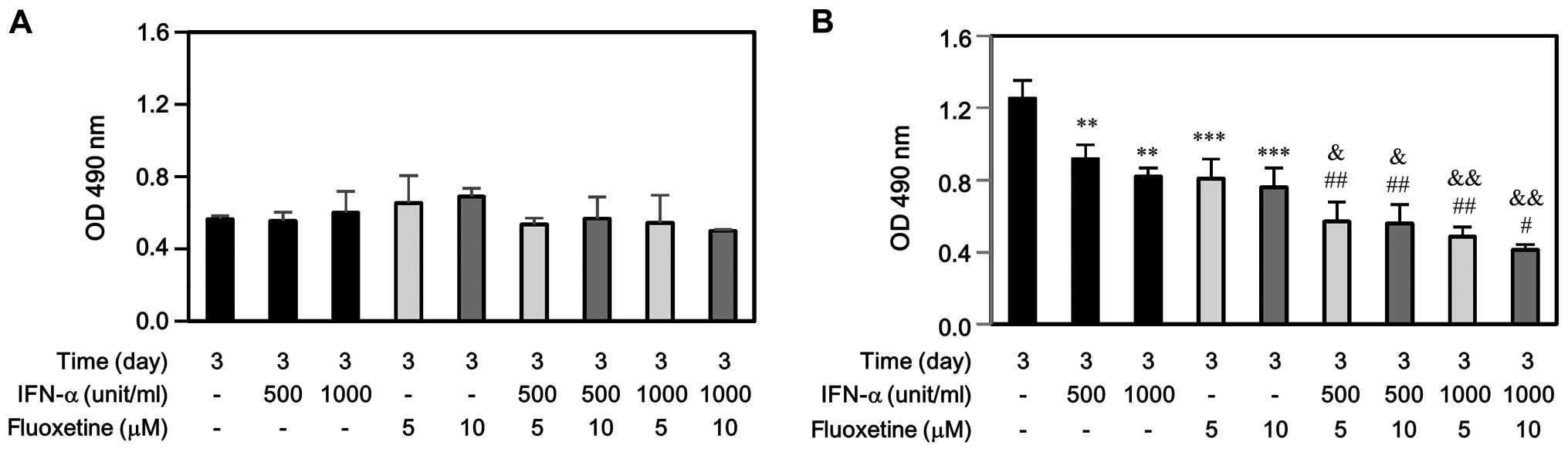
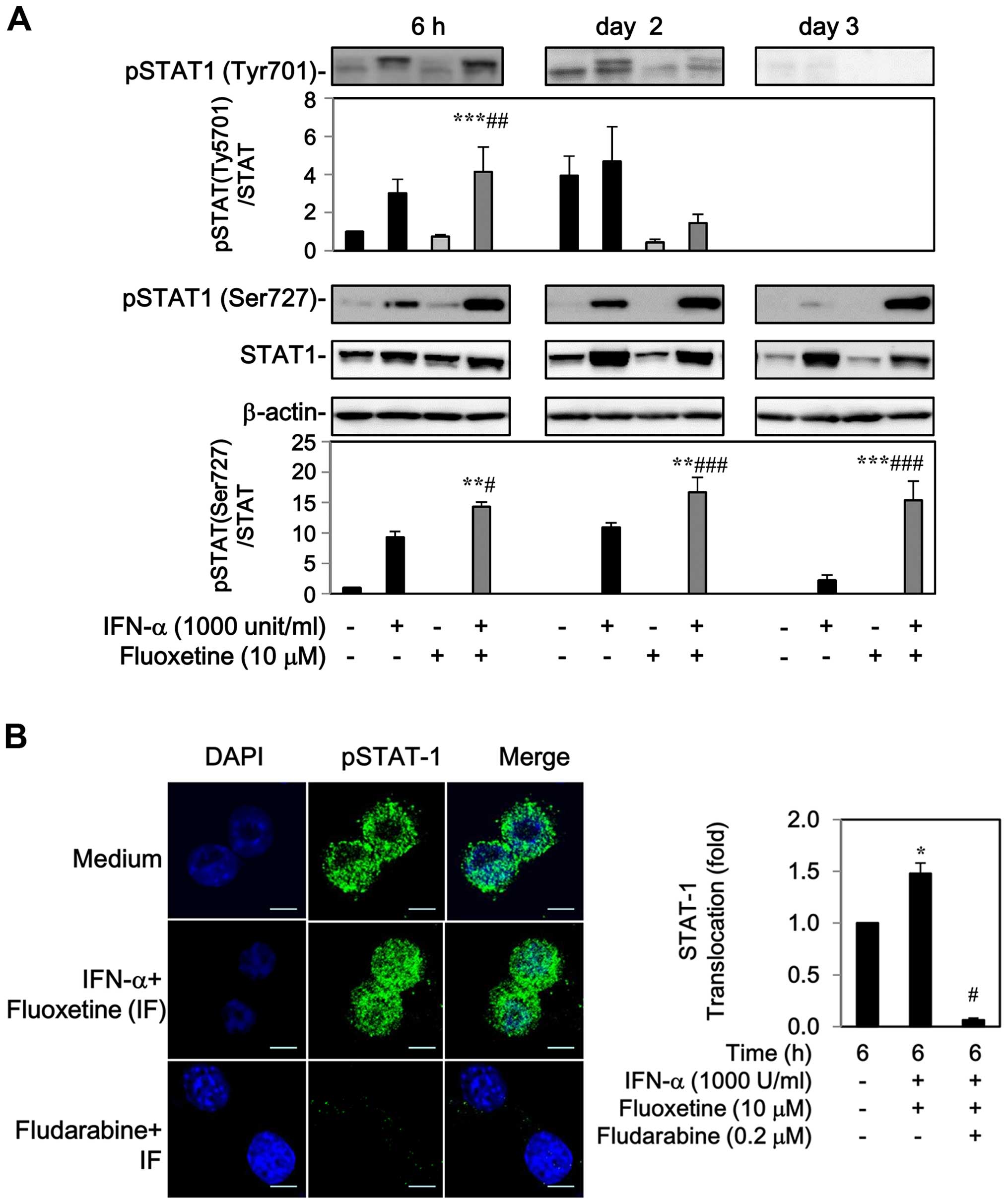
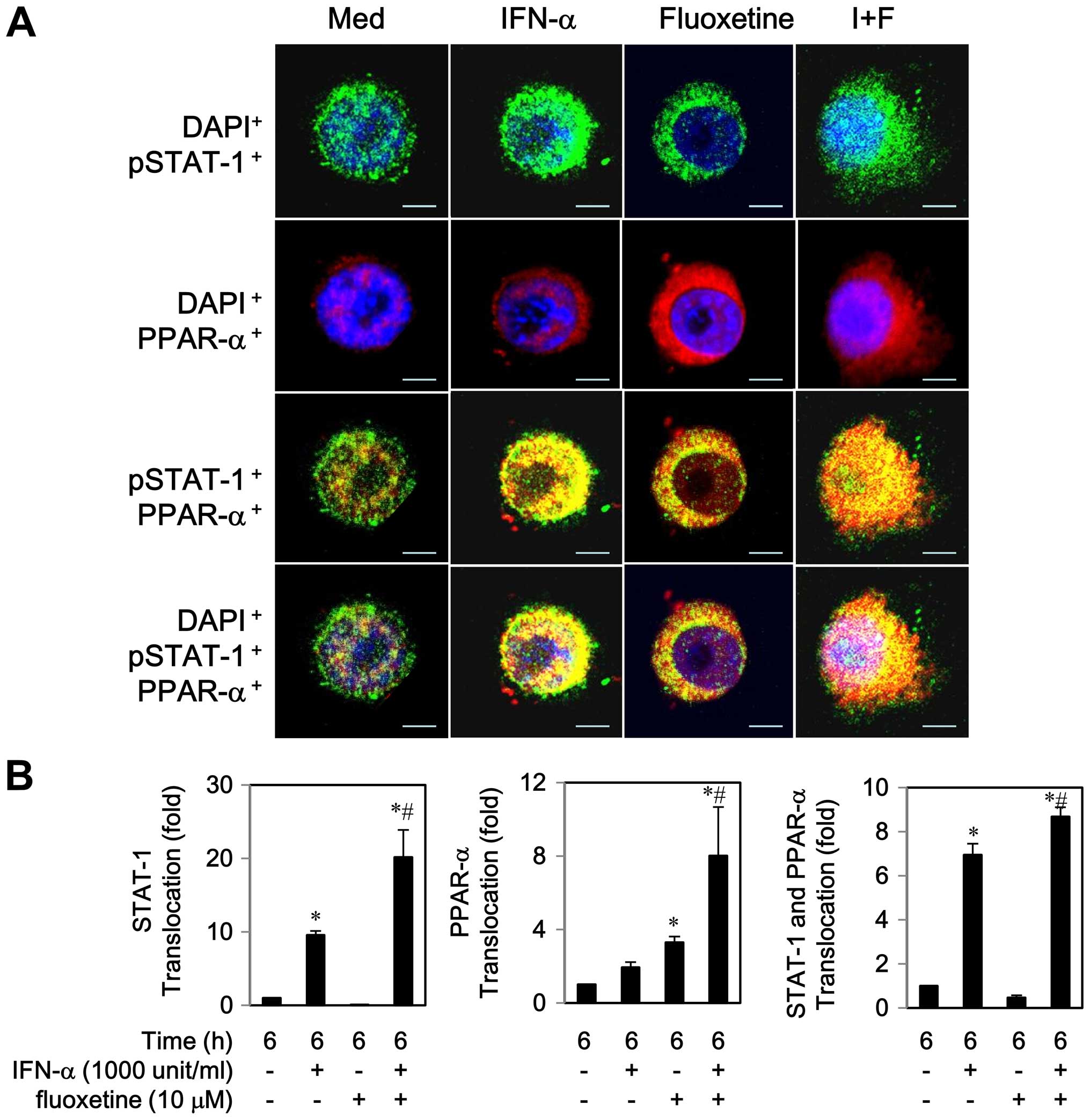
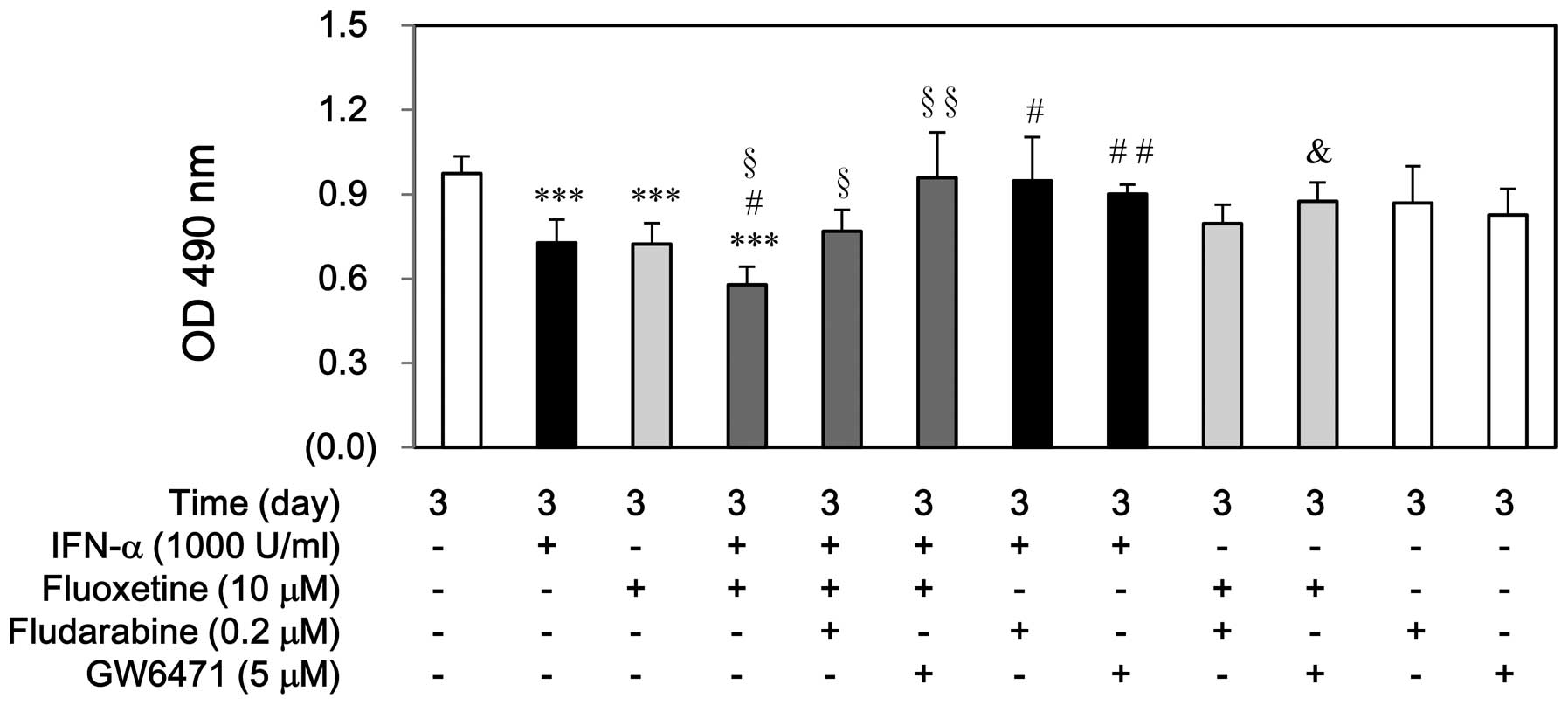
|
1
|
Caraglia M, Marra M, Pelaia G, Maselli R,
Caputi M, Marsico SA and Abbruzzese A: Alpha-interferon and its
effects on signal transduction pathways. J Cell Physiol.
202:323–335. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Santhanam S, Decatris M and O’Byrne K:
Potential of interferon-alpha in solid tumours: Part 2. BioDrugs.
16:349–372. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Caraglia M, Vitale G, Marra M, Budillon A,
Tagliaferri P and Abbruzzese A: Alpha-interferon and its effects on
signalling pathways within cells. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 5:475–485.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Caraglia M, Vitale G, Marra M, Del Prete
S, Lentini A, Budillon A, Beninati S and Abbruzzese A:
Translational and post-translational modifications of proteins as a
new mechanism of action of alpha-interferon: Review article. Amino
Acids. 26:409–417. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Inamura K, Matsuzaki Y, Uematsu N, Honda
A, Tanaka N and Uchida K: Rapid inhibition of MAPK signaling and
anti-proliferation effect via JAK/STAT signaling by
interferon-alpha in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1745:401–410. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Romerio F, Riva A and Zella D:
Interferon-alpha2b reduces phosphorylation and activity of MEK and
ERK through a Ras/Raf-independent mechanism. Br J Cancer.
83:532–538. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee WH, Liu FH, Lee YL and Huang HM:
Interferon-alpha induces the growth inhibition of human T-cell
leukaemia line Jurkat through p38alpha and p38beta. J Biochem.
147:645–650. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bazarbachi A, El-Sabban ME, Nasr R,
Quignon F, Awaraji C, Kersual J, Dianoux L, Zermati Y, Haidar JH,
Hermine O, et al: Arsenic trioxide and interferon-alpha synergize
to induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human T-cell
lymphotropic virus type I-transformed cells. Blood. 93:278–283.
1999.
|
|
9
|
Eriksen KW, Søndergaard H, Woetmann A,
Krejsgaard T, Skak K, Geisler C, Wasik MA and Odum N: The
combination of IL-21 and IFN-alpha boosts STAT3 activation,
cytotoxicity and experimental tumor therapy. Mol Immunol.
46:812–820. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kondo M, Nagano H, Wada H, Damdinsuren B,
Yamamoto H, Hiraoka N, Eguchi H, Miyamoto A, Yamamoto T, Ota H, et
al: Combination of IFN-alpha and 5-fluorouracil induces apoptosis
through IFN-alpha/beta receptor in human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Clin Cancer Res. 11:1277–1286. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fishman AI, Johnson B, Alexander B, Won J,
Choudhury M and Konno S: Additively enhanced antiproliferative
effect of interferon combined with proanthocyanidin on bladder
cancer cells. J Cancer. 3:107–112. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rodin G, Lloyd N, Katz M, Green E, Mackay
JA and Wong RK; Supportive Care Guidelines Group of Cancer Care
Ontario Program in Evidence-Based Care. The treatment of depression
in cancer patients: A systematic review. Support Care Cancer.
15:123–136. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sockalingam S and Abbey SE: Managing
depression during hepatitis C treatment. Can J Psychiatry.
54:614–625. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Serafeim A, Holder MJ, Grafton G, Chamba
A, Drayson MT, Luong QT, Bunce CM, Gregory CD, Barnes NM and Gordon
J: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors directly signal for
apoptosis in biopsy-like Burkitt lymphoma cells. Blood.
101:3212–3219. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peer D and Margalit R: Fluoxetine and
reversal of multidrug resistance. Cancer Lett. 237:180–187. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Roberts RA, Chevalier S, Hasmall SC, James
NH, Cosulich SC and Macdonald N: PPAR alpha and the regulation of
cell division and apoptosis. Toxicology. 181–182:167–170. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
van der Meer DL, Degenhardt T, Väisänen S,
de Groot PJ, Heinäniemi M, de Vries SC, Müller M, Carlberg C and
Kersten S: Profiling of promoter occupancy by PPARalpha in human
hepatoma cells via ChIP-chip analysis. Nucleic Acids Res.
38:2839–2850. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fryknäs M, Dhar S, Oberg F, Rickardson L,
Rydåker M, Göransson H, Gustafsson M, Pettersson U, Nygren P,
Larsson R, et al: STAT1 signaling is associated with acquired
crossresistance to doxorubicin and radiation in myeloma cell lines.
Int J Cancer. 120:189–195. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Torella D, Curcio A, Gasparri C, Galuppo
V, De Serio D, Surace FC, Cavaliere AL, Leone A, Coppola C, Ellison
GM, et al: Fludarabine prevents smooth muscle proliferation in
vitro and neointimal hyperplasia in vivo through specific
inhibition of STAT-1 activation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
292:H2935–H2943. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao L, Huang Y, Tian C, Taylor L,
Curthoys N, Wang Y, Vernon H and Zheng J: Interferon-αregulates
glutaminase 1 promoter through STAT1 phosphorylation: Relevance to
HIV-1 associated neurocognitive disorders. PLoS One. 7:e329952012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sangfelt O, Erickson S, Castro J, Heiden
T, Gustafsson A, Einhorn S and Grandér D: Molecular mechanisms
underlying interferon-alpha-induced G0/G1 arrest: CKI-mediated
regulation of G1 Cdk-complexes and activation of pocket proteins.
Oncogene. 18:2798–2810. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Prietzsch H, Brock J, Kleine HD, Liebe S
and Jaster R: Interferon-alpha inhibits cell cycle progression by
Ba/F3 cells through the antagonisation of interleukin-3 effects on
key regulators of G1/S transition. Cell Signal.
14:751–759. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maeda S, Wada H, Naito Y, Nagano H,
Simmons S, Kagawa Y, Naito A, Kikuta J, Ishii T, Tomimaru Y, et al:
Interferon-α acts on the S/G2/M phases to induce apoptosis in the
G1 phase of an IFNAR2-expressing hepatocellular carcinoma cell
line. J Biol Chem. 289:23786–23795. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Grebenová D, Kuzelová K, Fuchs O, Halada
P, Havlícek V, Marinov I and Hrkal Z: Interferon-alpha suppresses
proliferation of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells K562 by
extending cell cycle S-phase without inducing apoptosis. Blood
Cells Mol Dis. 32:262–269. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou Y, Wang S, Yue BG, Gobl A and Oberg
K: Effects of interferon alpha on the expression of p21cip1/waf1
and cell cycle distribution in carcinoid tumors. Cancer Invest.
20:348–356. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tanabe T, Kominsky SL, Subramaniam PS,
Johnson HM and Torres BA: Inhibition of the glioblastoma cell cycle
by type I IFNs occurs at both the G1 and S phases and correlates
with the upregulation of p21WAF1/CIP1. J Neurooncol.
48:225–232. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Peer D, Dekel Y, Melikhov D and Margalit
R: Fluoxetine inhibits multidrug resistance extrusion pumps and
enhances responses to chemotherapy in syngeneic and in human
xenograft mouse tumor models. Cancer Res. 64:7562–7569. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kannen V, Hintzsche H, Zanette DL, Silva
WA Jr, Garcia SB, Waaga-Gasser AM and Stopper H: Antiproliferative
effects of fluoxetine on colon cancer cells and in a colonic
carcinogen mouse model. PLoS One. 7:e500432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Stopper H, Garcia SB, Waaga-Gasser AM and
Kannen V: Antidepressant fluoxetine and its potential against colon
tumors. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 6:11–21. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Krishnan A, Hariharan R, Nair SA and
Pillai MR: Fluoxetine mediates G0/G1 arrest by inducing functional
inhibition of cyclin dependent kinase subunit (CKS)1. Biochem
Pharmacol. 75:1924–1934. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu KH, Yang ST, Lin YK, Lin JW, Lee YH,
Wang JY, Hu CJ, Lin EY, Chen SM, Then CK, et al: Fluoxetine, an
antidepressant, suppresses glioblastoma by evoking AMPAR-mediated
calcium-dependent apoptosis. Oncotarget. 6:5088–5101. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Stephanou A and Latchman DS: STAT-1: A
novel regulator of apoptosis. Int J Exp Pathol. 84:239–244. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lee CK, Smith E, Gimeno R, Gertner R and
Levy DE: STAT1 affects lymphocyte survival and proliferation
partially independent of its role downstream of IFN-gamma. J
Immunol. 164:1286–1292. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dimco G, Knight RA, Latchman DS and
Stephanou A: STAT1 interacts directly with cyclin D1/Cdk4 and
mediates cell cycle arrest. Cell Cycle. 9:4638–4649. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Roberts RA, James NH, Woodyatt NJ,
Macdonald N and Tugwood JD: Evidence for the suppression of
apoptosis by the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha
(PPAR alpha). Carcinogenesis. 19:43–48. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao W, Iskandar S, Kooshki M, Sharpe JG,
Payne V and Robbins ME: Knocking out peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha inhibits
radiation-induced apoptosis in the mouse kidney through activation
of NF-kappaB and increased expression of IAPs. Radiat Res.
167:581–591. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen C, Han YH, Yang Z and Rodrigues AD:
Effect of interferon-α2b on the expression of various
drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters in co-cultures of
freshly prepared human primary hepatocytes. Xenobiotica.
41:476–485. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|