoxanthin and its deacetylated product,
fucoxanthinol, induce apoptosis of primary effusion lymphomas.
Cancer Lett. 300:225–234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ishikawa C, Tafuku S, Kadekaru T, Sawada
S, Tomita M, Okudaira T, Nakazato T, Toda T, Uchihara JN, Taira N,
et al: Anti-adult T-cell leukemia effects of brown algae
fucoxanthin and its deacetylated product, fucoxanthinol. Int J
Cancer. 123:2702–2712. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sugawara T, Yamashita K, Sakai S, Asai A,
Nagao A, Shiraishi T, Imai I and Hirata T: Induction of apoptosis
in DLD-1 human colon cancer cells by peridinin isolated from the
dinoflagellate, Heterocapsa triquetra. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
71:1069–1072. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Haugan JA, Englert G, Aakermann T, Glinz
E, Liaaen-Jensen S, Balzarini J, Fransson B, Ragnarsson U and
Francis GW: Algal carotenoids 58. Isomerization studies on
peridinin. Acta Chem Scand. 48:769–779. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ishiyama M, Miyazono Y, Sasamoto K, Ohkura
Y and Ueno K: A highly water-soluble disulfonated tetrazolium salt
as a chromogenic indicator for NADH as well as cell viability.
Talanta. 44:1299–1305. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang C, Ao Z, Seth A and Schlossman SF: A
mitochondrial membrane protein defined by a novel monoclonal
antibody is preferentially detected in apoptotic cells. J Immunol.
157:3980–3987. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mori N and Prager D: Transactivation of
the interleukin-1alpha promoter by human T-cell leukemia virus type
I and type II Tax proteins. Blood. 87:3410–3417. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Besbes S, Mirshahi M, Pocard M and Billard
C: New dimension in therapeutic targeting of BCL-2 family proteins.
Oncotarget. 6:12862–12871. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li G, Chang H, Zhai YP and Xu W: Targeted
silencing of inhibitors of apoptosis proteins with siRNAs: A
potential anti-cancer strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:4943–4952. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dang CV: c-Myc target genes involved in
cell growth, apoptosis, and metabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 19:1–11.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dang CV: MYC on the path to cancer. Cell.
149:22–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pajic A, Spitkovsky D, Christoph B,
Kempkes B, Schuhmacher M, Staege MS, Brielmeier M, Ellwart J,
Kohlhuber F, Bornkamm GW, et al: Cell cycle activation by c-myc in
a Burkitt lymphoma model cell line. Int J Cancer. 87:787–793. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou J, Ching YQ and Chng WJ: Aberrant
nuclear factor-kappa B activity in acute myeloid leukemia: From
molecular pathogenesis to therapeutic target. Oncotarget.
6:5490–5500. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Iwanaga R, Ohtani K, Hayashi T and
Nakamura M: Molecular mechanism of cell cycle progression induced
by the oncogene product Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type I.
Oncogene. 20:2055–2067. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang Y, Ohtani K, Iwanaga R, Matsumura Y
and Nakamura M: Direct trans-activation of the human cyclin D2 gene
by the oncogene product Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type I.
Oncogene. 20:1094–1102. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Iwanaga R, Ozono E, Fujisawa J, Ikeda MA,
Okamura N, Huang Y and Ohtani K: Activation of the cyclin D2 and
cdk6 genes through NF-kappaB is critical for cell-cycle progression
induced by HTLV-I Tax. Oncogene. 27:5635–5642. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Duyao MP, Kessler DJ, Spicer DB,
Bartholomew C, Cleveland JL, Siekevitz M and Sonenshein GE:
Transactivation of the c-myc promoter by human T cell leukemia
virus type 1 tax is mediated by NF κB. J Biol Chem.
267:16288–16291. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kawakami A, Nakashima T, Sakai H, Urayama
S, Yamasaki S, Hida A, Tsuboi M, Nakamura H, Ida H, Migita K, et
al: Inhibition of caspase cascade by HTLV-I tax through induction
of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation. Blood. 94:3847–3854.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Akita K, Kawata S and Shimotohno K:
p21WAF1 modulates NF-kappaB signaling and induces
anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 in Tax-expressing rat fibroblast.
Virology. 332:249–257. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kawakami H, Tomita M, Matsuda T, Ohta T,
Tanaka Y, Fujii M, Hatano M, Tokuhisa T and Mori N: Transcriptional
activation of survivin through the NF-kappaB pathway by human
T-cell leukemia virus type I tax. Int J Cancer. 115:967–974. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hinz M, Krappmann D, Eichten A, Heder A,
Scheidereit C and Strauss M: NF-kappaB function in growth control:
Regulation of cyclin D1 expression and G0/G1-to-S-phase transition.
Mol Cell Biol. 19:2690–2698. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Viatour P, Merville MP, Bours V and
Chariot A: Phosphorylation of NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins:
Implications in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci.
30:43–52. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Casamayor A, Morrice NA and Alessi DR:
Phosphorylation of Ser-241 is essential for the activity of
3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1: Identification of
five sites of phosphorylation in vivo. Biochem J. 342:287–292.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB,
Gaffney PRJ, Reese CB and Cohen P: Characterization of a
3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates
and activates protein kinase Balpha. Curr Biol. 7:261–269. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pullen N, Dennis PB, Andjelkovic M, Dufner
A, Kozma SC, Hemmings BA and Thomas G: Phosphorylation and
activation of p70s6k by PDK1. Science. 279:707–710.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hollander MC, Blumenthal GM and Dennis PA:
PTEN loss in the continuum of common cancers, rare syndromes and
mouse models. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:289–301. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nakahata S, Ichikawa T, Maneesaay P, Saito
Y, Nagai K, Tamura T, Manachai N, Yamakawa N, Hamasaki M,
Kitabayashi I, et al: Loss of NDRG2 expression activates PI3K-AKT
signalling via PTEN phosphorylation in ATLL and other cancers. Nat
Commun. 5:33932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rahdar M, Inoue T, Meyer T, Zhang J,
Vazquez F and Devreotes PN: A phosphorylation-dependent
intramolecular interaction regulates the membrane association and
activity of the tumor suppressor PTEN. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:480–485. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Stoppa G, Rumiato E and Saggioro D: Ras
signaling contributes to survival of human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
virus type 1 (HTLV-1) Tax-positive T-cells. Apoptosis. 17:219–228.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Kamihira S, Atogami S, Sohda H, Momita S,
Yamada Y and Tomonaga M: Significance of soluble interleukin-2
receptor levels for evaluation of the progression of adult T-cell
leukemia. Cancer. 73:2753–2758. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nishioka C, Takemoto S, Kataoka S,
Yamanaka S, Moriki T, Shoda M, Watanabe T and Taguchi H: Serum
level of soluble CD30 correlates with the aggressiveness of adult
T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Cancer Sci. 96:810–815. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang X, Tang N, Hadden TJ and Rishi AK:
Akt, FoxO and regulation of apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1813:1978–1986. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dan HC, Sun M, Kaneko S, Feldman RI,
Nicosia SV, Wang HG, Tsang BK and Cheng JQ: Akt phosphorylation and
stabilization of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP). J
Biol Chem. 279:5405–5412. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cheng JQ, Jiang X, Fraser M, Li M, Dan HC,
Sun M and Tsang BK: Role of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein
in chemoresistance in ovarian cancer: Possible involvement of the
phosphoinositide-3 kinase/Akt pathway. Drug Resist Updat.
5:131–146. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liang Y-L, Wang L-Y, Wu H, Ma D-Z, Xu Z
and Zha X-L: PKB phosphorylation and survivin expression are
cooperatively regulated by disruption of microfilament
cytoskeleton. Mol Cell Biochem. 254:257–263. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pugazhenthi S, Nesterova A, Sable C,
Heidenreich KA, Boxer LM, Heasley LE and Reusch JE-B: Akt/protein
kinase B up-regulates Bcl-2 expression through cAMP-response
element-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 275:10761–10766. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|