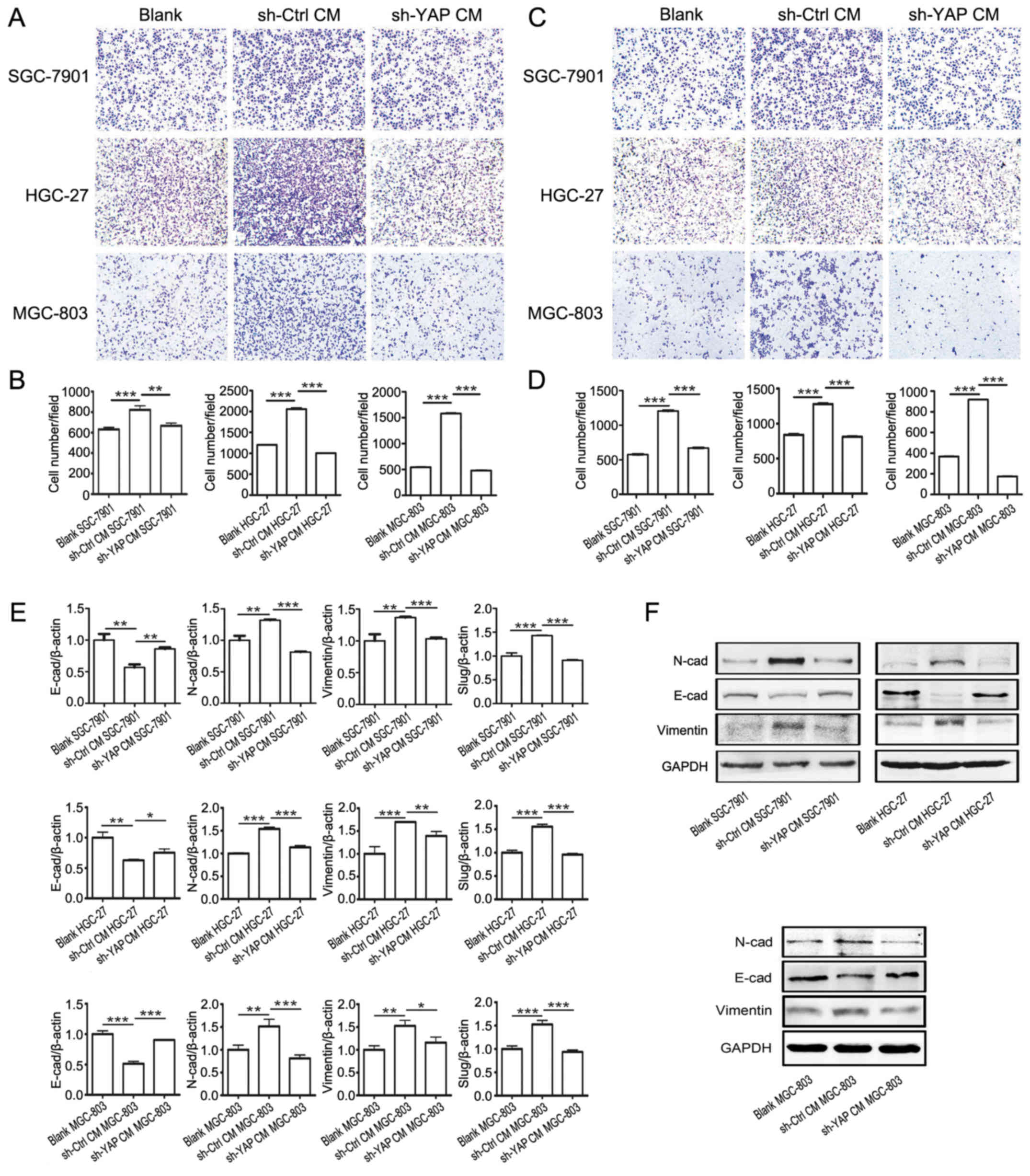
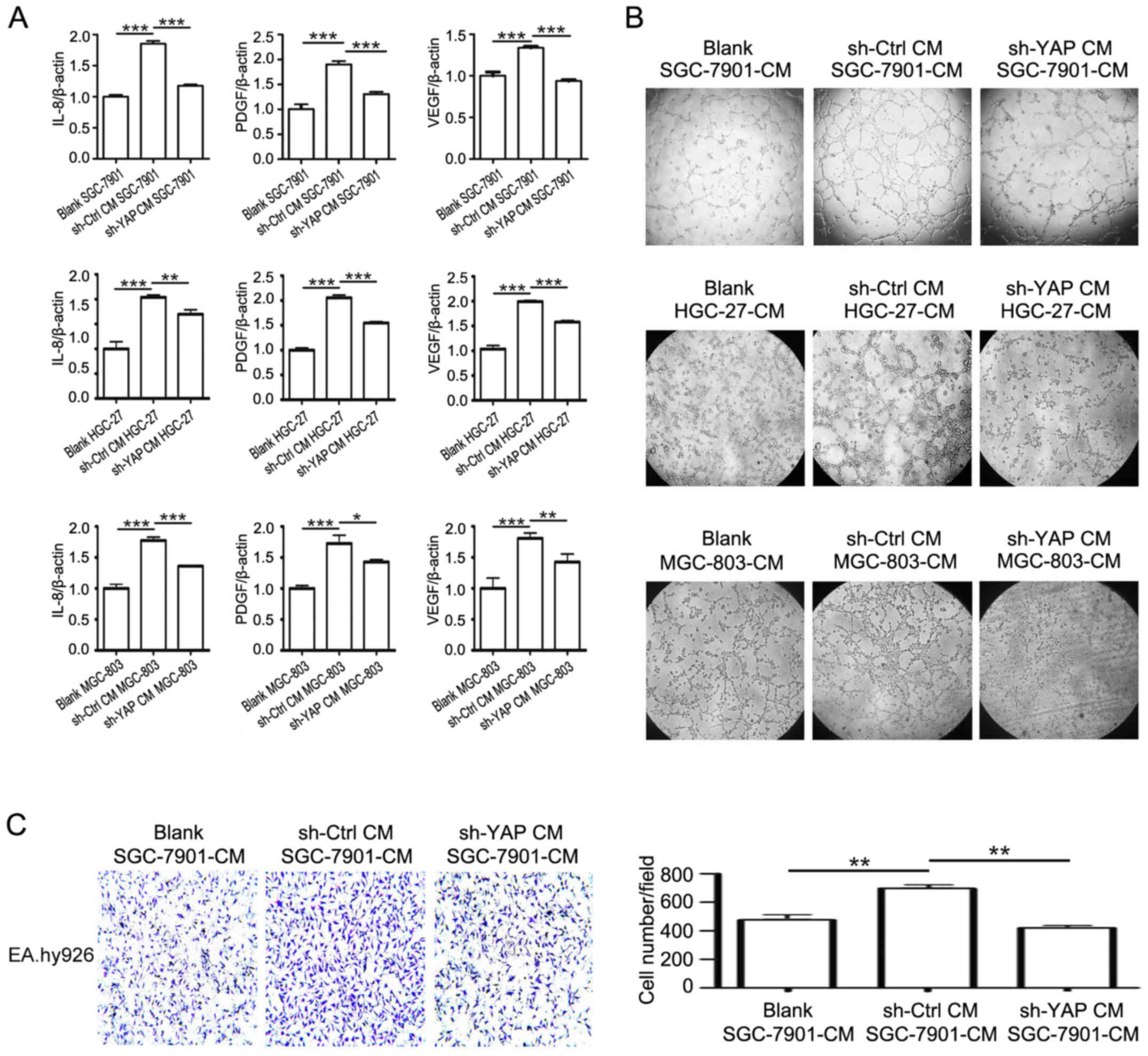
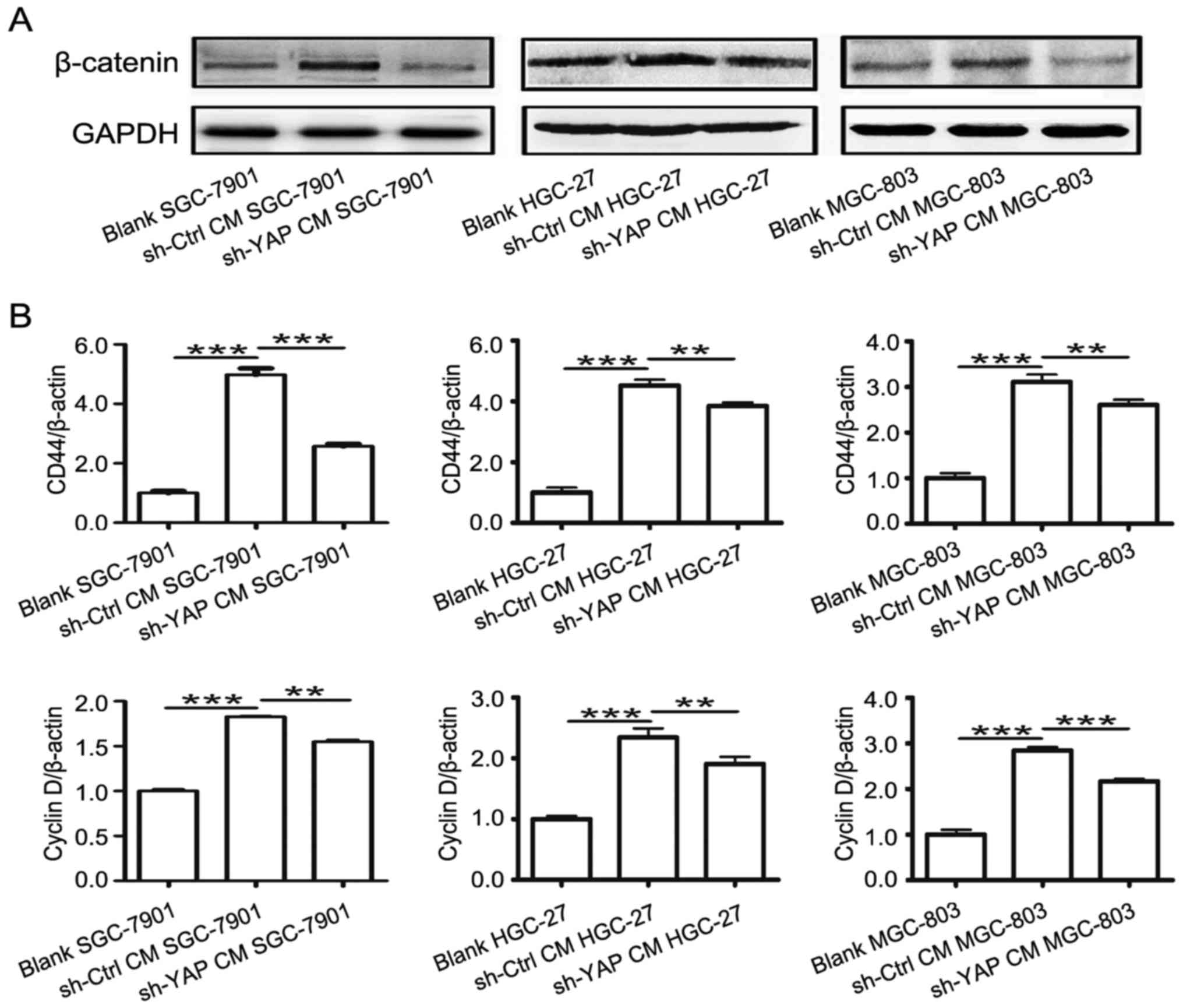
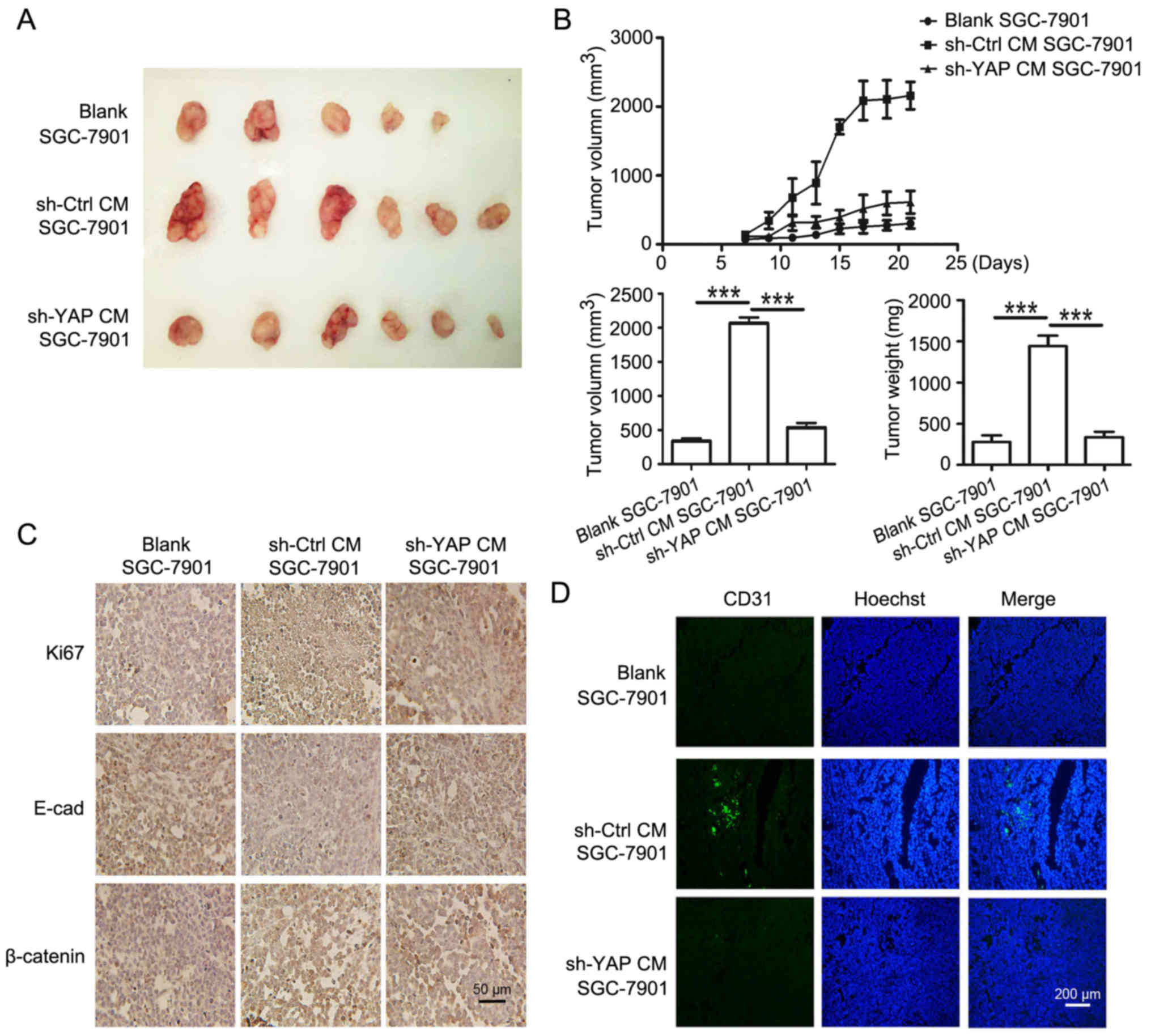
|
1
|
Tan YK and Fielding JW: Early diagnosis of
early gastric cancer. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:821–829.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bertuccio P, Chatenoud L, Levi F, Praud D,
Ferlay J, Negri E, Malvezzi M and La Vecchia C: Recent patterns in
gastric cancer: A global overview. Int J Cancer. 125:666–673. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pornsuksiri K, Chewatanakornkul S,
Kanngurn S, Maneechay W, Chaiyapan W and Sangkhathat S: Clinical
outcomes of gastrointestinal stromal tumor in southern Thailand.
World. J Gastrointest Oncol. 4:216–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yu B and Xie J: Identifying therapeutic
targets in gastric cancer: The current status and future direction.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 48:90–96. 2016.
|
|
6
|
Kasashima H, Yashiro M, Nakamae H,
Kitayama K, Masuda G, Kinoshita H, Fukuoka T, Hasegawa T, Nakane T,
Hino M, et al: CXCL1-chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 2 signaling
stimulates the recruitment of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells
into diffuse-type gastric cancer stroma. Am J Pathol.
186:3028–3039. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu L, Zhang X, Zhang B, Shi H, Yuan X, Sun
Y, Pan Z, Qian H and Xu W: Exosomes derived from gastric cancer
cells activate NF-κB pathway in macrophages to promote cancer
progression. Tumour Biol. 37:12169–12180. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang F, Wang M, Yang T, Cai J, Zhang Q,
Sun Z, Wu X, Zhang X, Zhu W, Qian H, et al: Gastric cancer-derived
MSC-secreted PDGF-DD promotes gastric cancer progression. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 140:1835–1848. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang M, Zhao C, Shi H, Zhang B, Zhang L,
Zhang X, Wang S, Wu X, Yang T, Huang F, et al: Deregulated
microRNAs in gastric cancer tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells:
Novel biomarkers and a mechanism for gastric cancer. Br J Cancer.
110:1199–1210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li W, Zhou Y, Yang J, Zhang X, Zhang H,
Zhang T, Zhao S, Zheng P, Huo J and Wu H: Gastric cancer-derived
mesenchymal stem cells prompt gastric cancer progression through
secretion of interleukin-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:522015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu FX, Zhao B and Guan KL: Hippo pathway
in organ size control, tissue homeostasis, and cancer. Cell.
163:811–828. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Harvey KF, Zhang X and Thomas DM: The
Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:246–257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moroishi T, Hansen CG and Guan KL: The
emerging roles of YAP and TAZ in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:73–79.
2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hua G, Lv X, He C, Remmenga SW, Rodabough
KJ, Dong J, Yang L, Lele SM, Yang P, Zhou J, et al: YAP induces
high-grade serous carcinoma in fallopian tube secretory epithelial
cells. Oncogene. 35:2247–2265. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Zhang J, Xu ZP, Yang YC, Zhu JS, Zhou Z
and Chen WX: Expression of Yes-associated protein in gastric
adenocarcinoma and inhibitory effects of its knockdown on gastric
cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 25:583–590. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun D, Li X, He Y, Li W, Wang Y, Wang H,
Jiang S and Xin Y: YAP1 enhances cell proliferation, migration, and
invasion of gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget.
7:81062–81076. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Calvo F, Ege N, Grande-Garcia A, Hooper S,
Jenkins RP, Chaudhry SI, Harrington K, Williamson P, Moeendarbary
E, Charras G, et al: Mechanotransduction and YAP-dependent matrix
remodelling is required for the generation and maintenance of
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Cell Biol. 15:637–646. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang J, Ji JY, Yu M, Overholtzer M,
Smolen GA, Wang R, Brugge JS, Dyson NJ and Haber DA: YAP-dependent
induction of amphiregulin identifies a non-cell-autonomous
component of the Hippo pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 11:1444–1450. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fujii M, Toyoda T, Nakanishi H, Yatabe Y,
Sato A, Matsudaira Y, Ito H, Murakami H, Kondo Y, Kondo E, et al:
TGF-β synergizes with defects in the Hippo pathway to stimulate
human malignant mesothelioma growth. J Exp Med. 209:479–494. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mo JS, Park HW and Guan KL: The Hippo
signaling pathway in stem cell biology and cancer. EMBO Rep.
15:642–656. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang T, Lee YW, Rui YF, Cheng TY, Jiang
XH and Li G: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote
growth and angiogenesis of breast and prostate tumors. Stem Cell
Res Ther. 4:702013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cao H, Xu W, Qian H, Zhu W, Yan Y, Zhou H,
Zhang X, Xu X, Li J, Chen Z, et al: Mesenchymal stem cell-like
cells derived from human gastric cancer tissues. Cancer Lett.
274:61–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xu X, Zhang X, Wang S, Qian H, Zhu W, Cao
H, Wang M, Chen Y and Xu W: Isolation and comparison of mesenchymal
stem-like cells from human gastric cancer and adjacent noncancerous
tissues. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:495–504. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bergfeld SA and DeClerck YA: Bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and the tumor
microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29:249–261. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Barcellos-de-Souza P, Gori V, Bambi F and
Chiarugi P: Tumor microenvironment: Bone marrow-mesenchymal stem
cells as key players. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1836:321–335.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li GC, Zhang HW, Zhao QC, Sun LI, Yang JJ,
Hong L, Feng F and Cai L: Mesenchymal stem cells promote tumor
angiogenesis via the action of transforming growth factor β1. Oncol
Lett. 11:1089–1094. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Su YJ, Lin WH, Chang YW, Wei KC, Liang CL,
Chen SC and Lee JL: Polarized cell migration induces cancer
type-specific CD133/integrin/Src/Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling
required for maintenance of cancer stem cell properties.
Oncotarget. 6:38029–38045. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen MJ, Wu DW, Wang YC, Chen CY and Lee
H: PAK1 confers chemoresistance and poor outcome in non-small cell
lung cancer via β-catenin-mediated stemness. Sci Rep. 6:349332016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lettini G, Sisinni L, Condelli V, Matassa
DS, Simeon V, Maddalena F, Gemei M, Lopes E, Vita G, Del Vecchio L,
et al: TRAP1 regulates stemness through Wnt/β-catenin pathway in
human colorectal carcinoma. Cell Death Differ. 23:1792–1803. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu D, Du L, Chen D, Ye Z, Duan H, Tu T,
Feng J, Yang Y, Chen Q and Yan X: Reduced CD146 expression promotes
tumorigenesis and cancer stemness in colorectal cancer through
activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget. 7:40704–40718.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang X, Xu J, Jiang T, Liu G, Wang D and
Lu Y: MicroRNA-195 suppresses colorectal cancer cells proliferation
via targeting FGF2 and regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Am J
Cancer Res. 6:2631–2640. 2016.
|
|
32
|
Gabrielyan A, Knaak S, Gelinsky M, Arnhold
S and Rösen-Wolff A: Hypoxia-conditioned media allows
species-specific attraction of bone marrow stromal cells without
need for recombinant proteins. BMC Vet Res. 10:562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bergfeld SA, Blavier L and DeClerck YA:
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells promote survival and
drug resistance in tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:962–975. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Han I, Yun M, Kim EO, Kim B, Jung MH and
Kim SH: Umbilical cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce
apoptosis in PC-3 prostate cancer cells through activation of JNK
and down-regulation of I3K/AKT signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther.
5:542014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhu M, Wang M, Yang F, Tian Y, Cai J, Yang
H, Fu H, Mao F, Zhu W, Qian H, et al: miR-155-5p inhibition
promotes the transition of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to
gastric cancer tissue derived MSC-like cells via NF-κB p65
activation. Oncotarget. 7:16567–16580. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Steinhardt AA, Gayyed MF, Klein AP, Dong
J, Maitra A, Pan D, Montgomery EA and Anders RA: Expression of
Yes-associated protein in common solid tumors. Hum Pathol.
39:1582–1589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao B, Li L, Lei Q and Guan KL: The
Hippo-YAP pathway in organ size control and tumorigenesis: An
updated version. Genes Dev. 24:862–874. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Azzolin L, Panciera T, Soligo S, Enzo E,
Bicciato S, Dupont S, Bresolin S, Frasson C, Basso G, Guzzardo V,
et al: YAP/TAZ incorporation in the β-catenin destruction complex
orchestrates the Wnt response. Cell. 158:157–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zuo QF, Zhang R, Li BS, Zhao YL, Zhuang Y,
Yu T, Gong L, Li S, Xiao B and Zou QM: MicroRNA-141 inhibits tumor
growth and metastasis in gastric cancer by directly targeting
transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif, TAZ. Cell
Death Dis. 6:e16232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Qiao Y, Lin SJ, Chen Y, Voon DC, Zhu F,
Chuang LS, Wang T, Tan P, Lee SC, Yeoh KG, et al: RUNX3 is a novel
negative regulator of oncogenic TEAD-YAP complex in gastric cancer.
Oncogene. 35:2664–2674. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Jiao S, Wang H, Shi Z, Dong A, Zhang W,
Song X, He F, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Wang W, et al: A peptide mimicking
VGLL4 function acts as a YAP antagonist therapy against gastric
cancer. Cancer Cell. 25:166–180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu C, Liu Y, Xu XX, Guo X, Sun GW and Ma
XJ: Mesenchymal stem cells enhance the metastasis of 3D-cultured
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. 16:5662016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ehmer U and Sage J: Control of
proliferation and cancer growth by the Hippo signaling pathway. Mol
Cancer Res. 14:127–140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Yagi H, Asanoma K, Ohgami T, Ichinoe A,
Sonoda K and Kato K: GEP oncogene promotes cell proliferation
through YAP activation in ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 35:4471–4480.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang J, Wang G, Chu SJ, Zhu JS, Zhang R,
Lu WW, Xia LQ, Lu YM, Da W and Sun Q: Loss of large tumor
suppressor 1 promotes growth and metastasis of gastric cancer cells
through upregulation of the YAP signaling. Oncotarget.
7:16180–16193. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhuang K, Yan Y, Zhang X, Zhang J, Zhang L
and Han K: Gastrin promotes the metastasis of gastric carcinoma
through the β-catenin/TCF-4 pathway. Oncol Rep. 36:1369–1376. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Guo F, Ren X, Dong Y, Hu X, Xu D, Zhou H,
Meng F, Tian W and Zhao Y: Constitutive expression of PPARγ
inhibits proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells and
down-regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway downstream target
genes TERT and ENAH. Gene. 584:31–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fan D, Ren B, Yang X, Liu J and Zhang Z:
Upregulation of miR-501-5p activates the wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway and enhances stem cell-like phenotype in gastric cancer. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:1772016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Marti P, Stein C, Blumer T, Abraham Y,
Dill MT, Pikiolek M, Orsini V, Jurisic G, Megel P, Makowska Z, et
al: YAP promotes proliferation, chemoresistance, and angiogenesis
in human cholangiocarcinoma through TEAD transcription factors.
Hepatology. 62:1497–1510. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Peng Y, Zhang X, Ma Q, Yan R, Qin Y, Zhao
Y, Cheng Y, Yang M, Wang Q, Feng X, et al: MiRNA-194 activates the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in gastric cancer by targeting the
negative Wnt regulator, SUFU. Cancer Lett. 385:117–127. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhang B, Shi Y, Gong A, Pan Z, Shi H, Yang
H, Fu H, Yan Y, Zhang X, Wang M, et al: HucMSC exosome-delivered
14-3-3ζ orchestrates self-control of the Wnt response via
modulation of YAP during cutaneous regeneration. Stem Cells.
34:2485–2500. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|