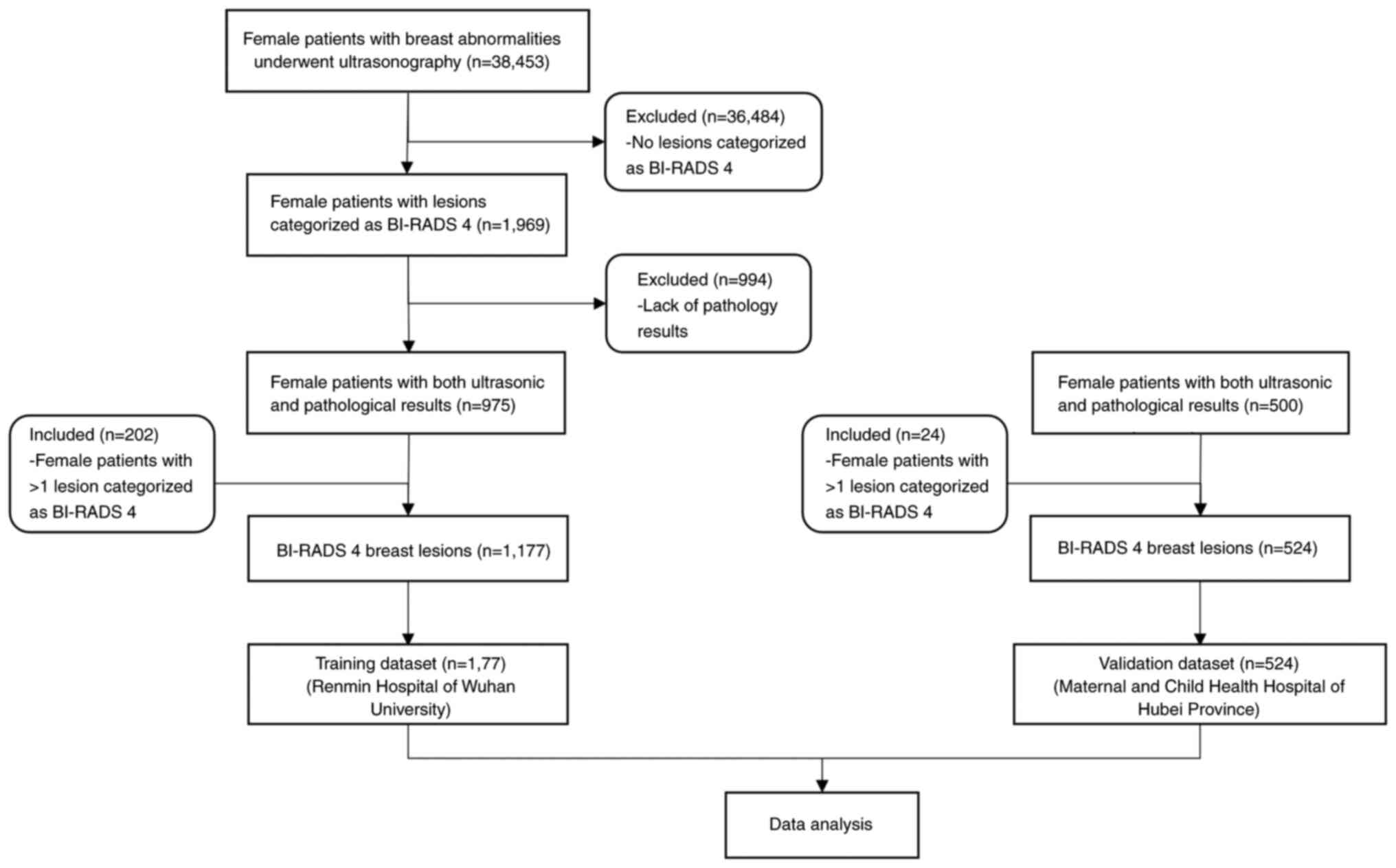
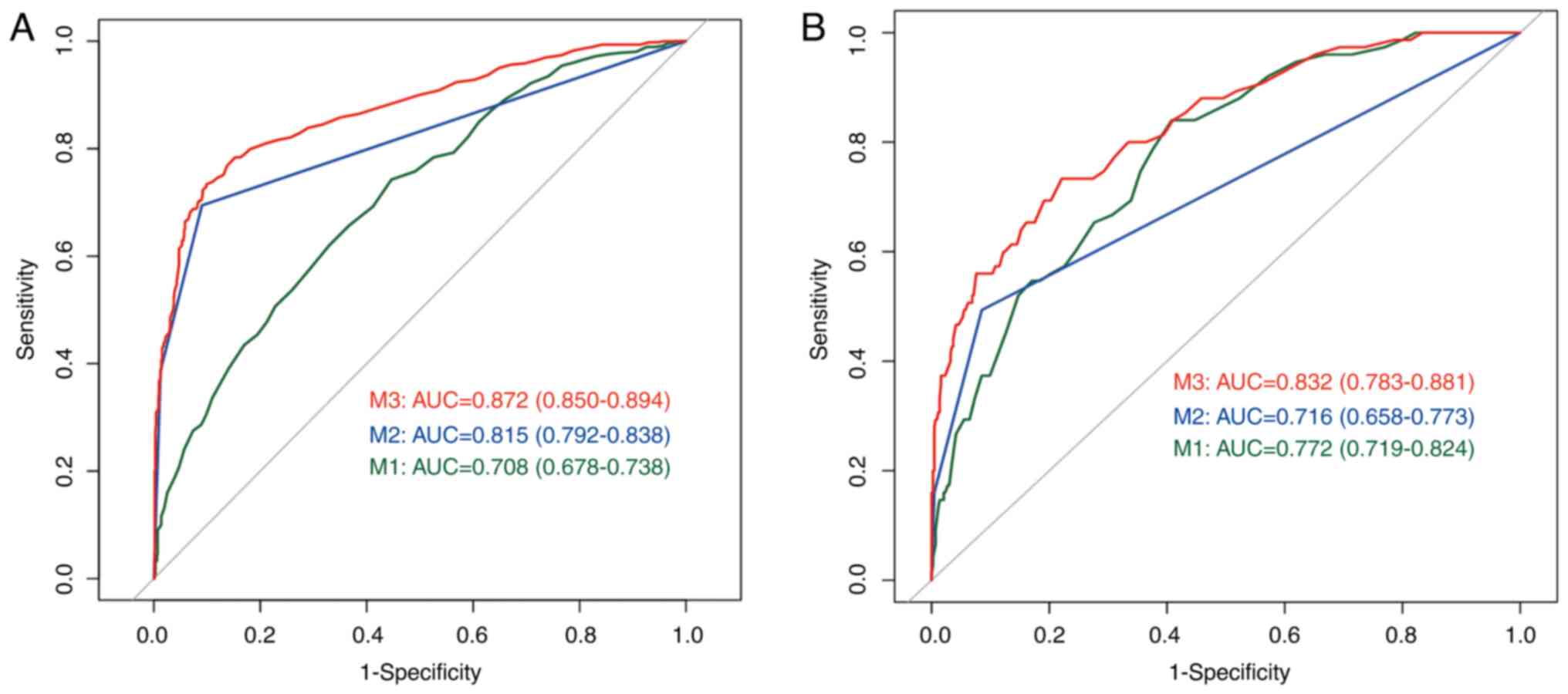
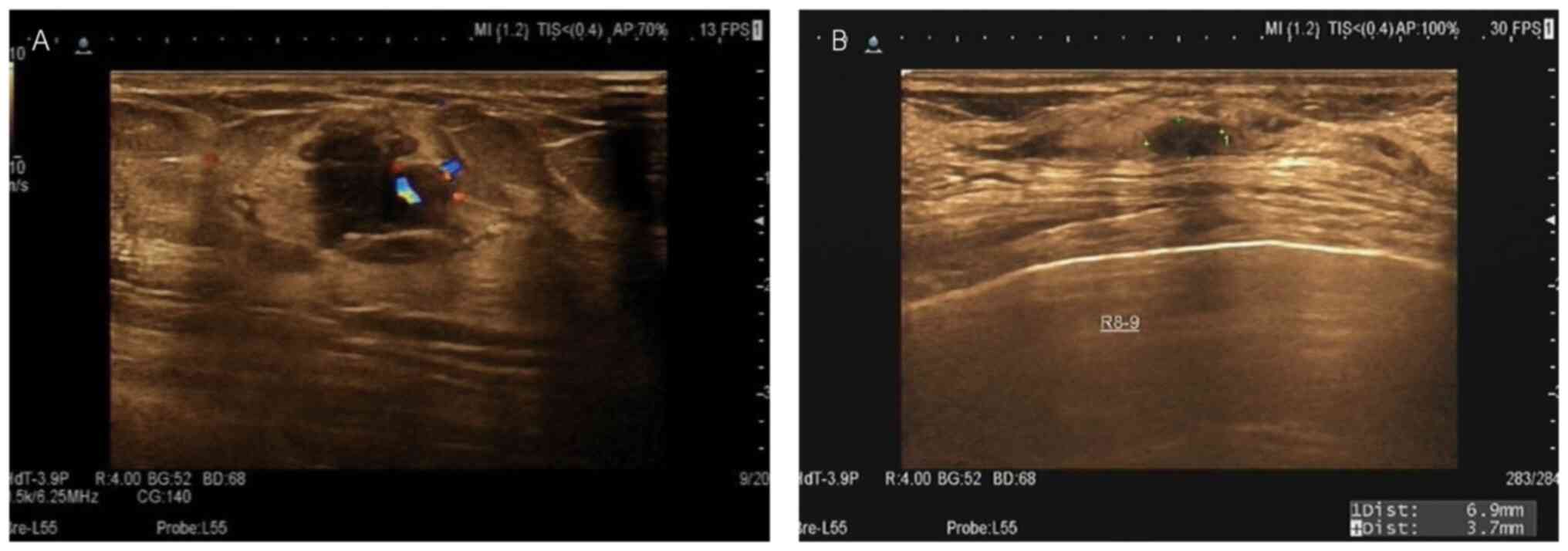
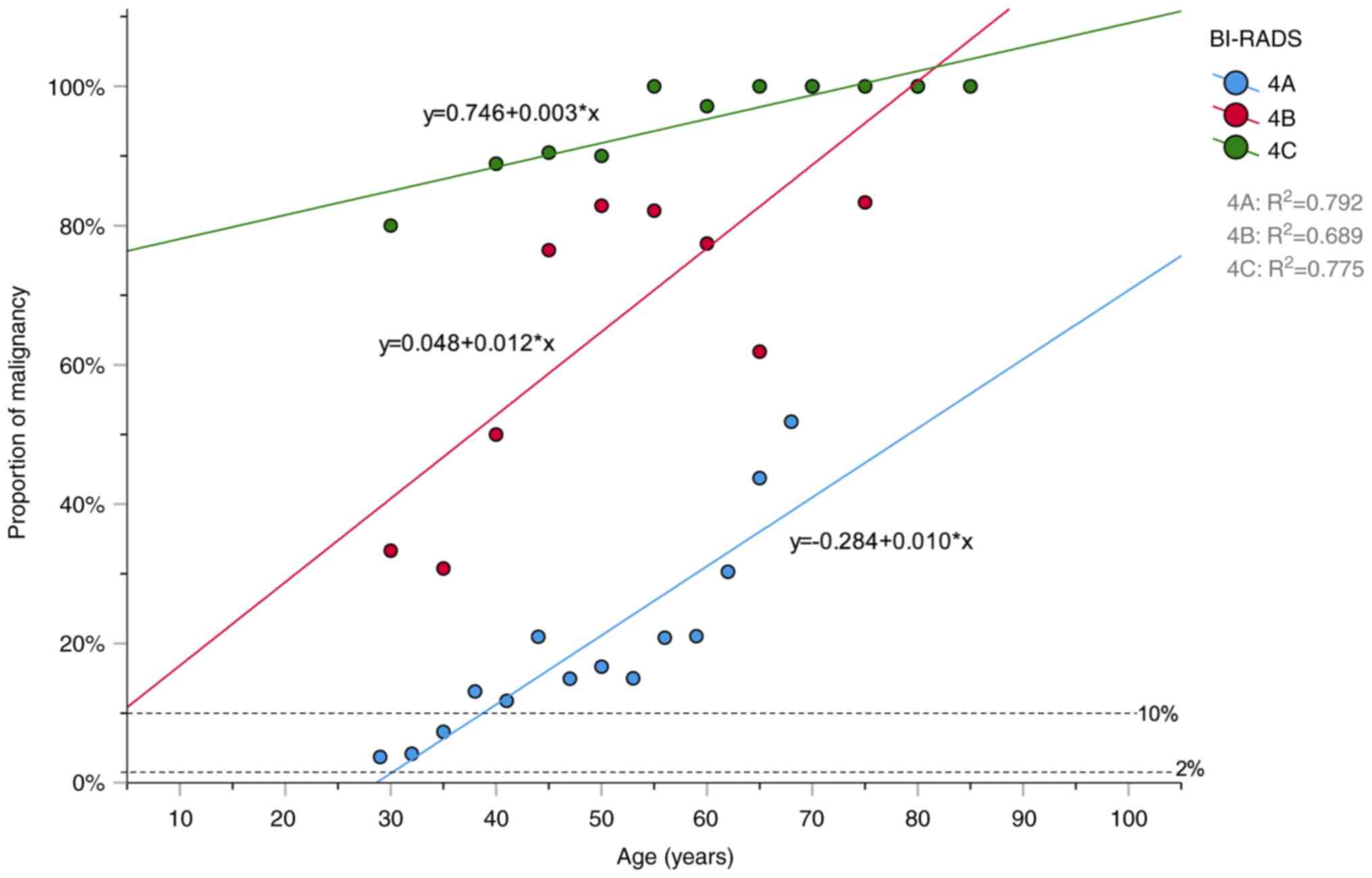
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–48.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tagliafico AS, Piana M, Schenone D, Lai R,
Massone AM and Houssami N: Overview of radiomics in breast cancer
diagnosis and prognostication. Breast. 49:74–80. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bevers TB, Helvie M, Bonaccio E, Calhoun
KE, DalyMB FarrarWB, Garber JE, Gray R, Greenberg CC, Greenup R, et
al: Breast cancer screening and diagnosis, version 3.2018, NCCN
clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
16:1362–1389. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Salmanoglu E, Klinger K, Bhimani C,
Sevrukov A and Thakur ML: Advanced approaches to imaging primary
breast cancer: An update. Clin Transl Imaging. 7:381–404. 2019.
|
|
5
|
Chong A, Weinstein SP, McDonald ES and
Conant EF: Digital breast tomosynthesis: Concepts and clinical
practice. Radiology. 292:1–14. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hou XY, Niu HY, Huang XL and Gao Y:
Correlation of breast ultrasound classifications with breast cancer
in Chinese women. Ultrasound Med Biol. 42:2616–2621.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Devolli-Disha E, Manxhuka-Kërliu S, Ymeri
H and Kutllovci A: Comparative accuracy of mammography and
ultrasound in women with breast symptoms according to age and
breast density. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 9:131–136. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kuhl CK: Abbreviated magnetic resonance
imaging (MRI) for breast cancer screening: Rationale, concept, and
transfer to clinical practice. Annu Rev Med. 70:501–519.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Magny SJ, Shikhman R and Keppke AL: Breast
imaging reporting and data system. In: StatPearls [Internet].
StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island, FL, 2023.
|
|
10
|
Lazarus E, Mainiero MB, Schepps B,
Koelliker SL and Livingston LS: BI-RADS lexicon for US and
mammography: Interobserver variability and positive predictive
value. Radiology. 239:385–391. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
He P, Cui LG, Chen W and Yang RL:
Subcategorization of ultrasonographic BI-RADS category 4:
Assessment of diagnostic accuracy in diagnosing breast lesions and
influence of clinical factors on positive predictive value.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 45:1253–1258. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hsu W, Zhou X, Petruse A, Chau N,
Lee-Felker S, Hoyt A, Wenger N, Elashoff D and Naeim A: Role of
clinical and imaging risk factors in predicting breast cancer
diagnosis among BI-RADS 4 cases. Clin Breast Cancer. 19:e142–e151.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kang YJ, Ahn SK, Kim SJ, Oh H, Han J and
Ko E: Relationship between mammographic density and age in the
United Arab Emirates population. J Oncol.
2019(7351350)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
McGuire A, Brown JAL, Malone C, McLaughlin
R and Kerin MJ: Effects of age on the detection and management of
breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 7:908–929. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Clendenen TV, Ge W, Koenig KL, Afanasyeva
Y, Agnoli C, Brinton LA, Darvishian F, Dorgan JF, Eliassen AH, Falk
RT, et al: Breast cancer risk prediction in women aged 35-50 years:
Impact of including sex hormone concentrations in the gail model.
Breast Cancer Research. 21(42)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:52–62.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Leong SP, Shen ZZ, Liu TJ, Agarwal G,
Tajima T, Paik NS, Sandelin K, Derossis A, Cody H, Foulkes WD, et
al: Is breast cancer the same disease in Asian and Western
countries? World J Surg. 34:2308–2324. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Spinelli Varella MA, Teixeira da Cruz J,
Rauber A, Varella IS, Fleck JF and Moreira LF: Role of BI-RADS
ultrasound subcategories 4A to 4C in predicting breast cancer. Clin
Breast Cancer. 18:e507–e511. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Raza S, Chikarmane SA, Neilsen SS, Zorn LM
and Birdwell RL: BI-RADS 3, 4, and 5 lesions: Value of US in
managementfollow-up and outcome. Radiology. 248:773–781.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cheung A (ed): WHO classification of
tumours 5th edition. World Health Organization, Geneva, 2018.
|
|
21
|
Lei S, Zheng R, Zhang S, Chen R, Wang S,
Sun K, Zeng H, Wei W and He J: Breast cancer incidence and
mortality in women in China: Temporal trends and projections to
2030. Cancer Biol Med. 18:900–909. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ, St Louis
J, Finkelstein DM, Yu KD, Chen WQ, Shao ZM and Goss PE: Breast
cancer in China. Lancet Oncol. 15:e279–e289. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li JW, Zhang K, Shi ZT, Zhang X, Xie J,
Liu JY and Chang C: Triple-negative invasive breast carcinoma: The
association between the sonographic appearances with
clinicopathological feature. Sci Rep. 8(9040)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tian L, Wang L, Qin Y and Cai J:
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the malignant ultrasound
features of triple-negative breast cancer. J Ultrasound Med.
39:2013–2025. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wojcinski S, Soliman AA, Schmidt J,
Makowski L, Degenhardt F and Hillemanns P: Sonographic features of
triple-negative and non-triple-negative breast cancer. J Ultrasound
Med. 31:1531–1541. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang K, Zou Z, Shen H, Huang G and Yang S:
Calcification, posterior acoustic, and blood flow: Ultrasonic
characteristics of triple-negative breast cancer. J Healthc Eng.
2022(9336185)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Fu CY, Hsu HH, Yu JC, Hsu GC, Hsu KF, Chan
DC, Ku CH, Lu TC and Chu CH: Influence of age on PPV of sonographic
BI-RADS categories 3, 4, and 5. Ultraschall Med. 32 (Suppl
1):S8–S13. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hu Y, Yang Y, Gu R, Jin L, Shen S, Liu F,
Wang H, Mei J, Jiang X, Liu Q and Su F: Does patient age affect the
PPV3 of ACR BI-RADS ultrasound categories 4 and 5 in the diagnostic
setting? Eur Radiol. 28:2492–2498. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Noonpradej S, Wangkulangkul P,
Woodtichartpreecha P and Laohawiriyakamol S: Prediction for breast
cancer in BI-RADS category 4 lesion categorized by age and breast
composition of women in Songklanagarind hospital. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 22:531–536. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Xie Y, Zhu Y, Chai W, Zong S, Xu S, Zhan W
and Zhang X: Downgrade BI-RADS 4A patients using nomogram based on
breast magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, and mammography.
Front Oncol. 12(807402)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Engmann NJ, Golmakani MK, Miglioretti DL,
Sprague BL and Kerlikowske K: Breast Cancer Surveillance
Consortium. Population-attributable risk proportion of clinical
risk factors for breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 3:1228–1236.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Corsetti V, Houssami N, Ferrari A,
Ghirardi M, Bellarosa S, Angelini O, Bani C, Sardo P, Remida G,
Galligioni E and Ciatto S: Breast screening with ultrasound in
women with mammography-negative dense breasts: Evidence on
incremental cancer detection and false positives, and associated
cost. Eur J Cancer. 44:539–544. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Le EPV, Wang Y, Huang Y, Hickman S and
Gilbert FJ: Artificial intelligence in breast imaging. Clin Radiol.
74:357–366. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lei YM, Yin M, Yu MH, Yu J, Zeng SE, Lv
WZ, Li J, Ye HR, Cui XW and Dietrich CF: Artificial intelligence in
medical imaging of the breast. Front Oncol.
11(600557)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|