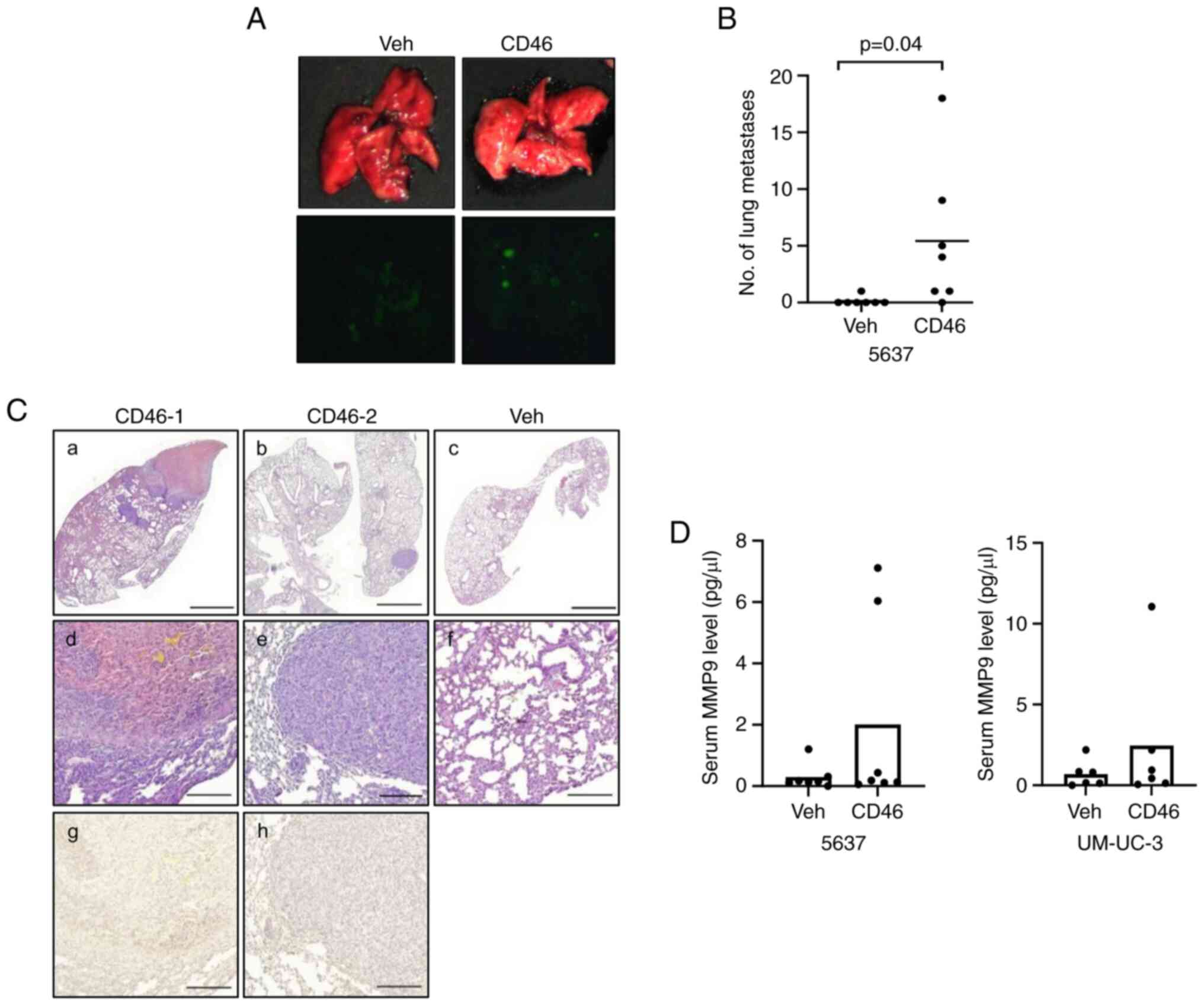
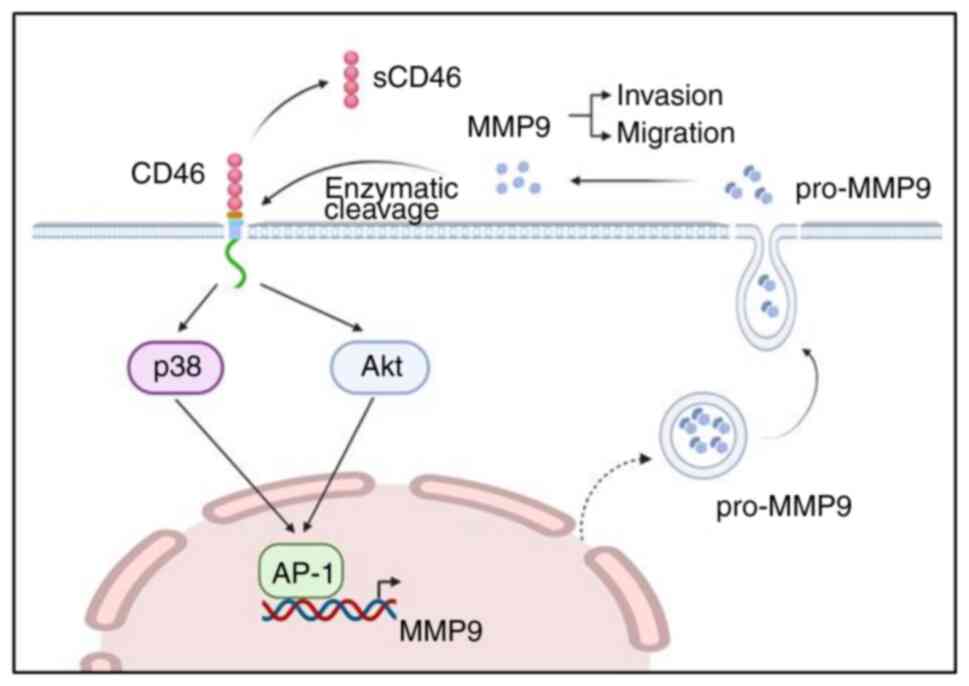
|
1
|
Yamamoto H, Fara AF, Dasgupta P and Kemper
C: CD46: The 'multitasker' of complement proteins. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 45:2808–2820. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Andrews PW, Knowles BB, Parkar M, Pym B,
Stanley K and Goodfellow PN: A human cell-surface antigen defined
by a monoclonal antibody and controlled by a gene on human
chromosome 1. Ann Hum Genet. 49:31–39. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hourcade D, Garcia AD, Post TW,
Taillon-Miller P, Holers VM, Wagner LM, Bora NS and Atkinson JP:
Analysis of the human regulators of complement activation (RCA)
gene cluster with yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs). Genomics.
12:289–300. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sherbenou DW, Aftab BT, Su Y, Behrens CR,
Wiita A, Logan AC, Acosta-Alvear D, Hann BC, Walter P, Shuman MA,
et al: Antibody-drug conjugate targeting CD46 eliminates multiple
myeloma cells. J Clin Invest. 126:4640–4653. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu YQ, Gao YD, Yang J and Guo W: A defect
of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in inducing interleukin-10
production from CD4+ T cells under CD46 costimulation in asthma
patients. J Asthma. 47:367–373. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Le Buanec H, Gougeon ML, Mathian A, Lebon
P, Dupont JM, Peltre G, Hemon P, Schmid M, Bizzini B, Künding T, et
al: IFN-α and CD46 stimulation are associated with active lupus and
skew natural T regulatory cell differentiation to type 1 regulatory
T (Tr1) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:18995–19000. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fishelson Z, Donin N, Zell S, Schultz S
and Kirschfink M: Obstacles to cancer immunotherapy: Expression of
membrane complement regulatory proteins (mCRPs) in tumors. Mol
Immunol. 40:109–123. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Blok VT, Daha MR, Tijsma OM, Weissglas MG,
van den Broek LJ and Gorter A: A possible role of CD46 for the
protection in vivo of human renal tumor cells from
complement-mediated damage. Lab Invest. 80:335–344. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Madjd Z, Durrant LG, Pinder SE, Ellis IO,
Ronan J, Lewis S, Rushmere NK and Spendlove I: Do poor-prognosis
breast tumours express membrane cofactor proteins (CD46)? Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 54:149–156. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kinugasa N, Higashi T, Nouso K,
Nakatsukasa H, Kobayashi Y, Ishizaki M, Toshikuni N, Yoshida K,
Uematsu S and Tsuji T: Expression of membrane cofactor protein
(MCP, CD46) in human liver diseases. Br J Cancer. 80:1820–1825.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Seya T, Hara T, Iwata K, Kuriyama S,
Hasegawa T, Nagase Y, Miyagawa S, Matsumoto M, Hatanaka M, Atkinson
JP, et al: Purification and functional properties of soluble forms
of membrane cofactor protein (CD46) of complement: Identification
of forms increased in cancer patients' sera. Int Immunol.
7:727–736. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maciejczyk A, Szelachowska J,
Szynglarewicz B, Szulc R, Szulc A, Wysocka T, Jagoda E, Lage H and
Surowiak P: CD46 Expression is an unfavorable prognostic factor in
breast cancer cases. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 19:540–546.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Surowiak P, Materna V, Maciejczyk A,
Kaplenko I, Spaczynski M, Dietel M, Lage H and Zabel M: CD46
expression is indicative of shorter revival-free survival for
ovarian cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 26:4943–4948. 2006.
|
|
14
|
Lu Z, Zhang C, Cui J, Song Q, Wang L, Kang
J, Li P, Hu X, Song H, Yang J and Sun Y: Bioinformatic analysis of
the membrane cofactor protein CD46 and microRNA expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 31:557–564. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Zeng J, Xu H, Huang C, Sun Y, Xiao H, Yu
G, Zhou H, Zhang Y, Yao W, Xiao W, et al: CD46 splice variant
enhances translation of specific mRNAs linked to an aggressive
tumor cell phenotype in bladder cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
24:140–153. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Do M, Thanh HD, To PK, Kim MS, Moon C and
Jung C: CD46 protects the bladder cancer cells from
cetuximab-mediated cytotoxicity. Sci Rep. 12:224202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Merdad A, Karim S, Schulten HJ, Dallol A,
Buhmeida A, Al-Thubaity F, Gari MA, Chaudhary AG, Abuzenadah AM and
Al-Qahtani MH: Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in
primary human breast cancer: MMP-9 as a potential biomarker for
cancer invasion and metastasis. Anticancer Res. 34:1355–1366.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hara I, Miyake H, Hara S, Arakawa S and
Kamidono S: Significance of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue
inhibitors of metalloproteinase expression in the recurrence of
superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol.
165:1769–1772. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sato H and Seiki M: Regulatory mechanism
of 92 kDa type IV collagenase gene expression which is associated
with invasiveness of tumor cells. Oncogene. 8:395–405.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis and c-Jun. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 96:6442004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ibrahim SAE, Abudu A, Johnson E, Aftab N,
Conrad S and Fluck M: The role of AP-1 in self-sufficient
proliferation and migration of cancer cells and its potential
impact on an autocrine/paracrine loop. Oncotarget. 9:34259–34278.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu G, Cheng Z, Huang Y, Zheng W, Yang S,
Lin C and Ye J: MyD88 mediates colorectal cancer cell
proliferation, migration and invasion via NF-κB/AP-1 signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 45:131–140. 2020.
|
|
23
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheng CY, Hsieh HL, Hsiao LD and Yang CM:
PI3-K/Akt/JNK/NF-κB is essential for MMP-9 expression and outgrowth
in human limbal epithelial cells on intact amniotic membrane. Stem
Cell Res. 9:9–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jian H, Zhao Y, Liu B and Lu S: SEMA4b
inhibits MMP9 to prevent metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer.
Tumour Biol. 35:11051–11056. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin CC, Kuo CT, Cheng CY, Wu CY, Lee CW,
Hsieh HL, Lee IT and Yang CM: IL-1 beta promotes A549 cell
migration via MAPKs/AP-1- and NF-kappaB-dependent matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression. Cell. Signal. 21:1652–1662. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ellerbroek SM, Halbleib JM, Benavidez M,
Warmka JK, Wattenberg EV, Stack MS and Hudson LG:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in epidermal growth
factor-stimulated matrix metalloproteinase-9 production and cell
surface association. Cancer Res. 61:1855–1861. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Funakoshi-Tago M, Tago K, Sonoda Y,
Tominaga S and Kasahara T: TRAF6 and C-SRC induce synergistic AP-1
activation via PI3-kinase-AKT-JNK pathway. Eur J Biochem.
270:1257–1268. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Do MH, To PK, Cho YS, Kwon SY, Hwang EC,
Choi C, Cho SH, Lee SJ, Hemmi S and Jung C: Targeting CD46 enhances
anti-tumoral activity of adenovirus type 5 for bladder cancer. Int
J Mol Sci. 19:26942018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nguyen TT, Thanh HD, Do MH and Jung C:
Complement regulatory protein CD46 manifests a unique role in
promoting the migration of bladder cancer cells. Chonnam Med J.
59:160–166. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Davies B, Waxman J, Wasan H, Abel P,
Williams G, Krausz T, Neal D, Thomas D, Hanby A and Balkwill F:
Levels of matrix metalloproteases in bladder cancer correlate with
tumor grade and invasion. Cancer Res. 53:5365–5369. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gerhards S, Jung K, Koenig F, Daniltchenko
D, Hauptmann S, Schnorr D and Loening SA: Excretion of matrix
metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in urine is associated with a high stage
and grade of bladder carcinoma. Urology. 57:675–679. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jung C, Kim RS, Zhang HJ, Lee SJ and Jeng
MH: HOXB13 induces growth suppression of prostate cancer cells as a
repressor of hormone-activated androgen receptor signaling. Cancer
Res. 64:9185–9192. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Papathoma AS, Petraki C, Grigorakis A,
Papakonstantinou H, Karavana V, Stefanakis S, Sotsiou F and Pintzas
A: Prognostic significance of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in
bladder cancer. Anticancer Res. 20:2009–2013. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cho YS, Do MH, Kwon SY, Moon C, Kim K, Lee
K, Lee SJ, Hemmi S, Joo YE, Kim MS and Jung C: Efficacy of
CD46-targeting chimeric Ad5/35 adenoviral gene therapy for
colorectal cancers. Oncotarget. 7:38210–38223. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Braicu C, Buse M, Busuioc C, Drula R,
Gulei D, Raduly L, Rusu A, Irimie A, Atanasov AG, Slaby O, et al: A
comprehensive review on MAPK: A promising therapeutic target in
cancer. Cancers (Basel). 11:16182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Datta SR, Brunet A and Greenberg ME:
Cellular survival: A play in three akts. Genes Dev. 13:2905–2927.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Park SL, Won SY, Song JH, Kambe T, Nagao
M, Kim WJ and Moon SK: EPO gene expression promotes proliferation,
migration and invasion via the p38MAPK/AP-1/MMP-9 pathway by
p21WAF1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Signal.
27:470–478. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Shaulian E and Karin M: AP-1 in cell
proliferation and survival. Oncogene. 20:2390–2400. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Meng Q, Xu J, Wang J, Zhang X, Yang H, Sun
H, Wu S, Aschner M, Li X, Zhang L, et al: Investigation of the
enhanced antitumour potency of CD46-specific chimeric antigen
receptor-T cells in human colorectal cancer liver metastases after
combination with nanotherapeutics. Nano Today. 52:1019852023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Van den Steen PE, Dubois B, Nelissen I,
Rudd PM, Dwek RA and Opdenakker G: Biochemistry and molecular
biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Crit
Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 37:375–536. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cardone J, Al Shouli S and Kemper C: A
novel role for CD46 in wound repair. Front Immunol. 2:282011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yan Y and Merlin D: Ste20-related
proline/alanine-rich kinase: A novel regulator of intestinal
inflammation. World J Gastroenterol. 14:6115–6121. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Guillot C and Lecuit T: Mechanics of
epithelial tissue homeostasis and morphogenesis. Science.
340:1185–1189. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Laronha H and Caldeira J: Structure and
function of human matrix metalloproteinases. Cells. 9:10762020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee SJ, Park SS, Lee US, Kim WJ and Moon
SK: Signaling pathway for TNF-alpha-induced MMP-9 expression:
Mediation through p38 MAP kinase, and inhibition by anti-cancer
molecule magnolol in human urinary bladder cancer 5637 cells. Int
Immunopharmacol. 8:1821–1826. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen YT, Yang CC, Shao PL, Huang CR and
Yip HK: Melatonin-mediated downregulation of ZNF746 suppresses
bladder tumorigenesis mainly through inhibiting the AKT-MMP-9
signaling pathway. J Pineal Res. 66:e125362019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Chang L and Karin M: Mammalian MAP kinase
signalling cascades. Nature. 410:37–40. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pulverer BJ, Hughes K, Franklin CC, Kraft
AS, Leevers SJ and Woodgett JR: Co-purification of
mitogen-activated protein kinases with phorbol ester-induced c-Jun
kinase activity in U937 leukaemic cells. Oncogene. 8:407–415.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Benbow U and Brinckerhoff CE: The AP-1
site and MMP gene regulation: What is all the fuss about? Matrix
Biol. 15:519–526. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gum R, Lengyel E, Juarez J, Chen JH, Sato
H, Seiki M and Boyd D: Stimulation of 92-kDa gelatinase B promoter
activity by ras is mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase
1-independent and requires multiple transcriptin factor binding
sites including closely spaced PEA3/ets and AP-1 sequences. J Biol
Chem. 271:10672–10680. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|