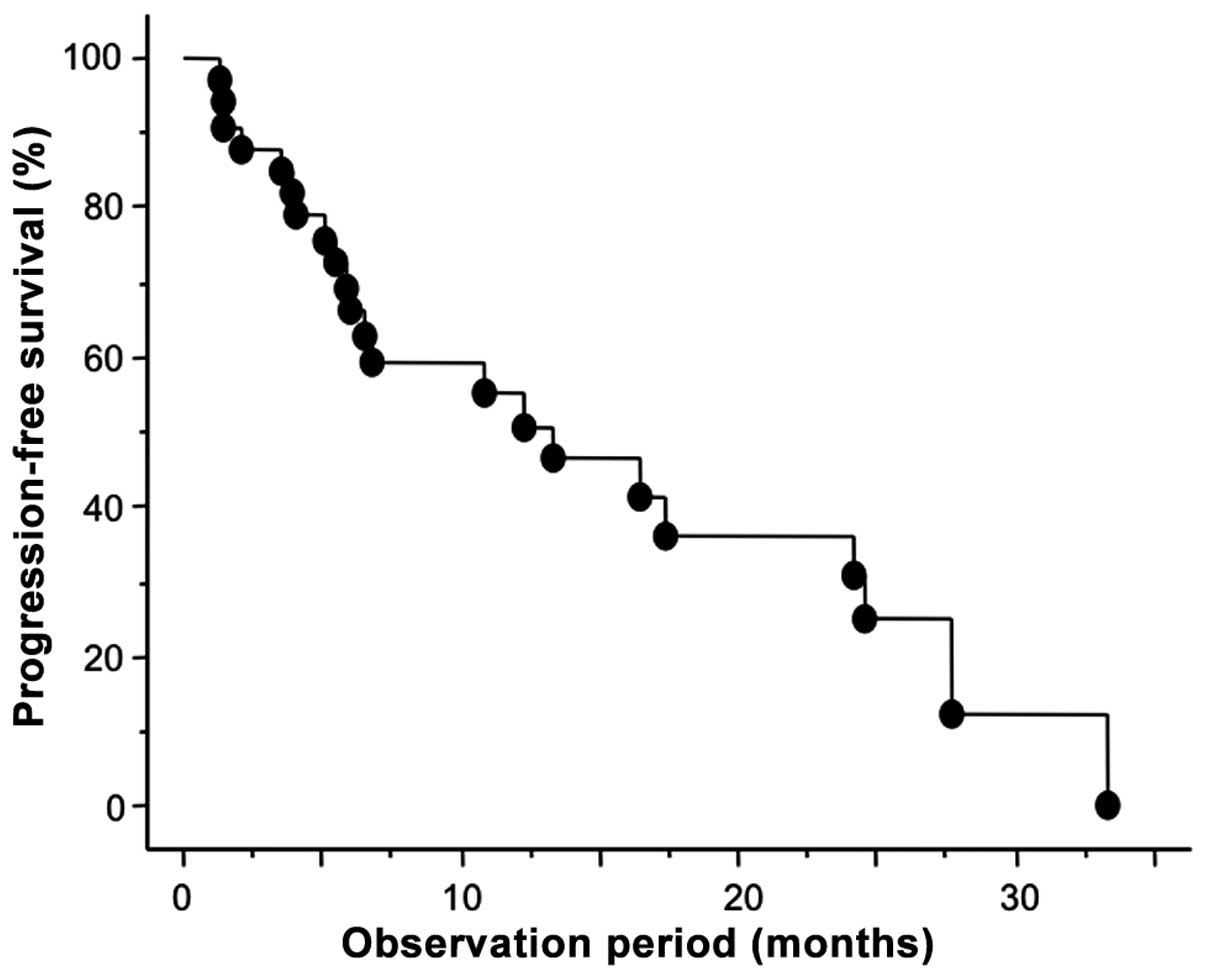
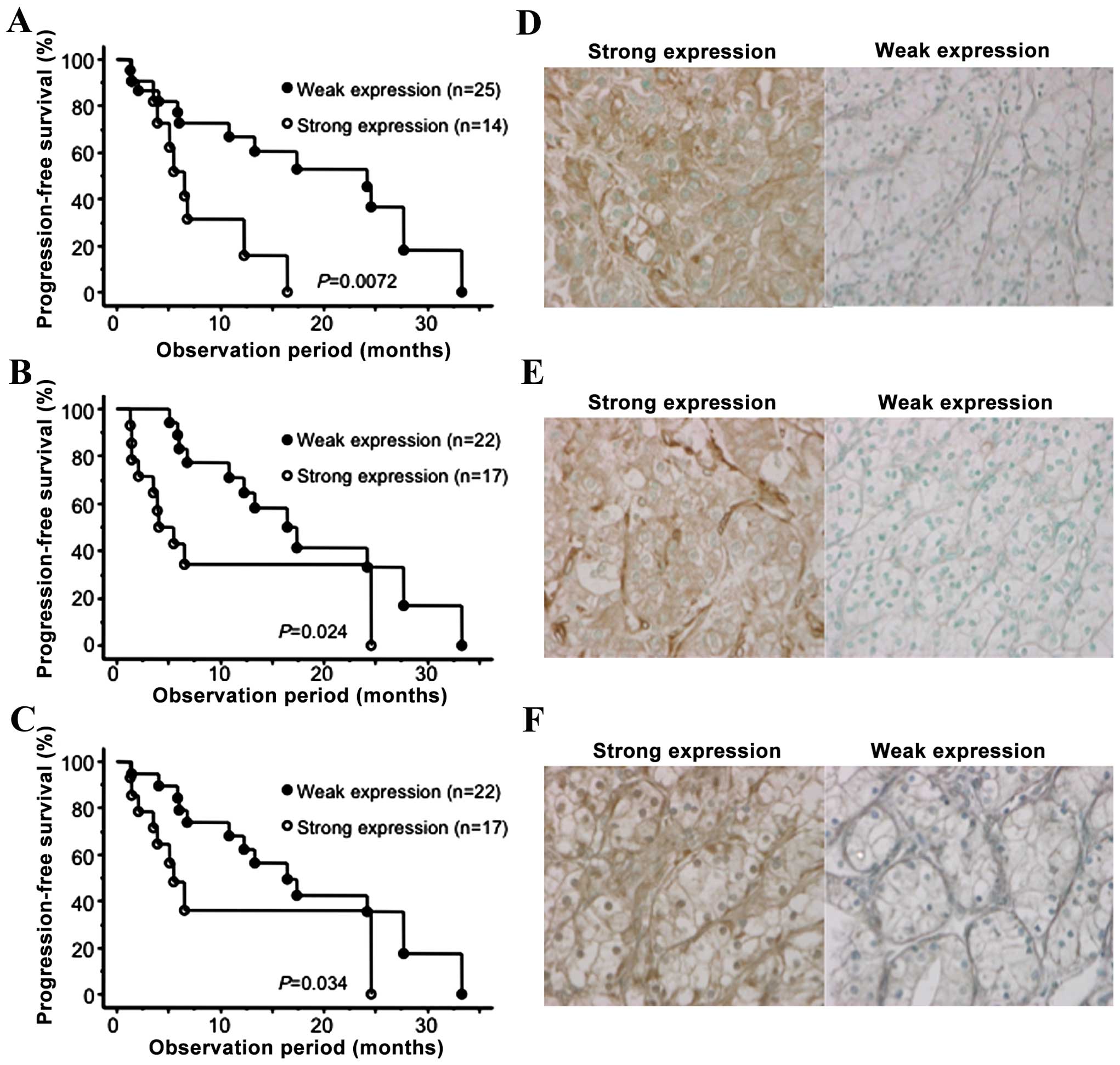
|
1
|
Rini BI, Rathmell WK and Godley P: Renal
cell carcinoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 20:300–306. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parton M, Gore M and Eisen T: Role of
cytokine therapy in 2006 and beyond for metastatic renal cell
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 24:5584–5592. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Figlin R, Sternberg C and Wood CG: Novel
agents and approaches for advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Urol.
188:707–715. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gan HK, Seruga B and Knox JJ: Sunitinib in
solid tumors. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 18:821–834. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mendel DB, Laird AD, Xin X, Louie SG,
Christensen JG, Li G, Schreck RE, Abrams TJ, Ngai TJ, Lee LB, et
al: In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase
inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and
platelet-derived growth factor receptors: Determination of a
pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin Cancer Res.
9:327–337. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P,
Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik
C, Kim ST, et al: Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 356:115–124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hutson TE, Figlin RA, Kuhn JG and Motzer
RJ: Targeted therapies for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: An
overview of toxicity and dosing strategies. Oncologist.
13:1084–1096. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Motzer RJ, Bacik J, Murphy BA, Russo P and
Mazumdar M: Interferon-alfa as a comparative treatment for clinical
trials of new therapies against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J
Clin Oncol. 20:289–296. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, Warren MA,
Golshayan AR, Sahi C, Eigl BJ, Ruether JD, Cheng T, North S, et al:
Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic
renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth
factor-targeted agents: Results from a large, multicenter study. J
Clin Oncol. 27:5794–5792. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Su D, Singer EA and Srinivasan R:
Molecular pathways in renal cell carcinoma: Recent advances in
genetics and molecular biology. Curr Opin Oncol. 27:217–223. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ruch JM and Kim EJ: Hedgehog signaling
pathway and cancer therapeutics: Progress to date. Drugs.
73:613–623. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Karnofsky DA, Abelmann WH, Craver LF and
Burchenal JH: The use of nitrogen mustards in the palliative
treatment of carcinoma. With particular reference to bronchogenic
carcinoma. Cancer. 1:634–656. 1948. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz A,
Balch CM, Haller DG and Morrow M: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual (6th).
Springer. New York, NY: 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kususda Y, Miyake H, Gleave ME and
Fujisawa M: Clusterin inhibition using OGX-011 synergistically
enhances antitumour activity of sorafenib in a human renal cell
carcinoma model. Br J Cancer. 106:1945–1952. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miyake H, Muramaki M, Kurahashi T,
Takenaka A and Fujisawa M: Expression of potential molecular
markers in prostate cancer: Correlation with clinicopathological
outcomes in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. Urol Oncol.
28:145–151. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li J, Wu T, Lu J, Cao Y, Song N, Yang T,
Dong R, Yang Y, Zang L, Du X and Wang S: Immunohistochemical
evidence of the prognostic value of hedgehog pathway components in
primary gallbladder carcinoma. Surg Today. 42:770–775. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sakai I, Miyake H and Fujisawa M: Acquired
resistance to sunitinib in human renal cell carcinoma cells is
mediated by constitutive activation of signal transduction pathways
associated with tumour cell proliferation. BJU Int. 112:E211–E220.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gore ME, Szczylik C, Porta C, Bracarda S,
Bjarnason GA, Oudard S, Hariharan S, Lee SH, Haanen J, Castellano
D, et al: Safety and efficacy of sunitinib for metastatic
renal-cell carcinoma: An expanded-access trial. Lancet Oncol.
10:757–763. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Miyake H, Miyazaki A, Harada K and
Fujisawa M: Assessment of efficacy, safety and quality of life of
110 patients treated with sunitinib as first-line therapy for
metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Experience in real-world clinical
practice in Japan. Med Oncol. 31:9782014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yuasa T, Takahashi S, Hatake K, Yonese J
and Fukui I: Biomarkers to predict response to sunitinib therapy
and prognosis in metastatic renal cell cancer. Cancer Sci.
102:1949–1957. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miyake H, Nishikawa M, Tei H, Furukawa J,
Harada K and Fujisawa M: Significance of circulating matrix
metalloproteinase-9 to tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2
ratio as a predictor of disease progression in patients with
metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving sunitinib. Urol Oncol.
32:584–588. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dormoy V, Danilin S, Lindner V, Thomas L,
Rothhut S, Coquard C, Helwig JJ, Jacqmin D, Lang H and Massfelder
T: The sonic hedgehog signaling pathway is reactivated in human
renal cell carcinoma and plays orchestral role in tumor growth. Mol
Cancer. 8:1232009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
D'Amato C, Rosa R, Marciano R, D'Amato V,
Formisano L, Nappi L, Raimondo L, Di Mauro C, Servetto A, Fulciniti
F, et al: Inhibition of Hedgehog signalling by NVP-LDE225
(Erismodegib) interferes with growth and invasion of human renal
cell carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 111:1168–1179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou J, Wu K, Gao D, Zhu G, Wu D, Wang X,
Chen Y, Du Y, Song W, Ma Z, et al: Reciprocal regulation of
hypoxia-inducible factor 2α and GLI1 expression associated with the
radioresistance of renal cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 90:942–951. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deprimo SE, Bello CL, Smeraglia J, Baum
CM, Spinella D, Rini BI, Michaelson MD, Motzer RJ, et al:
Circulating protein biomarkers of pharmacodynamic activity of
sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma:
Modulation of VEGF and VEGF-related proteins. J Transl Med.
5:322007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kontovinis LF, Papazisis KT, Touplikioti
P, Andreadis C, Mouratidou D and Kortsaris AH: Sunitinib treatment
for patients with clear-cell metastatic renal cell carcinoma:
Clinical outcomes and plasma angiogenesis markers. BMC Cancer.
9:822009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Javelaud D, Alexaki VI, Dennler S,
Mohammad KS, Guise TA and Mauviel A: TGF-β/SMAD/GLI2 signaling axis
in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Res. 71:5606–5610.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Grachtchouk M, Mo R, Yu S, Zhang X, Sasaki
H, Hui CC and Dlugosz AA: Basal cell carcinomas in mice
overexpressing Gli2 in skin. Nat Genet. 24:216–217. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Narita S, So A, Ettinger S, Hayashi N,
Muramaki M, Fazli L, Kim Y and Gleave ME: GLI2 knockdown using an
antisense oligonucleotide induces apoptosis and chemosensitizes
cells to paclitaxel in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:5769–5777. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang D, Ding Y, Zhou M, Rini BI, Petillo
D, Qian CN, Kahnoski R, Futreal PA, Furge KA and Teh BT:
Interleukin-8 mediates resistance to antiangiogenic agent sunitinib
in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 70:1063–1071. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hammers HJ, Verheul HM, Salumbides B,
Sharma R, Rudek M, Jaspers J, Shah P, Ellis L, Shen L, Paesante S,
et al: Reversible epithelial to mesenchymal transition and acquired
resistance to sunitinib in patients with renal cell carcinoma:
Evidence from a xenograft study. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:1525–1535.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|