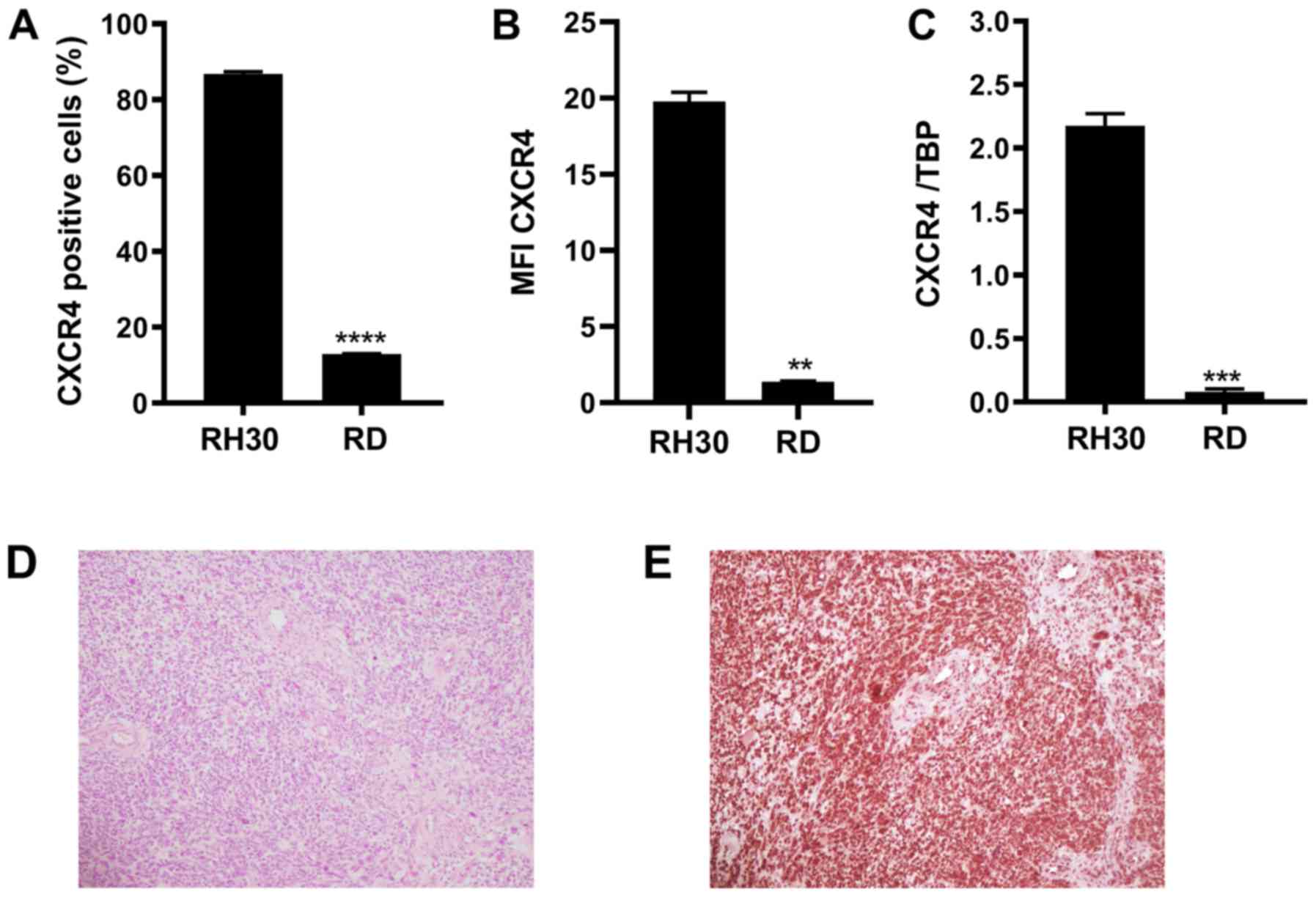
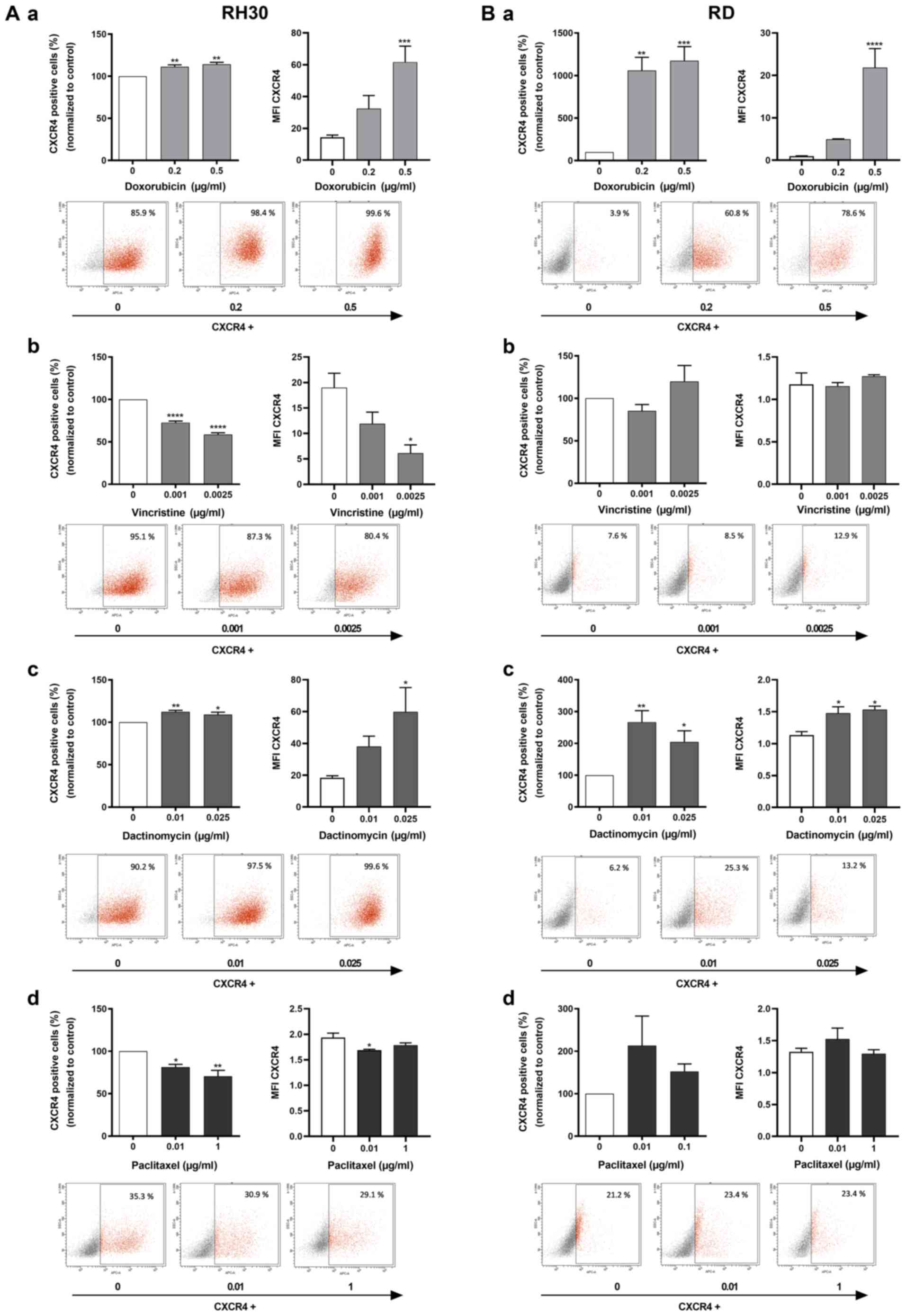
|
1
|
Ognjanovic S, Linabery AM, Charbonneau B
and Ross JA: Trends in childhood rhabdomyosarcoma incidence and
survival in the United States, 1975-2005. Cancer. 115:4218–4226.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Skapek SX, Ferrari A, Gupta AA, Lupo PJ,
Butler E, Shipley J, Barr FG and Hawkins DS: Rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat
Rev Dis Primers. 5:12019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rudzinski ER, Anderson JR, Hawkins DS,
Skapek SX, Parham DM and Teot LA: The World Health Organization
Classification of Skeletal Muscle Tumors in Pediatric
Rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the children's oncology group. Arch
Pathol Lab Med. 139:1281–1287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Davicioni E, Anderson MJ, Finckenstein FG,
Lynch JC, Qualman SJ, Shimada H, Schofield DE, Buckley JD, Meyer
WH, Sorensen PH, et al: Molecular classification of
rhabdomyo-sarcoma–genotypic and phenotypic determinants of
diagnosis: A report from the Children's Oncology Group. Am J
Pathol. 174:550–564. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Egas-Bejar D and Huh WW: Rhabdomyosarcoma
in adolescent and young adult patients: Current perspectives.
Adolesc Health Med Ther. 5:115–125. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dagher R and Helman L: Rhabdomyosarcoma:
An overview. Oncologist. 4:34–44. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oberlin O, Rey A, Lyden E, Bisogno G,
Stevens MC, Meyer WH, Carli M and Anderson JR: Prognostic factors
in metastatic rhabdo-myosarcomas: Results of a pooled analysis from
United States and European cooperative groups. J Clin Oncol.
26:2384–2389. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Perkins SM, Shinohara ET, DeWees T and
Frangoul H: Outcome for children with metastatic solid tumors over
the last four decades. PLoS One. 9:e1003962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Herrmann D, Seitz G, Fuchs J and
Armeanu-Ebinger S: Susceptibility of rhabdomyosarcoma cells to
macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity. OncoImmunology. 1:279–286. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Steeg PS: Tumor metastasis: Mechanistic
insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 12:895–904. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gupta GP and Massagué J: Cancer
metastasis: Building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo F, Wang Y, Liu J, Mok SC, Xue F and
Zhang W: CXCL12/CXCR4: A symbiotic bridge linking cancer cells and
their stromal neighbors in oncogenic communication networks.
Oncogene. 35:816–826. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chatterjee S, Behnam Azad B and Nimmagadda
S: The intricate role of CXCR4 in cancer. Adv Cancer Res.
124:31–82. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sison EA, McIntyre E, Magoon D and Brown
P: Dynamic chemotherapy-induced upregulation of CXCR4 expression: A
mechanism of therapeutic resistance in pediatric AML. Mol Cancer
Res. 11:1004–1016. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Diomedi-Camassei F, McDowell HP, De Ioris
MA, Uccini S, Altavista P, Raschellà G, Vitali R, Mannarino O, De
Sio L, Cozzi DA, et al: Clinical significance of CXC chemokine
receptor-4 and c-Met in childhood rhabdomyosarcoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:4119–4127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Müller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D,
Buchanan ME, McClanahan T, Murphy E, Yuan W, Wagner SN, et al:
Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis.
Nature. 410:50–56. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Z, Ma Q, Liu Q, Yu H, Zhao L, Shen S
and Yao J: Blockade of SDF-1/CXCR4 signalling inhibits pancreatic
cancer progression in vitro via inactivation of canonical Wnt
pathway. Br J Cancer. 99:1695–1703. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zeelenberg IS, Ruuls-Van Stalle L and Roos
E: The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is required for outgrowth of colon
carcinoma micrometastases. Cancer Res. 63:3833–3839.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Domanska UM, Kruizinga RC, Nagengast WB,
Timmer-Bosscha H, Huls G, de Vries EG and Walenkamp AM: A review on
CXCR4/CXCL12 axis in oncology: No place to hide. Eur J Cancer.
49:219–230. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kucia M, Jankowski K, Reca R, Wysoczynski
M, Bandura L, Allendorf DJ, Zhang J, Ratajczak J and Ratajczak MZ:
CXCR4-SDF-1 signalling, locomotion, chemotaxis and adhesion. J Mol
Histol. 35:233–245. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Strahm B, Durbin AD, Sexsmith E and Malkin
D: The CXCR4-SDF1alpha axis is a critical mediator of
rhabdomyo-sarcoma metastatic signaling induced by bone marrow
stroma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 25:1–10. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Libura J, Drukala J, Majka M, Tomescu O,
Navenot JM, Kucia M, Marquez L, Peiper SC, Barr FG,
Janowska-Wieczorek A, et al: CXCR4-SDF-1 signaling is active in
rhabdomyosarcoma cells and regulates locomotion, chemotaxis, and
adhesion. Blood. 100:2597–2606. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grymula K, Tarnowski M, Wysoczynski M,
Drukala J, Barr FG, Ratajczak J, Kucia M and Ratajczak MZ:
Overlapping and distinct role of CXCR7-SDF-1/ITAC and CXCR4-SDF-1
axes in regulating metastatic behavior of human rhabdomyosarcomas.
Int J Cancer. 127:2554–2568. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lev DC, Onn A, Melinkova VO, Miller C,
Stone V, Ruiz M, McGary EC, Ananthaswamy HN, Price JE and Bar-Eli
M: Exposure of melanoma cells to dacarbazine results in enhanced
tumor growth and metastasis in vivo. J Clin Oncol. 22:2092–2100.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim M, Koh YJ, Kim KE, Koh BI, Nam DH,
Alitalo K, Kim I and Koh GY: CXCR4 signaling regulates metastasis
of chemoresistant melanoma cells by a lymphatic metastatic niche.
Cancer Res. 70:10411–10421. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Muller A, Sonkoly E, Eulert C, Gerber PA,
Kubitza R, Schirlau K, Franken-Kunkel P, Poremba C, Snyderman C,
Klotz LO, et al: Chemokine receptors in head and neck cancer:
Association with metastatic spread and regulation during
chemotherapy. Int J Cancer. 118:2147–2157. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ratajczak MZ, Jadczyk T, Schneider G,
Kakar SS and Kucia M: Induction of a tumor-metastasis-receptive
microenvironment as an unwanted and underestimated side effect of
treatment by chemotherapy or radiotherapy. J Ovarian Res. 6:952013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Shaked Y, Henke E, Roodhart JM, Mancuso P,
Langenberg MH, Colleoni M, Daenen LG, Man S, Xu P, Emmenegger U, et
al: Rapid chemotherapy-induced acute endothelial progenitor cell
mobilization: Implications for antiangiogenic drugs as
chemo-sensitizing agents. Cancer Cell. 14:263–273. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Parameswaran R, Yu M, Lim M, Groffen J and
Heisterkamp N: Combination of drug therapy in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia with a CXCR4 antagonist. Leukemia. 25:1314–1323. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Juarez J, Bradstock KF, Gottlieb DJ and
Bendall LJ: Effects of inhibitors of the chemokine receptor CXCR4
on acute lympho-blastic leukemia cells in vitro. Leukemia.
17:1294–1300. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Domanska UM, Timmer-Bosscha H, Nagengast
WB, Oude Munnink TH, Kruizinga RC, Ananias HJ, Kliphuis NM, Huls G,
De Vries EG, de Jong IJ, et al: CXCR4 inhibition with AMD3100
sensitizes prostate cancer to docetaxel chemotherapy. Neoplasia.
14:709–718. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kalatskaya I, Berchiche YA, Gravel S,
Limberg BJ, Rosenbaum JS and Heveker N: AMD3100 is a CXCR7 ligand
with allosteric agonist properties. Mol Pharmacol. 75:1240–1247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
De Clercq E: Potential clinical
applications of the CXCR4 antagonist bicyclam AMD3100. Mini Rev Med
Chem. 5:805–824. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kajiyama H, Shibata K, Terauchi M, Ino K,
Nawa A and Kikkawa F: Involvement of SDF-1alpha/CXCR4 axis in the
enhanced peritoneal metastasis of epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Int
J Cancer. 122:91–99. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Smith MC, Luker KE, Garbow JR, Prior JL,
Jackson E, Piwnica-Worms D and Luker GD: CXCR4 regulates growth of
both primary and metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res.
64:8604–8612. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cabioglu N, Summy J, Miller C, Parikh NU,
Sahin AA, Tuzlali S, Pumiglia K, Gallick GE and Price JE:
CXCL-12/stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha transactivates HER2-neu
in breast cancer cells by a novel pathway involving Src kinase
activation. Cancer Res. 65:6493–6497. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li YM, Pan Y, Wei Y, Cheng X, Zhou BP, Tan
M, Zhou X, Xia W, Hortobagyi GN, Yu D, et al: Upregulation of CXCR4
is essential for HER2-mediated tumor metastasis. Cancer Cell.
6:459–469. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ray P, Lewin SA, Mihalko LA, Schmidt BT,
Luker KE and Luker GD: Noninvasive imaging reveals inhibition of
ovarian cancer by targeting CXCL12-CXCR4. Neoplasia. 13:1152–1161.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Schmid E, Stagno MJ, Yan J, Stournaras C,
Lang F, Fuchs J and Seitz G: Store-operated Ca(2+) entry in
rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 477:129–136.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Foucquier J and Guedj M: Analysis of drug
combinations: Current methodological landscape. Pharmacol Res
Perspect. 3:e001492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schols D, Struyf S, Van Damme J, Esté JA,
Henson G and De Clercq E: Inhibition of T-tropic HIV strains by
selective antagonization of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. J Exp
Med. 186:1383–1388. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Poty S, Désogère P, Goze C, Boschetti F,
D'huys T, Schols D, Cawthorne C, Archibald SJ, Maëcke HR and Denat
F: New AMD3100 derivatives for CXCR4 chemokine receptor targeted
molecular imaging studies: Synthesis, anti-HIV-1 evaluation and
binding affinities. Dalton Trans. 44:pp. 5004–5016. 2015,
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Stamatopoulos B, Meuleman N, De Bruyn C,
Pieters K, Mineur P, Le Roy C, Saint-Georges S, Varin-Blank N,
Cymbalista F, Bron D, et al: AMD3100 disrupts the cross-talk
between chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and a mesenchymal
stromal or nurse-like cell-based microenvironment: Pre-clinical
evidence for its association with chronic lymphocytic leukemia
treatments. Haematologica. 97:608–615. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Zlotnik A: New insights on the role of
CXCR4 in cancer metastasis. J Pathol. 215:211–213. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang J, Loberg R and Taichman RS: The
pivotal role of CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 axis in bone metastasis.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:573–587. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang Z, Ni C, Chen W, Wu P, Wang Z, Yin
J, Huang J and Qiu F: Expression of CXCR4 and breast cancer
prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer.
14:492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Laverdiere C, Hoang BH, Yang R, Sowers R,
Qin J, Meyers PA, Huvos AG, Healey JH and Gorlick R: Messenger RNA
expression levels of CXCR4 correlate with metastatic behavior and
outcome in patients with osteosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res.
11:2561–2567. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim RH, Li BD and Chu QD: The role of
chemokine receptor CXCR4 in the biologic behavior of human soft
tissue sarcoma. Sarcoma. 2011:5937082011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jankowski K, Kucia M, Wysoczynski M, Reca
R, Zhao D, Trzyna E, Trent J, Peiper S, Zembala M, Ratajczak J, et
al: Both hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and stromal-derived
factor-1 regulate the metastatic behavior of human rhabdomyosarcoma
cells, but only HGF enhances their resistance to radiochemotherapy.
Cancer Res. 63:7926–7935. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Marinello J, Delcuratolo M and Capranico
G: Anthracyclines as topoisomerase II poisons: From early studies
to new perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 19:192018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Mukhtar E, Adhami VM and Mukhtar H:
Targeting microtubules by natural agents for cancer therapy. Mol
Cancer Ther. 13:275–284. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sison EA, Magoon D, Li L, Annesley CE, Rau
RE, Small D and Brown P: Plerixafor as a chemosensitizing agent in
pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Efficacy and potential
mechanisms of resistance to CXCR4 inhibition. Oncotarget.
5:8947–8958. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liang JX, Gao W, Liang Y and Zhou XM:
Chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression and lung cancer prognosis: A
meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:5163–5174. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li YJ, Dai YL, Zhang WB, Li SJ and Tu CQ:
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of chemokine
receptor CXCR4 in patients with bone and soft tissue sarcoma: A
meta-analysis. Clin Exp Med. 17:59–69. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Tarnowski M, Grymula K, Liu R, Tarnowska
J, Drukala J, Ratajczak J, Mitchell RA, Ratajczak MZ and Kucia M:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is secreted by
rhabdomyosarcoma cells, modulates tumor metastasis by binding to
CXCR4 and CXCR7 receptors and inhibits recruitment of
cancer‑associated fibroblasts. Mol Cancer Res. 8:pp. 1328–1343.
2010, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tarnowski M, Grymula K, Reca R, Jankowski
K, Maksym R, Tarnowska J, Przybylski G, Barr FG, Kucia M and
Ratajczak MZ: Regulation of expression of stromal-derived factor-1
receptors: CXCR4 and CXCR7 in human rhabdomyosarcomas. Mol Cancer
Res. 8:1–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cheng X, Wang H, Zhang X, Zhao S, Zhou Z,
Mu X, Zhao C and Teng W: The Role of SDF-1/CXCR4/CXCR7 in Neuronal
Regeneration after Cerebral Ischemia. Front Neurosci. 11:5902017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Taromi S, Kayser G, Catusse J, von
Elverfeldt D, Reichardt W, Braun F, Weber WA, Zeiser R and Burger
M: CXCR4 antagonists suppress small cell lung cancer progression.
Oncotarget. 7:85185–85195. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
De Clercq E: Inhibition of HIV infection
by bicyclams, highly potent and specific CXCR4 antagonists. Mol
Pharmacol. 57:833–839. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sun X, Cheng G, Hao M, Zheng J, Zhou X,
Zhang J, Taichman RS, Pienta KJ and Wang J: CXCL12 / CXCR4 / CXCR7
chemokine axis and cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
29:709–722. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Balabanian K, Lagane B, Infantino S, Chow
KY, Harriague J, Moepps B, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Thelen M and
Bachelerie F: The chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12 binds to and signals
through the orphan receptor RDC1 in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem.
280:35760–35766. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Burns JM, Summers BC, Wang Y, Melikian A,
Berahovich R, Miao Z, Penfold ME, Sunshine MJ, Littman DR, Kuo CJ,
et al: A novel chemokine receptor for SDF-1 and I-TAC involved in
cell survival, cell adhesion, and tumor development. J Exp Med.
203:2201–2213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Heesen M, Berman MA, Charest A, Housman D,
Gerard C and Dorf ME: Cloning and chromosomal mapping of an orphan
chemokine receptor: Mouse RDC1. Immunogenetics. 47:364–370. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Mitra P, De A, Ethier MF, Mimori K, Kodys
K, Shibuta K, Mori M, Madison JM, Miller-Graziano C and Barnard GF:
Loss of chemokine SDF-1alpha-mediated CXCR4 signalling and receptor
internalization in human hepatoma cell line HepG2. Cell Signal.
13:311–319. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Honczarenko M, Douglas RS, Mathias C, Lee
B, Ratajczak MZ and Silberstein LE: SDF-1 responsiveness does not
correlate with CXCR4 expression levels of developing human bone
marrow B cells. Blood. 94:2990–2998. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Rabin RL, Park MK, Liao F, Swofford R,
Stephany D and Farber JM: Chemokine receptor responses on T cells
are achieved through regulation of both receptor expression and
signaling. J Immunol. 162:3840–3850. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Busillo JM and Benovic JL: Regulation of
CXCR4 signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1768:952–963. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Moriuchi M, Moriuchi H, Turner W and Fauci
AS: Cloning and analysis of the promoter region of CXCR4, a
coreceptor for HIV-1 entry. J Immunol. 159:4322–4329.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wegner SA, Ehrenberg PK, Chang G, Dayhoff
DE, Sleeker AL and Michael NL: Genomic organization and functional
char-acterization of the chemokine receptor CXCR4, a major entry
co‑receptor for human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Biol Chem.
273:4754–4760. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Marchese A, Raiborg C, Santini F, Keen JH,
Stenmark H and Benovic JL: The E3 ubiquitin ligase AIP4 mediates
ubiquiti-nation and sorting of the G protein-coupled receptor
CXCR4. Dev Cell. 5:709–722. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Slagsvold T, Marchese A, Brech A and
Stenmark H: CISK attenuates degradation of the chemokine receptor
CXCR4 via the ubiquitin ligase AIP4. EMBO J. 25:3738–3749. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Schioppa T, Uranchimeg B, Saccani A,
Biswas SK, Doni A, Rapisarda A, Bernasconi S, Saccani S, Nebuloni
M, Vago L, et al: Regulation of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 by
hypoxia. J Exp Med. 198:1391–1402. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang X, Li C, Chen Y, Hao Y, Zhou W, Chen
C and Yu Z: Hypoxia enhances CXCR4 expression favoring microglia
migration via HIF-1alpha activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
371:283–288. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|