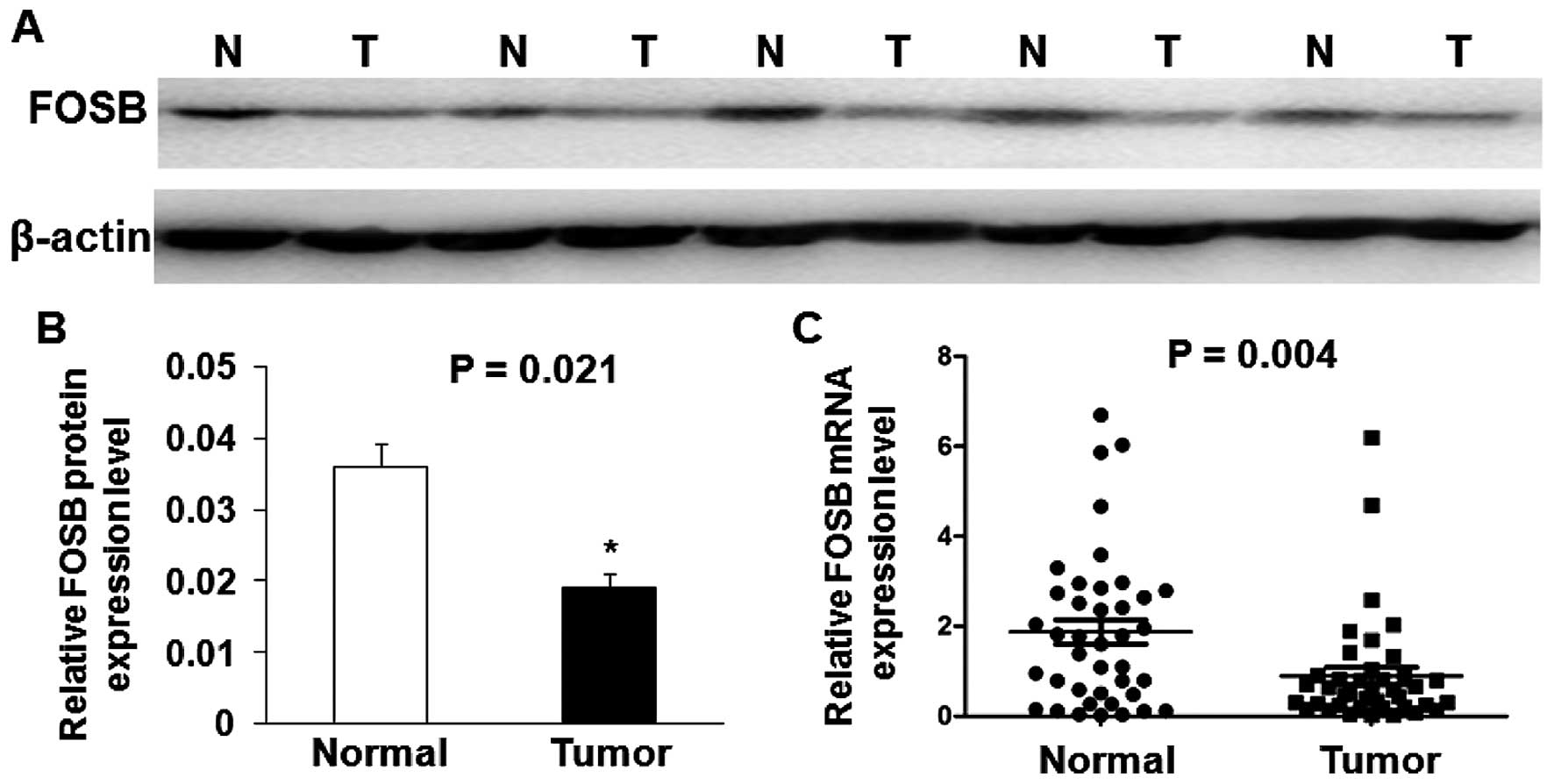
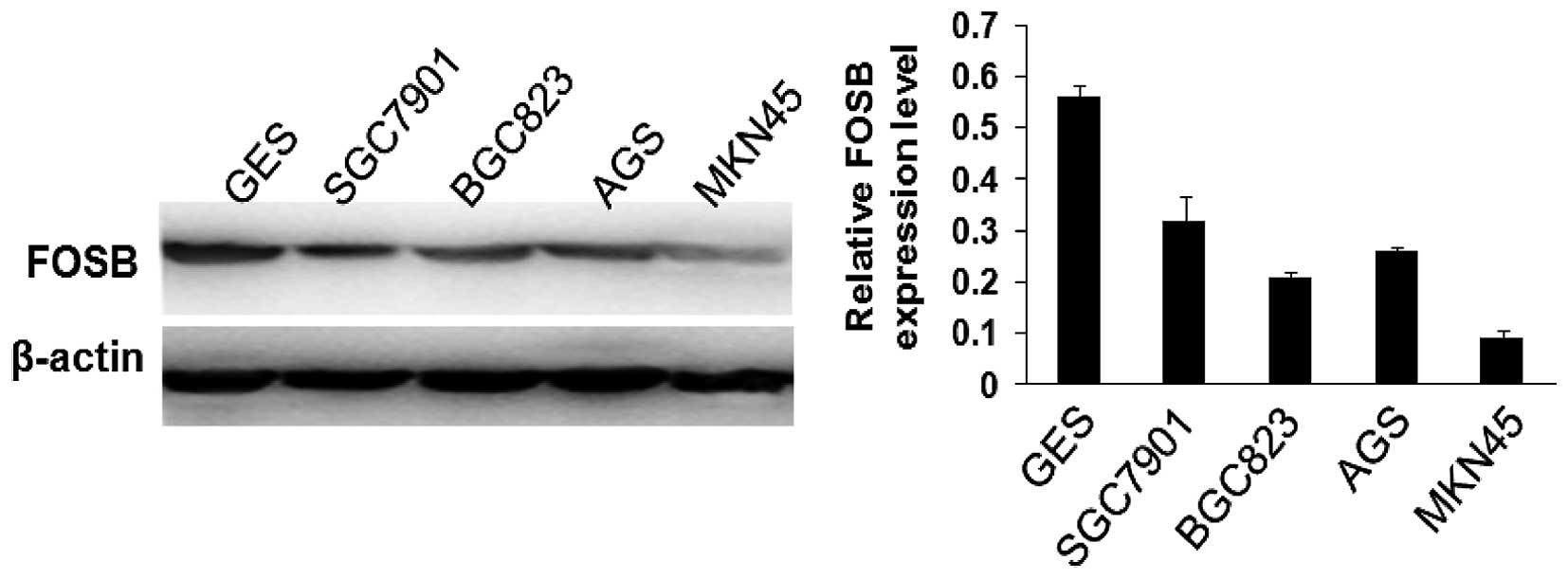
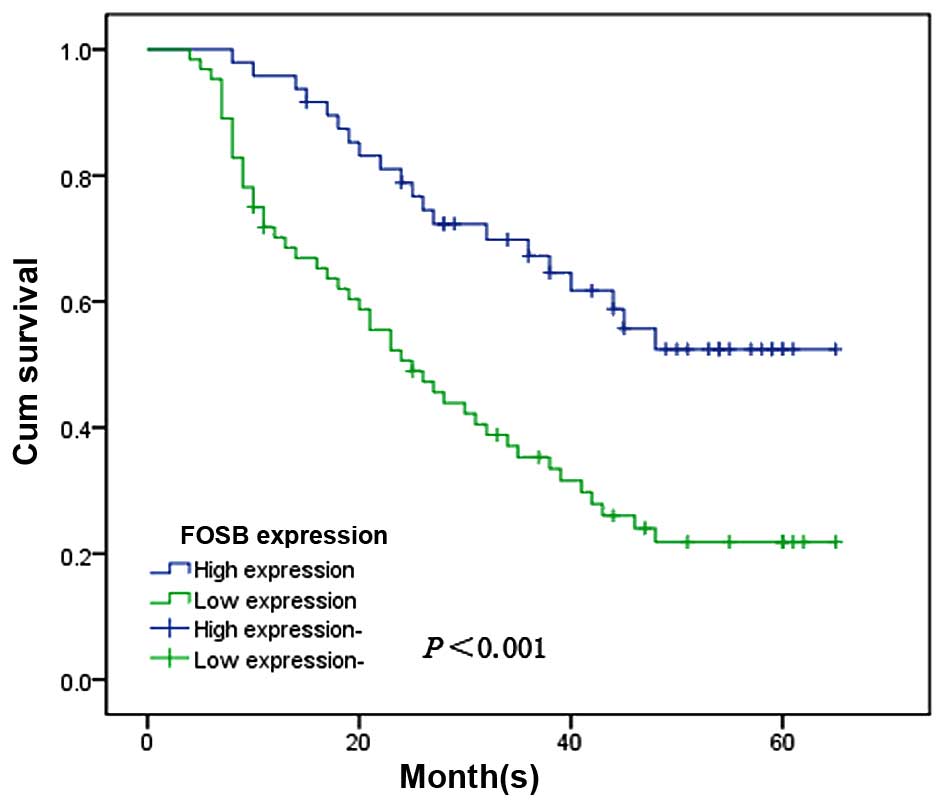
|
1
|
Ajani JA, Bentrem DJ, Besh S, D’Amico TA,
Das P, Denlinger C, Fakih MG, Fuchs CS, Gerdes H, Glasgow RE, et
al; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Gastric cancer, version
2.2013: Featured updates to the NCCN Guidelines. J Natl Compr Canc
Netw. 11:531–546. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin Y, Ueda J, Kikuchi S, Totsuka Y, Wei
WQ, Qiao YL and Inoue M: Comparative epidemiology of gastric cancer
between Japan and China. World J Gastroenterol. 17:4421–4428. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Howlett M, Menheniott TR, Judd LM and
Giraud AS: Cytokine signalling via gp130 in gastric cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1793:1623–1633. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siderovski DP, Blum S, Forsdyke RE and
Forsdyke DR: A set of human putative lymphocyte
G0/G1 switch genes includes genes homologous
to rodent cytokine and zinc finger protein-encoding genes. DNA Cell
Biol. 9:579–587. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martin-Gallardo A, McCombie WR, Gocayne
JD, FitzGerald MG, Wallace S, Lee BM, Lamerdin J, Trapp S, Kelley
JM, Liu LI, et al: Automated DNA sequencing and analysis of 106
kilobases from human chromosome 19q13.3. Nat Genet. 1:34–39. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zerial M, Toschi L, Ryseck RP, Schuermann
M, Müller R and Bravo R: The product of a novel growth factor
activated gene, fos B, interacts with JUN proteins enhancing their
DNA binding activity. EMBO J. 8:805–813. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hess J, Angel P and Schorpp-Kistner M:
AP-1 subunits: Quarrel and harmony among siblings. J Cell Sci.
117:5965–5973. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krosl J and Sauvageau G: AP-1 complex is
effector of Hox-induced cellular proliferation and transformation.
Oncogene. 19:5134–5141. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mechta F, Lallemand D, Pfarr CM and Yaniv
M: Transformation by ras modifies AP1 composition and activity.
Oncogene. 14:837–847. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pospelova TV, Medvedev AV, Kukushkin AN,
Svetlikova SB, van der Eb AJ, Dorsman JC and Pospelov VA: E1A +
cHa-ras transformed rat embryo fibroblast cells are characterized
by high and constitutive DNA binding activities of AP-1 dimers with
significantly altered composition. Gene Expr. 8:19–32.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chung JY, Huang C, Meng X, Dong Z and Yang
CS: Inhibition of activator protein 1 activity and cell growth by
purified green tea and black tea polyphenols in H-ras-transformed
cells: Structure-activity relationship and mechanisms involved.
Cancer Res. 59:4610–4617. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Darne C, Martinez A, Lallemand D, Morel L,
Jean C, Saru JP, Schmid HP and Manin M: Down-regulation of AP1
activities after polarization of vas deferens epithelial cells
correlates with androgen-induced gene expression. J Steroid Biochem
Mol Biol. 72:103–113. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ng DC, Shafaee S, Lee D and Bikle DD:
Requirement of an AP-1 site in the calcium response region of the
involucrin promoter. J Biol Chem. 275:24080–24088. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Milde-Langosch K, Kappes H, Riethdorf S,
Löning T and Bamberger AM: FosB is highly expressed in normal
mammary epithelia, but down-regulated in poorly differentiated
breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 77:265–275. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim JH, Lee JY, Lee KT, Lee JK, Lee KH,
Jang KT, Heo JS, Choi SH and Rhee JC: RGS16 and FosB underexpressed
in pancreatic cancer with lymph node metastasis promote tumor
progression. Tumour Biol. 31:541–548. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Yu JC, Kang WM and Ma ZQ:
Treatment strategy for early gastric cancer. Surg Oncol.
21:119–123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mahar AL, Coburn NG, Singh S, Law C and
Helyer LK: A systematic review of surgery for non-curative gastric
cancer. Gastric Cancer. 15(Suppl 1): S125–S137. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Piazuelo MB and Correa P: Gastric cáncer:
Overview. Colomb Med (Cali). 44:192–201. 2013.
|
|
19
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
van Seventer GA, Salmen HJ, Law SF,
O’Neill GM, Mullen MM, Franz AM, Kanner SB, Golemis EA and van
Seventer JM: Focal adhesion kinase regulates beta1
integrin-dependent T cell migration through an HEF1 effector
pathway. Eur J Immunol. 31:1417–1427. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Milde-Langosch K: The Fos family of
transcription factors and their role in tumourigenesis. Eur J
Cancer. 41:2449–2461. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ryseck RP and Bravo R: c-JUN, JUN B, and
JUN D differ in their binding affinities to AP-1 and CRE consensus
sequences: Effect of FOS proteins. Oncogene. 6:533–542.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yamaoka Y, Kato M and Asaka M: Geographic
differences in gastric cancer incidence can be explained by
differences between Helicobacter pylori strains. Intern Med.
47:1077–1083. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang F, Sun GP, Zou YF, Zhong F, Ma T, Li
XQ and Wu D: Helicobacter pylori infection predicts favorable
outcome in patients with gastric cancer. Curr Oncol. 20:e388–e395.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lucibello FC, Slater EP, Jooss KU, Beato M
and Müller R: Mutual transrepression of Fos and the glucocorticoid
receptor: Involvement of a functional domain in Fos which is absent
in FosB. EMBO J. 9:2827–2834. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Angel P and Karin M: The role of Jun, Fos
and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1072:129–157. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rosen JM, Zahnow C, Kazansky A and Raught
B: Composite response elements mediate hormonal and developmental
regulation of milk protein gene expression. Biochem Soc Symp.
63:101–113. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|