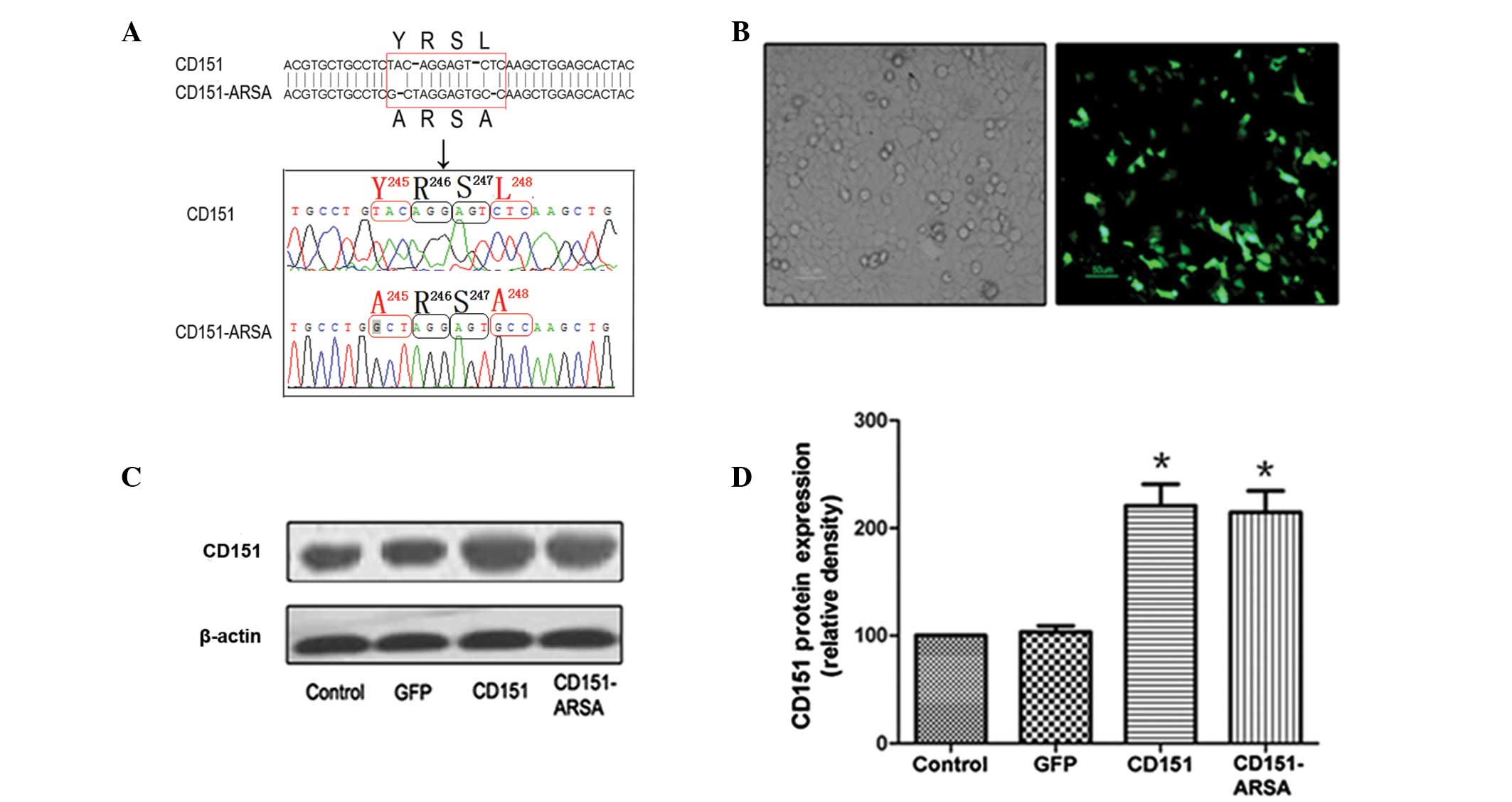
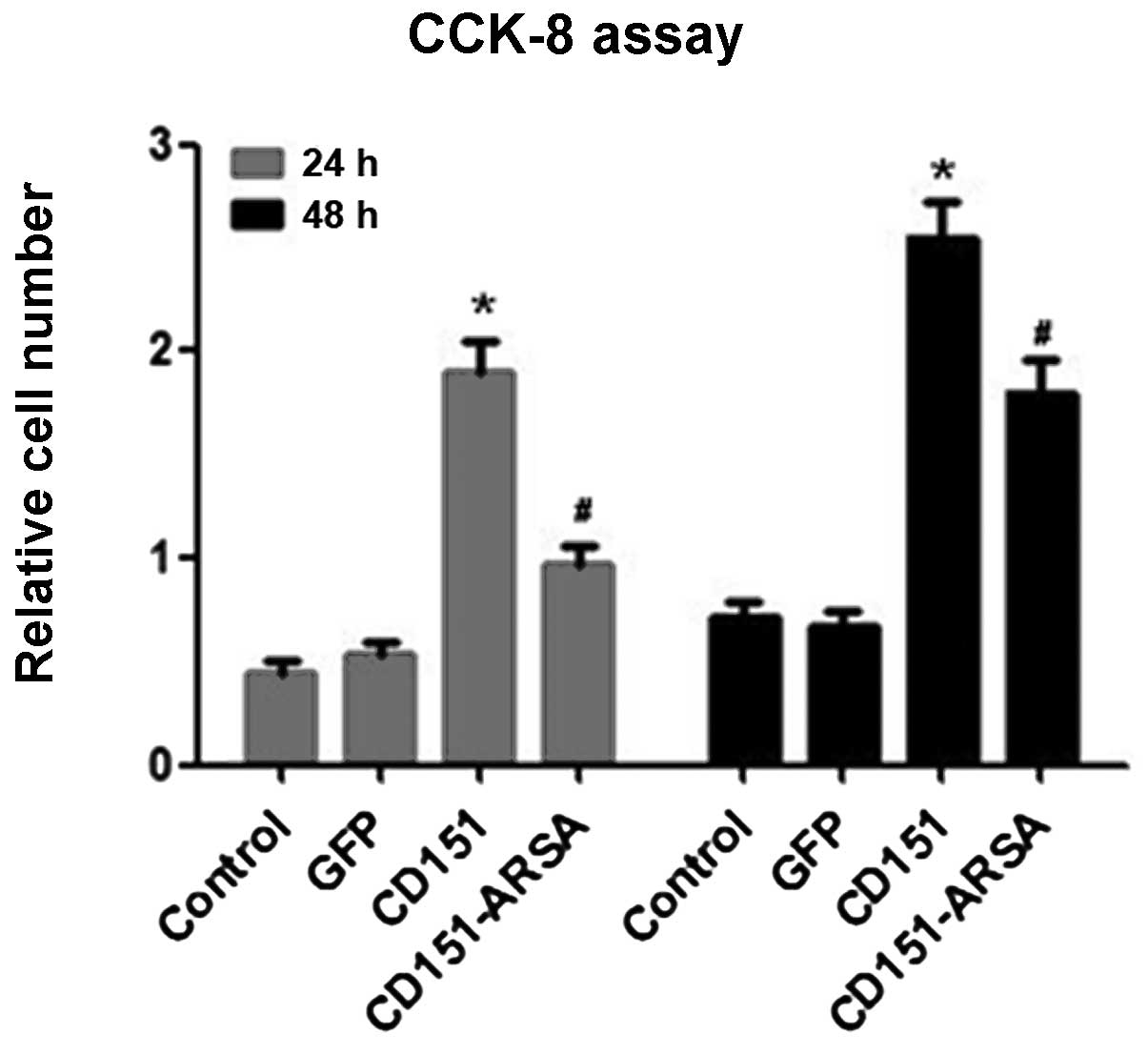
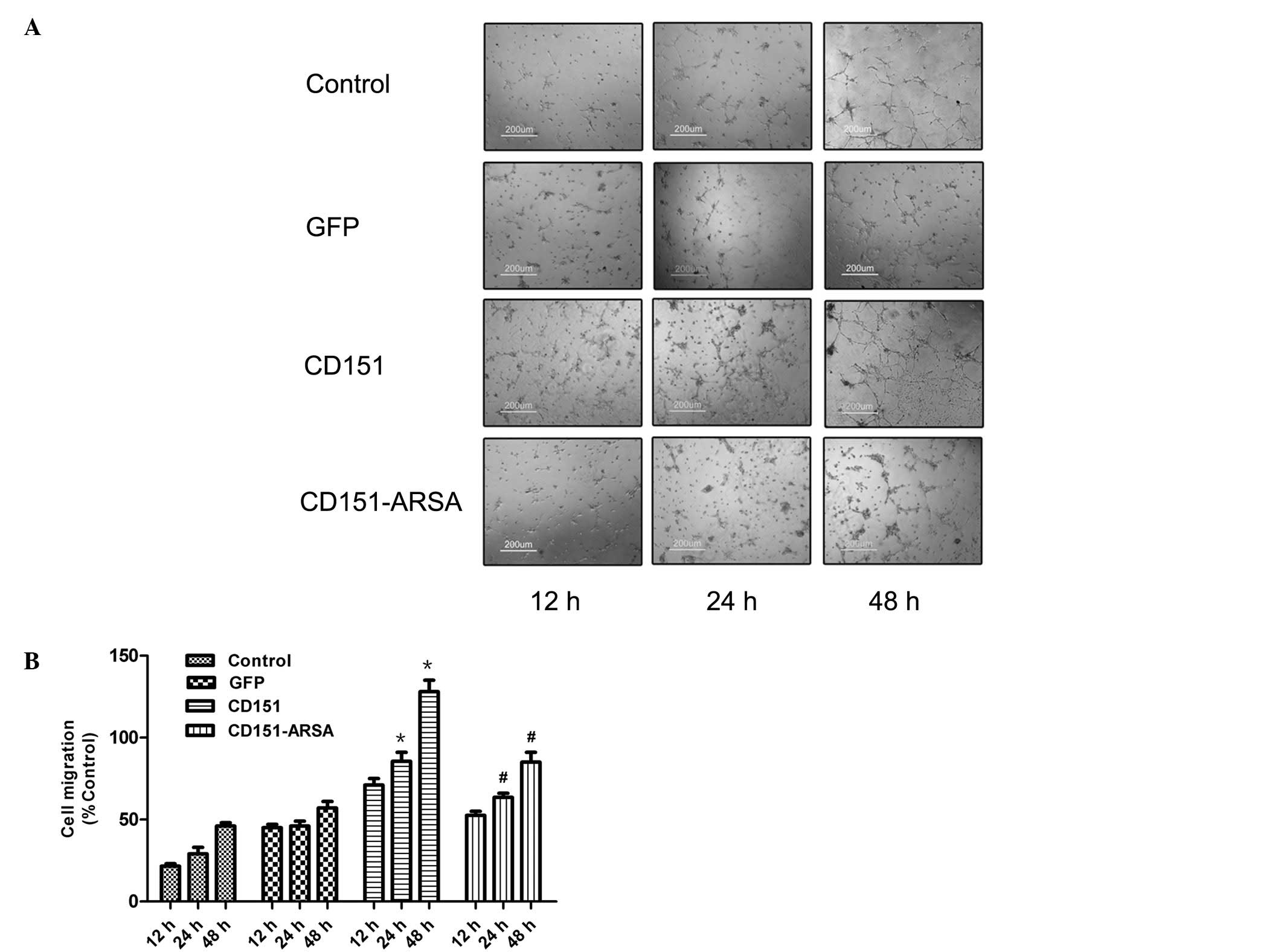
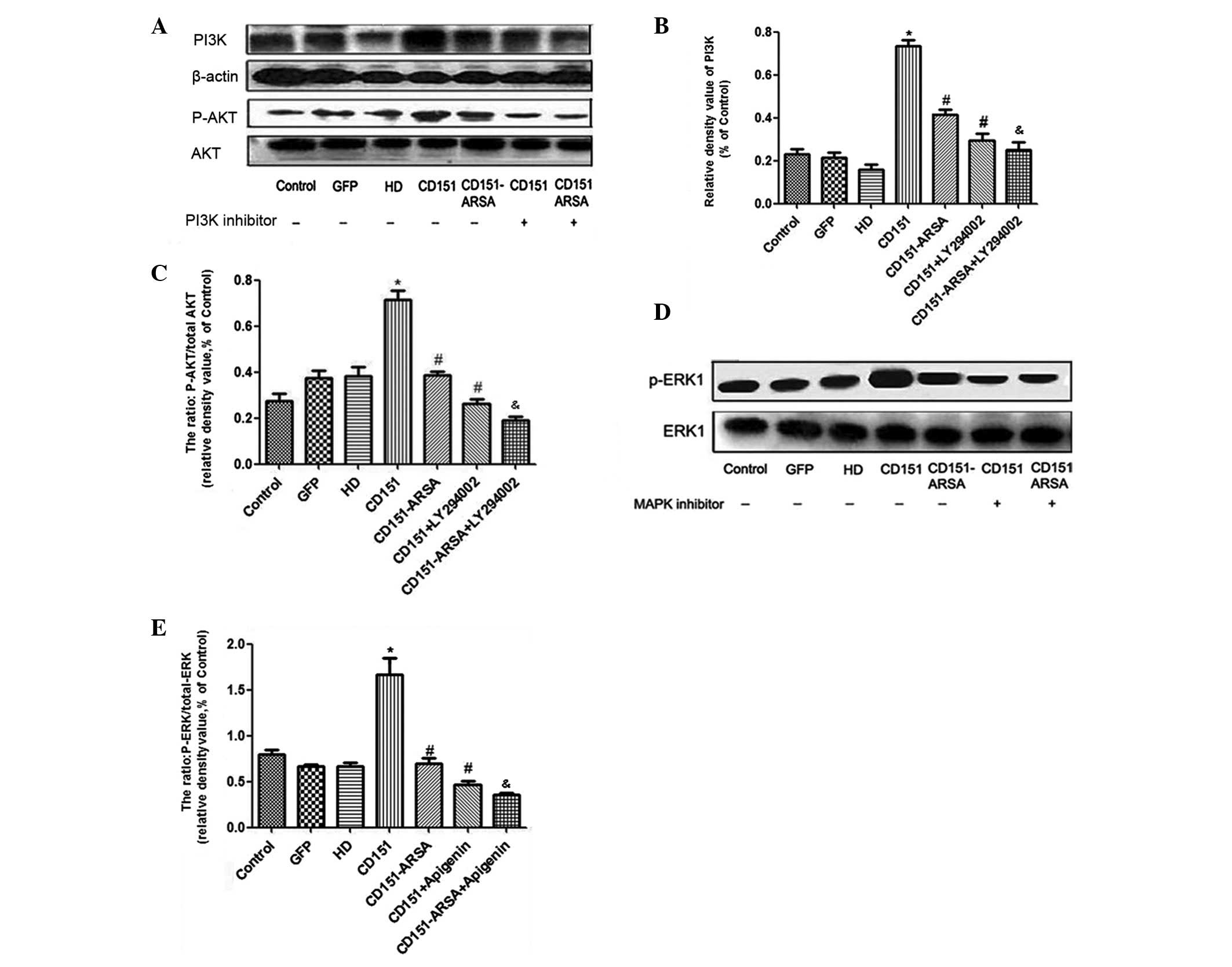
|
1
|
Fitter S, Tetaz TJ, Berndt MC and Ashman
LK: Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a novel platelet-endothelial
cell tetra-span antigen, PETA-3. Blood. 86:1348–1355.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hasegawa H, Utsunomiya Y, Kishimoto K,
Yanagisawa K and Fujita S: SFA-1, a novel cellular gene induced by
human T-cell leukemia virus type 1, is a member of the
transmembrane 4 superfamily. J Virol. 70:3258–3263. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sincock PM, Mayrhofer G and Ashman LK:
Localization of the transmembrane 4 superfamily (TM4SF) member
PETA-3 (CD151) in normal human tissues: comparison with CD9, CD63,
and alpha5beta1 integrin. J Histochem Cytochem. 45:515–525. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sincock PM, Fitter S, Parton RG, Berndt
MC, Gamble JR and Ashman LK: PETA-3/CD151, a member of the
transmembrane 4 superfamily, is localised to the plasma membrane
and endocytic system of endothelial cells, associates with multiple
integrins and modulates cell function. J Cell Sci. 112:833–844.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yauch RL, Berditchevski F, Harler MB,
Reichner J and Hemler ME: Highly stoichiometric, stable, and
specific association of integrin alpha3beta1 with CD151 provides a
major link to phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase, and may regulate cell
migration. Mol Biol Cell. 9:2751–2765. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang XA, Kazarov AR, Yang X, Bontrager
AL, Stipp CS and Hemler ME: Function of the tetraspanin
CD151-alpha6beta1 integrin complex during cellular morphogenesis.
Mol Biol Cell. 13:1–11. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hemler ME: Integrin associated proteins.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 10:578–585. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Serru V, Le Naour F, Billard M, et al:
Selective tetraspan-integrin complexes (CD81/alpha4beta1,
CD151/alpha3beta1, CD151/alpha6beta1) under conditions disrupting
tetraspan interactions. Biochem J. 340:103–111. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang XA, Bontrager AL and Hemler ME:
Transmembrane-4 superfamily proteins associate with activated
protein kinase C (PKC) and link PKC to specific beta(1) integrins.
J Biol Chem. 276:25005–25013. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wright MD, Geary SM, Fitter S, et al:
Characterization of mice lacking the tetraspanin superfamily member
CD151. Mol Cell Biol. 24:5978–5988. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takeda Y, Kazarov AR, Butterfield CE, et
al: Deletion of tetraspanin Cd151 results in decreased pathologic
angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Blood. 109:1524–1532. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lan RF, Liu ZX, Liu XC, Song YE and Wang
DW: CD151 promotes neovascularization and improves blood perfusion
in a rat hind-limb ischemia model. J Endovasc Ther. 12:469–478.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zuo H, Liu Z, Liu X, et al: CD151 gene
delivery after myocardial infarction promotes functional
neovascularization and activates FAK signaling. Mol Med.
15:307–315. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu WF, Zuo HJ, Chai BL, et al: Role of
tetraspanin CD151-alpha3/alpha6 integrin complex: Implication in
angiogenesis CD151-integrin complex in angiogenesis. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 43:642–650. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zheng ZZ and Liu ZX: Activation of the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase Akt pathway mediates
CD151-induced endothelial cell proliferation and cell migration.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:340–348. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zuo H, Liu Z, Yang J, et al: Activation of
the ERK signaling pathway is involved in CD151-induced angiogenic
effects on the formation of CD151-integrin complexes. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 31:805–812. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zuo H, Liu Z, Liu X, et al: Assessment of
myocardial blood perfusion improved by CD151 in pig myocardial
infarction model. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:70–77. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bretscher MS and Aguado-Velasco C:
Membrane traffic during cell locomotion. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
10:537–541. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kobayashi T, Vischer UM, Rosnoblet C, et
al: The tetraspanin CD63/lamp3 cycles between endocytic and
secretory compartments in human endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell.
11:1829–1843. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Duffield A, Kamsteeg EJ, Brown AN, Pagel P
and Caplan MJ: The tetraspanin CD63 enhances the internalization of
the H,K-ATPase beta-subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:15560–15565. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Caswell PT, Vadrevu S and Norman JC:
Integrins: masters and slaves of endocytic transport. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 10:843–853. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu L, He B, Liu WM, Zhou D, Cox JV and
Zhang XA: Tetraspanin CD151 promotes cell migration by regulating
integrin trafficking. J Biol Chem. 282:31631–31642. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ohno H, Stewart J, Fournier MC, et al:
Interaction of tyrosine-based sorting signals with
clathrin-associated proteins. Science. 269:1872–1875. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bonifacino JS and Traub LM: Signals for
sorting of transmembrane proteins to endosomes and lysosomes. Annu
Rev Biochem. 72:395–447. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Auricchio A, Hildinger M, O’Connor E, Gao
GP and Wilson JM: Isolation of highly infectious and pure
adeno-associated virus type 2 vectors with a single-step
gravity-flow column. Hum Gene Ther. 12:71–76. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Berditchevski F and Odintsova E:
Characterization of integrin-tetraspanin adhesion complexes: role
of tetraspanins in integrin signaling. J Cell Biol. 146:477–492.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fitter S, Sincock PM, Jolliffe CN and
Ashman LK: Transmembrane 4 superfamily protein CD151 (PETA-3)
associates with beta 1 and alpha IIb beta 3 integrins in
haemopoietic cell lines and modulates cell-cell adhesion. Biochem
J. 338:61–70. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Conner SD and Schmid SL: Regulated portals
of entry into the cell. Nature. 422:37–44. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Carmeliet P: Mechanisms of angiogenesis
and arteriogenesis. Nat Med. 6:389–395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rey S and Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1-dependent mechanisms of vascularization and vascular
remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. 86:236–242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ulrich F and Heisenberg CP: Trafficking
and cell migration. Traffic. 10:811–818. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mellman I and Nelson WJ: Coordinated
protein sorting, targeting and distribution in polarized cells. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:833–845. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|