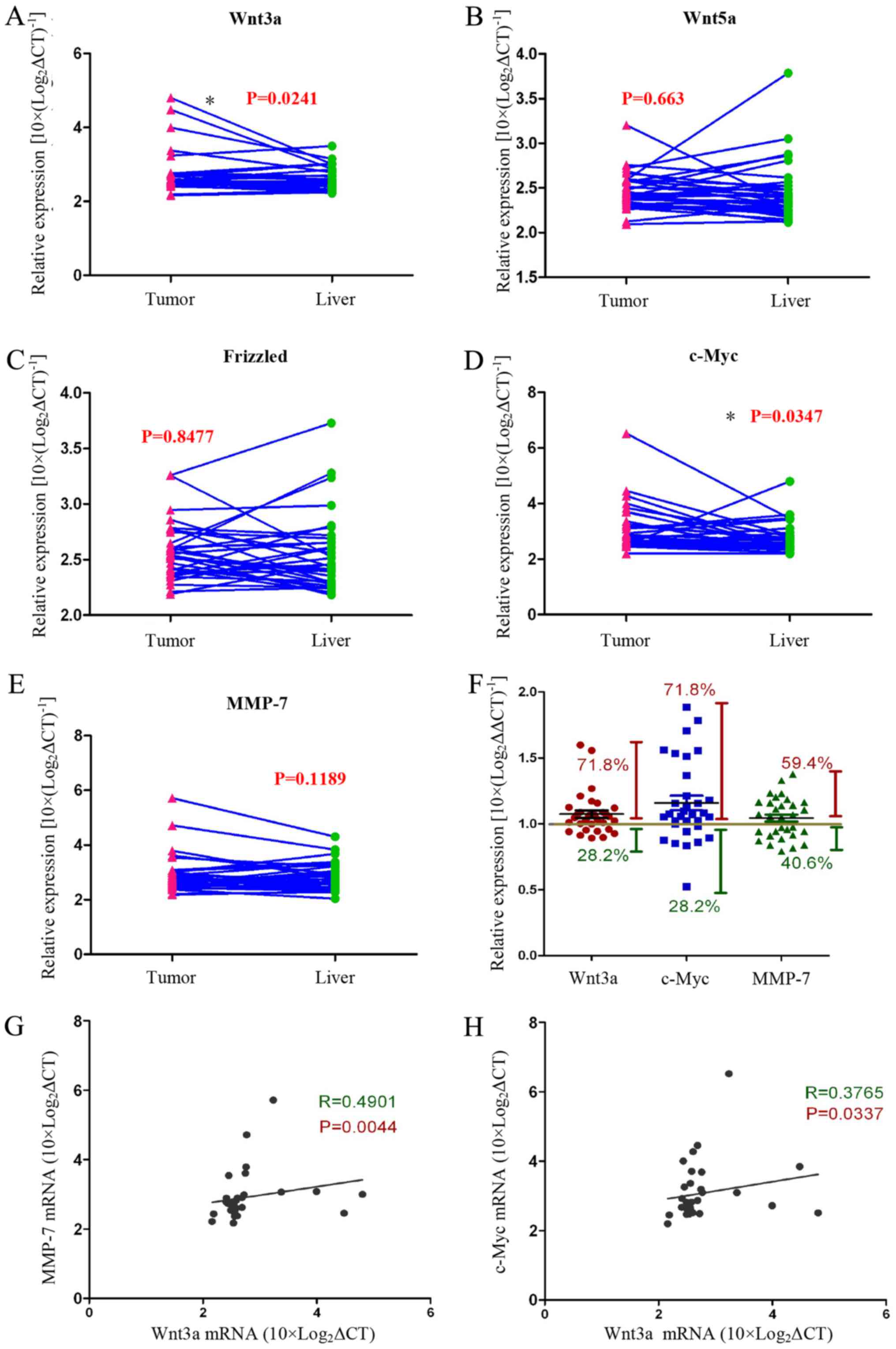
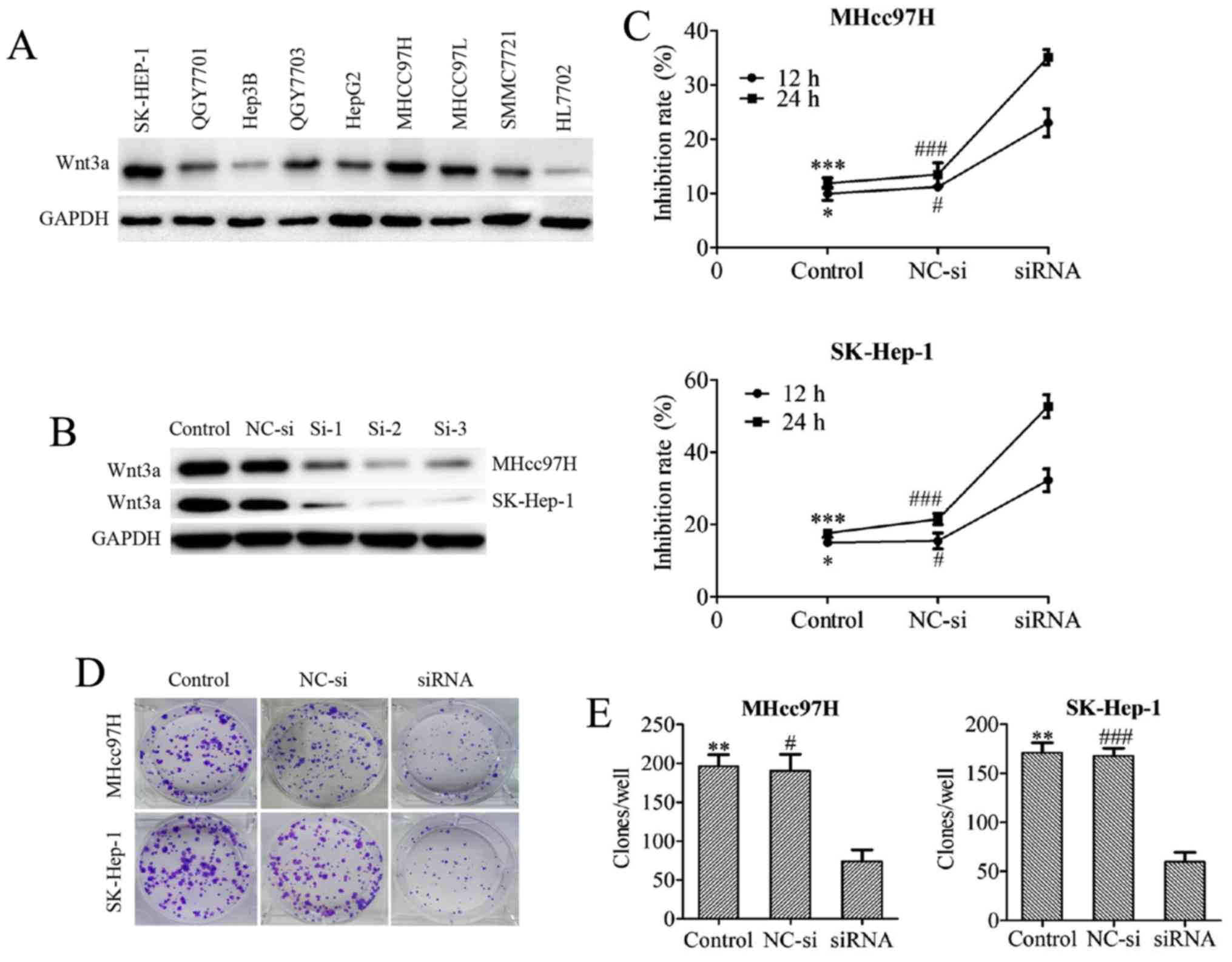
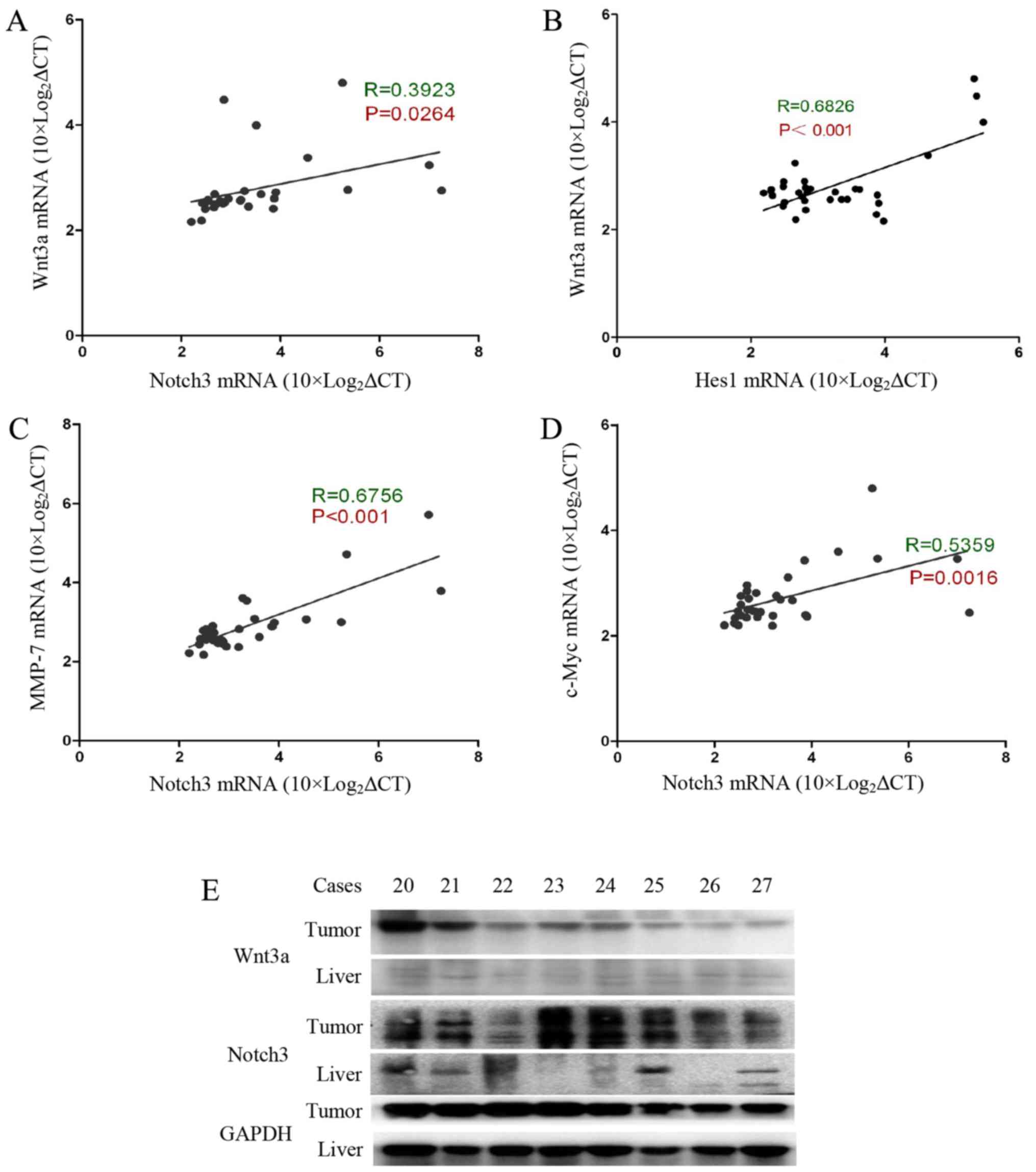
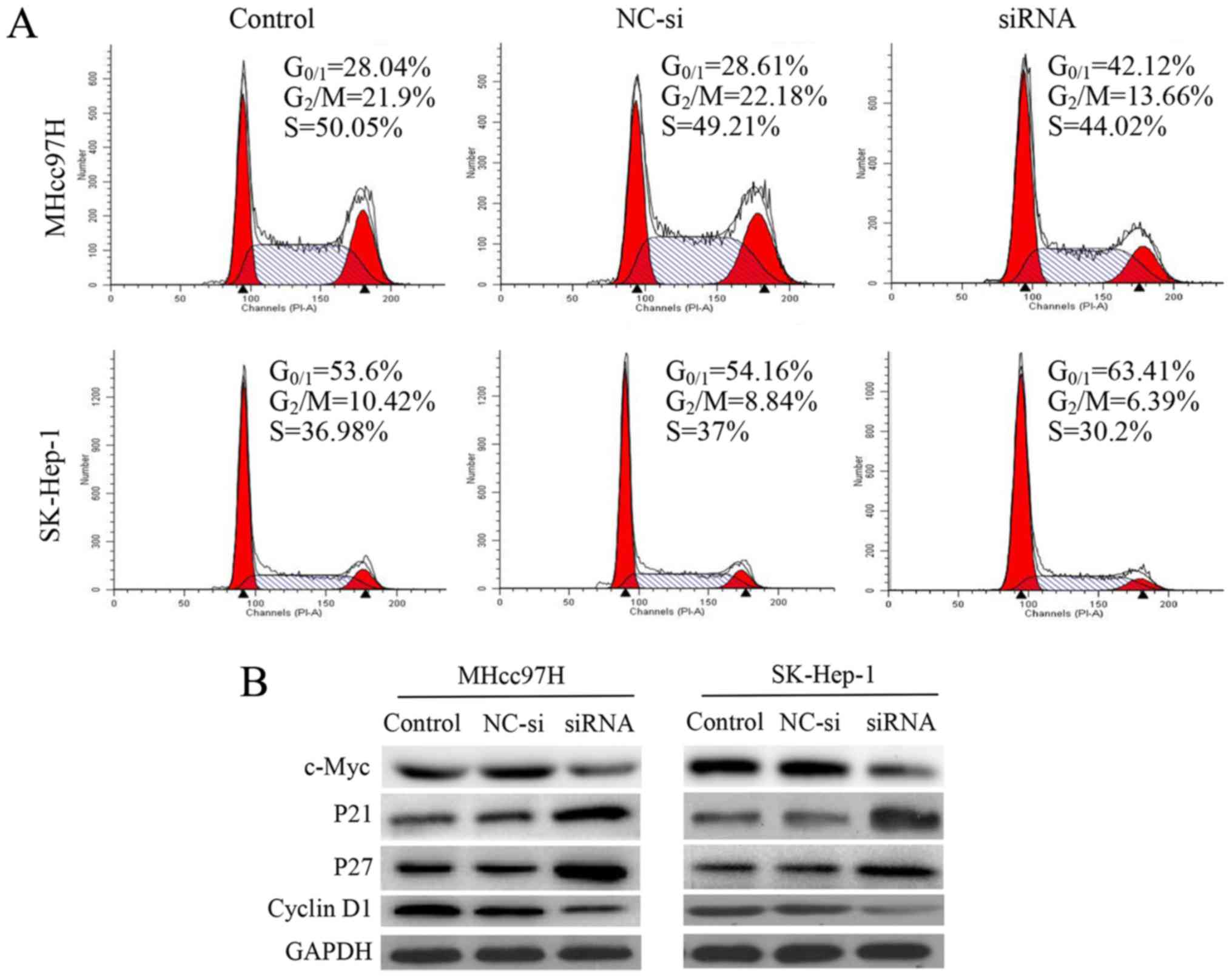
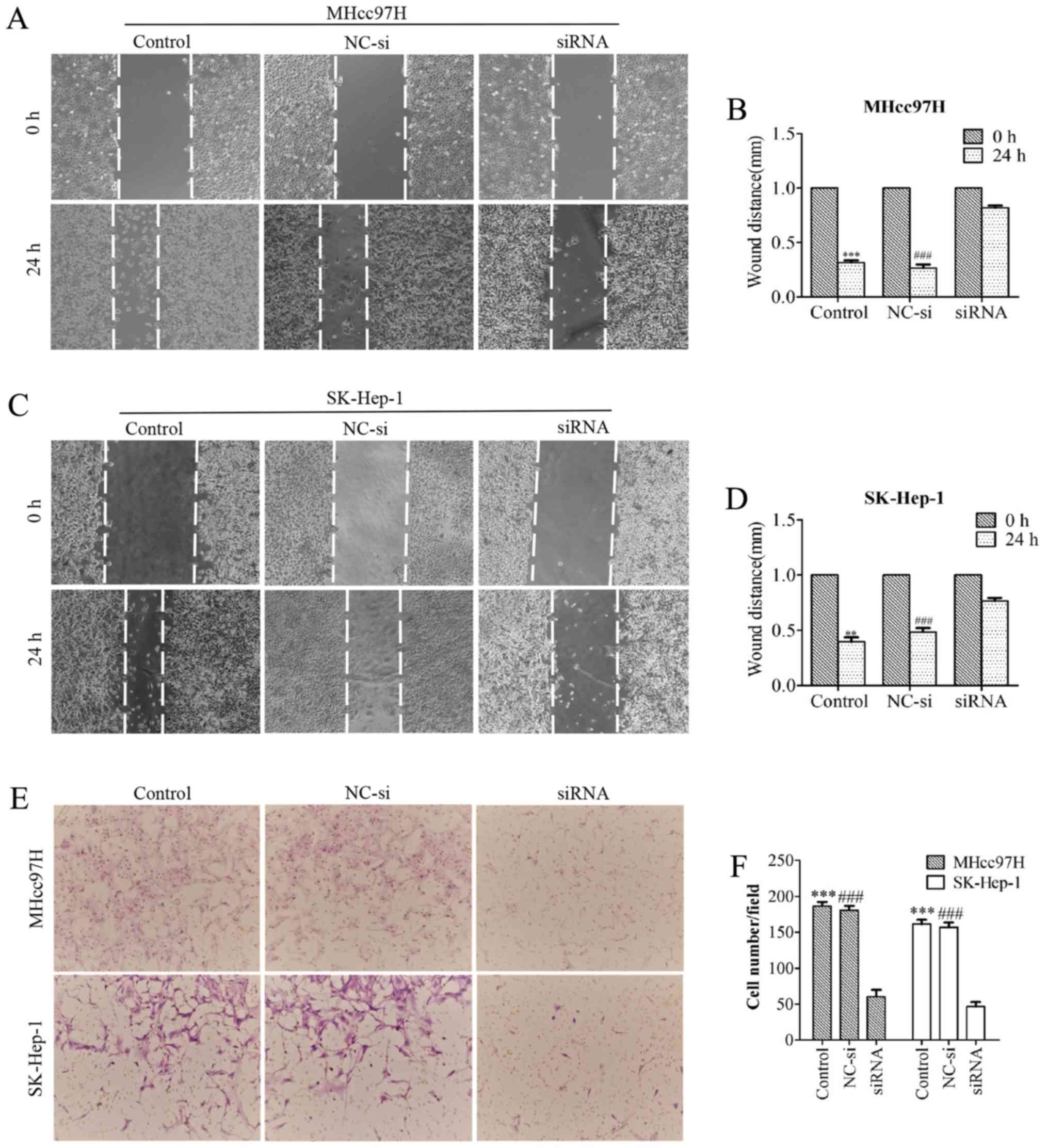
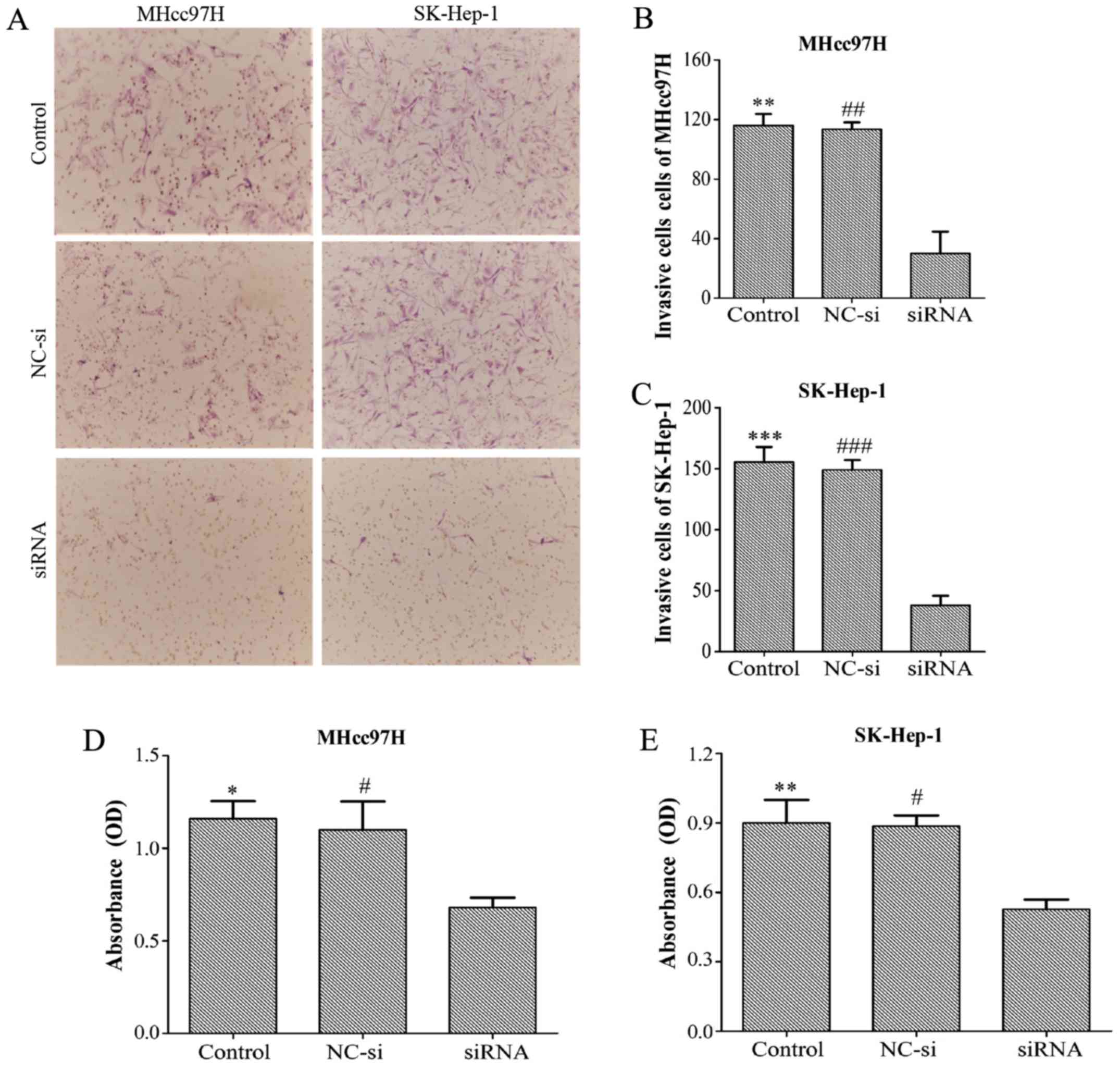
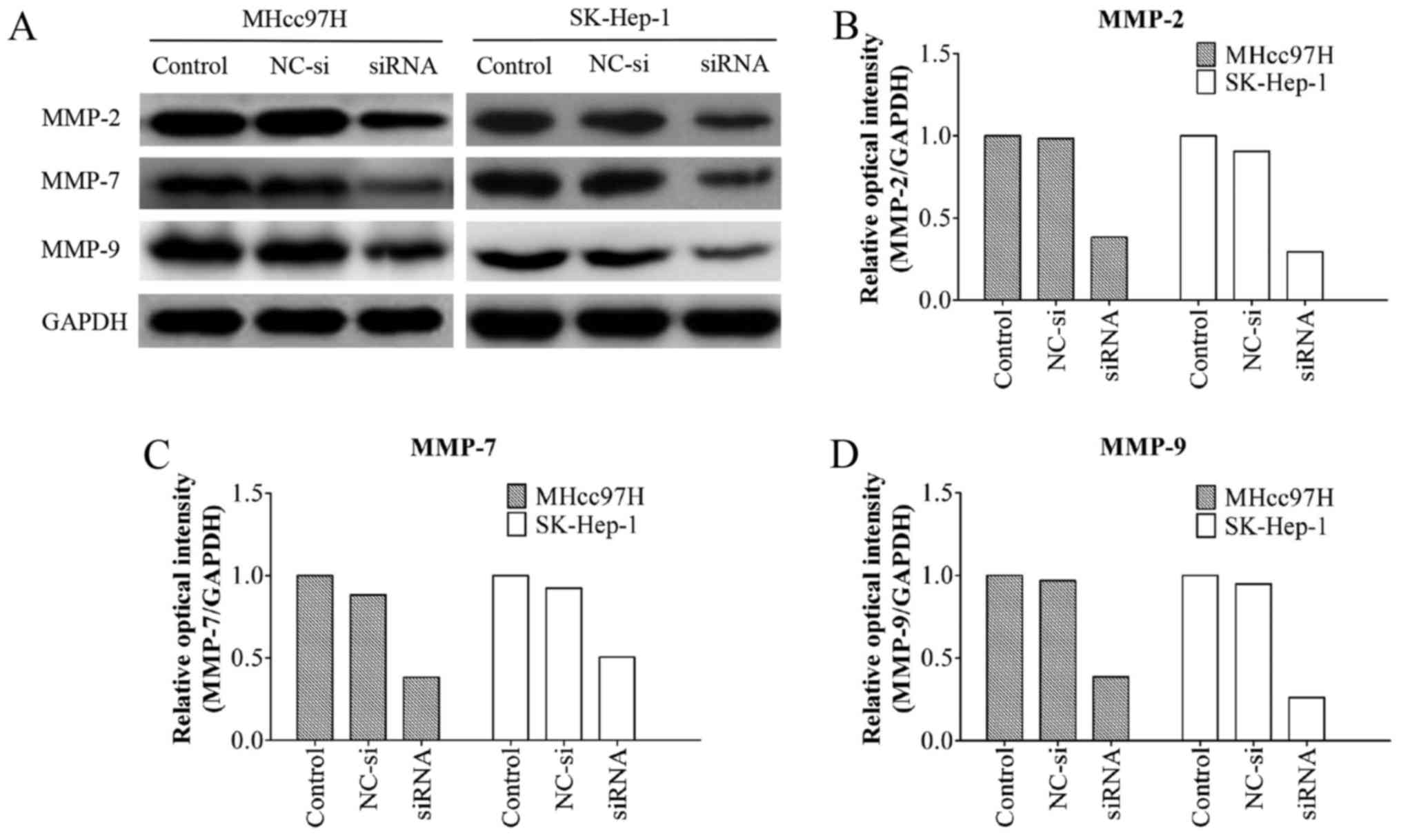
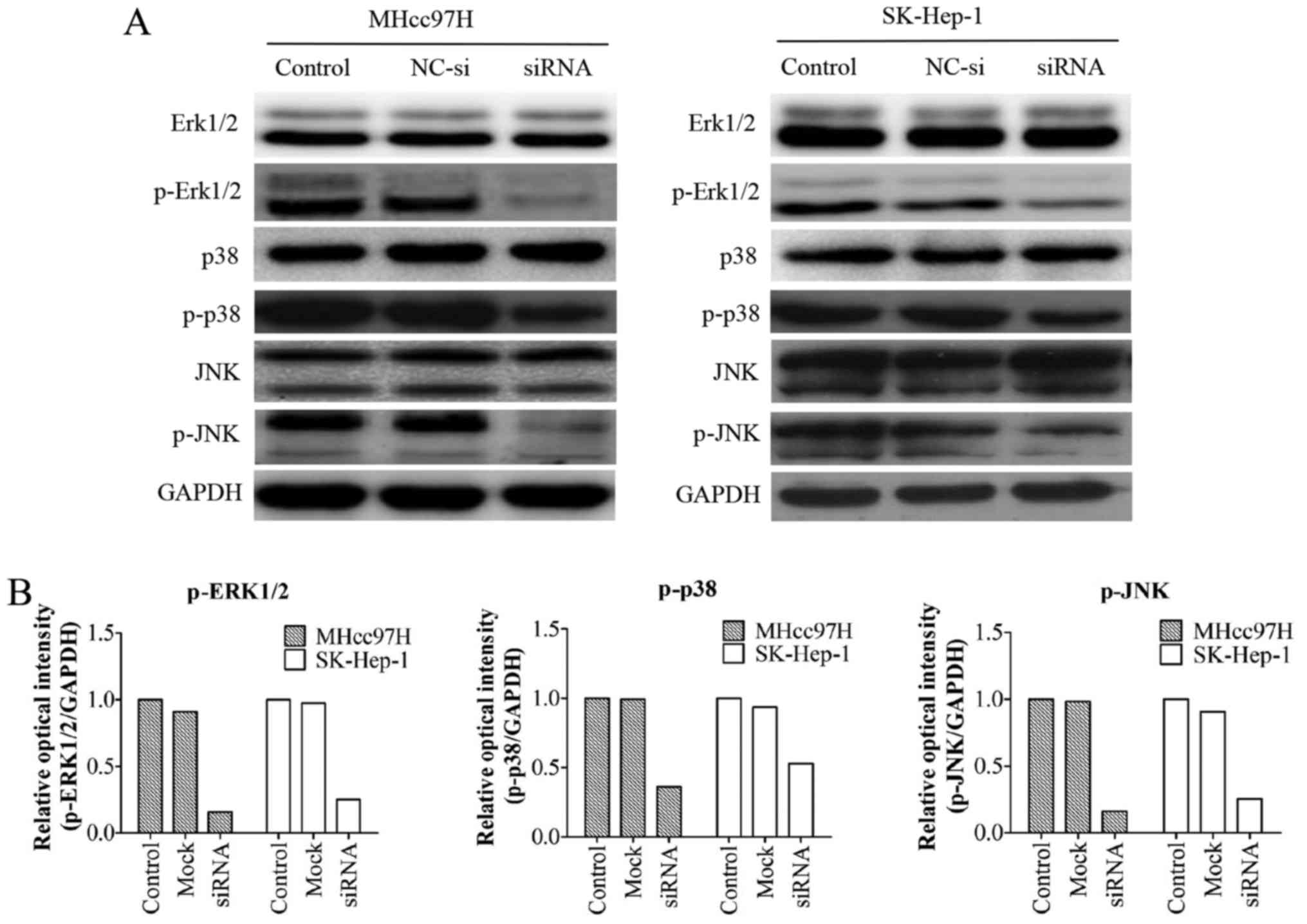
|
1
|
Fitzmaurice C, Dicker D, Pain A, Hamavid
H, Moradi-Lakeh M, MacIntyre MF, Allen C, Hansen G, Woodbrook R,
Wolfe C, et al Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration: The
global burden of cancer 2013. JAMA Oncol. 1:505–527. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Du ZG, Wei YG, Chen KF and Li B: Risk
factors associated with early and late recurrence after curative
resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: A single institution's
experience with 398 consecutive patients. Hepatobiliary Pancreat
Dis Int. 13:153–161. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang LY, Chang RM, Lau WY, Ou DP, Wu W and
Zeng ZJ: Mesohepatectomy for centrally located large hepatocellular
carcinoma: Indications, techniques, and outcomes. Surgery.
156:1177–1187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oishi N, Yamashita T and Kaneko S:
Molecular biology of liver cancer stem cells. Liver Cancer.
3:71–84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cadigan KM and Nusse R: Wnt signaling: A
common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 11:3286–3305. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pai SG, Carneiro BA, Mota JM, Costa R,
Leite CA, Barroso-Sousa R, Kaplan JB, Chae YK and Giles FJ:
Wnt/beta-catenin pathway: Modulating anticancer immune response. J
Hematol Oncol. 10:1012017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eterno V, Zambelli A, Villani L, Tuscano
A, Manera S, Spitaleri A, Pavesi L and Amato A: AurkA controls
self-renewal of breast cancer-initiating cells promoting wnt3a
stabilization through suppression of miR-128. Sci Rep. 6:284362016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee MA, Park JH, Rhyu SY, Oh ST, Kang WK
and Kim HN: Wnt3a expression is associated with MMP-9 expression in
primary tumor and metastatic site in recurrent or stage IV
colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:1252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li C, Song G, Zhang S, Wang E and Cui Z:
Wnt3a increases the metastatic potential of non-small cell lung
cancer cells in vitro in part via its upregulation of Notch3. Oncol
Rep. 33:1207–1214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tanaka M, Kuriyama S, Itoh G, Maeda D,
Goto A, Tamiya Y, Yanagihara K, Yashiro M and Aiba N: Mesothelial
cells create a novel tissue niche that facilitates gastric cancer
invasion. Cancer Res. 77:684–695. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Leung WK, He M, Chan AW, Law PT and Wong
N: Wnt/β-catenin activates MiR-183/96/182 expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma that promotes cell invasion. Cancer Lett.
362:97–105. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peng YY, He YH, Chen C, Xu T, Li L, Ni MM,
Meng XM, Huang C and Li J: NLRC5 regulates cell proliferation,
migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 376:10–21. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liao CH, Yeh CT, Huang YH, Wu SM, Chi HC,
Tsai MM, Tsai CY, Liao CJ, Tseng YH, Lin YH, et al: Dickkopf 4
positively regulated by the thyroid hormone receptor suppresses
cell invasion in human hepatoma cells. Hepatology. 55:910–920.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang Q, Lu C, Fang T, Wang Y, Hu W, Qiao
J, Liu B, Liu J, Chen N, Li M, et al: Notch3 functions as a
regulator of cell self-renewal by interacting with the β-catenin
pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:3669–3679. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jia S, Lu J, Qu T, Feng Y, Wang X, Liu C
and Ji J: MAGI1 inhibits migration and invasion via blocking
MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Chin J Cancer Res.
29:25–35. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shao Q, Luo X, Yang D, Wang C, Cheng Q,
Xiang T and Ren G: Phospholipase Cδ1 suppresses cell migration and
invasion of breast cancer cells by modulating KIF3A-mediated
ERK1/2/β-catenin/MMP7 signalling. Oncotarget. 8:29056–29066.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng Q, Yuan F, Lu F, Zhang B, Chen T,
Chen X, Cheng Y, Li N, Ma L and Tong T: CSIG promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation by activating c-MYC
expression. Oncotarget. 6:4733–4744. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Okazaki I and Inagaki Y: Novel strategies
for hepatocellular carcinoma based on MMPs science. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 12:753–763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gai JQ, Sheng X, Qin JM, Sun K, Zhao W and
Ni L: The effect and mechanism of bufalin on regulating
hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis via
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 48:338–348. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lian J, Tang J, Shi H, Li H, Zhen T, Xie
W, Zhang F, Yang Y and Han A: Positive feedback loop of
hepatoma-derived growth factor and β-catenin promotes
carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 6:29357–29374.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Driskell RR, Goodheart M, Neff T, Liu X,
Luo M, Moothart C, Sigmund CD, Hosokawa R, Chai Y and Engelhardt
JF: Wnt3a regulates Lef-1 expression during airway submucosal gland
morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 305:90–102. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Galceran J, Fariñas I, Depew MJ, Clevers H
and Grosschedl R: Wnt3a−/−-like phenotype and limb
deficiency in Lef1 (−/−)Tcf1 (−/−) mice. Genes Dev. 13:709–717.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qiang YW, Chen Y, Brown N, Hu B, Epstein
J, Barlogie B and Shaughnessy JD Jr: Characterization of
Wnt/beta-catenin signalling in osteoclasts in multiple myeloma. Br
J Haematol. 148:726–738. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wallace K, Marek CJ, Hoppler S and Wright
MC: Glucocorticoid-dependent transdifferentiation of pancreatic
progenitor cells into hepatocytes is dependent on transient
suppression of WNT signalling. J Cell Sci. 123:2103–2110. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang SH, Li N, Wei Y, Li QR and Yu ZP:
β-catenin deacetylation is essential for WNT-induced proliferation
of breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 9:973–978. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Brabletz T, Jung A, Dag S, Hlubek F and
Kirchner T: beta-catenin regulates the expression of the matrix
metalloproteinase-7 in human colorectal cancer. Am J Pathol.
155:1033–1038. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu D, Nakano J, Ishikawa S, Yokomise H,
Ueno M, Kadota K, Urushihara M and Huang CL: Overexpression of
matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) correlates with tumor
proliferation, and a poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer.
Lung Cancer. 58:384–391. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Erdal E, Ozturk N, Cagatay T,
Eksioglu-Demiralp E and Ozturk M: Lithium-mediated downregulation
of PKB/Akt and cyclin E with growth inhibition in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 115:903–910. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim W, Khan SK and Yang Y: Interacting
network of Hippo, Wnt/β-catenin and Notch signaling represses liver
tumor formation. BMB Rep. 50:1–2. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Li J, Dai W, Xia Y, Chen K, Li S, Liu T,
Zhang R, Wang J, Lu W and Zhou Y: et al Astaxanthin inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells via Inhibition of NF-κB P65 and Wnt/β-catenin in
vitro. Mar Drugs. 13:6064–6081. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang R, Sun Q, Wang P, Liu M, Xiong S, Luo
J, Huang H, Du Q, Geller DA and Cheng B: Notch and Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway play important roles in activating liver cancer
stem cells. Oncotarget. 7:5754–5768. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun Q, Wang R, Luo J, Wang P, Xiong S, Liu
M and Cheng B: Notch1 promotes hepatitis B virus X protein-induced
hepatocarcinogenesis via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Int J Oncol.
45:1638–1648. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gao W, Kim H, Feng M, Phung Y, Xavier CP,
Rubin JS and Ho M: Inactivation of Wnt signaling by a human
antibody that recognizes the heparan sulfate chains of glypican-3
for liver cancer therapy. Hepatology. 60:576–587. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Koch A, Waha A, Hartmann W, Hrychyk A,
Schüller U, Waha A, Wharton KA Jr, Fuchs SY, von Schweinitz D and
Pietsch T: Elevated expression of Wnt antagonists is a common event
in hepatoblastomas. Clin Cancer Res. 11:4295–4304. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Akinyeke T, Matsumura S, Wang X, Wu Y,
Schalfer ED, Saxena A, Yan W, Logan SK and Li X: Metformin targets
c-MYC oncogene to prevent prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis.
34:2823–2832. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li Y, Liu H, Lai C, Du X, Su Z and Gao S:
The Lin28/let-7a/c-Myc pathway plays a role in non-muscle invasive
bladder cancer. Cell Tissue Res. 354:533–541. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bruyère C and Meijer L: Targeting
cyclin-dependent kinases in anti-neoplastic therapy. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 25:772–779. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang ST, Ho HJ, Lin JT, Shieh JJ and Wu
CY: Simvastatin-induced cell cycle arrest through inhibition of
STAT3/SKP2 axis and activation of AMPK to promote p27 and p21
accumulation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis.
8:e26262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yoon MK, Mitrea DM, Ou L and Kriwacki RW:
Cell cycle regulation by the intrinsically disordered proteins p21
and p27. Biochem Soc Trans. 40:981–988. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gao J, Ding F, Liu Q and Yao Y: Knockdown
of MACC1 expression suppressed hepatocellular carcinoma cell
migration and invasion and inhibited expression of MMP2 and MMP9.
Mol Cell Biochem. 376:21–32. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ha TY, Hwang S, Moon KM, Won YJ, Song GW,
Kim N, Tak E, Ryoo BY and Hong HN: Sorafenib inhibits migration and
invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through suppression of
matrix metalloproteinase expression. Anticancer Res. 35:1967–1976.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Guo JR, Li W, Wu Y, Wu LQ, Li X, Guo YF,
Zheng XH, Lian XL, Huang HF and Chen YZ: Hepatocyte growth factor
promotes proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of myeloid
leukemia cells through PI3K-AKT and MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Am
J Transl Res. 8:3630–3644. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Luo Y, Wu JY, Lu M-H, Shi Z, Na N and Di
J-M: Carvacrol alleviates prostate cancer cell proliferation,
migration, and invasion through regulation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK
signaling pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:14696932016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yang Y, Ye Y, Qiu Q, Xiao Y, Huang M, Shi
M, Liang L, Yang X and Xu H: Triptolide inhibits the migration and
invasion of rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes by blocking the
activation of the JNK MAPK pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 41:8–16.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|