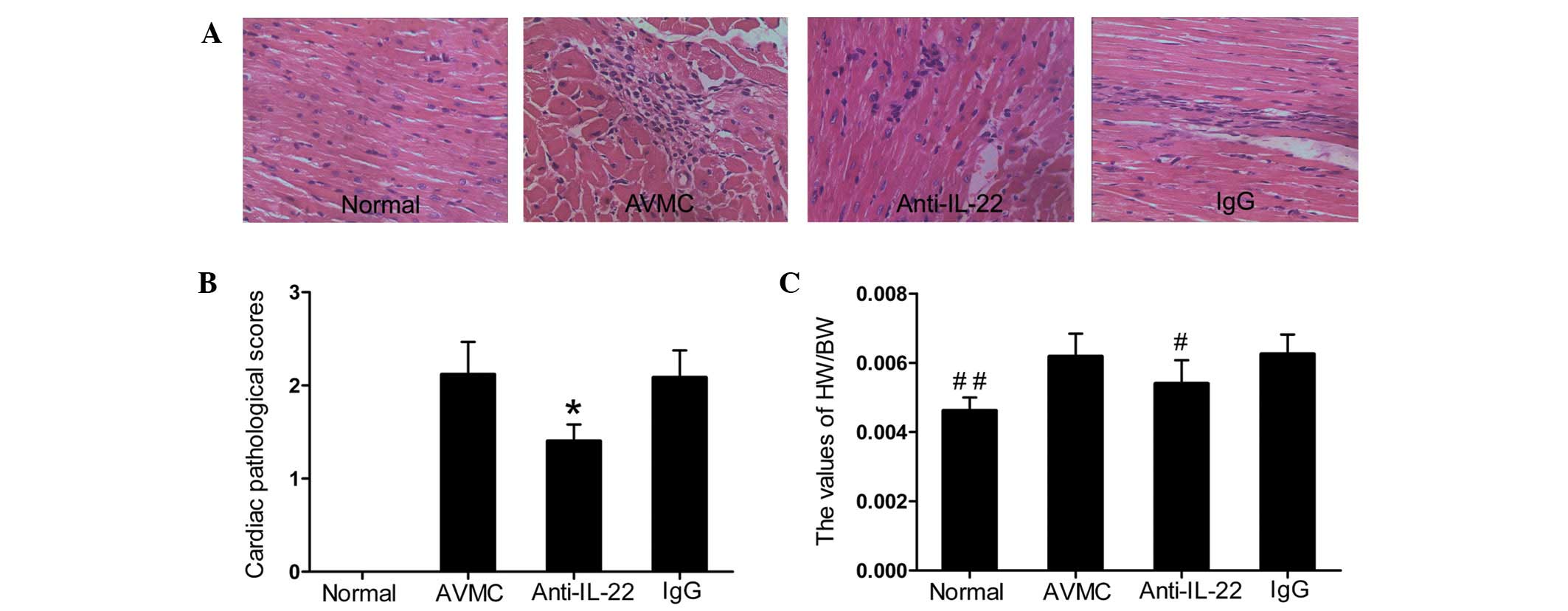
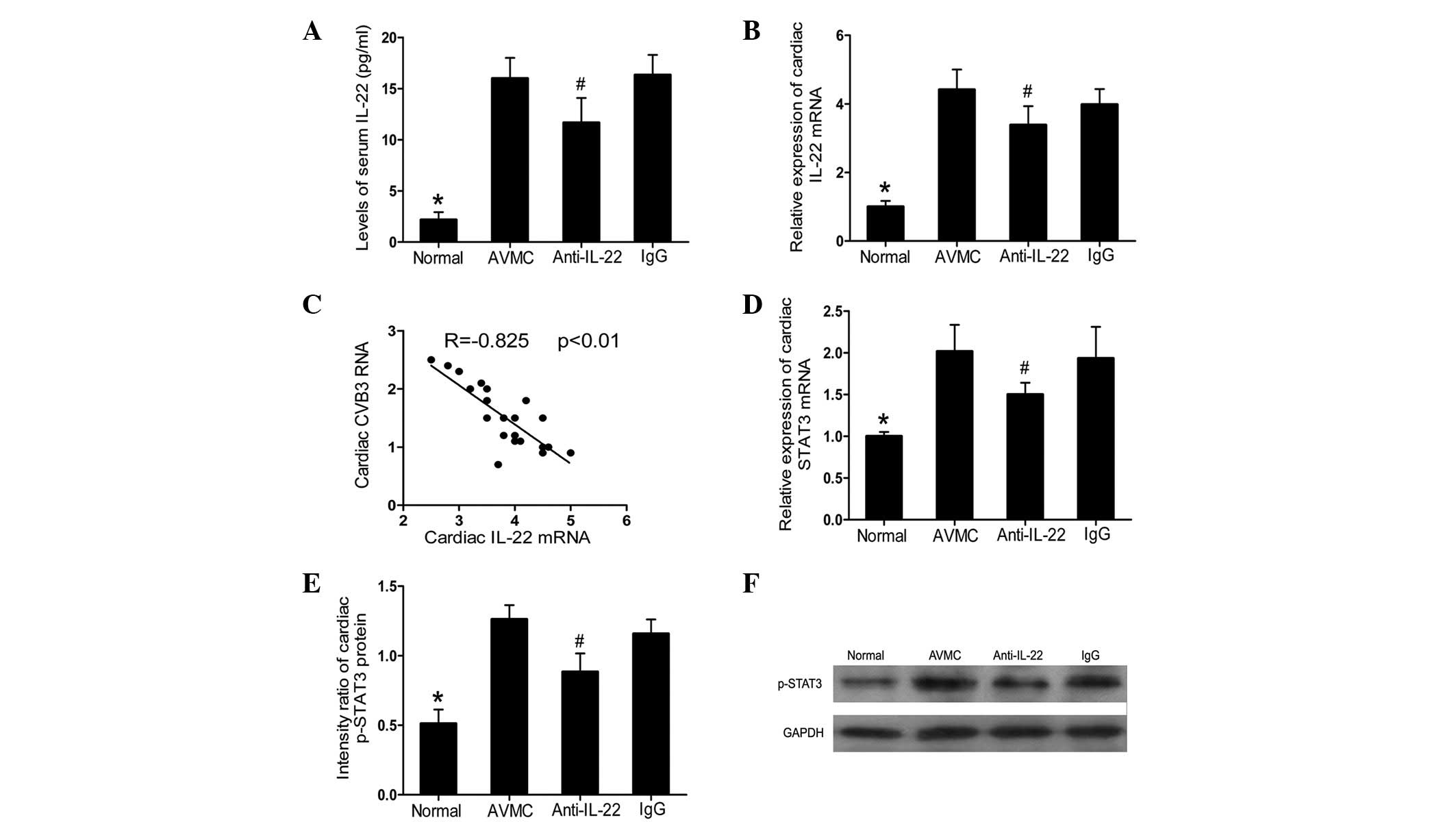
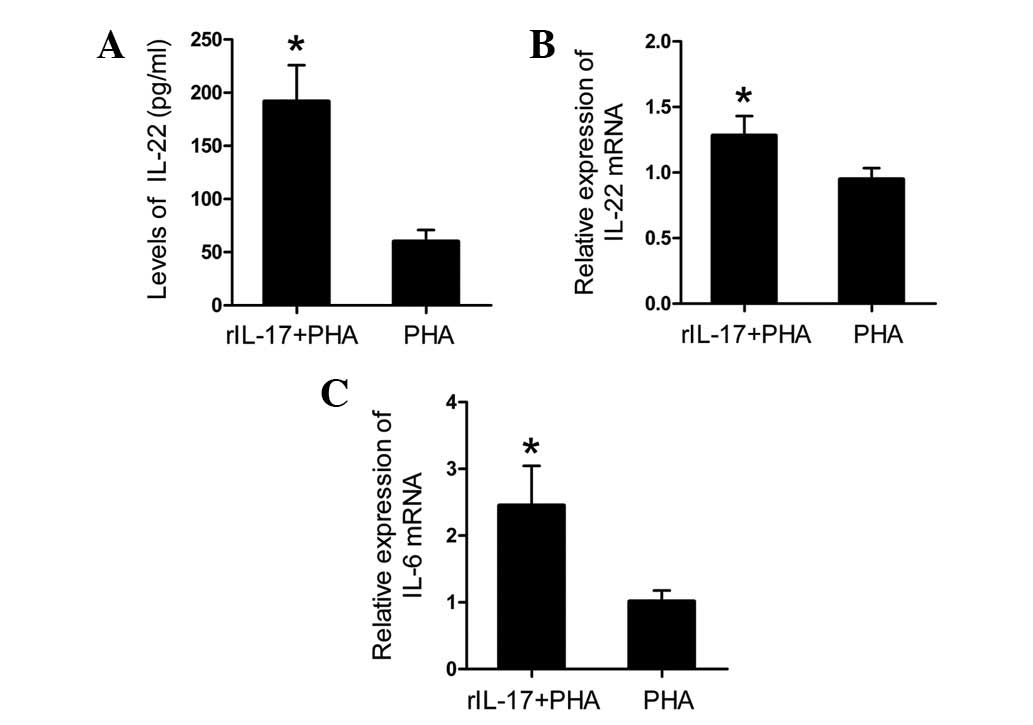
|
1
|
Dennert R, Crijns HJ and Heymans S: Acute
viral myocarditis. Eur Heart J. 29:2073–2082. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gupta S, Markham DW, Drazner MH and Mammen
PP: Fulminant myocarditis. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med.
5:693–706. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cooper LT Jr: Myocarditis. N Engl J Med.
360:1526–1538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fairweather D and Rose NR:
Coxsackievirus-induced myocarditis in mice: a model of autoimmune
disease for studying immunotoxicity. Methods. 41:118–122. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yuan J, Yu M, Lin QW, Cao AL, Yu X, Dong
JH, Wang JP, Zhang JH, Wang M, Guo HP, Cheng X and Liao YH: Th17
cells contribute to viral replication in coxsackievirus B3-induced
acute viral myocarditis. J Immunol. 185:4004–4010. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang F, Wu WF, Yan YL, Pang Y, Kong Q and
Huang YL: Expression of IL-23/Th17 pathway in a murine model of
Coxsackie virus B3-induced viral myocarditis. Virol J. 8:3012011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Trifari S, Kaplan CD, Tran EH, Crellin NK
and Spits H: Identification of a human helper T cell population
that has abundant production of interleukin 22 and is distinct from
T(H)-17, T(H)1 and T(H)2 cells. Nat Immunol. 10:864–871. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sonnenberg GF, Fouser LA and Artis D:
Border patrol: regulation of immunity, inflammation and tissue
homeostasis at barrier surfaces by IL-22. Nat Immunol. 12:383–390.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Radaeva S, Sun R, Pan HN, Hong F and Gao
B: Interleukin 22 (IL-22) plays a protective role in T
cell-mediated murine hepatitis: IL-22 is a survival factor for
hepatocytes via STAT3 activation. Hepatology. 39:1332–1342. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ziesché E, Bachmann M, Kleinert H,
Pfeilschifter J and Mühl H: The interleukin-22/STAT3 pathway
potentiates expression of inducible nitric-oxide synthase in human
colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 282:16006–16015.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takahashi K, Hirose K, Kawashima S, Niwa
Y, Wakashin H, Iwata A, Tokoyoda K, Renauld JC, Iwamoto I, Nakayama
T and Nakajima H: IL-22 attenuates IL-25 production by lung
epithelial cells and inhibits antigen-induced eosinophilic airway
inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 128:1067–1076. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang P, Bai F, Zenewicz LA, Dai J, Gate D,
Cheng G, Yang L, Qian F, Yuan X, Montgomery RR, Flavell RA, Town T
and Fikrig E: IL-22 signaling contributes to West Nile encephalitis
pathogenesis. PLoS One. 7:e441532012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Missé D, Yssel H, Trabattoni D, Oblet C,
Lo Caputo S, Mazzotta F, Pène J, Gonzalez JP, Clerici M and Veas F:
IL-22 participates in an innate anti-HIV-1 host-resistance network
through acute-phase protein induction. J Immunol. 178:407–415.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zenewicz LA, Yancopoulos GD, Valenzuela
DM, Murphy AJ, Karow M and Flavell RA: Interleukin-22 but not
interleukin-17 provides protection to hepatocytes during acute
liver inflammation. Immunity. 27:647–659. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huber S, Gagliani N, Zenewicz LA, Huber
FJ, Bosurgi L, Hu B, Hedl M, Zhang W, O’Connor W Jr, Murphy AJ,
Valenzuela DM, Yancopoulos GD, Booth CJ, Cho JH, Ouyang W, Abraham
C and Flavell RA: IL-22BP is regulated by the inflammasome and
modulates tumorigenesis in the intestine. Nature. 491:259–263.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Laurence A, O’Shea JJ and Watford WT:
Interleukin-22: a sheep in wolf’s clothing. Nat Med. 14:247–249.
2008.
|
|
17
|
Sonnenberg GF, Nair MG, Kirn TJ, Zaph C,
Fouser LA and Artis D: Pathological versus protective functions of
IL-22 in airway inflammation are regulated by IL-17A. J Exp Med.
207:1293–1305. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kong Q, Wu W, Yang F, Liu Y, Xue Y, Gao M,
Lai W, Pan X, Yan Y, Pang Y and Deng Y: Increased expressions of
IL-22 and Th22 cells in the coxsackievirus B3-Induced mice acute
viral myocarditis. Virol J. 9:2322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakae S, Komiyama Y, Nambu A, Sudo K,
Iwase M, Homma I, Sekikawa K, Asano M and Iwakura Y:
Antigen-specific T cell sensitization is impaired in
IL-17-deficient mice, causing suppression of allergic cellular and
humoral responses. Immunity. 17:375–387. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eriksson U, Ricci R, Hunziker L, Kurrer
MO, Oudit GY, Watts TH, Sonderegger I, Bachmaier K, Kopf M and
Penninger JM: Dendritic cell-induced autoimmune heart failure
requires cooperation between adaptive and innate immunity. Nat Med.
9:1484–1490. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stange J, Hepworth MR, Rausch S, Zajic L,
Kühl AA, Uyttenhove C, Renauld JC, Hartmann S and Lucius R: IL-22
mediates host defense against an intestinal intracellular parasite
in the absence of IFN-γ at the cost of Th17-driven immunopathology.
J Immunol. 188:2410–2418. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liang SC, Tan XY, Luxenberg DP, Karim R,
Dunussi-Joannopoulos K, Collins M and Fouser LA: Interleukin
(IL)-22 and IL-17 are coexpressed by Th17 cells and cooperatively
enhance expression of antimicrobial peptides. J Exp Med.
203:2271–2279. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aujla SJ, Chan YR, Zheng M, Fei M, Askew
DJ, Pociask DA, Reinhart TA, McAllister F, Edeal J, Gaus K, Husain
S, Kreindler JL, Dubin PJ, Pilewski JM, Myerburg MM, Mason CA,
Iwakura Y and Kolls JK: IL-22 mediates mucosal host defense against
Gram-negative bacterial pneumonia. Nat Med. 14:275–281. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liang SC, Long AJ, Bennett F, Whitters MJ,
Karim R, Collins M, Goldman SJ, Dunussi-Joannopoulos K, Williams
CM, Wright JF and Fouser LA: An IL-17F/A heterodimer protein is
produced by mouse Th17 cells and induces airway neutrophil
recruitment. J Immunol. 179:7791–7799. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yao Z, Fanslow WC, Seldin MF, Rousseau AM,
Painter SL, Comeau MR, Cohen JI and Spriggs MK: Herpesvirus Saimiri
encodes a new cytokine, IL-17, which binds to a novel cytokine
receptor. Immunity. 3:811–821. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gaffen SL: Structure and signalling in the
IL-17 receptor family. Nat Rev Immunol. 9:556–567. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Komiyama Y, Nakae S, Matsuki T, Nambu A,
Ishigame H, Kakuta S, Sudo K and Iwakura Y: IL-17 plays an
important role in the development of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 177:566–573. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dauer DJ, Ferraro B, Song L, Yu B, Mora L,
Buettner R, Enkemann S, Jove R and Haura EB: Stat3 regulates genes
common to both wound healing and cancer. Oncogene. 24:3397–3408.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bollrath J and Greten FR: IKK/NF-kappaB
and STAT3 pathways: central signalling hubs in
inflammation-mediated tumour promotion and metastasis. EMBO Rep.
10:1314–1319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fairweather D, Stafford KA and Sung YK:
Update on coxsackievirus B3 myocarditis. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
24:401–407. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Woodruff JF and Woodruff JJ: Involvement
of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of coxsackievirus B3 heart
disease. J Immunol. 113:1726–1734. 1974.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Duhen T, Geiger R, Jarrossay D,
Lanzavecchia A and Sallusto F: Production of interleukin 22 but not
interleukin 17 by a subset of human skin-homing memory T cells. Nat
Immunol. 10:857–863. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
O’Connor W Jr, Kamanaka M, Booth CJ, Town
T, Nakae S, Iwakura Y, Kolls JK and Flavell RA: A protective
function for interleukin 17A in T cell-mediated intestinal
inflammation. Nat Immunol. 10:603–609. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Smith E, Stark MA, Zarbock A, Burcin TL,
Bruce AC, Vaswani D, Foley P and Ley K: IL-17A inhibits the
expansion of IL-17A-producing T cells in mice through ‘short-loop’
inhibition via IL-17 receptor. J Immunol. 181:1357–1364. 2008.
|
|
35
|
von Vietinghoff S and Ley K: IL-17A
controls IL-17F production and maintains blood neutrophil counts in
mice. J Immunol. 183:865–873. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|