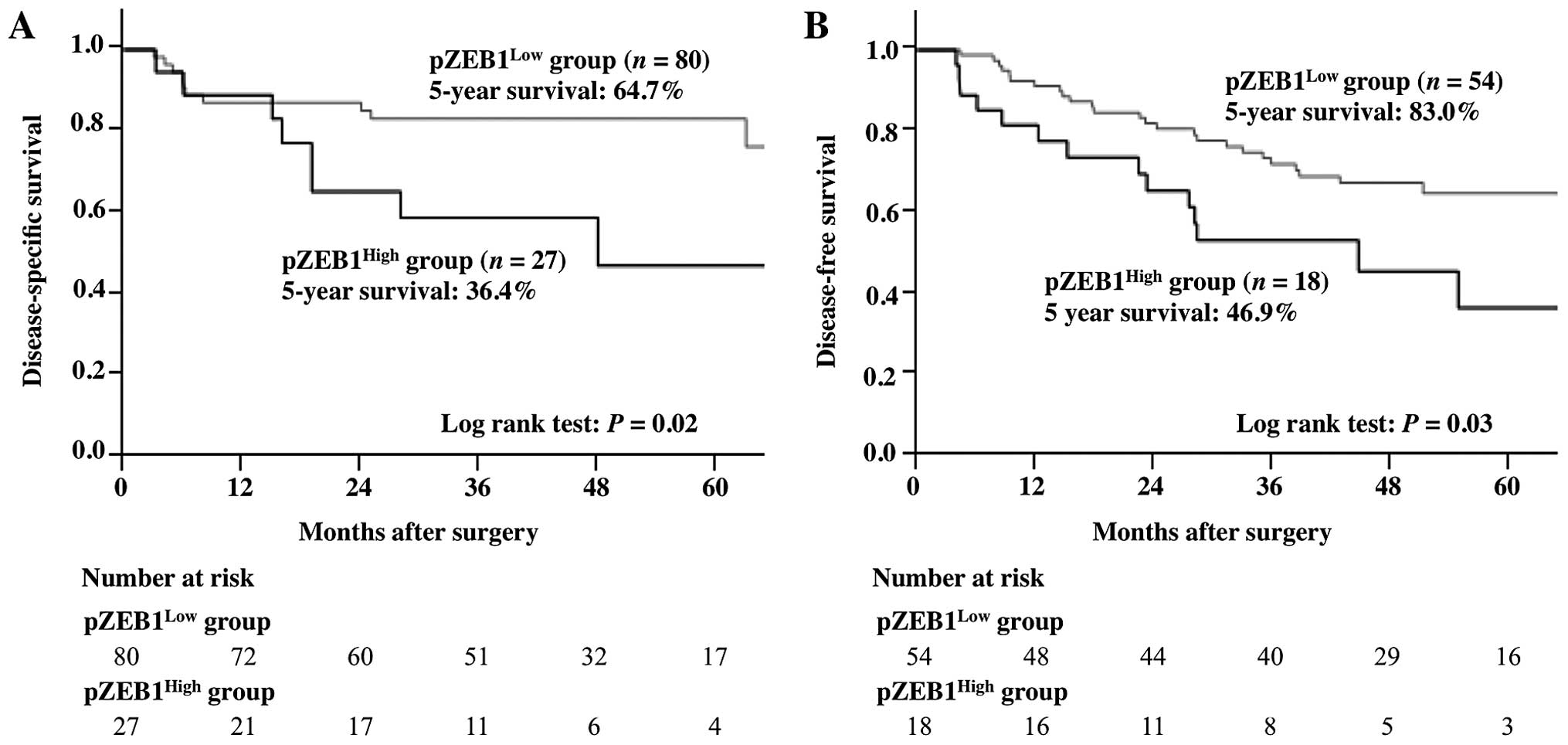
|
1
|
Macdonald JS, Smalley SR, Benedetti J, et
al: Chemoradiotherapy after surgery compared with surgery alone for
adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction. N Engl
Med. 345:725–730. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP, et
al: Perioperative chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable
gastroesophageal cancer. N Engl Med. 355:11–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sakuramoto S, Sasako M, Yamaguchi T, et
al: Adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer with S-1, an oral
fluoropyrimidine. N Engl Med. 357:1810–1820. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Allum W, Garofalo A, Degiuli M and
Schuhmacher C: The first European Union Network of Excellence for
Gastric Cancer conference, Rome, Italy, April 2008. Gastric Cancer.
12:56–65. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yonemura Y, Elnemr A, Endou Y, et al:
Multidisciplinary therapy for treatment of patients with peritoneal
carcinomatosis from gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol.
2:85–97. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gotzmann J, Mikula M, Eger A, et al:
Molecular aspects of epithelial cell plasticity: implications for
local tumor invasion and metastasis. Mutat Res. 566:9–20. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cavallaro U and Christofori G: Cell
adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nature
Rev Cancer. 4:118–132. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tomita K, van Bokhoven A, van Leenders GJ,
et al: Cadherin switching in human prostate cancer progression.
Cancer Res. 60:3650–3654. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rieger-Christ KM, Cain JW, Braasch JW, et
al: Expression of classic cadherins type I in urothelial neoplastic
progression. Hum Pathol. 32:18–23. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Christiansen JJ and Rajasekaran AK:
Reassessing epithelial to mesenchymal transition as a prerequisite
for carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res. 66:8319–8326.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Klymkowsky MW and Savagner P:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: a cancer researcher's conceptual
friend and foe. Am J Pathol. 174:1588–1593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Tanaka K, et al:
Clinical significance of z inc finger E-box b inding homeobox 1
(ZEB1) in human gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 106:280–285. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jia B, Liu H, Kong Q, et al:
Overexpression of ZEB1 associated with metastasis and invasion in
patients with gastric carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 366:223–229.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang GJ, Zhou T, Tian HP, et al: High
expression of ZEB1 correlates with liver metastasis and poor
prognosis in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 5:564–568.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Hlubek F, et
al: A transient, EMT-linked loss of basement membranes indicates
metastasis and poor survival in colorectal cancer.
Gastroenterology. 131:830–840. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Eger A, Aigner K, Sonderegger S, et al:
Delta EF1 is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin and
regulates epithelial plasticity in breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
24:2375–2385. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ohira T, Gemmill RM, Ferguson K, et al:
WNT7a induces E-cadherin in lung cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 100:10429–10434. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chua HL, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Clare SE, et
al: NF-kappa B represses E-cadherin expression and enhances
epithelial to mesenchymal transition of mammary epithelial cells:
potential involvement of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2. Oncogene. 26:711–724.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Graham TR, Zhau HE, Odero-Marah VA, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor-I-dependent up-regulation of ZEB1 drives
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human prostate cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 68:2479–2488. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Abe N, Watanabe T, Toda H, et al:
Prognostic significance of carcinoembryonic antigen levels in
peritoneal washes in patients with gastric cancer. Am J Surg.
181:356–361. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ito S, Nakanishi H, Kodera Y, et al:
Prospective validation of quantitative CEA mRNA detection in
peritoneal washes in gastric carcinoma patients. Br J Cancer.
93:986–992. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kodera Y, Nakanishi H, Ito S, et al:
Prognostic significance of intraperitoneal cancer cells in gastric
carcinoma: detection of cytokeratin 20 mRNA in peritoneal washes,
in addition to detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Gastric
Cancer. 8:142–148. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Murai T, Yamada S, Fuchs BC, et al:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition predicts prognosis in clinical
gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 109:684–689. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schmalhofer O, Brabletz S and Brabletz T:
E-cadherin, beta-catenin and ZEB1 in malignant progression of
cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:151–166. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
De Wever O, Pauwels P, De Craene B, et al:
Molecular and pathological signatures of epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions at the cancer invasion front. Histochem Cell Biol.
130:481–494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Waldmann J, Feldmann G, Slater EP, et al:
Expression of the zinc-finger transcription factor Snail in
adrenocortical carcinoma is associated with decreased survival. Br
J Cancer. 99:1900–1907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer development and its
clinical significance. Cancer Sci. 101:293–299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rosivatz E, Becker I, Specht K, et al:
Differential expression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition
regulators Snail, SIP1 and Twist in gastric cancer. Am J Pathol.
161:1881–1891. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Wahlbuhl M, et
al: The transcriptional repressor ZEB1 promotes metastasis and loss
of cell polarity in cancer. Cancer Res. 68:537–544. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Drake JM, Strohbehn G, Bair TB, et al:
ZEB1 enhances transendothelial migration and represses the
epithelial phenotype of prostate cancer cells. Mol Biol Cell.
20:2207–2217. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Takeyama Y, Sato M, Horio M, et al:
Knockdown of ZEB 1, a master epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
(EMT) gene, suppresses anchorage-independent cell growth of lung
cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 296:216–224. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Singh M, Spoelstra NS, Jean A, et al: ZEB1
expression in type I vs type II endometrial cancers: a marker of
aggressive disease. Mod Pathol. 21:912–923. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhou YM, Cao L, Li B, et al:
Clinicopathological significance of ZEB1 protein in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:1700–1706. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kurahara H, Takao S, Maemura K, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and mesenchymal-epithelial
transition via regulation of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2 expression in
pancreatic cancer. J Surg Oncol. 105:655–661. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Toll A, Masferrer E, Hernández-Ruiz ME, et
al: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition markers are associated
with an increased metastatic risk in primary cutaneous squamous
cell carcinomas but are attenuated in lymph node metastases. J
Dermatol Sci. 72:93–102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Aokage K, Ishii G, Ohtaki Y, et al:
Dynamic molecular changes associated with epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and subsequent mesenchymal-epithelial transition in the
early phase of metastatic tumor formation. Int J Cancer.
128:1585–1595. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|