|
1
|
Baldo L, Plent S, Skerjanec S and Meanwell
C: Novel use of bivalirudin in the treatment of acute coronary
syndrome US Patent 20090247465 A1. Filed March 27, 2009; issued
October 1, 2009.
|
|
2
|
Di Cera E: Thrombin. Mol Aspects Med.
29:203–254. 2008.
|
|
3
|
Nar H: The role of structural information
in the discovery of direct thrombin and factor Xa inhibitors.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 33:279–288. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bock PE, Panizzi P and Verhamme I:
Exosites in the substrate specificity of blood coagulation
reactions. J Thromb Haemost. 5:81–94. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gustafsson D: Combinations comprising a
low molecular weight thrombin inhibitor and a prodrug of a low
molecular weight thrombin inhibitor US Patent 20080113960 A1. Filed
November 9, 2007; issued May 15, 2008.
|
|
6
|
Robert S, Ghiotto J, Pirotte B, et al: Is
thrombin generation the new rapid, reliable and relevant
pharmacological tool for the development of anticoagulant drugs?
Pharmacol Res. 59:160–166. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee CJ and Ansell JE: Direct thrombin
inhibitors. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 72:581–592. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Harenberg J, Marx S, Krejczy M and Wehling
M: New anticoagulants-promising and failed developments. Br J
Pharmacol. 165:363–372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nutescu EA and Wittkowsky AK: Direct
thrombin inhibitors for anticoagulation. Ann Pharmacother.
38:99–109. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fareed J and Jeske WP: Small-molecule
direct antithrombins: argatroban. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol.
17:127–138. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
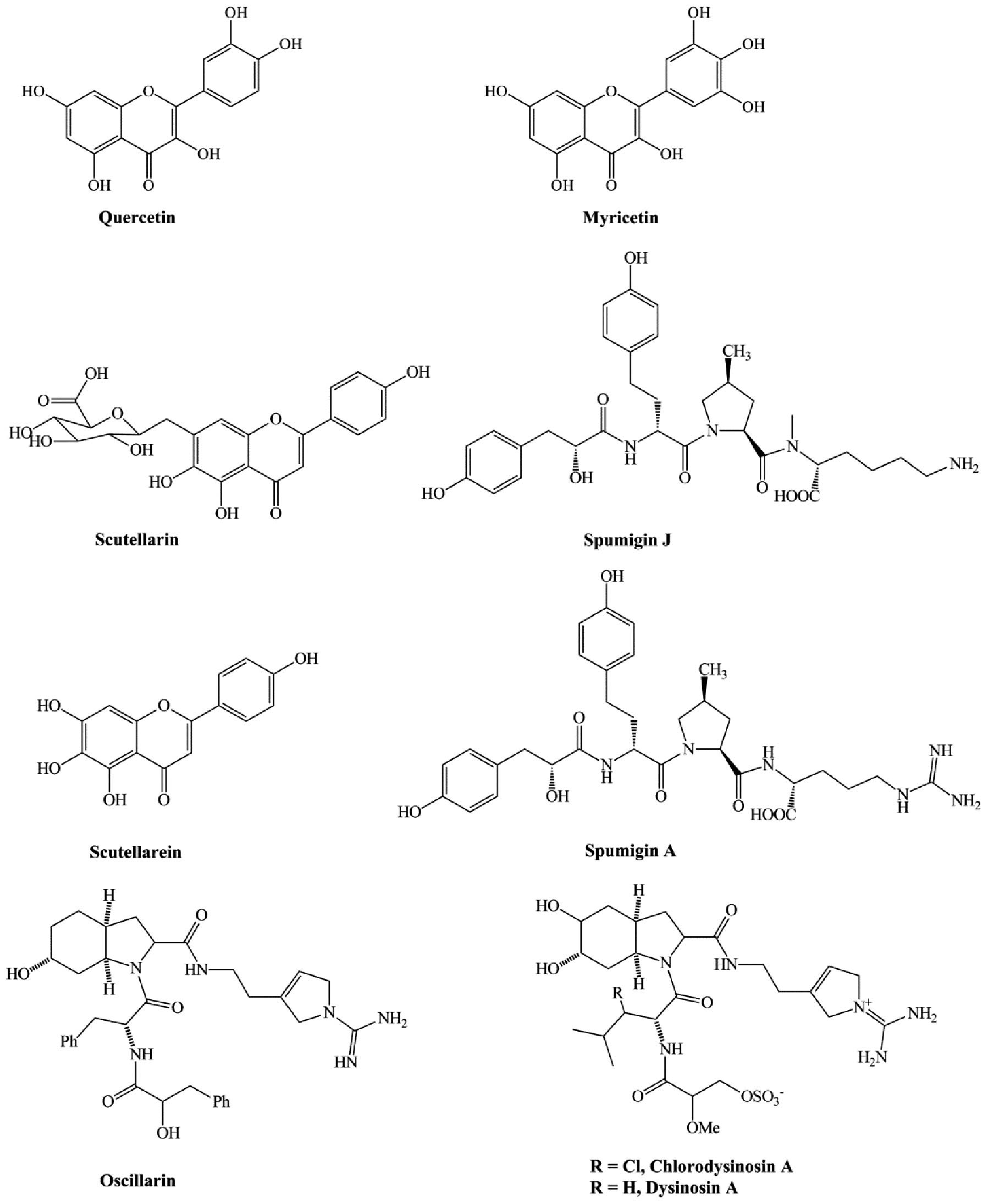
Owoo G and Burgos RA: Argatroban
formulations and methods for making and using same US Patent
7915290 B2. Filed February 29, 2008; issued March 29, 2011.
|
|
12
|
Blech S, Ebner T, Ludwig-Schwellinger E,
Stangier J and Roth W: The metabolism and disposition of the oral
direct thrombin inhibitor, dabigatran, in humans. Drug Metab
Dispos. 36:386–399. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fugate JE, Rabinstein AA, McBane RD and
Lanzino G: Dabigatran: a primer for neurosurgeons. World Neurosurg.
79:154–158. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Franchini M and Mannucci PM: A new era for
anticoagulants. Eur J Intern Med. 20:562–568. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eriksson BI, Smith H, Yasothan U and
Kirkpatrick P: Dabigatran etexilate. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
7:557–558. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Greinacher A and Lubenow N: Recombinant
hirudin in clinical practice: focus on lepirudin. Circulation.
103:1479–1484. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Frame JN, Rice L, Bartholomew JR and
Whelton A: Rationale and design of the PREVENT-HIT study: a
randomized, open-label pilot study to compare desirudin and
argatroban in patients with suspected heparin-induced
thrombocytopenia with or without thrombosis. Clin Ther. 32:626–636.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gosselin RC, Dager WE, King JH, et al:
Effect of direct thrombin inhibitors, bivalirudin, lepirudin, and
argatroban, on prothrombin time and INR values. Am J Clin Pathol.
121:593–599. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Warkentin TE: Bivalent direct thrombin
inhibitors: hirudin and bivalirudin. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol.
17:105–125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gross PL and Weitz JI: New anticoagulants
for treatment of venous thromboembolism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 28:380–386. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Greinacher A, Lubenow N and Eichler P:
Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions associated with lepirudin
in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Circulation.
108:2062–2065. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lewis CM and Deschler DG: Desirudin
reduces the rate of microvenous thrombosis in a rat model.
Laryngoscope. 118:1149–1152. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Blombäck B, Blombäck M, Olsson P, Svendsen
L and Aberg G: Synthetic peptides with anticoagulant and
vasodilating activity. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 107:59–61.
1969.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Costanzo MJ, Maryanoff BE, Hecker LR, et
al: Potent thrombin inhibitors that probe the S1 subsite:
tripeptide transition state analogues based on a
heterocycle-activated carbonyl group. J Med Chem. 39:3039–3043.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kudryavtsev K, Shulga D, Chupakhin V, et
al: Design of small-molecule thrombin inhibitors based on the
cis-5-phenylproline scaffold. Russ Chem Bull Int Ed. 60:685–693.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Isaacs RC, Solinsky MG, Cutrona KJ, et al:
Structure-based design of novel groups for use in the P1 position
of thrombin inhibitor scaffolds. Part 1: Weakly basic azoles.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 16:338–342. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Inghardt T and Nystrm JE:
Amidinobenzylamine derivatives and their use as thrombin inhibitors
US Patent 6599894. PCT Pub No. WO00/42059. Filed January 13, 2000;
issued July 29, 2003.
|
|
28
|
Inghardt T, Karlsson O, Linschoten M and
Nystrom JE: New amidino derivatives and their use as thrombin
inhibitors US Patent 20070249578 A1. Filed June 6, 2007; issued
October 25, 2007.
|
|
29
|
Inghardt T, Johansson A and Svensson A:
New mandelic acid derivatives and their use as thrombin inhibitors
US Patent 20100087651 Al. Filed June 25, 2009; issued April 8,
2010.
|
|
30
|
Kreutter KD, Lu T, Lee L, et al: Orally
efficacious thrombin inhibitors with cyanofluorophenylacetamide as
the P2 motif. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 18:2865–2870. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zega A, Mlinšek G, Šolmajer T,
Trampuš-Bakija A, Stegnar M and Urleb U: Thrombin inhibitors built
on an azaphenylalanine scaffold. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
14:1563–1567. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Urleb U, Zega A, Stegnar M, Trampus BA,
Solmajer T and Mlinsek G: Amidinophenylalanine derivatives as
thrombin inhibitors US Patent 20080004256 A1. Filed September 12,
2007; issued January 3, 2008.
|
|
33
|
Isaacs RC, Solinsky MG, Cutrona KJ, et al:
Structure-based design of novel groups for use in the P1 position
of thrombin inhibitor scaffolds. Part 2: N-acetamidoimidazoles
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 18:2062–2066. 2008.
|
|
34
|
Staas DD, Savage KL, Sherman VL, et al:
Discovery of potent, selective 4-fluoroproline-based thrombin
inhibitors with improved metabolic stability. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
14:6900–6916. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Brånalt J, Gustafsson D, Nilsson I and
Polla M: Compounds 148 US Patent 8119673 B2. Filed June 23, 2009;
issued February 21, 2012.
|
|
36
|
Lange UE, Baucke D, Hornberger W, Mack H,
Seitz W and Höffken HW: Orally active thrombin inhibitors. Part 2:
Optimization of the P2-moiety. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 16:2648–2653.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Young MB, Barrow JC, Kristen L, et al:
Discovery and evaluation of potent P1 aryl heterocycle-based
thrombin inhibitors. J Med Chem. 47:2995–3008. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Burgey CS, Robinson KA, Williams PD,
Coburn C, Lyle TA and Sanderson PE: Pyrazinone thrombin inhibitors
US Patent 6455532 B1. Filed June 1, 2000; issued September 24,
2002.
|
|
39
|
Nantermet PG, Burgey CS, Robinson KA, et
al: P2 pyridine N-oxide thrombin inhibitors: a novel peptidomimetic
scaffold. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 15:2771–2775. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang S: Boronic acid thrombin inhibitors
US Patent 20070185060 A1. Filed March 9, 2005; issued August 9,
2007.
|
|
41
|
Ilaš J, Tomašić T and Kikelj D: Novel
potent and selective thrombin inhibitors based on a central
1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-one scaffold. J Med Chem. 51:2863–2867.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu Y, Yang X, Gong G, Yang W, He G and Li
F: Oral thrombin inhibitor and preparation method and medical use
thereof WIPO Patent 2012174856 A1. Filed June 15, 2012; issued
December 27, 2012.
|
|
43
|
Poyarkov AA, Poyarkova SA, Smirnova IV and
Kukhar VP: Liporetro-D-peptides-a novel class of highly selective
thrombin inhibitors. Thromb Res. 129:97–105. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Burke JM and Berzal-Herranz A: In vitro
selection and evolution of RNA: applications for catalytic RNA,
molecular recognition, and drug discovery. FASEB J. 7:106–112.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bock LC, Griffin LC, Latham JA, Vermaas EH
and Toole JJ: Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind
and inhibit human thrombin. Nature. 355:564–566. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lancellotti S and De Cristofaro R:
Nucleotide-derived thrombin inhibitors: a new tool for an old
issue. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 7:19–28. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
White R, Rusconi C, Scardino E, et al:
Generation of species cross-reactive aptamers using ‘toggle’ SELEX.
Mol Ther. 4:567–573. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mazurov AV, Titaeva EV, Khaspekova SG, et
al: Characteristics of a new DNA aptamer, direct inhibitor of
thrombin. Bull Exp Biol Med. 150:422–425. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tasset DM, Kubik MF and Steiner W:
Oligonucleotide inhibitors of human thrombin that bind distinct
epitopes. J Mol Biol. 272:688–698. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bompiani KM, Monroe DM, Church FC and
Sullenger BA: A high affinity, antidote-controllable prothrombin
and thrombin-binding RNA aptamer inhibits thrombin generation and
thrombin activity. J Thromb Haemost. 10:870–880. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nimjee SM, Rusconi CP, Harrington RA and
Sullenger BA: The potential of aptamers as anticoagulants. Trends
Cardiovasc Med. 15:41–45. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
van de Locht A, Lamba D, Bauer M, et al:
Two heads are better than one: crystal structure of the insect
derived double domain Kazal inhibitor rhodniin in complex with
thrombin. EMBO J. 14:5149–5157. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Markwardt F: The comeback of hirudin - an
old-established anticoagulant agent. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin
Morphol Blutforsch. 115:10–23. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Salzet M: Leech thrombin inhibitors. Curr
Pharm Des. 8:493–503. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Strube KH, Kröger B, Bialojan S, Otte M
and Dodt J: Isolation, sequence analysis and cloning of haemadin.
An anticoagulant peptide from the Indian leech. J Biol Chem.
268:8590–8595. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Markwardt F: State-of-the-Art Review:
antithrombotic agents from hematophagous animals. Clin Appl Thromb
Hemost. 2:75–82. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Salzet M, Chopin V, Baert J, Matias I and
Malecha J: Theromin, a novel leech thrombin inhibitor. J Biol Chem.
275:30774–30780. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Francischetti IM, Valenzuela JG and
Ribeiro JM: Anophelin: kinetics and mechanism of thrombin
inhibition. Biochemistry. 38:16678–16685. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Waidhet-Kouadio P, Yuda M, Ando K and
Chinzei Y: Purification and characterization of a thrombin
inhibitor from the salivary glands of a malarial vector mosquito,
Anopheles stephensi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1381:227–233.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Watanabe RM, Soares TS, Morais-Zani K, et
al: A novel trypsin Kazal-type inhibitor from Aedes aegypti
with thrombin coagulant inhibitory activity. Biochimie. 92:933–939.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Soares TS, Watanabe RM, Tanaka-Azevedo AM,
et al: Expression and functional characterization of boophilin, a
thrombin inhibitor from Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus
midgut. Vet Parasitol. 521–528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Macedo-Ribeiro S, Almeida C, Calisto BM,
et al: Isolation, cloning and structural characterisation of
boophilin, a multifunctional Kunitz-type proteinase inhibitor from
the cattle tick. PLoS One. 3:e16242008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ciprandi A, de Oliveira SK, Masuda A, Horn
F and Termignoni C: Boophilus microplus: Its saliva contains
microphilin, a small thrombin inhibitor. Exp Parasitol. 114:40–46.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Liao M, Zhou J, Gong H, et al: Hemalin, a
thrombin inhibitor isolated from a midgut cDNA library from the
hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. J Insect Physiol.
55:165–173. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Iwanaga S, Okada M, Isawa H, Morita A,
Yuda M and Chinzei Y: Identification and characterization of novel
salivary thrombin inhibitors from the ixodidae tick,
Haemaphysalis longicornis. Eur J Biochem. 270:1926–1934.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Noeske-Jungblut C, Haendler B, Donner P,
Alagon A, Possani L and Schleuning WD: Triabin, a highly potent
exosite inhibitor of thrombin. J Biol Chem. 270:28629–28634. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Campos I, Amino R, Sampaio C, et al:
Infestin, a thrombin inhibitor present in Triatoma infestans
midgut, a Chagas’ disease vector: gene cloning, expression and
characterization of the inhibitor. Insect Biochem Mol Biol.
32:991–997. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Araujo R, Campos I, Tanaka A, et al:
Brasiliensin: a novel intestinal thrombin inhibitor from
Triatoma brasiliensis (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) with an
important role in blood intake. Int J Parasitol. 37:1351–1358.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Mende K, Petoukhova O, Koulitchkova V, et
al: Dipetalogastin, a potent thrombin inhibitor from the
blood-sucking insect Dipetalogaster maximus. Eur J Biochem.
266:583–590. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Osipov AV, Filkin SY, Makarova YV, Tsetlin
VI and Utkin YN: A new type of thrombin inhibitor, noncytotoxic
phospholipase A2, from the Naja haje cobra venom. Toxicon.
55:186–194. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Arocas V, Zingali RB, Guillin MC, Bon C
and Jandrot-Perrus M: Bothrojaracin: a potent two-site-directed
thrombin inhibitor. Biochemistry. 35:9083–9089. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yang X, Wang Y, Lu Z, et al: A novel
serine protease inhibitor from the venom of Vespa bicolor
Fabricius. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 153:116–120.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lu X, Ma Y, Wu J and Lai R: Two serine
protease inhibitors from the skin secretions of the toad,
Bombina microdeladigitora. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem
Mol Biol. 149:608–612. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Liu L, Ma H, Yang N, et al: A series of
natural flavonoids as thrombin inhibitors: structure-activity
relationships. Thromb Res. 126:e365–e378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Doljak B, Cateni F, Anderluh M, Procida G,
Zilic J and Zacchigna M: Glycerolipids as selective thrombin
inhibitors from the fungus Stereum hirsutum. Drug Dev Ind
Pharm. 32:635–643. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Li NG, Song SL, Shen MZ, et al: Mannich
bases of scutellarein as thrombin-inhibitors: design, synthesis,
biological activity and solubility. Bioorg Med Chem. 20:6919–1923.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Anas AR, Kisugi T, Umezawa T, et al:
Thrombin inhibitors from the freshwater cyanobacterium Anabaena
compacta. J Nat Prod. 75:1546–1552. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hanessian S, Therrien E, Zhang J, et al:
From natural products to achiral drug prototypes: potent thrombin
inhibitors based on P2/P3 dihydropyrid-2-one core motifs. Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 19:5429–5432. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Martin JA, Parekh P, Kim Y, et al:
Selection of an aptamer antidote to the anticoagulant drug
bivalirudin. PLoS One. 8:e573412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hon SF, Li HL and Cheng PW: Use of direct
thrombin inhibitor for treatment of cerebral venous thrombosis. J
Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 21:e11–e15. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Moshfeghi AA and Puliafito CA: Pegaptanib
sodium for the treatment of neovascular age-related macular
degeneration. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 14:671–682. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Ku SK, Kim TH and Bae JS: Anticoagulant
activities of persicarin and isorhamnetin. Vascul Pharmacol.
58:272–279. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Robert S, Baccelli C, Devel P, Dogné JM
and Quetin-Leclercq J: Effects of leaf extracts from Croton
zambesicus Müell. Arg on hemostasis. J Ethnopharmacol. 128:641–648.
2010.
|