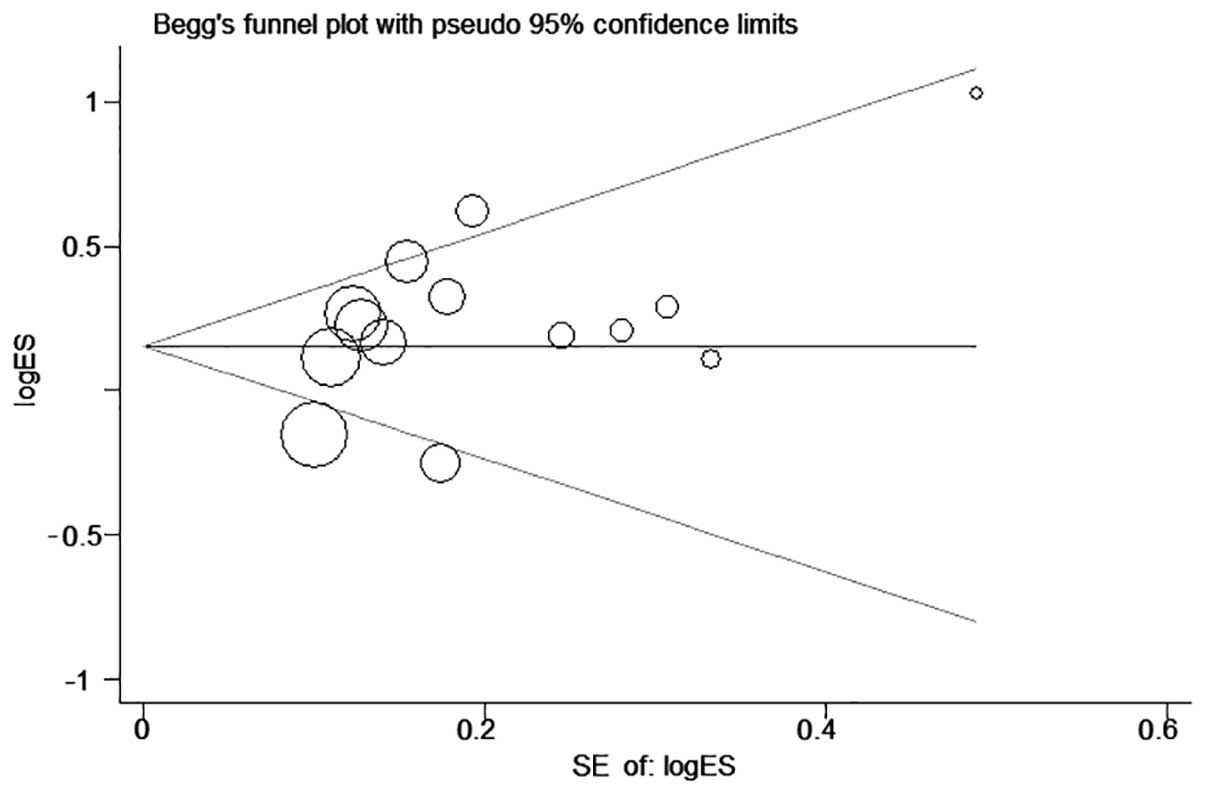
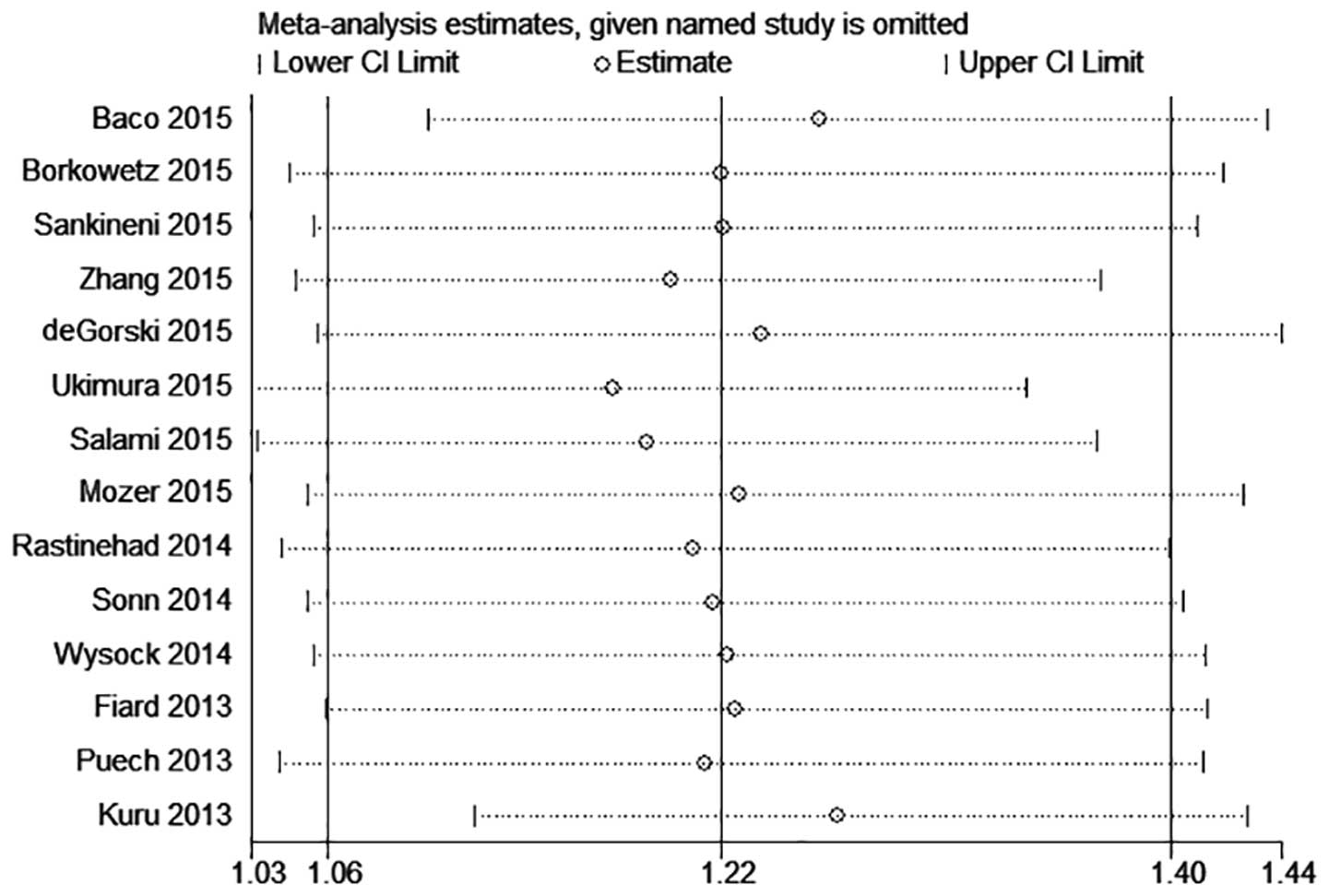
|
1
|
Soerjomataram I, Lortet-Tieulent J, Parkin
DM, Ferlay J, Mathers C, Forman D and Bray F: Global burden of
cancer in 2008: A systematic analysis of disability-adjusted
life-years in 12 world regions. Lancet. 380:1840–1850. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miyagawa T, Ishikawa S, Kimura T, Suetomi
T, Tsutsumi M, Irie T, Kondoh M and Mitake T: Real-time virtual
sonography for navigation during targeted prostate biopsy using
magnetic resonance imaging data. Int J Urol. 17:855–860. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Babaian RJ, Toi A, Kamoi K, Troncoso P,
Sweet J, Evans R, Johnston D and Chen M: A comparative analysis of
sextant and an extended 11-core multisite directed biopsy strategy.
J Urol. 163:152–157. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Presti JC Jr, O'Dowd GJ, Miller MC, Mattu
R and Veltri RW: Extended peripheral zone biopsy schemes increase
cancer detection rates and minimize variance in prostate specific
antigen and age related cancer rates: Results of a community
multi-practice study. J Urol. 169:125–129. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Campos-Fernandes JL, Bastien L, Nicolaiew
N, Robert G, Terry S, Vacherot F, Salomon L, Allory Y, Vordos D,
Hoznek A, et al: Prostate cancer detection rate in patients with
repeated extended 21-sample needle biopsy. Eur Urol. 55:600–606.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sonn GA, Margolis DJ and Marks LS: Target
detection: Magnetic resonance imaging-ultrasound fusion-guided
prostate biopsy. Urol Oncol. 32:903–911. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dickinson L, Ahmed HU, Allen C, Barentsz
JO, Carey B, Futterer JJ, Salomon L, Allory Y, Vordos D, Hoznek A,
et al: Magnetic resonance imaging for the detection, localisation,
and characterisation of prostate cancer: Recommendations from a
European consensus meeting. Eur Urol. 59:477–494. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Barentsz JO, Richenberg J, Clements R,
Choyke P, Verma S, Villeirs G, Rouviere O, Logager V and Fütterer
JJ: European Society of Urogenital Radiology: ESUR prostate MR
guidelines 2012. Eur Radiol. 22:746–757. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haffner J, Lemaitre L, Puech P, Haber GP,
Leroy X, Jones JS and Villers A: Role of magnetic resonance imaging
before initial biopsy: Comparison of magnetic resonance
imaging-targeted and systematic biopsy for significant prostate
cancer detection. BJU Int. 108:E171–E178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hambrock T, Somford DM, Hoeks C, Bouwense
SA, Huisman H, Yakar D, van Oort IM, Witjes JA, Fütterer JJ and
Barentsz JO: Magnetic resonance imaging guided prostate biopsy in
men with repeat negative biopsies and increased prostate specific
antigen. J Urol. 183:520–527. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moore CM, Robertson NL, Arsanious N,
Middleton T, Villers A, Klotz L, Taneja SS and Emberton M:
Image-guided prostate biopsy using magnetic resonance
imaging-derived targets: A systematic review. Eur Urol. 63:125–140.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sankineni S, George AK, Brown AM,
Rais-Bahrami S, Wood BJ, Merino MJ, Pinto PA, Choyke PL and Turkbey
B: Posterior subcapsular prostate cancer: Identification with mpMRI
and MRI/TRUS fusion-guided biopsy. Abdom Imaging. 40:2557–2565.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Q, Wang W, Yang R, Zhang G, Zhang B,
Li W, Huang H and Guo H: Free-hand transperineal targeted prostate
biopsy with real-time fusion imaging of multiparametric magnetic
resonance imaging and transrectal ultrasound: Single-center
experience in China. Int Urol Nephrol. 47:727–733. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
de Gorski A, Rouprêt M, Peyronnet B, Le
Cossec C, Granger B, Comperat E and Cussenot O: Accuracy of
magnetic resonance imaging/ultrasound fusion targeted biopsies to
diagnose clinical significant prostate cancer in enlarged compared
to smaller prostates. J Urol. 194:669–673. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ukimura O, Marien A, Palmer S, Villers A,
Aron M, de Castro AA, Leslie S, Shoji S, Matsugasumi T, Gross M, et
al: Trans-rectal ultrasound visibility of prostate lesions
identified by magnetic resonance imaging increases accuracy of
image-fusion targeted biopsies. World J Urol. 33:1669–1676. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Junker D, Schäfer G, Heidegger I, Bektic
J, Ladurner M, Jaschke W and Aigner F: Multiparametric magnetic
resonance imaging/transrectal ultrasound fusion targeted biopsy of
the prostate: Preliminary results of a prospective single-centre
study. Urol Int. 94:313–318. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shoji S, Hiraiwa S, Endo J, Hashida K,
Tomonaga T, Nakano M, Sugiyama T, Tajiri T, Terachi T and Uchida T:
Manually controlled targeted prostate biopsy with real-time fusion
imaging of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging and
transrectal ultrasound: An early experience. Int J Urol.
22:173–178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Salami SS, Ben-Levi E, Yaskiv O, Ryniker
L, Turkbey B, Kavoussi LR, Villani R and Rastinehad AR: In patients
with a previous negative prostate biopsy and a suspicious lesion on
magnetic resonance imaging, is a 12-core biopsy still necessary in
addition to a targeted biopsy? BJU Int. 115:562–570. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mozer P, Rouprêt M, Le Cossec C, Granger
B, Comperat E, de Gorski A, Cussenot O and Renard-Penna R: First
round of targeted biopsies using magnetic resonance
imaging/ultrasonography fusion compared with conventional
transrectal ultrasonography-guided biopsies for the diagnosis of
localised prostate cancer. BJU Int. 115:50–57. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rastinehad AR, Turkbey B, Salami SS,
Yaskiv O, George AK, Fakhoury M, Beecher K, Vira MA, Kavoussi LR,
Siegel DN, et al: Improving detection of clinically significant
prostate cancer: Magnetic resonance imaging/transrectal ultrasound
fusion guided prostate biopsy. J Urol. 191:1749–1754. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fiard G, Hohn N, Descotes JL, Rambeaud JJ,
Troccaz J and Long JA: Targeted MRI-guided prostate biopsies for
the detection of prostate cancer: Initial clinical experience with
real-time 3-dimensional transrectal ultrasound guidance and
magnetic resonance/transrectal ultrasound image fusion. Urology.
81:1372–1378. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vourganti S, Rastinehad A, Yerram NK, Nix
J, Volkin D, Hoang A, Turkbey B, Gupta GN, Kruecker J, Linehan WM,
et al: Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound
fusion biopsy detect prostate cancer in patients with prior
negative transrectal ultrasound biopsies. J Urol. 188:2152–2157.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Delongchamps NB, Peyromaure M, Schull A,
Beuvon F, Bouazza N, Flam T, Zerbib M, Muradyan N, Legman P and
Cornud F: Prebiopsy magnetic resonance imaging and prostate cancer
detection: Comparison of random and targeted biopsies. J Urol.
189:493–499. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Puech P, Rouvière O, Renard-Penna R,
Villers A, Devos P, Colombel M, Bitker MO, Leroy X,
Mège-Lechevallier F, Comperat E, et al: Prostate cancer diagnosis:
Multiparametric MR-targeted biopsy with cognitive and transrectal
US-MR fusion guidance versus systematic biopsy-prospective
multicenter study. Radiology. 268:461–469. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Volkin D, Turkbey B, Hoang AN,
Rais-Bahrami S, Yerram N, Walton-Diaz A, Nix JW, Wood BJ, Choyke PL
and Pinto PA: Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and
subsequent MRI/ultrasonography fusion-guided biopsy increase the
detection of anteriorly located prostate cancers. BJU Int.
114:E43–E49. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sonn GA, Chang E, Natarajan S, Margolis
DJ, Macairan M, Lieu P, Nix JW, Wood BJ, Choyke PL and Pinto PA:
Value of targeted prostate biopsy using magnetic
resonance-ultrasound fusion in men with prior negative biopsy and
elevated prostate-specific antigen. Eur Urol. 65:809–815. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wysock JS, Rosenkrantz AB, Huang WC,
Stifelman MD, Lepor H, Deng FM, Melamed J and Taneja SS: A
prospective, blinded comparison of magnetic resonance (MR)
imaging-ultrasound fusion and visual estimation in the performance
of MR-targeted prostate biopsy: The PROFUS trial. Eur Urol.
66:343–351. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kuru TH, Roethke MC, Seidenader J,
Simpfendörfer T, Boxler S, Alammar K, Rieker P, Popeneciu VI, Roth
W, Pahernik S, et al: Critical evaluation of magnetic resonance
imaging targeted, transrectal ultrasound guided transperineal
fusion biopsy for detection of prostate cancer. J Urol.
190:1380–1386. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baco E, Rud E, Eri LM, Moen G, Vlatkovic
L, Svindland A, Eggesbø HB and Ukimura O: A randomized controlled
trial to assess and compare the outcomes of two-core prostate
biopsy guided by fused magnetic resonance and transrectal
ultrasound images and traditional 12-core systematic biopsy. Eur
Urol. 69:149–156. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Siddiqui MM, Rais-Bahrami S, Turkbey B,
George AK, Rothwax J, Shakir N, Okoro C, Raskolnikov D, Parnes HL,
Linehan WM, et al: Comparison of MR/ultrasound fusion-guided biopsy
with ultrasound-guided biopsy for the diagnosis of prostate cancer.
JAMA. 313:390–397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Borkowetz A, Platzek I, Toma M, Laniado M,
Baretton G, Froehner M, Koch R, Wirth M and Zastrow S: Comparison
of systematic transrectal biopsy to transperineal magnetic
resonance imaging/ultrasound-fusion biopsy for the diagnosis of
prostate cancer. BJU Int. 116:873–879. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ploussard G, Salomon L, Xylinas E, Allory
Y, Vordos D, Hoznek A, Abbou CC and de la Taille A: Pathological
findings and prostate specific antigen outcomes after radical
prostatectomy in men eligible for active surveillance - does the
risk of misclassification vary according to biopsy criteria? J
Urol. 183:539–544. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dominguez-Escrig JL, McCracken SR and
Greene D: Beyond diagnosis: Evolving prostate biopsy in the era of
focal therapy. Prostate Cancer. 2011:3862072011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Valerio M, Donaldson I, Emberton M, Ehdaie
B, Hadaschik BA, Marks LS, Mozer P, Rastinehad AR and Ahmed HU:
Detection of clinically significant prostate cancer using magnetic
resonance imaging-ultrasound fusion targeted biopsy: A systematic
review. Eur Urol. 68:8–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Puech P, Potiron E, Lemaitre L, Leroy X,
Haber GP, Crouzet S, Kamoi K and Villers A: Dynamic
contrast-enhanced-magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of
intraprostatic prostate cancer: Correlation with radical
prostatectomy specimens. Urology. 74:1094–1099. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Carroll PR, Parsons JK, Andriole G,
Bahnson RR, Castle EP, Catalona WJ, Dahl DM, Davis JW, Epstein JI,
Etzioni RB, et al: NCCN Guidelines Insights: Prostate Cancer Early
Detection, Version 2.2016. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 14:509–519.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|