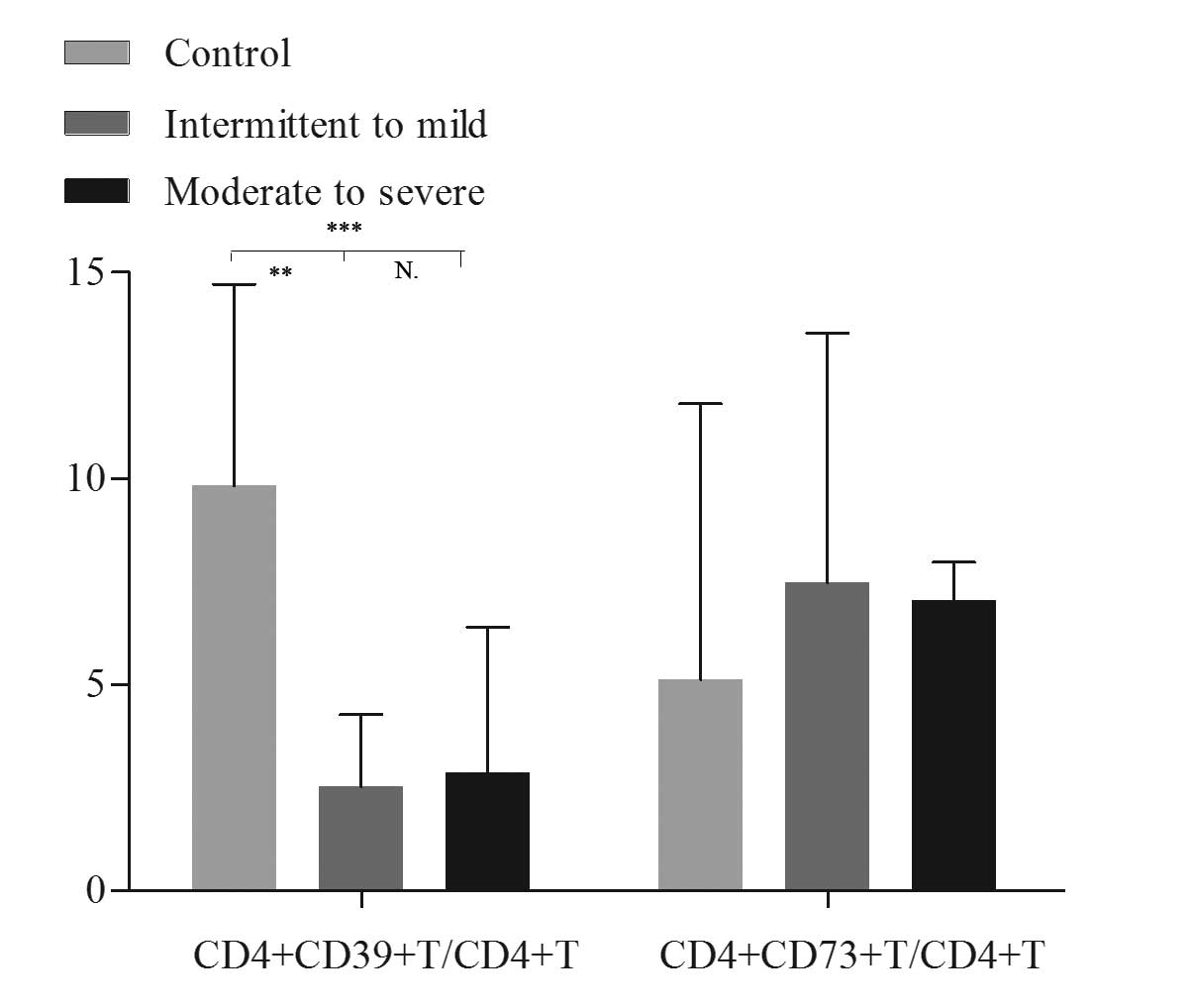
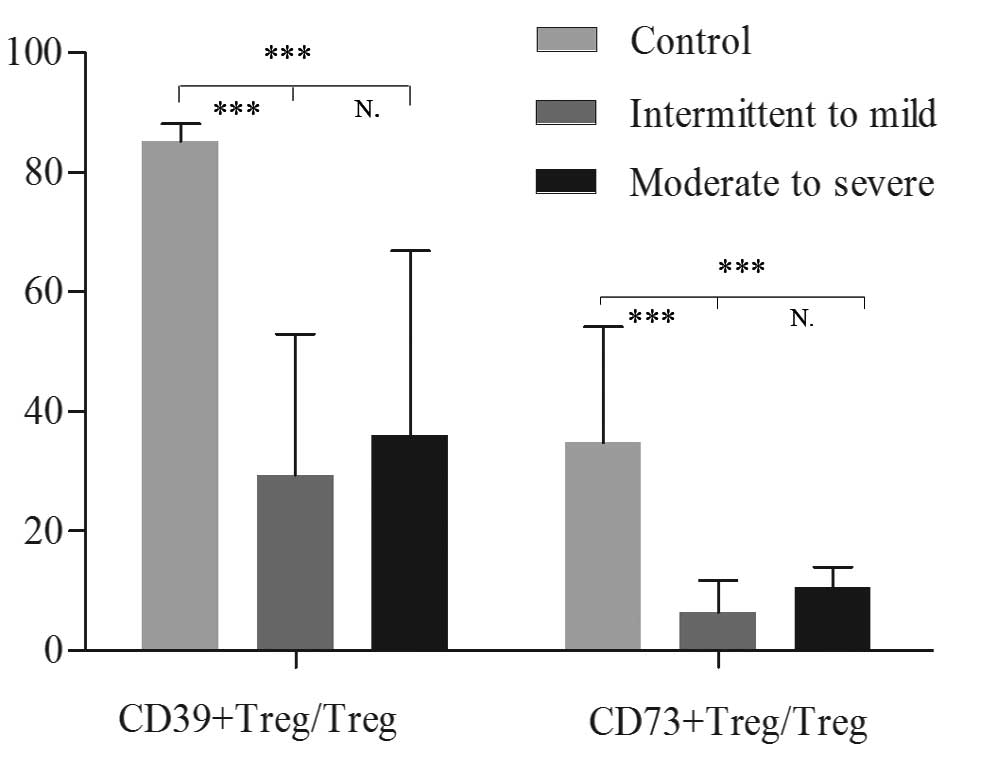
|
1
|
Shevach EM:
CD4+CD25+ suppressor T cells: more questions
than answers. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:389–400. 2002.
|
|
2
|
Tesmer LA, Lundy SK, Sarkar S and Fox DA:
Th17 cells in human disease. Immunol Rev. 223:87–113. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weaver CT, Harrington LE, Mangan PR,
Gavrieli M and Murphy KM: Th17: an effector CD4 T cell lineage with
regulatory T cell ties. Immunity. 24:677–688. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou L, Chong MM and Littman DR:
Plasticity of CD4+ T cell lineage differentiation.
Immunity. 30:646–655. 2009.
|
|
5
|
Dong C: TH17 cells in development: an
updated view of their molecular identity and genetic programming.
Nat Rev Immunol. 8:337–348. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen Q, Yang W, Gupta S, Biswas P, Smith
P, Bhagat G and Pernis AB: IRF-4-binding protein inhibits
interleukin-17 and interleukin-21 production by controlling the
activity of IRF-4 transcription factor. Immunity. 29:899–911. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro
CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ, Cua DJ and Littman DR: The orphan
nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of
proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell.
126:1121–1133. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Josefowicz SZ and Rudensky A: Control of
regulatory T cell lineage commitment and maintenance. Immunity.
30:616–625. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee YK, Mukasa R, Hatton RD and Weaver CT:
Developmental plasticity of Th17 and Treg cells. Curr Opin Immunol.
21:274–280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kryczek I, Wu K, Zhao E, Wei S, Vatan L,
Szeliga W, Huang E, Greenson J, Chang A, Roliński J, et al:
IL-17+ regulatory T cells in the microenvironments of
chronic inflammation and cancer. J Immunol. 186:4388–4395.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bovenschen HJ, van de Kerkhof PC, van Erp
PE, Woestenenk R, Joosten I and Koenen HJ: Foxp3+
regulatory T cells of psoriasis patients easily differentiate into
IL-17A-producing cells and are found in lesional skin. J Invest
Dermatol. 131:1853–1860. 2011.
|
|
12
|
Liu T, Song CH, Liu AM, Xie C, Zhao F,
Chen X, Cheng L and Yang PC: Forkhead box P3+ T cells
express interleukin-17 in nasal mucosa of patients with both
allergic rhinitis and polyposis. Clin Exp Immunol. 163:59–64.
2011.
|
|
13
|
Iellem A, Mariani M, Lang R, Recalde H,
Panina-Bordignon P, Sinigaglia F and D’Ambrosio D: Unique
chemotactic response profile and specific expression of chemokine
receptors CCR4 and CCR8 by CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells. J Exp
Med. 194:847–853. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Paust S, Lu L, McCarty N and Cantor H:
Engagement of B7 on effector T cells by regulatory T cells prevents
autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:10398–10403. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lehmann J, Huehn J, de la Rosa M, Maszyna
F, Kretschmer U, Krenn V, Brunner M, Scheffold A and Hamann A:
Expression of the integrin alpha Ebeta 7 identifies unique subsets
of CD25+ as well as CD25- regulatory T cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 99:13031–13036. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Salomon B, Lenschow DJ, Rhee L, Ashourian
N, Singh B, Sharpe A and Bluestone JA: B7/CD28 costimulation is
essential for the homeostasis of the
CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells that
control autoimmune diabetes. Immunity. 12:431–440. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu W, Putnam AL, Xu-Yu Z, Szot GL, Lee
MR, Zhu S, Gottlieb PA, Kapranov P, Gingeras TR, Fazekas de St
Groth B, et al: CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3
and suppressive function of human CD4+ Treg cells. J Exp
Med. 203:1701–1711. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Deaglio S, Dwyer KM, Gao W, Friedman D,
Usheva A, Erat A, Chen JF, Enjyoji K, Linden J, Oukka M, et al:
Adenosine generation catalyzed by CD39 and CD73 expressed on
regulatory T cells mediates immune suppression. J Exp Med.
204:1257–1265. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Borsellino G, Kleinewietfeld M, Di Mitri
D, Sternjak A, Diamantini A, Giometto R, Höpner S, Centonze D,
Bernardi G, Dell’Acqua ML, et al: Expression of ectonucleotidase
CD39 by Foxp3+ Treg cells: hydrolysis of extracellular
ATP and immune suppression. Blood. 110:1225–1232. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fletcher JM, Lonergan R, Costelloe L,
Kinsella K, Moran B, O’Farrelly C, Tubridy N and Mills KH:
CD39+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells suppress
pathogenic Th17 cells and are impaired in multiple sclerosis. J
Immunol. 183:7602–7610. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang S, Apasov S, Koshiba M and Sitkovsky
M: Role of A2a extracellular adenosine receptor-mediated signaling
in adenosine mediated inhibition of T-cell activation and
expansion. Blood. 90:1600–1610. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Boulet LP, FitzGerald JM, Levy ML, Cruz
AA, Pedersen S, Haahtela T and Bateman ED: A guide to the
translation of the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) strategy
into improved care. Eur Respir J. 39:1220–1229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shi YH, Shi GC, Wan HY, Jiang LH, Ai XY,
Zhu HX, Tang W, Ma JY, Jin XY and Zhang BY: Co-existence of Th1/Th2
and Th17/Treg imbalances in patients with allergic asthma and its
significance. Chin Med J (Engl). 124:1951–1956. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gavin MA, Rasmussen JP, Fontenot JD, Vasta
V, Manganiello VC, Beavo JA and Rudensky AY: Foxp3-dependent
programme of regulatory T cell differentiation. Nature.
445:771–775. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Flores-Borja F, Jury EC, Mauri C and
Ehrenstein MR: Defects in CTLA-4 are associated with abnormal
regulatory T cell function in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:19396–19401. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Annunziato F, Cosmi L, Santarlasci V,
Maggi L, Liotta F, Mazzinghi B, Parente E, Filì L, Ferri S, Frosali
F, et al: Phenotypic and functional features of human Th17 cells. J
Exp Med. 204:1849–1861. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|