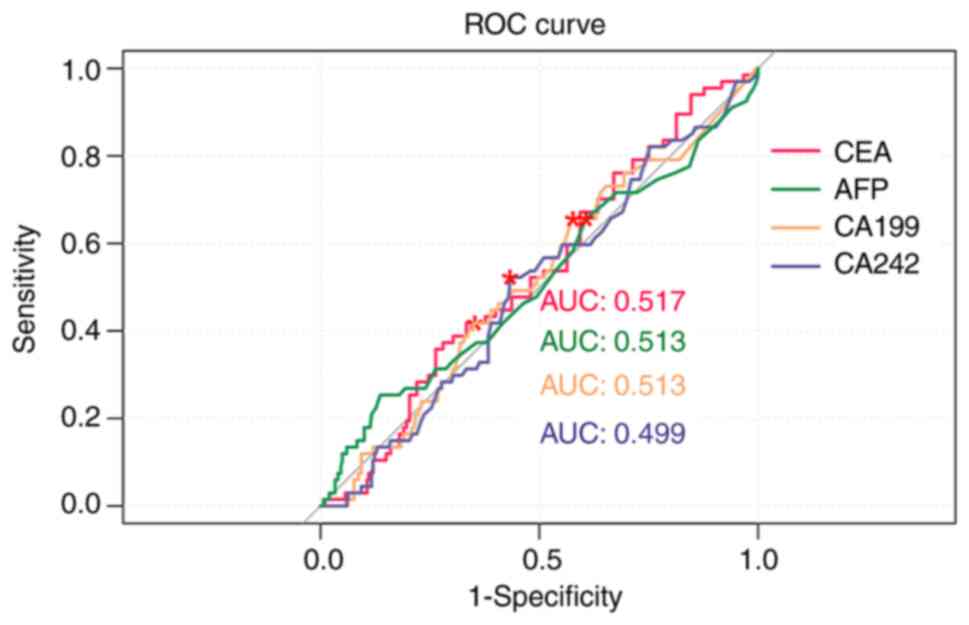
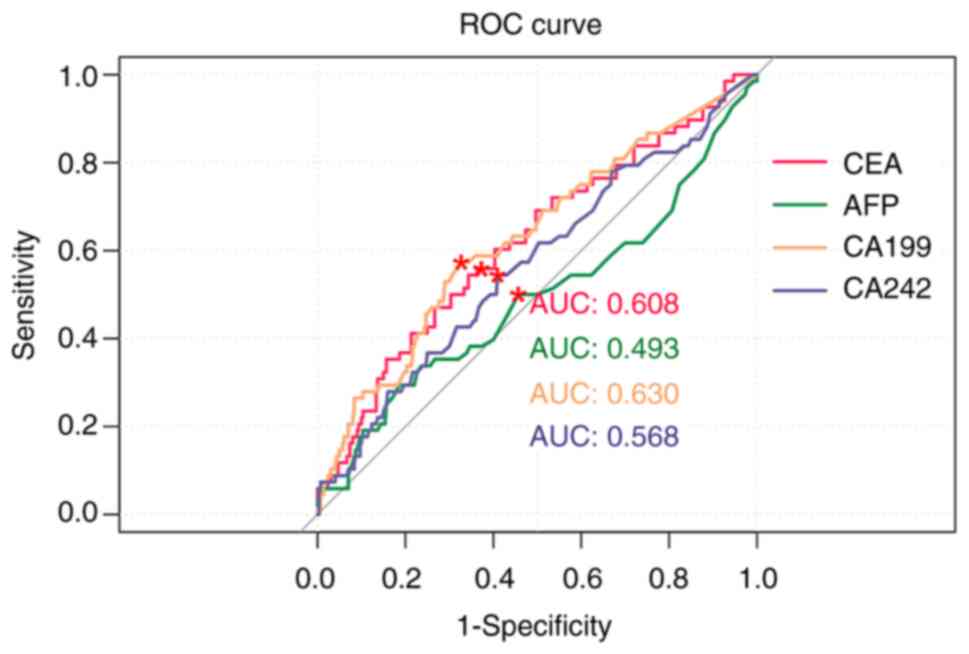
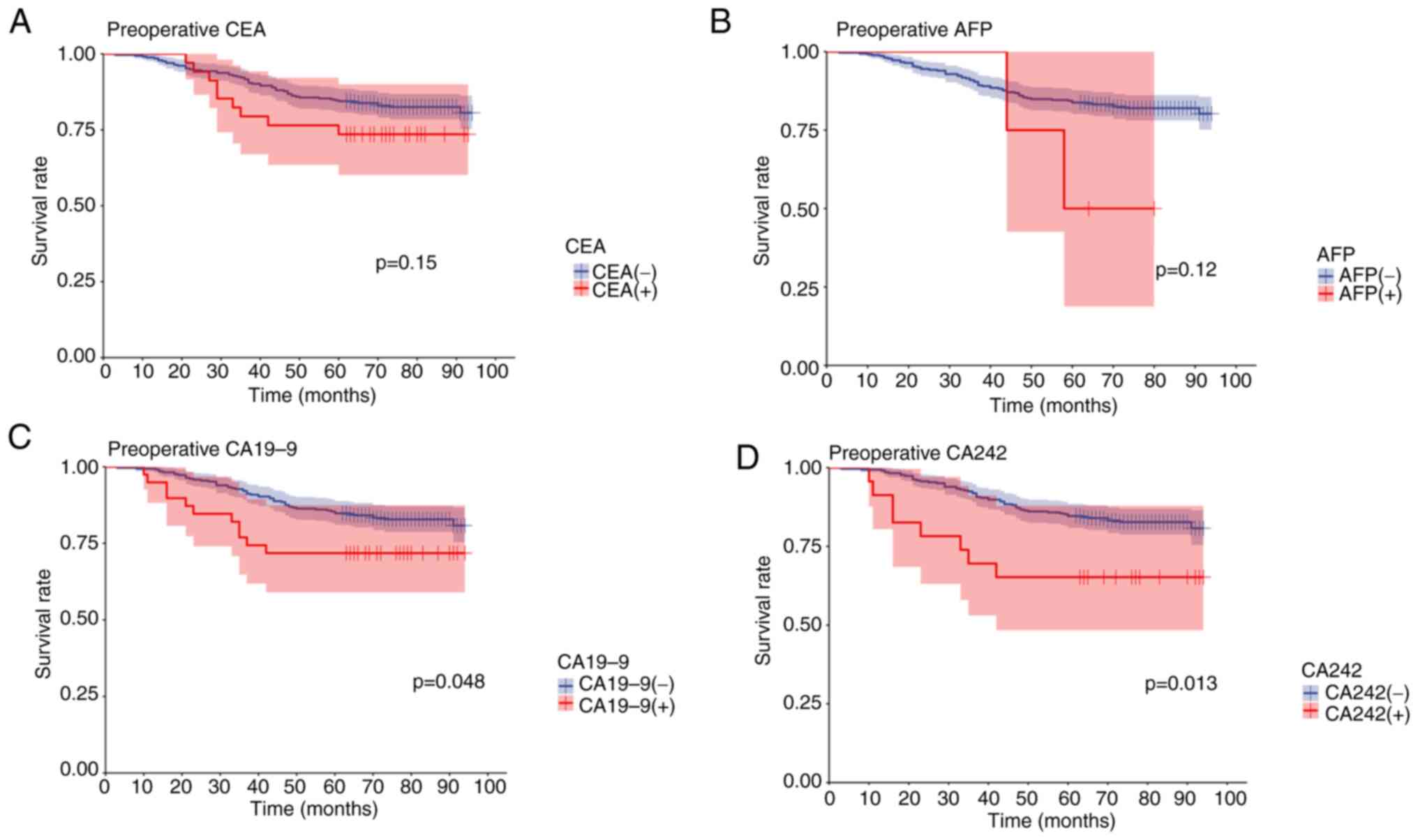
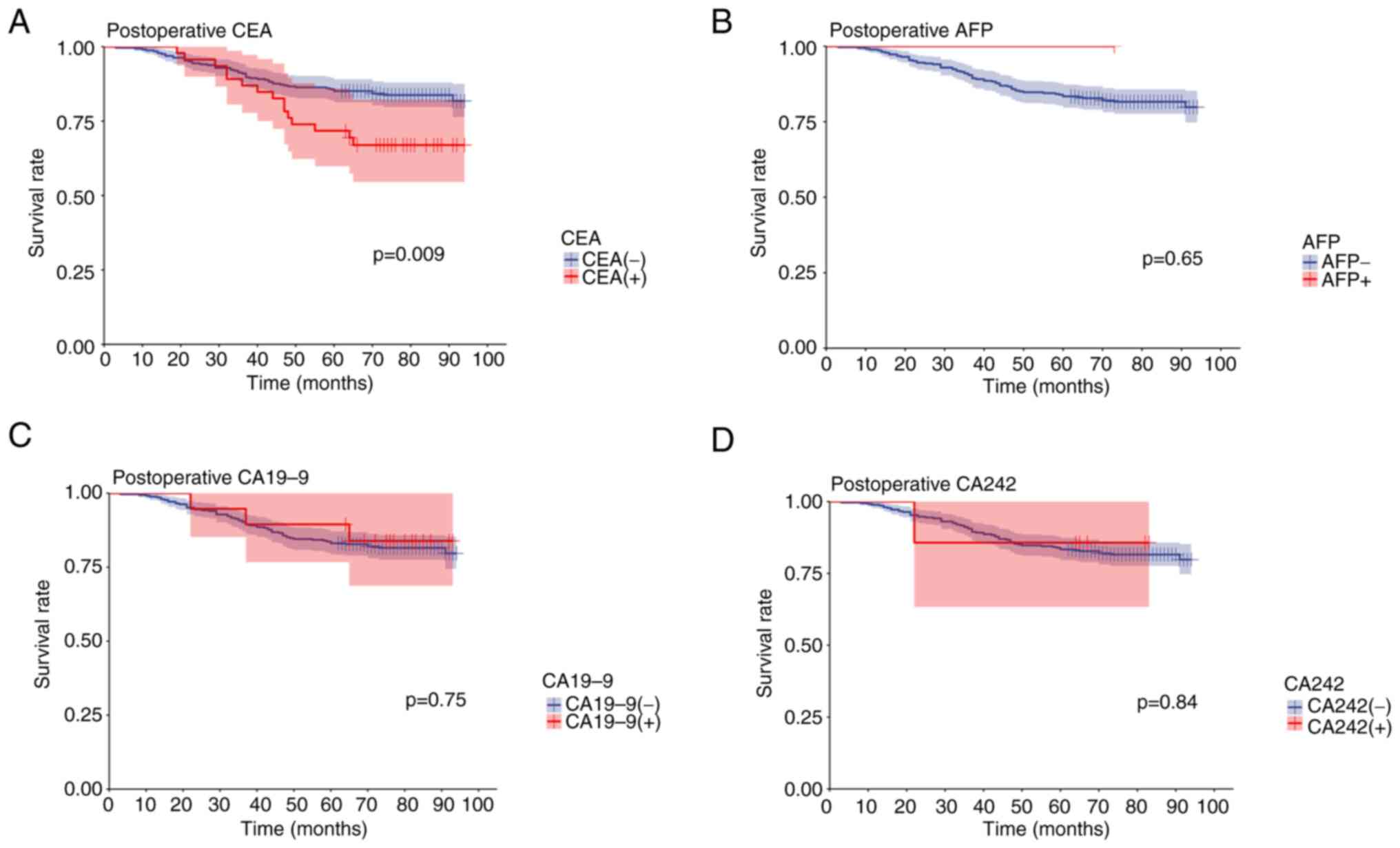
|
1
|
Rocken C: Predictive biomarkers in gastric
cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 149:467–481. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Luan F, Li X, Cheng X, Huangfu L, Han J,
Guo T, Du H, Wen X and Ji J: TNFRSF11B activates Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and promotes gastric cancer progression. Int J Biol Sci.
16:1956–1971. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ajani JA, D'Amico TA, Bentrem DJ, Chao J,
Cooke D, Corvera C, Das P, Enzinger PC, Enzler T, Fanta P, et al:
Gastric cancer, version 2.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines
in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 20:167–192. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van
Grieken NC and Lordick F: Gastric cancer. Lancet. 396:635–648.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rihawi K, Ricci AD, Rizzo A, Brocchi S,
Marasco G, Pastore LV, Llimpe FLR, Golfieri R and Renzulli M:
Tumor-associated macrophages and inflammatory microenvironment in
gastric cancer: Novel translational implications. Int J Mol Sci.
22(3805)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ricci AD, Rizzo A and Brandi G: DNA damage
response alterations in gastric cancer: Knocking down a new wall.
Future Oncol. 17:865–868. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zong L, Abe M, Seto Y and Ji J: The
challenge of screening for early gastric cancer in China. Lancet.
388(2606)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Guven DC, Erul E, Kaygusuz Y, Akagunduz B,
Kilickap S, De Luca R and Rizzo A: Immune checkpoint
inhibitor-related hearing loss: A systematic review and analysis of
individual patient data. Support Care Cancer.
31(624)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rizzo A, Santoni M, Mollica V, Logullo F,
Rosellini M, Marchetti A, Faloppi L, Battelli N and Massari F:
Peripheral neuropathy and headache in cancer patients treated with
immunotherapy and immuno-oncology combinations: The MOUSEION-02
study. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 17:1455–1466.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hadfield MJ, Mistry H, Pelcovits A, Bansal
R, Andrea S, Chergui A, Ramphal K, Austin M and Khurshid H: Risk
factors for immunotherapy-related adverse events (IrAE) in patients
treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Am J Clin Oncol.
46:183–184. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fujiya K, Tokunaga M, Makuuchi R,
Nishiwaki N, Omori H, Takagi W, Hirata F, Hikage M, Tanizawa Y,
Bando E, et al: Early detection of nonperitoneal recurrence may
contribute to survival benefit after curative gastrectomy for
gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 20 (Suppl 1):S141–S149.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Park JS, Choe EA, Park S, Nam CM, Hyung
WJ, Noh SH, Lee S, Kim HS, Jung M, Chung HC and Rha SY: Detection
of asymptomatic recurrence improves survival of gastric cancer
patients. Cancer Med. 10:3249–3260. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shibata C, Nakano T, Yasumoto A, Mitamura
A, Sawada K, Ogawa H, Miura T, Ise I, Takami K, Yamamoto K and
Katayose Y: Comparison of CEA and CA19-9 as a predictive factor for
recurrence after curative gastrectomy in gastric cancer. BMC Surg.
22(213)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zheng CY, Wu J, Chen CS, Huang ZN, Tang
YH, Qiu WW, He QC, Lin GS, Chen QY, Lu J, et al: A scoring model
for predicting early recurrence of gastric cancer with normal
preoperative tumor markers: A multicenter study. Eur J Surg Oncol.
49(107094)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Passos I, Stefanidou E,
Meditskou-Eythymiadou S, Mironidou-Tzouveleki M, Manaki V, Magra V,
Laskou S, Mantalovas S, Pantea S, Kesisoglou I and Sapalidis K: A
review of the significance in measuring preoperative and
postoperative carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) values in patients
with medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC). Medicina (Kaunas).
57(609)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hammarström S: The carcinoembryonic
antigen (CEA) family: Structures, suggested functions and
expression in normal and malignant tissues. Semin Cancer Biol.
9:67–81. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sun W, Liu Y, Shou D, Sun Q, Shi J, Chen
L, Liang T and Gong W: AFP (alpha fetoprotein): Who are you in
gastrology? Cancer Lett. 357:43–46. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kamiimabeppu D, Wakatsuki T, Takahari D,
Fukuda N, Shimozaki K, Osumi H, Nakayama I, Ogura M, Ooki A,
Shinozaki E, et al: Treatment efficacy of ramucirumab-containing
chemotherapy in patients with alpha-fetoprotein producing gastric
cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 28:121–129. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kawahara K, Makino H, Kametaka H, Hoshino
I, Fukada T, Seike K, Kawasaki Y and Otsuka M: Outcomes of surgical
resection for gastric cancer liver metastases: A retrospective
analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 18(41)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mihmanli M, Dilege E, Demir U, Coskun H,
Eroglu T and Uysalol MD: The use of tumor markers as predictors of
prognosis in gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 51:1544–1547.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nakajima K, Ochiai T, Suzuki T, Shimada H,
Hayashi H, Yasumoto A, Takeda A, Hishikawa E and Isono K: Impact of
preoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen, CA 19-9 and alpha
fetoprotein levels in gastric cancer patients. Tumour Biol.
19:464–469. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Moyer S: Pharmacokinetics of naproxen
sodium. Cephalalgia. 6 (Suppl 4):S77–S80. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kochi M, Fujii M, Kanamori N, Kaiga T,
Kawakami T, Aizaki K, Kasahara M, Mochizuki F, Kasakura Y and
Yamagata M: Evaluation of serum CEA and CA19-9 levels as prognostic
factors in patients with gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 3:177–186.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Suenaga Y, Kanda M, Ito S, Mochizuki Y,
Teramoto H, Ishigure K, Murai T, Asada T, Ishiyama A, Matsushita H,
et al: Prognostic significance of perioperative tumor marker levels
in stage II/III gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol.
11:17–27. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wakatsuki K, Matsumoto S, Migita K,
Kunishige T, Nakade H, Miyao S and Sho M: Risk factors and risk
scores for predicting early recurrence after curative gastrectomy
in patients with stage III gastric cancer. J Gastrointest Surg.
24:1758–1769. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yagi S, Kumagai K, Nunobe S, Ishizuka N,
Yamaguchi T, Imai Y, Tsuda M, Haruta S, Fukunaga H, Yamada T and
Goto M: Risk factors for early recurrence after radical gastrectomy
followed by adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II or III gastric
cancer: A multicenter, retrospective study. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
54:403–415. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Nobre KEL, Pereira MA, Ramos MFKP, Ribeiro
U, Zilberstein B, Cecconello I and Dias AR: Recurrence in PN0
gastric cancer: Risk factors in the occident. Arq Bras Cir Dig.
34(e1562)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Jeong SA, Yook JH, Yoo MW, Kim BS, Lee IS,
Kim S, Gong CS and Ko CS: Analysis of risk factors affecting
long-term survival in elderly patients with advanced gastric
cancer. Aging Clin Exp Res. 35:2211–2218. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ma X, Zhou X, Guo J, Feng X, Zhao M, Zhang
P, Zhang C, Gong S, Wu N, Zhang Y, et al: CA19-9 is a significant
prognostic factor in stage III gastric cancer patients undergoing
radical gastrectomy. BMC Surg. 24(31)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
You W, Cai Z, Sheng N, Yan L, Wan H, Wang
Y, Ouyang J, Xie L, Wu X and Wang Z: Construction and validation of
convenient clinicopathologic signatures for predicting the
prognosis of stage I-III gastric cancer. Front Oncol.
12(848783)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kodera Y, Yamamura Y, Torii A, Uesaka K,
Hirai T, Yasui K, Morimoto T, Kato T and Kito T: The prognostic
value of preoperative serum levels of CEA and CA19-9 in patients
with gastric cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 91:49–53. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|