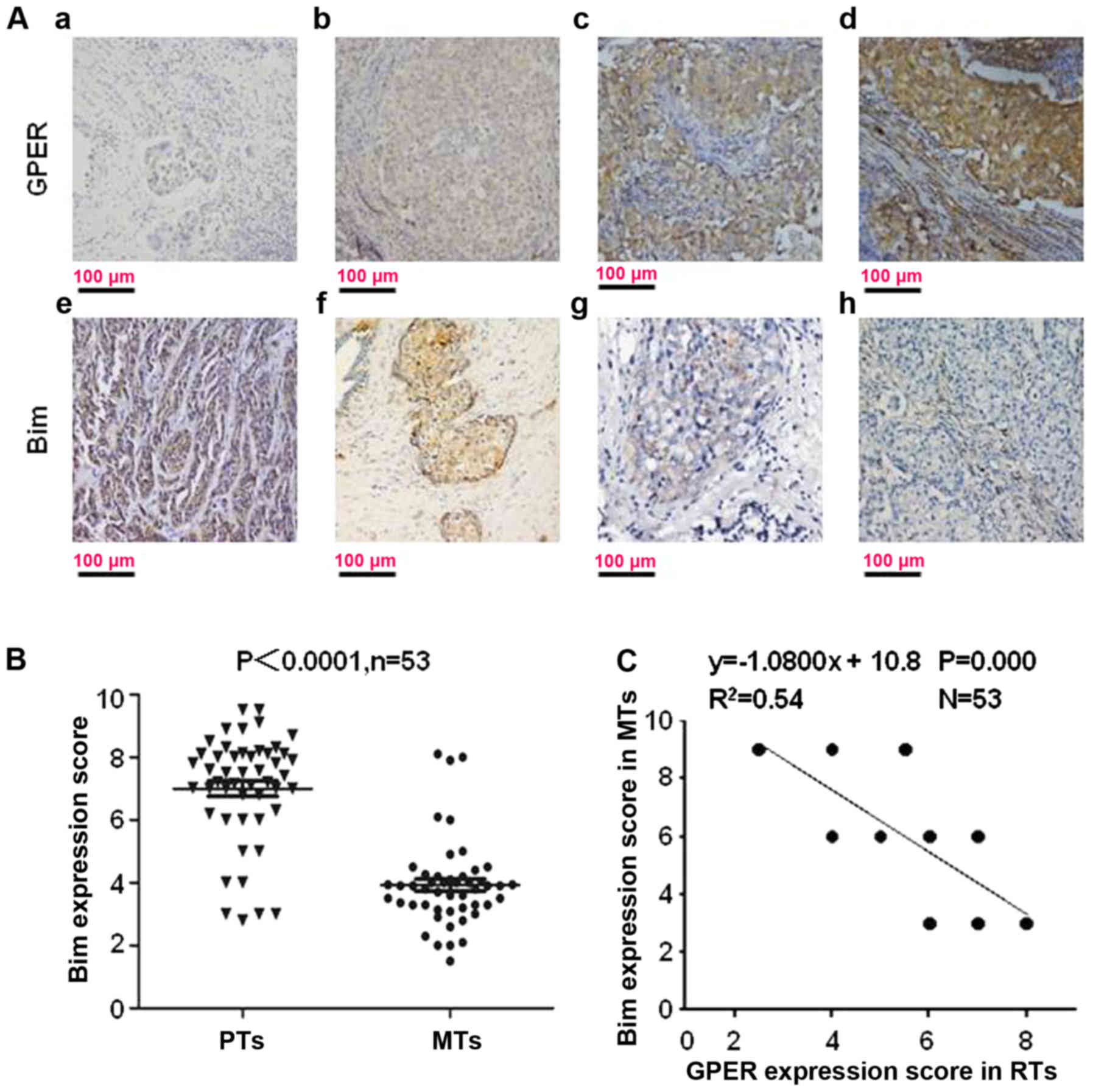
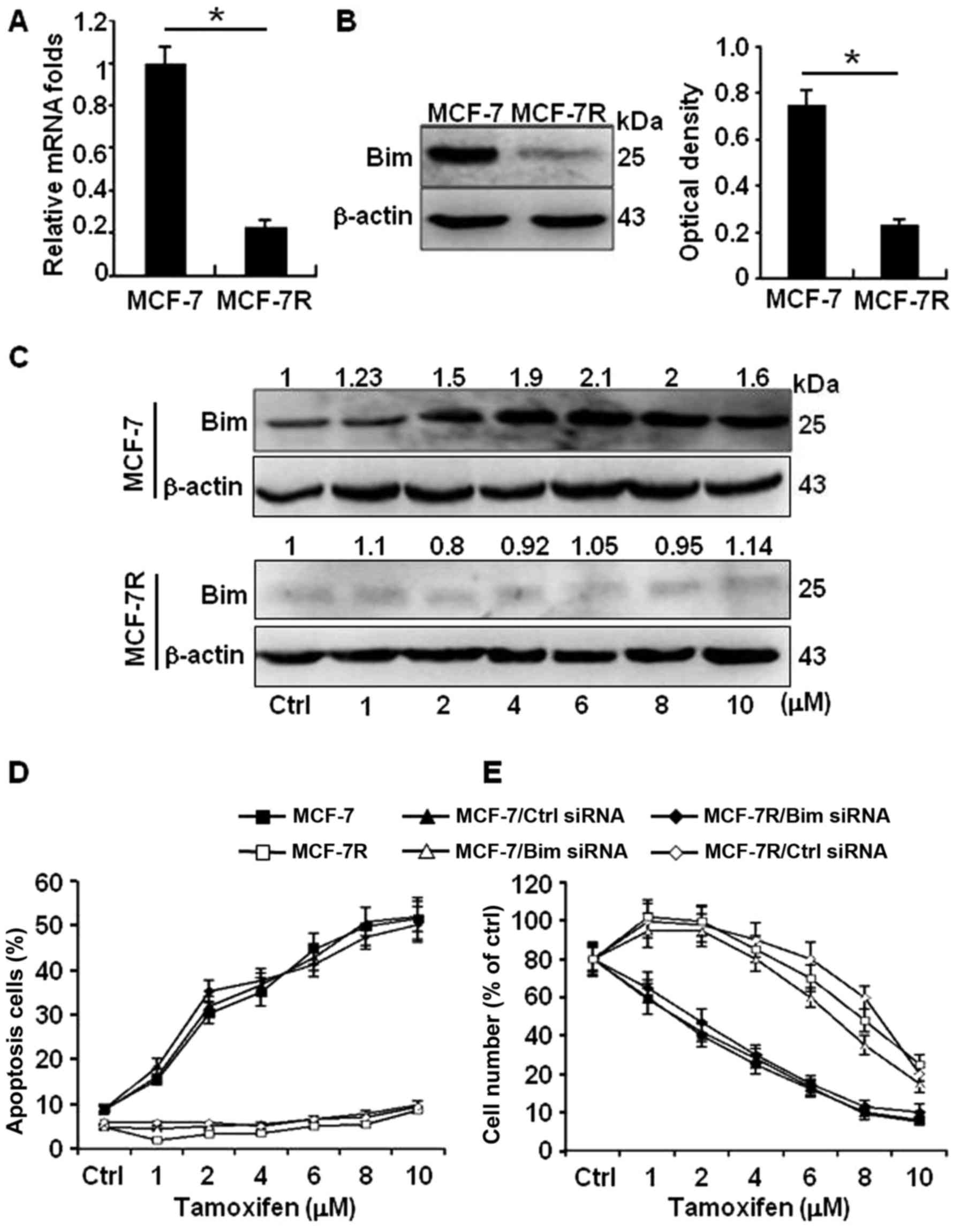
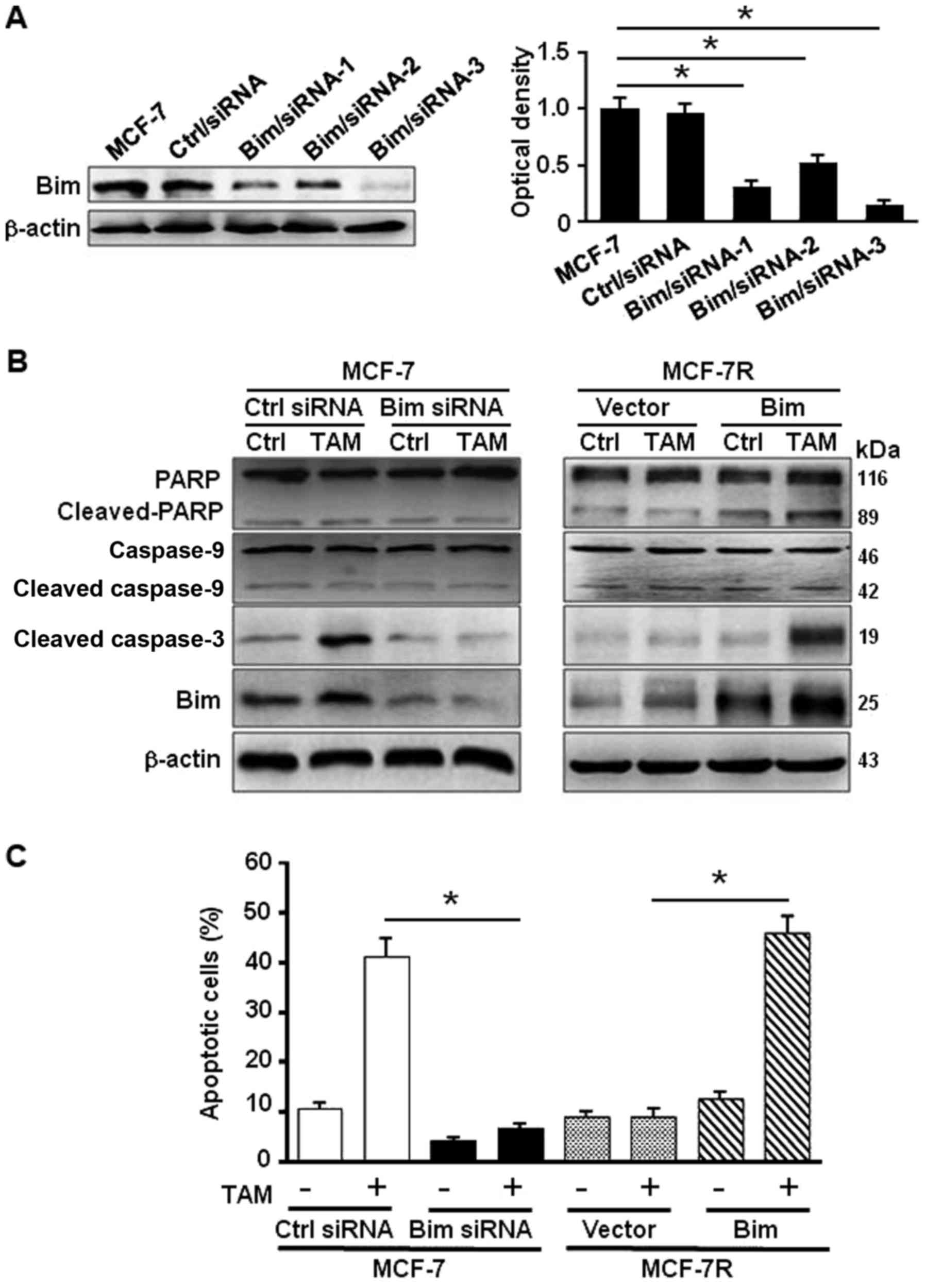
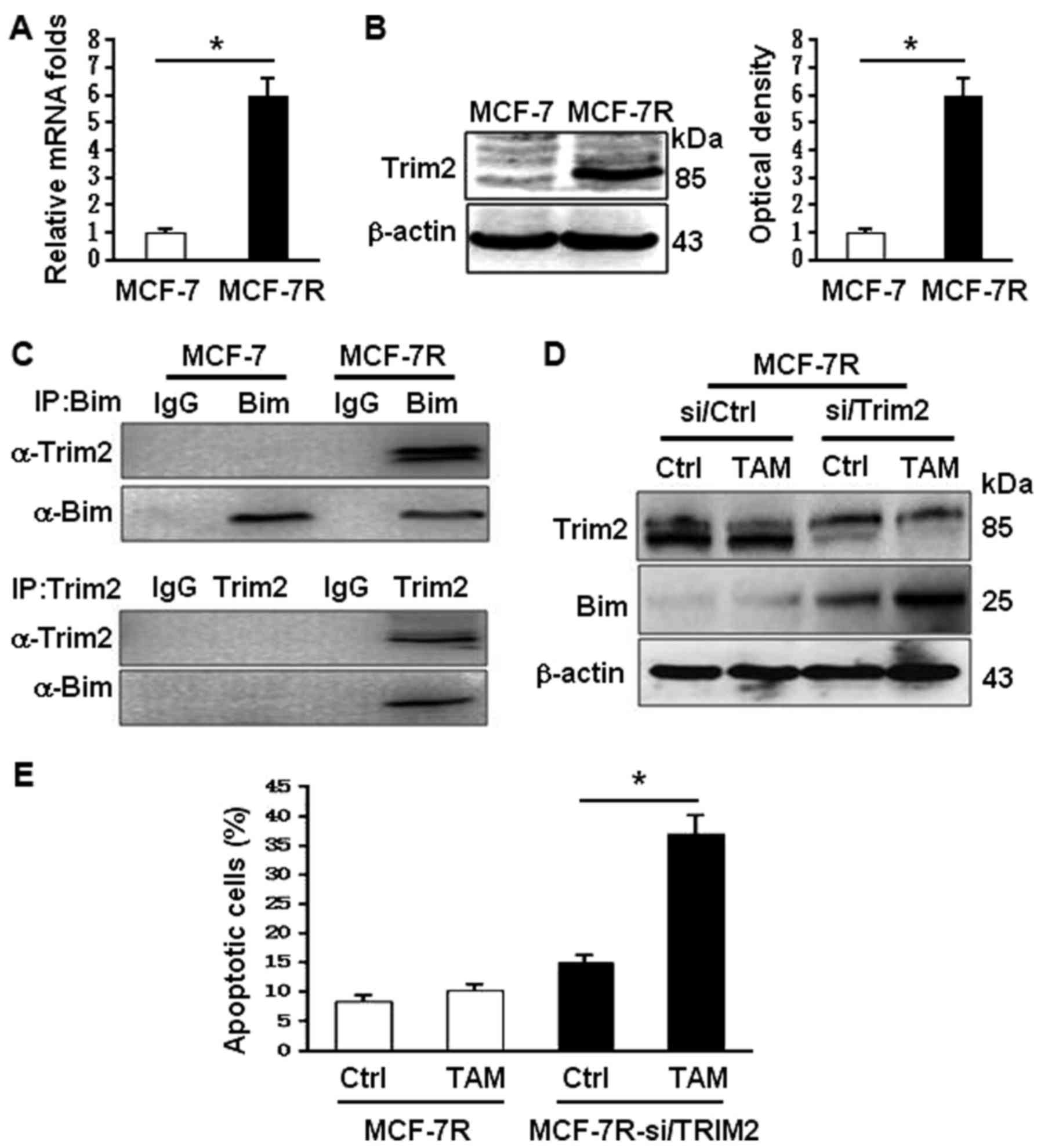
|
1
|
Briest S and Stearns V: Tamoxifen
metabolism and its effect on endocrine treatment of breast cancer.
Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 7:185–192. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yuan J, Liu M, Yang L, Tu G, Zhu Q, Chen
M, Cheng H, Luo H, Fu W, Li Z, et al: Acquisition of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in the
tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cell: A new role for G
protein-coupled estrogen receptor in mediating tamoxifen resistance
through cancer-associated fibroblast-derived fibronectin and
β1-integrin signaling pathway in tumor cells. Breast Cancer Res.
17:692015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Willis SN and Adams JM: Life in the
balance: How BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 17:617–625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Strasser A: The role of BH3-only proteins
in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:189–200. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Villunger A, Scott C, Bouillet P and
Strasser A: Essential role for the BH3-only protein Bim but
redundant roles for Bax, Bcl-2, and Bcl-w in the control of
granulocyte survival. Blood. 101:2393–2400. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kirschnek S, Vier J, Gautam S, Frankenberg
T, Rangelova S, Eitz-Ferrer P, Grespi F, Ottina E, Villunger A,
Häcker H, et al: Molecular analysis of neutrophil spontaneous
apoptosis reveals a strong role for the pro-apoptotic BH3-only
protein Noxa. Cell Death Differ. 18:1805–1814. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang WF, Liu AH, Zhao HJ, Dong HM, Liu LY
and Cai SX: BIM gene polymorphism lowers the efficacy of EGFR-TKIs
in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer with sensitive EGFR
mutations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 94:e12632015.J. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gu Z, Wang X, Qi R, Wei L, Huo Y, Ma Y,
Shi L, Chang Y, Li G and Zhou L: Oridonin induces apoptosis in
uveal melanoma cells by upregulation of Bim and downregulation of
Fatty Acid Synthase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 457:187–193. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Merino D, Best SA, Asselin-Labat ML,
Vaillant F, Pal B, Dickins RA, Anderson RL, Strasser A, Bouillet P,
Lindeman GJ, et al: Pro-apoptotic Bim suppresses breast tumor cell
metastasis and is a target gene of SNAI2. Oncogene. 34:3926–3934.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Park SH, Ito K, Olcott W, Katsyv I,
Halstead-Nussloch G and Irie HY: PTK6 inhibition promotes apoptosis
of Lapatinib-resistant Her2+ breast cancer cells by
inducing Bim. Breast Cancer Res. 17:862015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Follin-Arbelet V, Misund K, Naderi EH,
Ugland H, Sundan A and Blomhoff HK: The natural compound forskolin
synergizes with dexamethasone to induce cell death in myeloma cells
via BIM. Sci Rep. 5:130012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reginato MJ, Mills KR, Becker EB, Lynch
DK, Bonni A, Muthuswamy SK and Brugge JS: Bim regulation of lumen
formation in cultured mammary epithelial acini is targeted by
oncogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 25:4591–4601. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dai Y and Grant S: BCL2L11/Bim as a
dual-agent regulating autophagy and apoptosis in drug resistance.
Autophagy. 11:416–418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hatakeyama S: TRIM proteins and cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 11:792–804. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zoumpoulidou G, Broceño C, Li H, Bird D,
Thomas G and Mittnacht S: Role of the tripartite motif protein 27
in cancer development. J Natl Cancer Inst. 104:941–952. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu C, Huang X, Hou S, Hu B and Li H:
Silencing of tripartite motif (TRIM) 29 inhibits proliferation and
invasion and increases chemosensitivity to cisplatin in human lung
squamous cancer NCI-H520 cells. Thorac Cancer. 6:31–37. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ozato K, Shin DM, Chang TH and Morse HC
III: TRIM family proteins and their emerging roles in innate
immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:849–860. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qiu F, Xiong JP, Deng J and Xiang XJ:
TRIM29 functions as an oncogene in gastric cancer and is regulated
by miR-185. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:5053–5061. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y and He D, Yang L, Wen B, Dai J,
Zhang Q, Kang J, He W, Ding Q and He D: TRIM26 functions as a novel
tumor suppressor of hepatocellular carcinoma and its downregulation
contributes to worse prognosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
463:458–465. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Williams MD, Zhang L, Elliott DD, Perrier
ND, Lozano G, Clayman GL and El-Naggar AK: Differential gene
expression profiling of aggressive and nonaggressive follicular
carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 42:1213–1220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ivanov SV, Panaccione A, Nonaka D, Prasad
ML, Boyd KL, Brown B, Guo Y, Sewell A and Yarbrough WG: Diagnostic
SOX10 gene signatures in salivary adenoid cystic and breast
basal-like carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 109:444–451. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thompson S, Pearson AN, Ashley MD, Jessick
V, Murphy BM, Gafken P, Henshall DC, Morris KT, Simon RP and Meller
R: Identification of a novel Bcl-2-interacting mediator of cell
death (Bim) E3 ligase, tripartite motif-containing protein 2
(TRIM2), and its role in rapid ischemic tolerance-induced
neuroprotection. J Biol Chem. 286:19331–19339. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Balastik M, Ferraguti F, Pires-da Silva A,
Lee TH, Alvarez-Bolado G, Lu KP and Gruss P: Deficiency in
ubiquitin ligase TRIM2 causes accumulation of neurofilament light
chain and neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:12016–12021. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mo Z, Liu M, Yang F, Luo H, Li Z, Tu G and
Yang G: GPR30 as an initiator of tamoxifen resistance in
hormone-dependent breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R1142013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ignatov A, Ignatov T, Weissenborn C,
Eggemann H, Bischoff J, Semczuk A, Roessner A, Costa SD and
Kalinski T: G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor GPR30 and tamoxifen
resistance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 128:457–466.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ignatov A, Ignatov T, Roessner A, Costa SD
and Kalinski T: Role of GPR30 in the mechanisms of tamoxifen
resistance in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
123:87–96. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Prossnitz ER, Arterburn JB, Smith HO,
Oprea TI, Sklar LA and Hathaway HJ: Estrogen signaling through the
transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor GPR30. Annu Rev Physiol.
70:165–190. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fujiwara S, Terai Y, Kawaguchi H, Takai M,
Yoo S, Tanaka Y, Tanaka T, Tsunetoh S, Sasaki H, Kanemura M, et al:
GPR30 regulates the EGFR-Akt cascade and predicts lower survival in
patients with ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. 5:352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Filardo EJ, Quinn JA, Bland KI and
Frackelton AR Jr: Estrogen-induced activation of Erk-1 and Erk-2
requires the G protein-coupled receptor homolog, GPR30, and occurs
via trans-activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor
through release of HB-EGF. Mol Endocrinol. 14:1649–1660. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lv Y, Song S, Zhang K, Gao H and Ma R:
CHIP regulates AKT/FoxO/Bim signaling in MCF7 and MCF10A cells.
PLoS One. 8:e833122013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Periyasamy-Thandavan S, Takhar S, Singer
A, Dohn MR, Jackson WH, Welborn AE, LeRoith D, Marrero M,
Thangaraju M, Huang S, et al: Insulin-like growth factor 1
attenuates antiestrogen- and antiprogestin-induced apoptosis in
ER+ breast cancer cells by MEK1 regulation of the
BH3-only pro-apoptotic protein Bim. Breast Cancer Res. 14:R522012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yu T, Liu M, Luo H, Wu C, Tang X, Tang S,
Hu P, Yan Y, Wang Z and Tu G: GPER mediates enhanced cell viability
and motility via non-genomic signaling induced by 17β-estradiol in
triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
143:392–403. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu K, Li A, Rao M, Liu M, Dailey V, Yang
Y, Di Vizio D, Wang C, Lisanti MP, Sauter G, et al: DACH1 is a cell
fate determination factor that inhibits cyclin D1 and breast tumor
growth. Mol Cell Biol. 26:7116–7129. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fu M, Liu M, Sauve AA, Jiao X, Zhang X, Wu
X, Powell MJ, Yang T, Gu W, Avantaggiati ML, et al: Hormonal
control of androgen receptor function through SIRT1. Mol Cell Biol.
26:8122–8135. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han BJ, Li W, Jiang GB, Lai SH, Zhang C,
Zeng CC and Liu YJ: Effects of daidzein in regards to cytotoxicity
in vitro, apoptosis, reactive oxygen species level, cell cycle
arrest and the expression of caspase and Bcl-2 family proteins.
Oncol Rep. 34:1115–1120. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tomicic MT, Meise R, Aasland D, Berte N,
Kitzinger R, Krämer OH, Kaina B and Christmann M: Apoptosis induced
by temozolomide and nimustine in glioblastoma cells is supported by
JNK/c-Jun-mediated induction of the BH3-only protein BIM.
Oncotarget. 6:33755–33768. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang LM, Zhao XC, Sun WB, Li R and Jiang
XJ: Sevoflurane post-conditioning protects primary rat cortical
neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation/resuscitation via
down-regulation in mitochondrial apoptosis axis of Bid, Bim,
Puma-Bax and Bak mediated by Erk1/2. J Neurol Sci. 357:80–87. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hiscox S, Jiang WG, Obermeier K, Taylor K,
Morgan L, Burmi R, Barrow D and Nicholson RI: Tamoxifen resistance
in MCF7 cells promotes EMT-like behaviour and involves modulation
of β-catenin phosphorylation. Int J Cancer. 118:290–301. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ward A, Balwierz A, Zhang JD, Küblbeck M,
Pawitan Y, Hielscher T, Wiemann S and Sahin Ö: Re-expression of
microRNA-375 reverses both tamoxifen resistance and accompanying
EMT-like properties in breast cancer. Oncogene. 32:1173–1182. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Thewes V, Simon R, Schroeter P, Schlotter
M, Anzeneder T, Büttner R, Benes V, Sauter G, Burwinkel B,
Nicholson RI, et al: Reprogramming of the ERRα and ERα target gene
landscape triggers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 75:720–731. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|