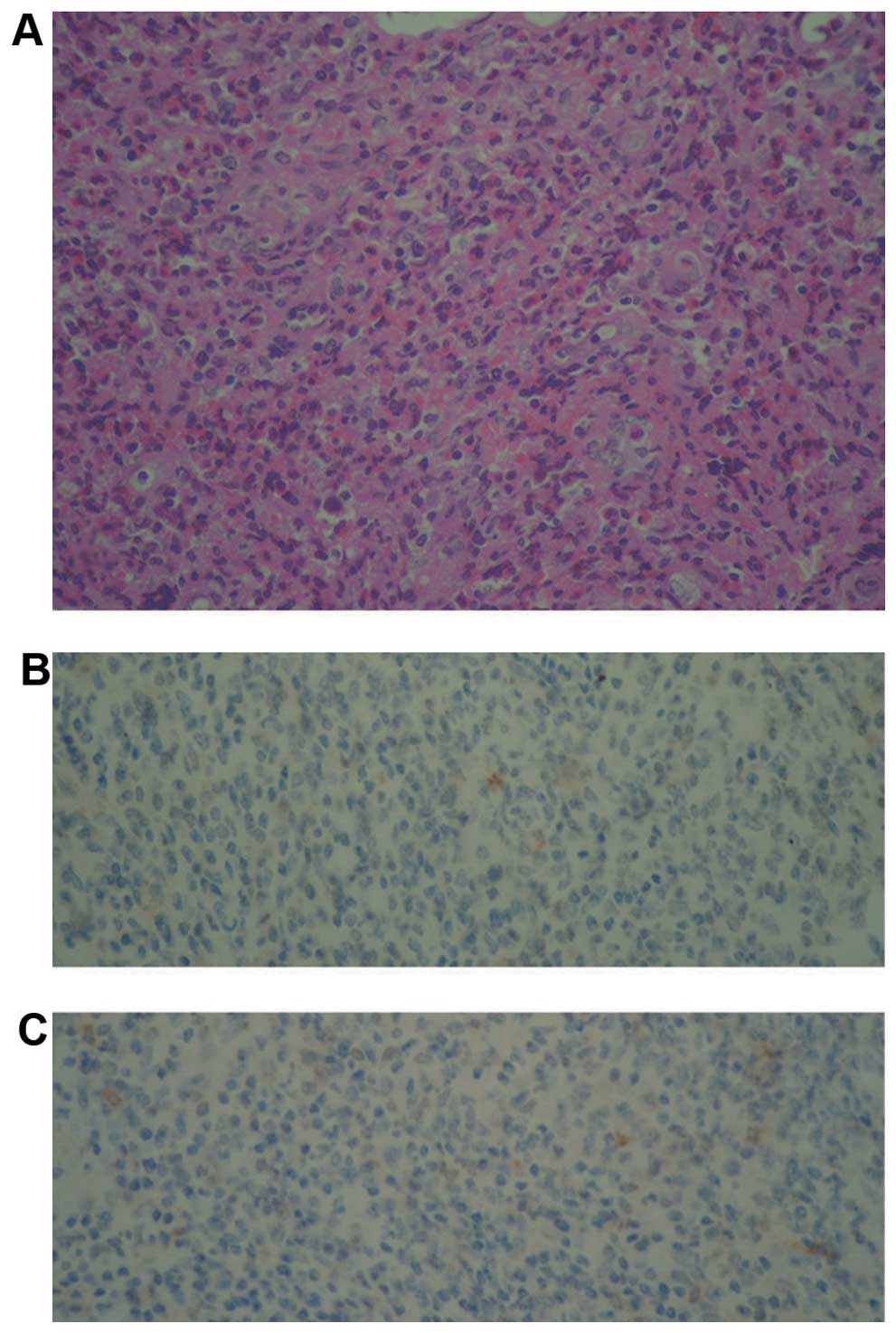
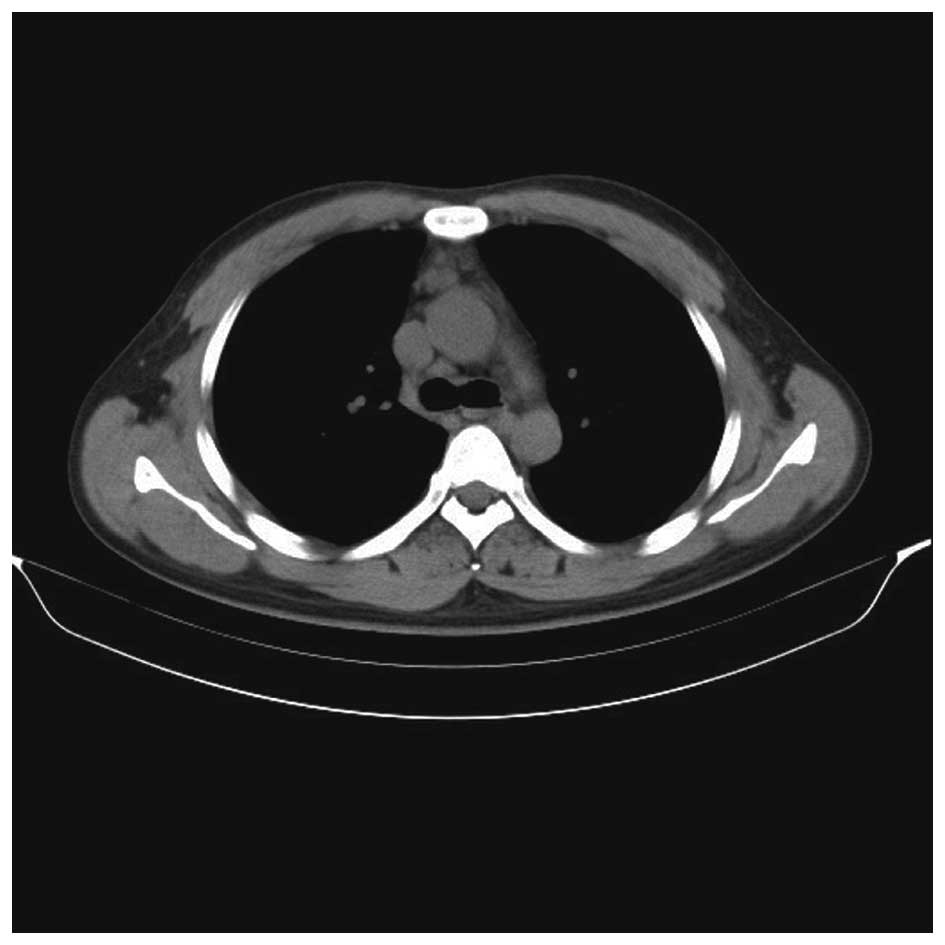
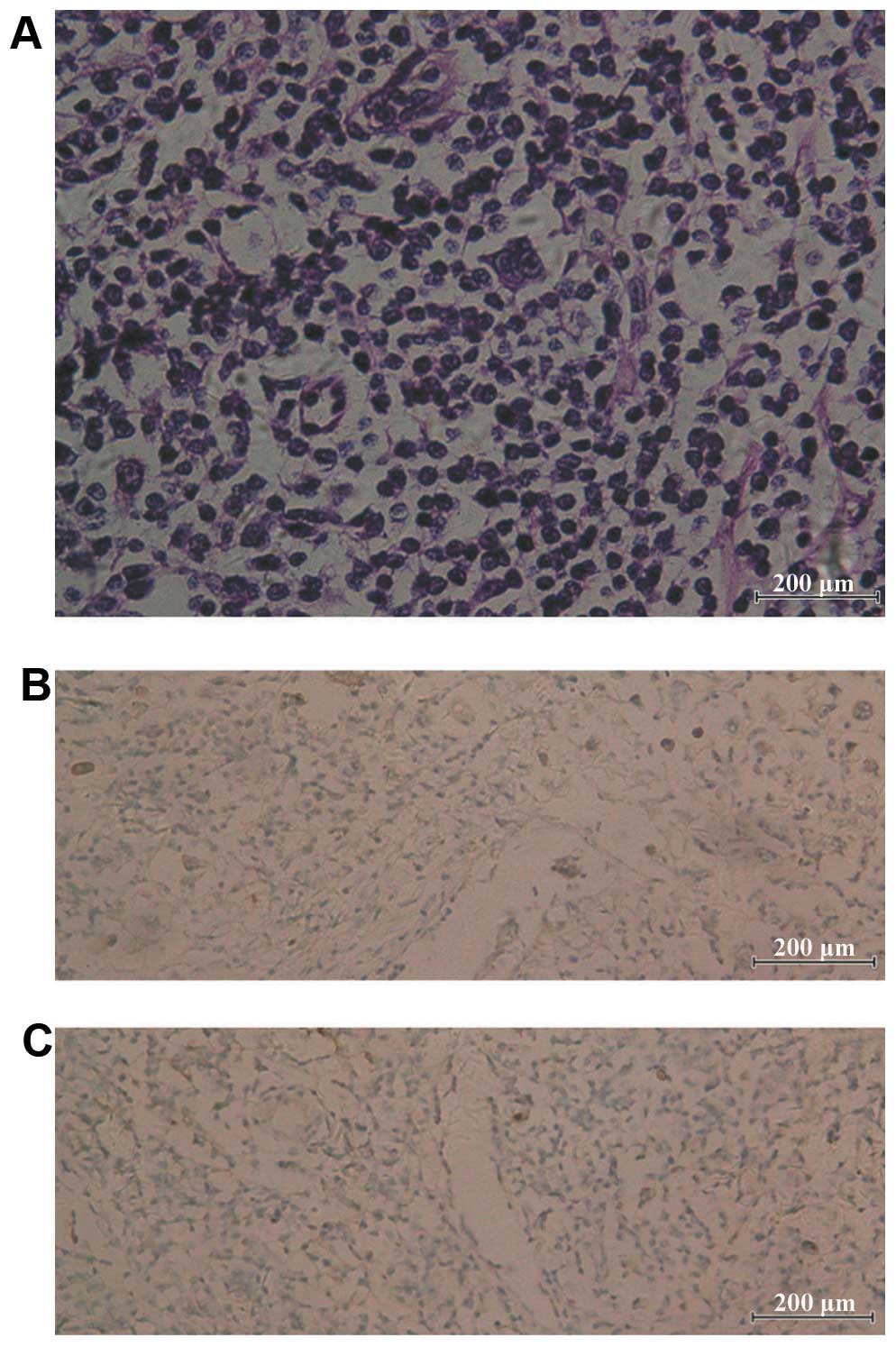
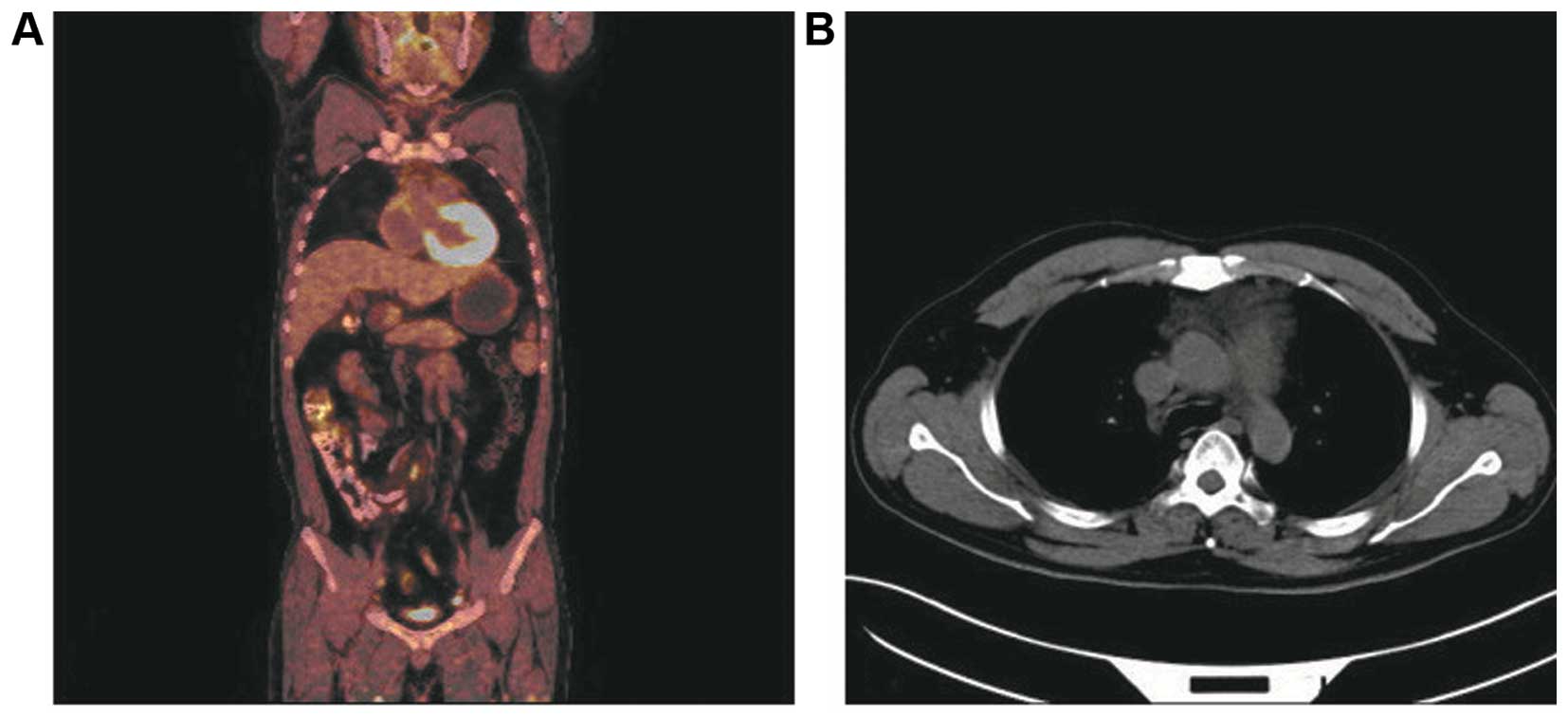
|
1
|
Pan Z, Sharma S and Sharma P: Primary
langerhans cell histiocytosis of the vulva: Report of a case and
brief review of the literature. Indian J Pathol Microbiol.
52:65–68. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shanley DJ, Lerud KS and Luetkehans TJ:
Development of pulmonary histiocytosis X after chemotherapy for
Hodgkin disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 155:741–742. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
L'Hoste RJ Jr, Arrowsmith WR, Leonard GL
and McGaw H: Eosinophilic granuloma occurring in a patient with
Hodgkin disease. Hum Pathol. 13:592–595. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Adu-Poku K, Thomas DW, Khan MK, Holgate CS
and Smith ME: Langerhans cell histiocytosis in sequential
discordant lymphoma. J Clin Pathol. 58:104–106. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dehkordi NR, Rajabi P, Naimi A and
Heidarpour M: Langerhans cell histiocytosis following Hodgkin
lymphoma: A case report from Iran. J Res Med Sci. 15:58–61.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee JS, Ko GH, Kim HC, Jang IS, Jeon KN
and Lee JH: Langerhans cell sarcoma arising from Langerhans cell
histiocytosis: A case report. J Korean Med Sci. 21:577–580. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Egeler RM, Neglia JP, Puccetti DM, Brennan
CA and Nesbit ME: Association of Langerhans cell histiocytosis with
malignant neoplasms. Cancer. 71:865–873. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
de Ibarrola Andrés C, Toscano R, Lahuerta
JJ and Martínez-González MA: Simultaneous occurrence of Hodgkin's
disease, nodal Langerhans' cell histiocytosis and multiple myeloma
IgA(kappa). Virchows Arch. 434:259–262. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Neumann MP and Frizzera G: The coexistence
of Langerhans' cell granulomatosis and malignant lymphoma may take
different forms: Report of seven cases with a review of the
literature. Hum Pathol. 17:1060–1065. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ardekian L, Peled M, Rosen D, Rachmiel A,
Abu el-Naaj I and Laufer D: Clinical and radiographic features of
eosinophilic granuloma in the jaws: Review of 41 lesions treated by
surgery and low-dose radiotherapy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol
Oral Radiol Endod. 87:238–242. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lichtenstein L: Histiocytosis X;
integration of eosinophilic granuloma of bone, Letterer-Siwe
disease, and Schüller-Christian disease as related manifestations
of a single nosologic entity. AMA Arch Pathol. 56:84–102.
1953.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Piattelli A and Paolantonio M:
Eosinophilic granuloma of the mandible involving the periodontal
tissues. A case report. J Periodontol. 66:731–736. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Haupt R, Minkov M, Astigarraga I, Schäfer
E, Nanduri V, Jubran R, Egeler RM, Janka G, Micic D,
Rodriguez-Galindo C, et al: Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH):
Guidelines for diagnosis, clinical work-up, and treatment for
patients till the age of 18 years. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
60:175–184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Willman CL: Detection of clonal
histiocytes in Langerhans cell histiocytosis: Biology and clinical
significance. Br J Cancer Suppl. 23:S29–S33. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Egeler RM, Neglia JP, Aricò M, Favara BE,
Heitger A, Nesbit ME and Nicholson HS: The relation of Langerhans
cell histiocytosis to acute leukemia, lymphomas, and other solid
tumors. The LCH-malignancy study group of the histiocyte society.
Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 12:369–378. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shin MS, Buchalter SE and Ho KJ:
Langerhans' cell histiocytosis associated with Hodgkin's disease: A
case report. J Natl Med Assoc. 86:65–69. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Naumann R, Beuthien-Baumann B, Fischer R,
Kittner T, Bredow J, Kropp J, Ockert D and Ehninger G: Simultaneous
occurrence of Hodgkin's lymphoma and eosinophilic granuloma: A
potential pitfall in positron emission tomography imaging. Clin
Lymphoma. 3:121–124. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fotos JS, Flemming DJ and Tulchinsky M:
False-positive PET/CT for lymphoma recurrence secondary to
Langerhans cell. Clin Nucl Med. 36:717–719. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|