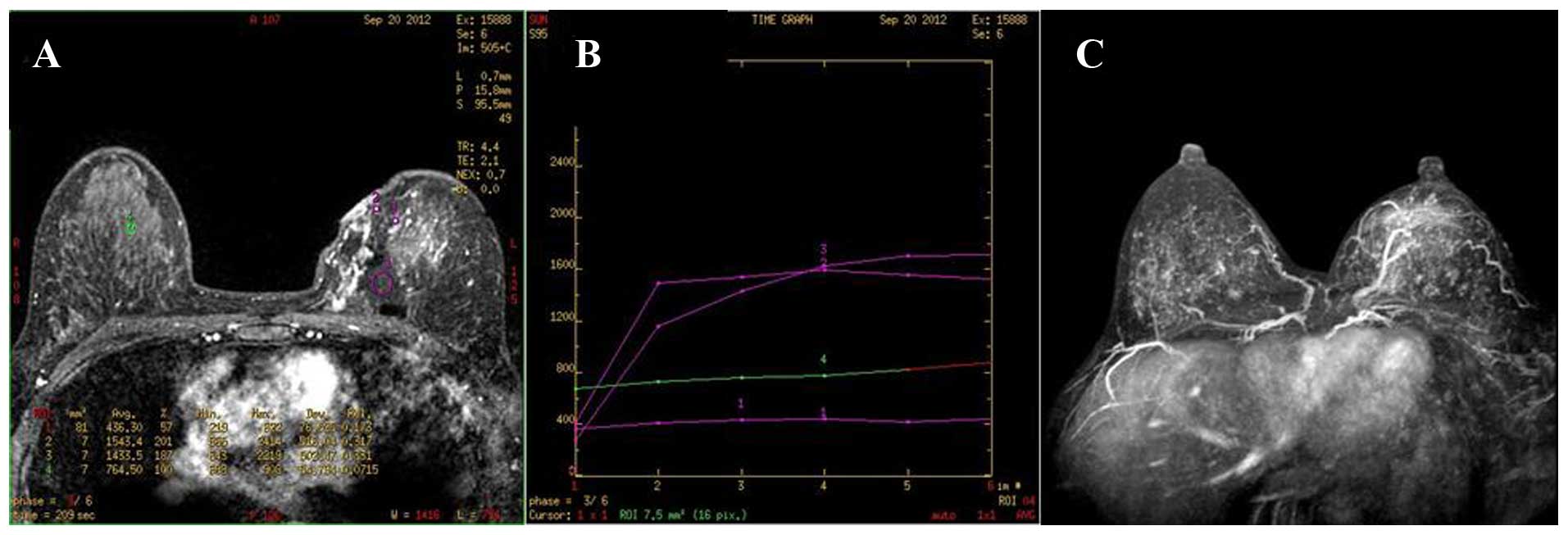
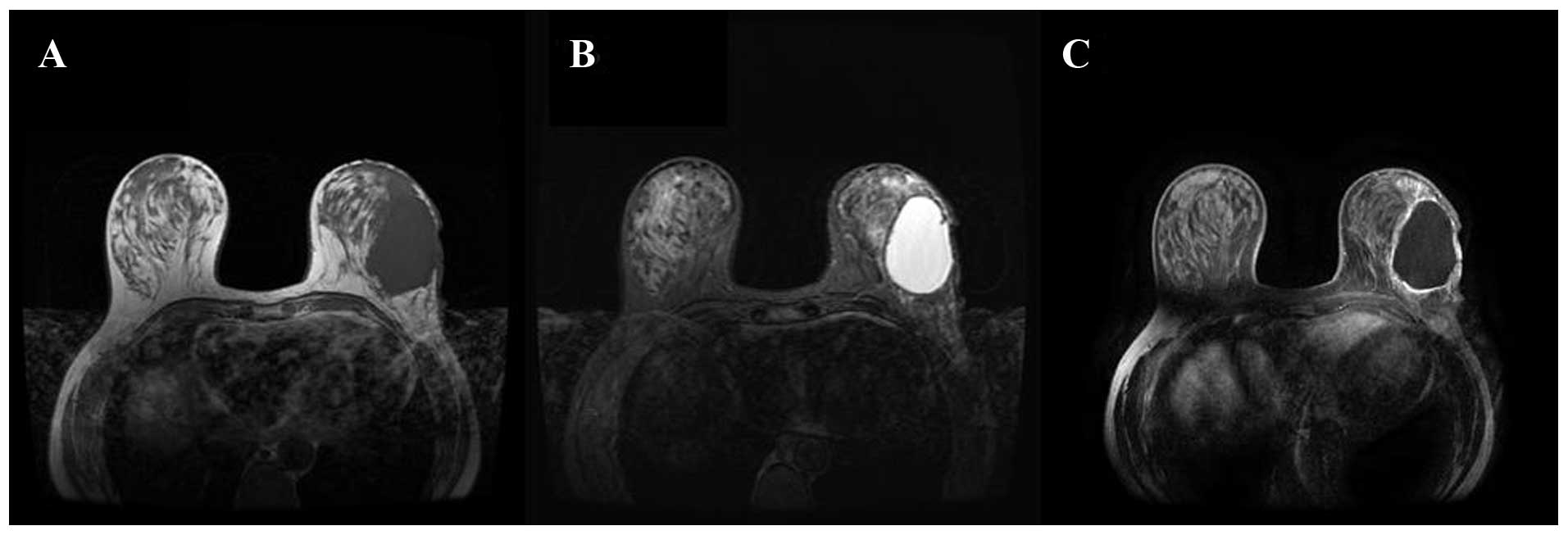
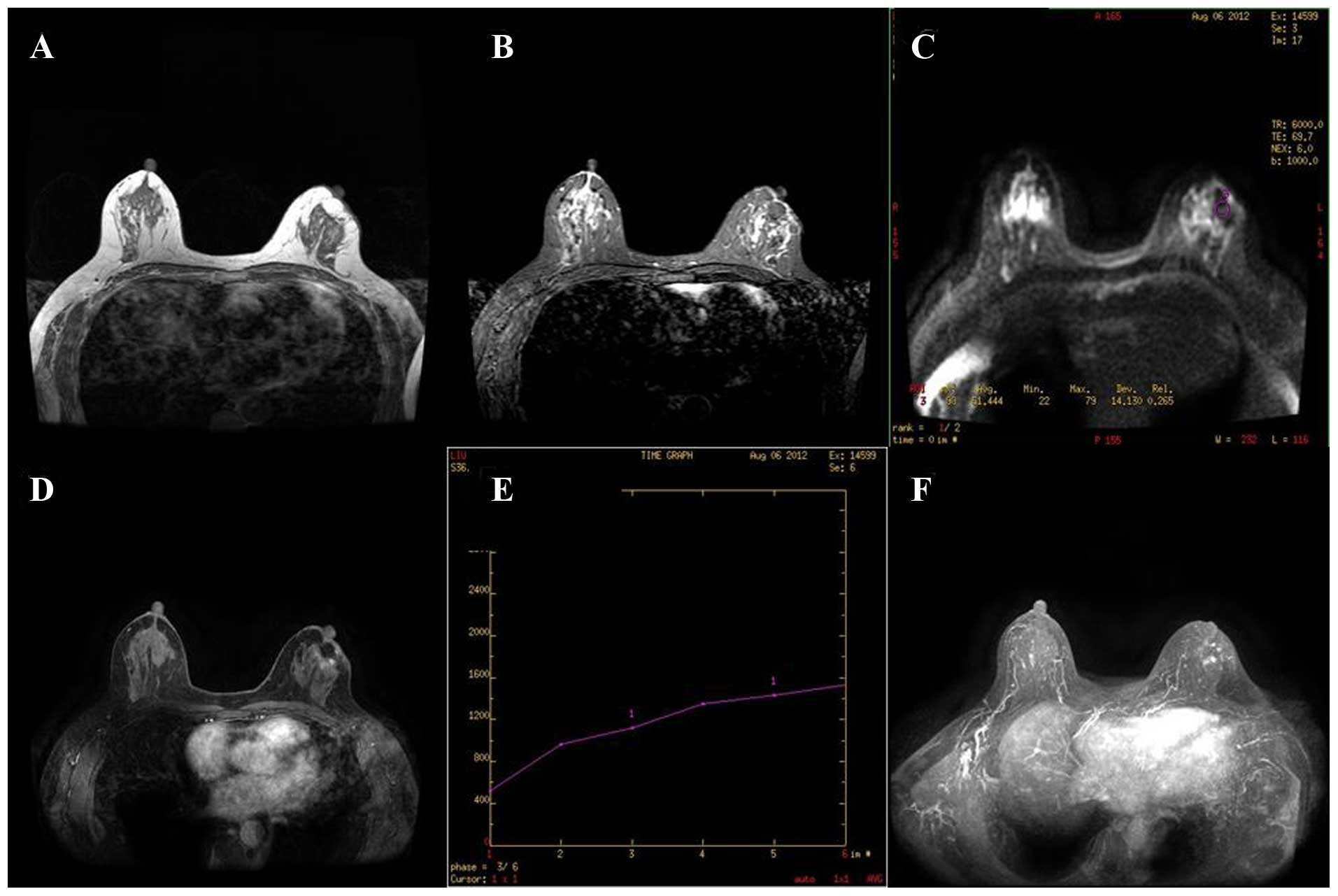
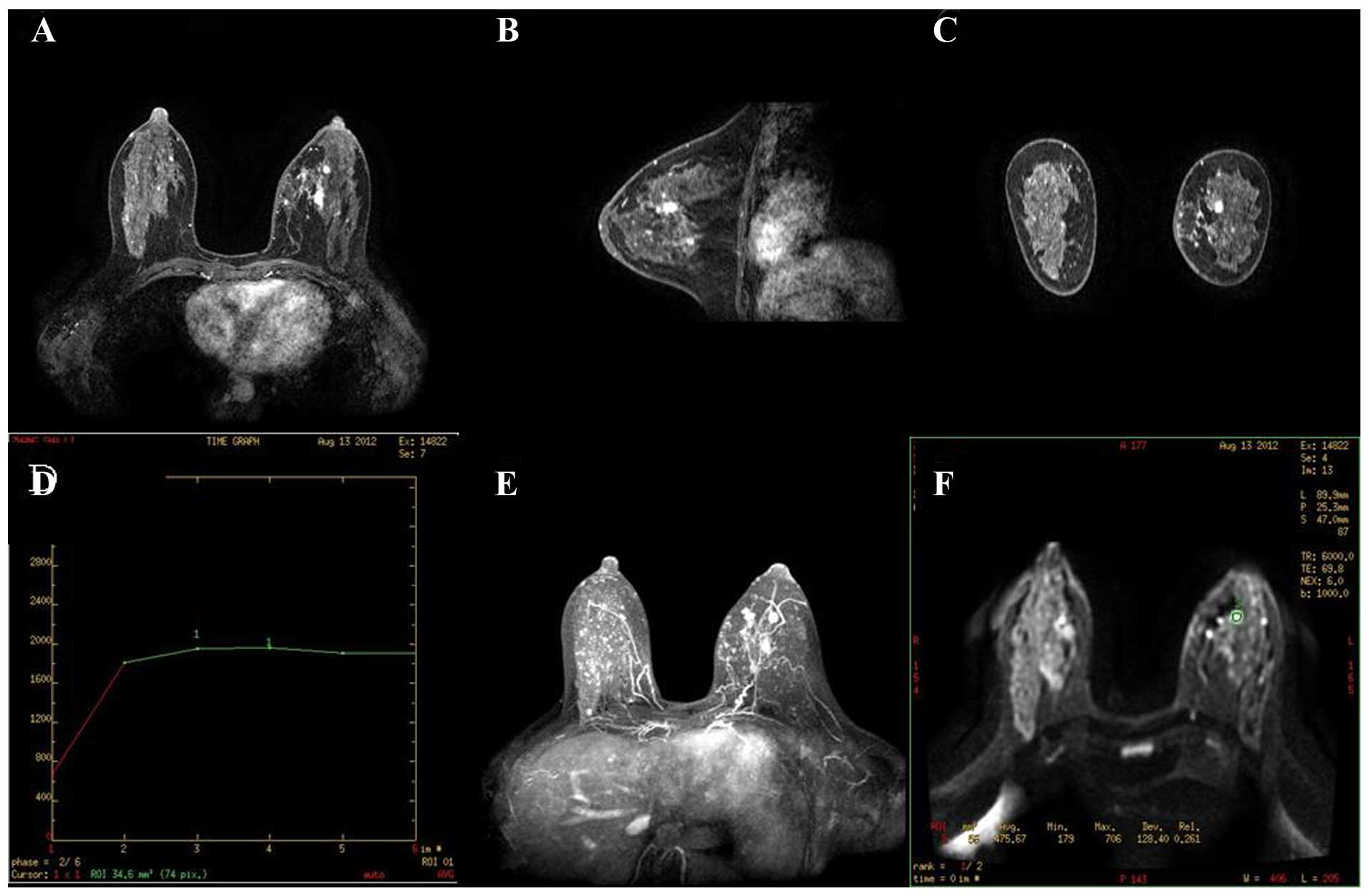
|
1
|
Murray PJ, Wivell G and Denton E: Breast
cancer screening and diagnosis in the 21st century within the UK.
Post Reprod Health. 21:105–111. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pak F, Kanan HR and Alikhassi A: Breast
cancer detection and classification in digital mammography based on
non-subsampled contourlet transform (NSCT) and Super resolution.
Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 122:89–107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mann RM, Balleyguier C, Baltzer PA, Bick
U, Colin C, Cornford E, Evans A, Fallenberg E, Forrai G, Fuchsjäger
MH, et al: Breast MRI: EUSOBI recommendations for women's
information. Eur Radiol. 25:3669–3678. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chetlen A, Mack J and Chan T: Breast
cancer screening controversies: Who, when, why, and how? Clin
Imaging. 2015.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Giess CS, Yeh ED, Raza S and Birdwell RL:
Background parenchymal enhancement at breast MR imaging: Normal
patterns, diagnostic challenges and potential for false-positive
and false-negative interpretation. Radiographics. 34:234–247. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
El-Bolkainy TM, Shabaan HA, Abodeif WT,
El-Bolkainy MN and El-Tony A: Intra-operative diagnosis of breast
mass-lesions: Comparison of the validity of touch smear preparation
and frozen section techniques. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 20:63–69.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Niu Y, Fu XL, Yu Y, Wang PP and Cao XC:
Intra-operative frozen section diagnosis of breast lesions: A
retrospective analysis of 13,243 Chinese patients. Chin Med J
(Engl). 120:630–615. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wen MC, Chen JT and Ho WL: Frozen-section
diagnosis in surgical pathology: A quality assurance study.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 13:534–539. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Law Y, Cheung PS, Lau S and Lo GG: Impact
of magnetic resonance imaging on preoperative planning for breast
cancer surgery. Hong Kong Med J. 19:294–299. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Houssami N, Turner R and Morrow M:
Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging in breast cancer:
Meta-analysis of surgical outcomes. Ann Surg. 257:249–255. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vilar VS, Goldman SM, Ricci MD, et al:
Analysis by MRI of residual tumor after radiofrequency ablation for
early stage breast cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 198:W285–W291.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yili Z, Xiaoyan H, Hongwen D, Yun Z, Xin
C, Peng W and Youmin G: The value of diffusion-weighted imaging in
assessing the ADC changes of tissues adjacent to breast carcinoma.
BMC Cancer. 9:182009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brunner AH, Sagmeister T, Kremer J, Riss P
and Brustmann H: The accuracy of frozen section analysis in
ultrasound- guided core needle biopsy of breast lesions. BMC
Cancer. 9:3412009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bellolio JE, Guzmán GP, Orellana CJ, Roa
SJC, Villaseca HM, Araya OJC, Tapia EO and Ineda NV: Diagnostic
value of frozen section biopsy during surgery for breast lesions or
neoplasms. Rev Med Chil. 137:1173–1178. 2009.(In Spanish).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Geramizadeh B, Larijani TR, Owji SM,
Attaran SY, Torabinejad S, Aslani FS, Monabati A, Kumar PV and
Tabei SZ: Accuracy of intra-operative frozen section consultation
in south of Iran during four years. Indian J Pathol Microbiol.
53:414–417. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brun JL, Cortez A, Rouzier R, Callard P,
Bazot M, Uzan S and Daraï E: Factors influencing the use and
accuracy of frozen section diagnosis of epithelial ovarian tumors.
Am J Obstet Gynecol. 199:244.e1–e7. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kim JH, Kim TJ, Park YG, Lee SH, Lee CW,
Song MJ, Lee KH, Hur SY, Bae SN and Park JS: Clinical analysis of
intra-operative frozen section proven borderline tumors of the
ovary. Gynecol Oncol. 20:176–180. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Slama J, Dundr P, Dusek L and Cibula D:
High false negative rate of frozen section examination of sentinel
lymph nodes in patients with cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
129:384–388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saunders C and Taylor D: Expanding the
indications for MRI in the diagnosis and treatment of breast
cancer: What is best practice? J Med Radiat Sci. 62:47–53. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Almotairi M, Oudjhane K and Chavhan GB:
Pediatric multifocal liver lesions evaluated by MRI. Indian J
Radiol Imaging. 25:296–302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kuijs VJ, Moossdorff M, Schipper RJ,
Beets-Tan RG, Heuts EM, Keymeulen KB, Smidt ML and Lobbes MB: The
role of MRI in axillary lymph node imaging in breast cancer
patients: A systematic review. Insights Imaging. 6:203–215. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chae EY, Cha JH, Kim HH, et al: Evaluation
of residual disease using breast MRI after excisional biopsy for
breast cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 200:1167–1173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rovera F, Masciocchi P, Coglitore A, La
Rosa S, Dionigi G, Marelli M, Boni L and Dionigi R: Neuroendocrine
carcinomas of the breast. Int J Surg. 6(Suppl 1): S113–S115. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|