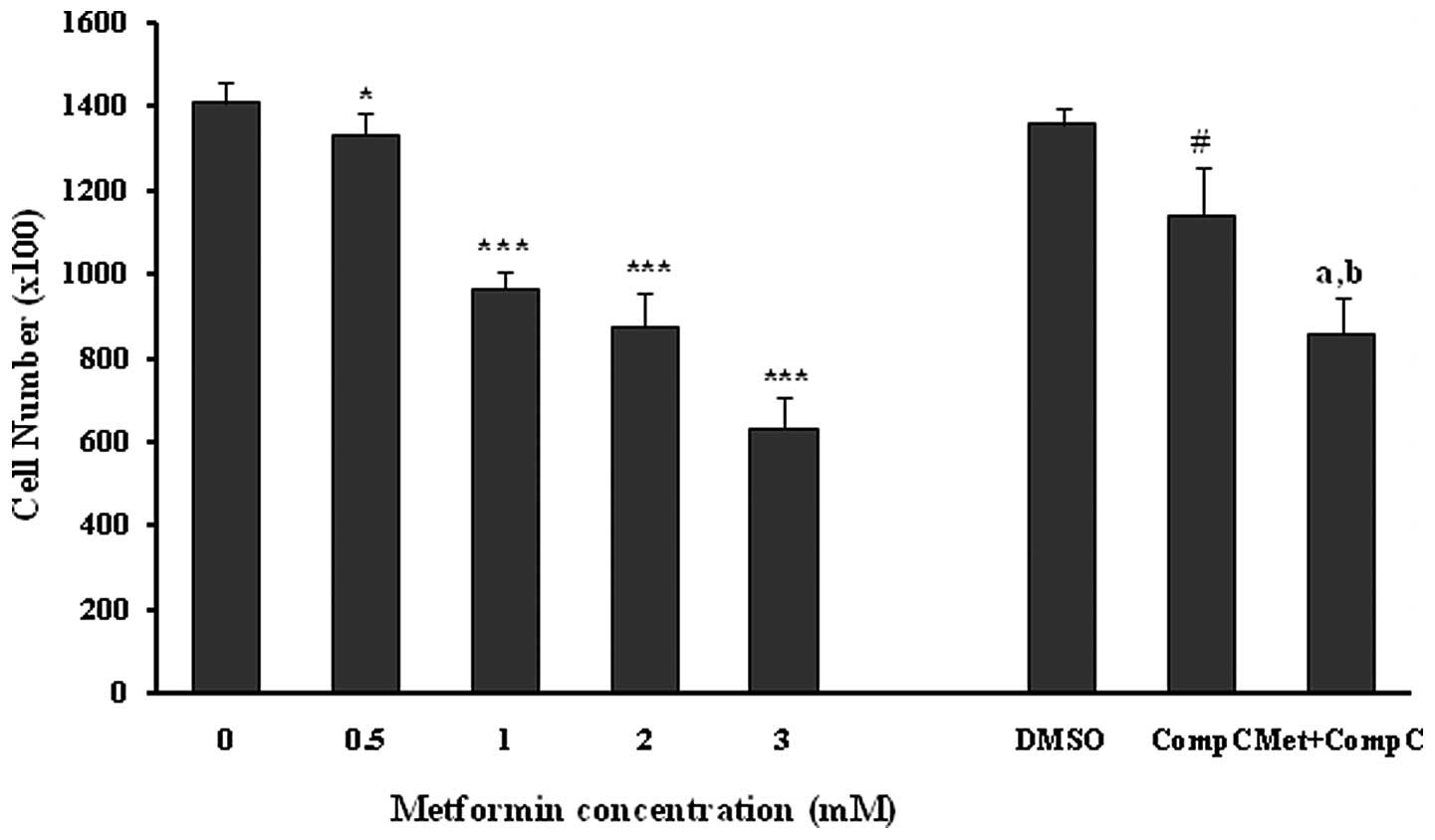
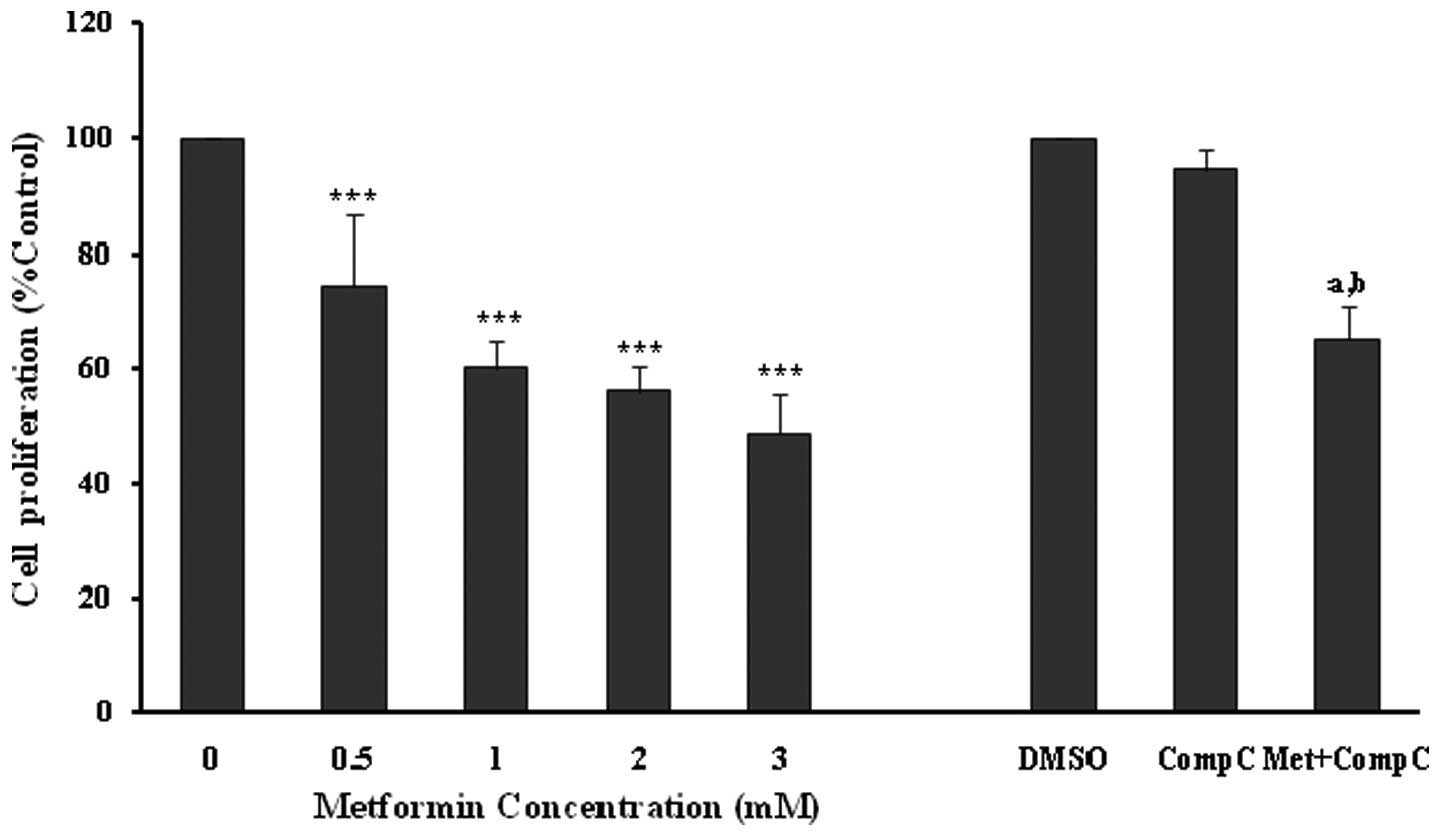
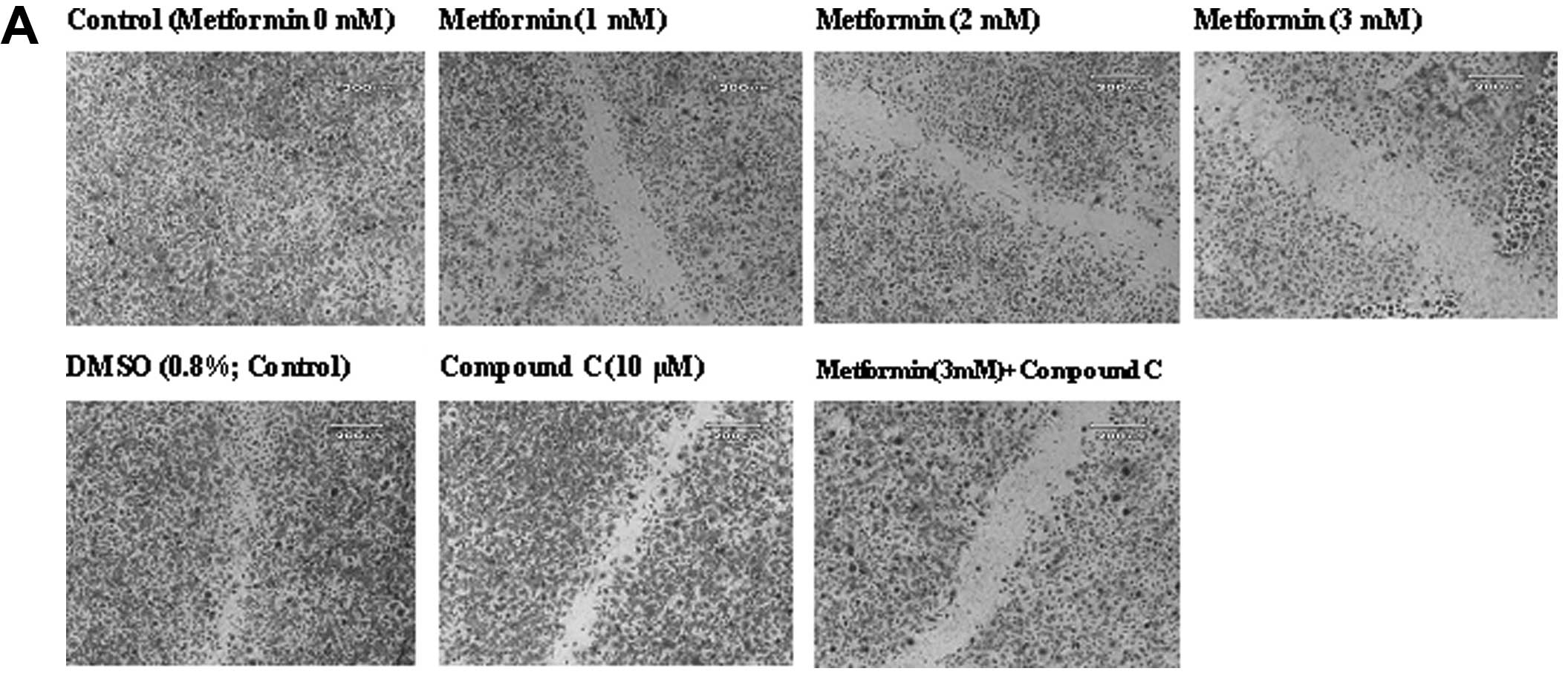
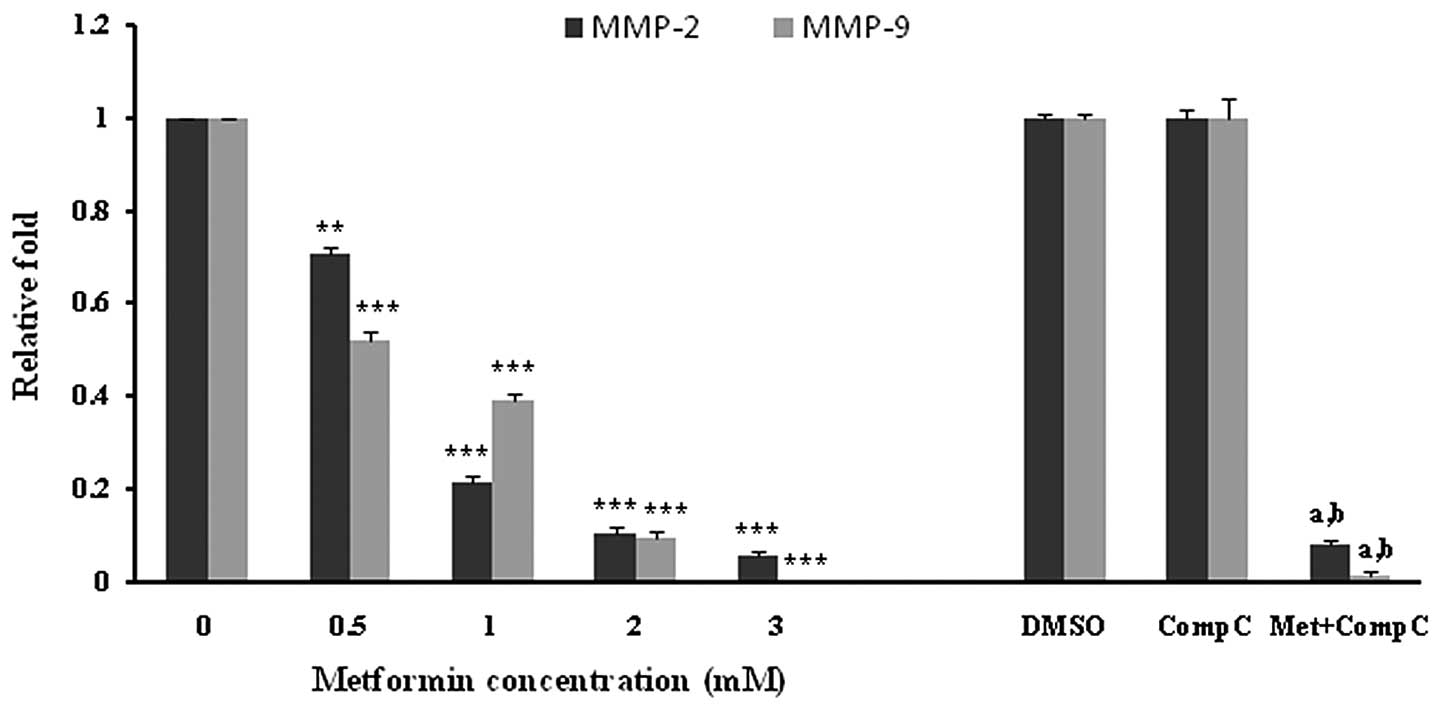
|
1
|
D LiSC YeungMM HassanM KonoplevaJL
AbbruzzeseAntidiabetic therapies affect risk of pancreatic
cancerGastroenterology137482488200910.1053/j.gastro.2009.04.01319375425
|
|
2
|
JM EvansLA DonnellyAM Emslie-SmithDR
AlessiAD MorrisMetformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic
patientsBMJ33013041305200510.1136/bmj.38415.708634.F715849206
|
|
3
|
G LibbyLA DonnellyPT DonnanDR AlessiAD
MorrisJM EvansNew users of metformin are at low risk of incident
cancer: a cohort study among people with type 2 diabetesDiabetes
Care3216201625200910.2337/dc08-217519564453
|
|
4
|
G ZhouR MyersY LiY ChenX ShenJ
Fenyk-MelodyM WuJ VentreT DoebberN FujiiRole of AMP-activated
protein kinase in mechanism of metformin actionJ Clin
Invest10811671174200110.1172/JCI1350511602624
|
|
5
|
MR OwenE DoranAP HalestrapEvidence that
metformin exerts its anti-diabetic effects through inhibition of
complex 1 of the mitochondrial respiratory chainBiochem
J15348200010839993
|
|
6
|
N HayN SonenbergUpstream and downstream of
mTORGenes Dev1819261945200410.1101/gad.1212704
|
|
7
|
CS BeeversF LiL LiuS HuangCurcumin
inhibits the mammalian target of rapamycin-mediated signaling
pathways in cancer cellsInt J
Cancer119757764200610.1002/ijc.2193216550606
|
|
8
|
SA HawleyJ BoudeauJL ReidKJ MustardL UddTP
MakelaDR AlessiDG HardieComplexes between the LKB1 tumor
suppressor, STRAD alpha/beta and MO25 alpha/beta are upstream
kinases in the AMP-activated protein kinase cascadeJ
Biol228200310.1186/1475-4924-2-2814511394
|
|
9
|
JM LizcanoO GoranssonR TothM DeakNA
MorriceJ BoudeauSA HawleyL UddTP MakelaDG HardieLKB1 is a master
kinase that activates 13 kinases of the AMPK subfamily, including
MARK/PAR-1EMBO J23833843200410.1038/sj.emboj.760011014976552
|
|
10
|
H JiMR RamseyDN HayesLKB1 modulates lung
cancer differentiation and
metastasisNature448807810200710.1038/nature0603017676035
|
|
11
|
J FolkmanPA D'AmoreBlood vessel formation:
what is its molecular
basis?Cell8711531155199610.1016/S0092-8674(00)81810-38980221
|
|
12
|
R KalluriBasement membranes: structure,
assembly and role in tumour angiogenesisNat Rev
Cancer3422433200310.1038/nrc109412778132
|
|
13
|
TA HaasEndothelial cell regulation of
matrix metalloproteinasesCan J Physiol
Pharmacol8317200510.1139/y04-120
|
|
14
|
JP SluijterDP de KleijinG
PasterkampVascular remodeling and protease inhibition: bench to
bedsideCardiovas
Res69595603200610.1016/j.cardiores.2005.11.02616387286
|
|
15
|
BK TanR AdyaJ ChenS FarhatullahD HeutlingD
MitchellH LehnertHS RandevaMetformin decreases angiogenesis via
NF-kappaB and Erk1/2/Erk5 pathways by increasing the antiangiogenic
thrombospondin-1Cardiovasc
Res83566574200910.1093/cvr/cvp13119414528
|
|
16
|
DO XavierLS AmaralMA GomesMetformin
inhibits inflammatory angiogenesis in a murine sponge modelBiomed
Pharmacother64220225201010.1016/j.biopha.2009.08.00420053525
|
|
17
|
NJ LinfordDM Dorsa17beta-estradiol and the
phytoestrogen genistein attenuate neuronal apoptosis induced by the
endoplasmic reticulum calcium-ATPase inhibitor
thapsigarginSteroids6710291040200210.1016/S0039-128X(02)00062-4
|
|
18
|
SL BowkerSR MajumdarP VeugelersJA
JohnsonIncreased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2
diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulinDiabetes
Care29254258200610.2337/diacare.29.02.06.dc05-1558
|
|
19
|
CJ CurrieCD PooleEA GaleThe influence of
glucose-lowering therapies on cancer risk in type 2
diabetesDiabetologia5217661777200910.1007/s00125-009-1440-619572116
|
|
20
|
JL WrightJL StanfordMetformin use and
prostate cancer in Caucasian men: results from a population-based
case-control studyCancer Causes
Control2016171622200910.1007/s10552-009-9407-y19653109
|
|
21
|
RM MemmottJR MercadoCR MaierS KawabataSD
FoxPA DennisMetformin prevents tobacco carcinogen - induced lung
tumorigenesisCancer Prev Res
(Phila)310661076201010.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-005520810672
|
|
22
|
YP HwangHG JeongMetformin blocks migration
and invasion of tumour cells by inhibition of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 activation through a calcium and protein kinase
Ca-dependent pathway:
phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced/extracellular
signal-regulated kinase/activator protein-1Br J
Pharmacol160119512112010
|
|
23
|
G SchaferBiguanides. A review of history,
pharmacodynamics and therapyDiabete Metab914816319836352352
|
|
24
|
M StumvollN NurjhanG PerrielloG DaileyJE
GerichMetabolic effects of metformin in non-insulin-dependent
diabetes mellitusN Engl J
Med333550554199510.1056/NEJM1995083133309037623903
|
|
25
|
RS HundalM KrssakS DufourMechanism by
which metformin reduces glucose production in type 2
diabetesDiabetes4920632069200010.2337/diabetes.49.12.206311118008
|
|
26
|
HS HundalT RamlalR ReyesLA LeiterA
KlipCellular mechanism of metformin action involves glucose
transporter translocation from an intracellular pool to the plasma
membrane in L6 muscle cellsEndocrinology131116511731992
|
|
27
|
D GaluskaLA NolteJR ZierathH
Wallberg-HenrikssonEffect of metformin on insulin-stimulated
glucose transport in isolated skeletal muscle obtained from
patients with
NIDDMDiabetologia37826832199410.1007/BF004043407988785
|
|
28
|
HZ LinSQ YangC ChuckareeF KuhajdaG
RonnetAM DiehlMetformin reverses fatty liver disease in obese,
leptin-deficient miceNat Med69981003200010.1038/7969710973319
|
|
29
|
DG HardieSA HawleyJW ScottAMP-activated
protein kinase - development of the energy sensor conceptJ
Physiol574715200610.1113/jphysiol.2006.10894416644800
|
|
30
|
KR LaderouteK AminJM CalaoaganM KnappT LeJ
OrdunaM ForetzB Viollet5′-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is
induced by low-oxygen and glucose deprivation conditions found in
solid-tumor microenvironmentsMol Cell Biol26533653472006
|
|
31
|
X LiY HanW PangC LiX XieJY ShyyY
ZhuAMP-activated protein kinase promotes the differentiation of
endothelial progenitor cellsArterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol2817891795200810.1161/ATVBAHA.108.17245218599796
|
|
32
|
D NagataM MogiK WalshAMP-activated protein
kinase (AMPK) signaling in endothelial cells is essential for
angiogenesis in response to hypoxic stressJ Biol
Chem2783100031006200310.1074/jbc.M30064320012788940
|
|
33
|
BA KefasY CaiK KerckhofsZ LingG MartensH
HeimbergD PipeleersM Van de CasteeleMetformin-induced stimulation
of AMP-activated protein kinase in beta-cells impairs their glucose
responsiveness and can lead to apoptosisBiochem
Pharmacol68409416200410.1016/j.bcp.2004.04.00315242807
|
|
34
|
M SaitohK NagaiK NakagawaT YamamuraS
YamamotoT NishizakiAdenosine induces apoptosis in the human gastric
cancer cells via an intrinsic pathway relevant to activation of
AMP-activated protein kinaseBiochem
Pharmacol6720052011200410.1016/j.bcp.2004.01.020
|
|
35
|
R RattanS GiriAK SinghI
Singh5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside
inhibits cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo via
AMP-activated protein kinaseJ Biol
Chem2803958239593200510.1074/jbc.M50744320016176927
|
|
36
|
A IsakovicL HarhajiD StevanovicZ MarkovicM
Sumarac-DumanovicV StarcevicD MicicV TrajkovicDual antiglioma
action of metformin: cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-dependent
apoptosisCell Mol Life
Sci6412901302200710.1007/s00018-007-7080-417447005
|
|
37
|
W ZhouWF HanLE LandreeFatty acid synthase
inhibition activates AMP-activated protein kinase in SKOV3 human
ovarian cancer cellsCancer
Res6729642971200710.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-343917409402
|
|
38
|
R OkoshiT OzakiH YamamotoK AndoN KoidaS
OnoT KodaT KamijoA NakagawaraH KizakiActivation of AMP-activated
protein kinase induces p53-dependent apoptotic cell death in
response to energetic stressJ Biol
Chem28339793987200810.1074/jbc.M70523220018056705
|
|
39
|
DR AlessiK SakamotoJR
BayascasLKB1-dependent signaling pathwaysAnnu Rev
Biochem75137163200610.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.14270216756488
|
|
40
|
MM ShawWK GurrRJ McCrimmonDF SchorderetRS
Sherwin5'AMP-activated protein kinase alpha deficiency enhances
stress-induced apoptosis in BHK and PC12 cellsJ Cell Mol
Med112862982007
|
|
41
|
MB AntonoffJ D'CunhaTeaching an old drug
new tricks: metformin as a targeted therapy for lung cancerSemin
Thorac Cardiovasc
Surg22195196201010.1053/j.semtcvs.2010.10.01521167452
|
|
42
|
LQ Hong-BrownCR BrownDS HuberCH
LangLopinavir impairs protein synthesis and induces eEF2
phosphorylation via the activation of AMP-activated protein kinaseJ
Cell Biochem105814823200810.1002/jcb.2188218712774
|
|
43
|
JE KimHC ChoiLosartan inhibits vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation through activation of
AMP-activated protein kinaseKorean J Physiol
Pharmacol14299304201010.4196/kjpp.2010.14.5.29921165328
|
|
44
|
R HanemaaijerP KoolwijkL le ClercqWJ de
VreeVW van HinsberghRegulation of matrix metalloproteinase
expression in human vein and microvascular endothelial cells.
Effects of tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1 and phorbol
esterBiochem J158038091993
|
|
45
|
Y MorizaneA ThanosK TakeuchiAMP-activated
protein kinase suppresses matix metalloproteinase-9 expression in
mouse embryonic fibroblastsJ Biol
Chem2861603016038201110.1074/jbc.M110.19939821402702
|