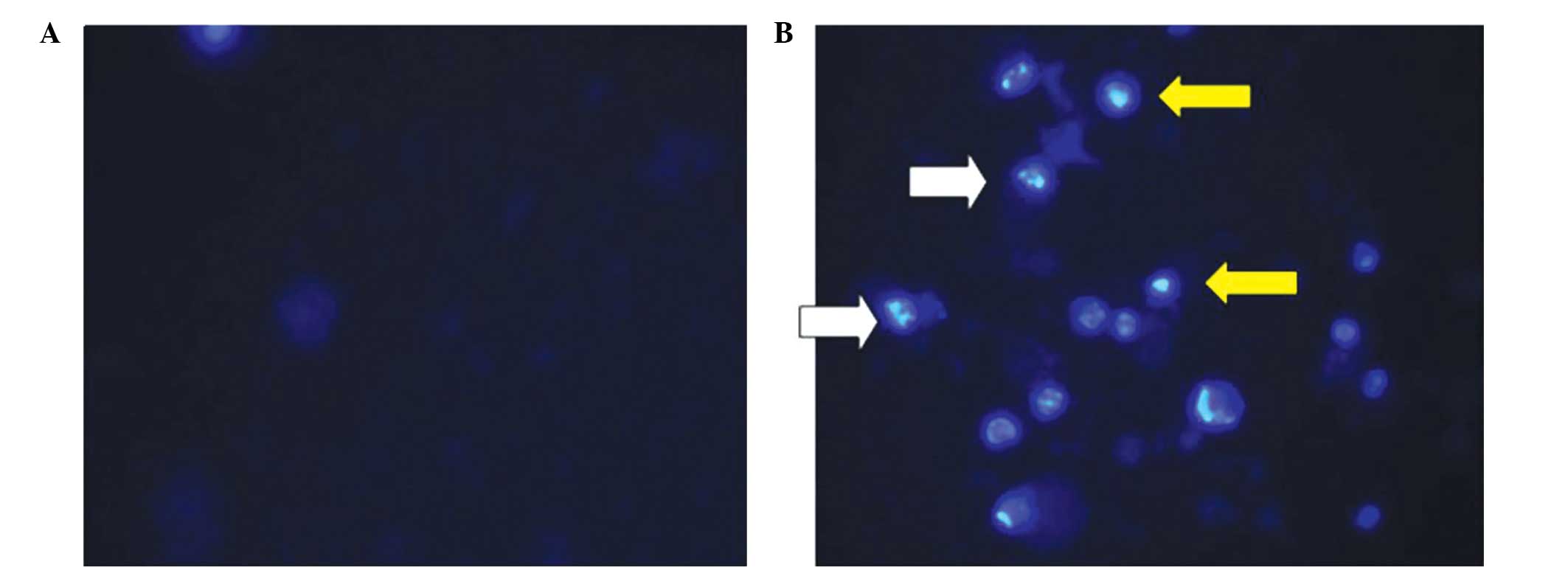
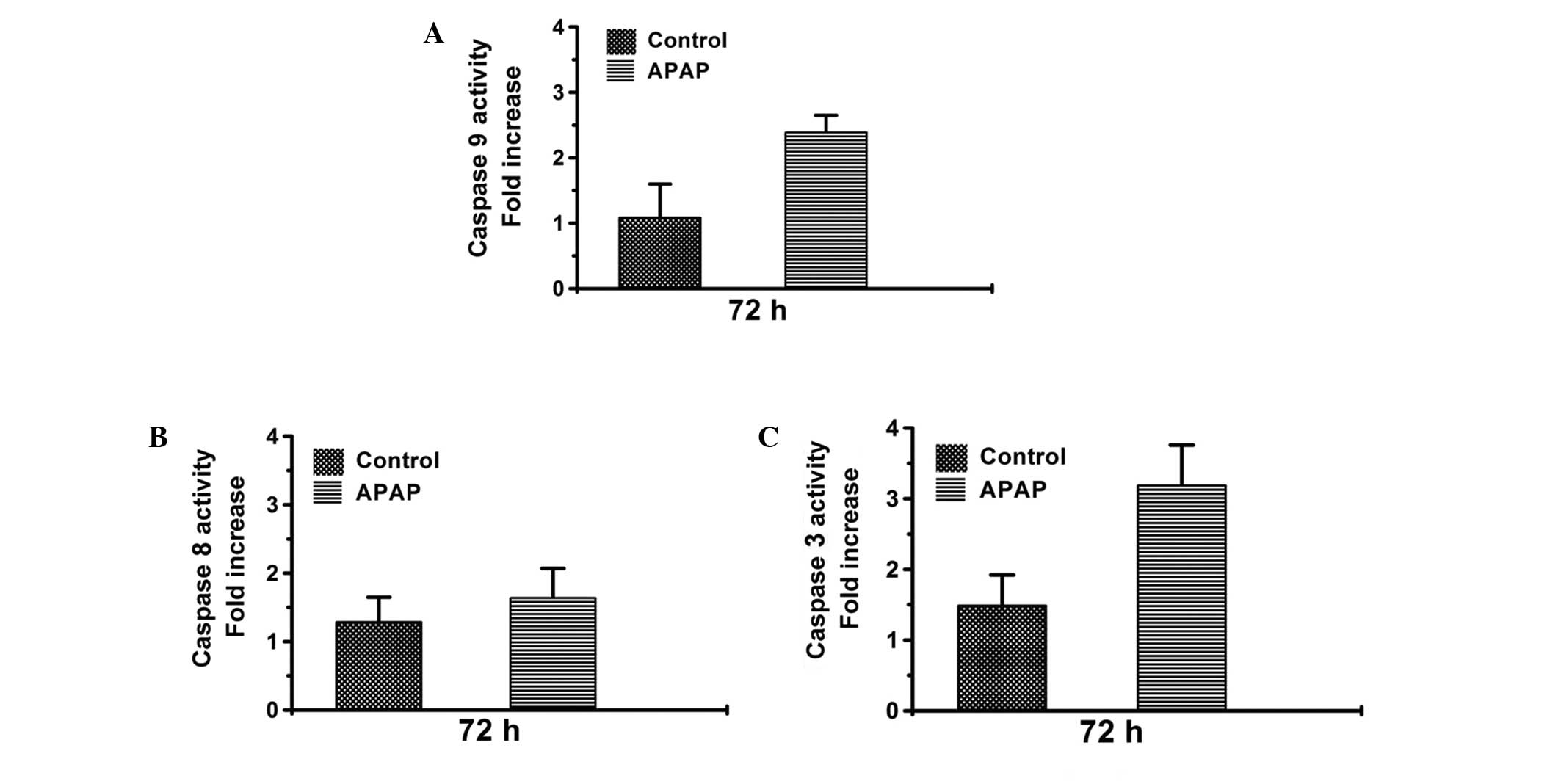
|
1
|
Rumack BH: Acetaminophen misconceptions.
Hepatology. 40:10–15. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cuzzolin L, Antonucci R and Fanos V:
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) efficacy and safety in the newborn.
Curr Drug Metab. 14:178–185. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Klotz U: Paracetamol (acetaminophen) - a
popular and widely used nonopioid analgesic. Arzneimittelforschung.
62:355–359. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sullivan JE and Farrar HC: Section on
Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Committee on Drugs: Fever
and antipyretic use in children. Pediatrics. 127:580–587. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Young RJ: Dextropropoxyphene overdosage.
Pharmacological considerations and clinical management. Drugs.
26:70–79. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Simkin S, Hawton K, Kapur N and Gunnell D:
What can be done to reduce mortality from paracetamol overdoses? A
patient interview study. QJM. 105:41–51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hawton K, Bergen H, Simkin S, et al:
Impact of different pack sizes of paracetamol in the United Kingdom
and Ireland on intentional overdoses: a comparative study. BMC
Public Health. 11:4602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hawton K, Townsend E, Deeks J, et al:
Effects of legislation restricting pack sizes of paracetamol and
salicylate on self poisoning in the United Kingdom: before and
after study. BMJ. 322:1203–1207. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Daly FF, Fountain JS, Murray L, Graudins A
and Buckley NA: Guidelines for the management of paracetamol
poisoning in Australia and New Zealand - explanation and
elaboration. A consensus statement from clinical toxicologists
consulting to the Australasian poisons information centres. Med J
Aust. 188:296–301. 2008.
|
|
10
|
Gopi KS, Reddy AG, Jyothi K and Kumar BA:
Acetaminophen-in duced hepato- and nephrotoxicity and amelioration
by silymarin and Terminalia chebula in rats. Toxicol Int.
17:64–66. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abdel-Zaher AO, Abdel-Hady RH, Mahmoud MM
and Farrag MM: The potential protective role of alpha-lipoic acid
against acetaminophen-induced hepatic and renal damage. Toxicology.
243:261–270. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cermik H, Taslipinar MY, Aydin I, et al:
The relationship between N-acetylcysteine, hyperbaric oxygen, and
inflammation in a rat model of acetaminophen-induced
nephrotoxicity. Inflammation. 36:1145–1152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ucar F, Taslipinar MY, Alp BF, et al: The
effects of N-acetylcysteine and ozone therapy on oxidative stress
and inflammation in acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity model. Ren
Fail. 35:640–647. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liang YL, Zhang ZH, Liu XJ, et al:
Melatonin protects against apoptosis-inducing factor
(AIF)-dependent cell death during acetaminophen-induced acute liver
failure. PLoS One. 7:e519112012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Amaral SS, Oliveira AG, Marques PE, et al:
Altered responsiveness to extracellular ATP enhances acetaminophen
hepatotoxicity. Cell Commun Signal. 11:102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Badmann A, Langsch S, Keogh A, Brunner T,
Kaufmann T and Corazza N: TRAIL enhances paracetamol-induced liver
sinusoidal endothelial cell death in a Bim- and Bid-dependent
manner. Cell Death Dis. 3:e4472012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Badmann A, Keough A, Kaufmann T, Bouillet
P, Brunner T and Corazza N: Role of TRAIL and the pro-apoptotic
Bcl-2 homolog Bim in acetaminophen-induced liver damage. Cell Death
Dis. 2:e1712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McGill MR, Yan HM, Ramachandran A, Murray
GJ, Rollins DE and Jaeschke H: HepaRG cells: a human model to study
mechanisms of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Hepatology. 53:974–982.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao X, Cong X, Zheng L, Xu L, Yin L and
Peng J: Dioscin, a natural steroid saponin, shows remarkable
protective effect against acetaminophen-induced liver damage in
vitro and in vivo. Toxicol Lett. 214:69–80. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mobasher MA, Gonzalez-Rodriguez A,
Santamaria B, et al: Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B modulates
GSK3beta/Nrf2 and IGFIR signaling pathways in acetaminophen-induced
hepatotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 4:e6262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ramachandran A, McGill MR, Xie Y, Ni HM,
Ding WX and Jaeschke H: Receptor interacting protein kinase 3 is a
critical early mediator of acetaminophen-induced hepatocyte
necrosis in mice. Hepatology. 58:2099–2108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ahmad ST, Arjumand W, Nafees S, et al:
Hesperidin alleviates acetaminophen induced toxicity in Wistar rats
by abrogation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation.
Toxicol Lett. 208:149–161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Inkielewicz-Stepniak I and Knap N: Effect
of exposure to fluoride and acetaminophen on oxidative/nitrosative
status of liver and kidney in male and female rats. Pharmacol Rep.
64:902–911. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Slitt AM, Dominick PK, Roberts JC and
Cohen SD: Effect of ribose cysteine pretreatment on hepatic and
renal acetaminophen metabolite formation and glutathione depletion.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 96:487–494. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yousef MI, Omar SA, El-Guendi MI and
Abdelmegid LA: Potential protective effects of quercetin and
curcumin on paracetamol-induced histological changes, oxidative
stress, impaired liver and kidney functions and haematotoxicity in
rat. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:3246–3261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Jia Y, Yang M, Yang P, Tian Y,
Xiao A and Wen A: The impaired disposition of probe drugs is due to
both liver and kidney dysfunctions in CCl(4)-model rats. Environ
Toxicol Pharmacol. 33:453–458. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao YL, Zhou GD, Yang HB, Wang JB, Shan
LM, Li RS and Xiao XH: Rhein protects against acetaminophen-induced
hepatic and renal toxicity. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:1705–1710. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Roomi MW, Kalinovsky T, Ivanov V, Rath M
and Niedzwiecki A: A nutrient mixture prevents acetaminophen
hepatic and renal toxicity in ICR mice. Hum Exp Toxicol.
27:223–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Posadas I, Santos P and Cena V:
Acetaminophen induces human neuroblastoma cell death through NFKB
activation. PLoS One. 7:e501602012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Posadas I, Vellecco V, Santos P,
Prieto-Lloret J and Cena V: Acetaminophen potentiates
staurosporine-induced death in a human neuroblastoma cell line. Br
J Pharmacol. 150:577–585. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jaeschke H: Comments on ‘glycogen synthase
kinase-3 mediates acetaminophen-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma
cells’. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 314:1401–1404. 2005.
|
|
32
|
Macanas-Pirard P, Yaacob NS, Lee PC,
Holder JC, Hinton RH and Kass GE: Glycogen synthase kinase-3
mediates acetaminophen-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma cells. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 313:780–789. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bilir A, Guneri AD and Altinoz MA:
Acetaminophen and DMSO modulate growth and gemcitabine cytotoxicity
in FM3A breast cancer cells in vitro. Neoplasma. 51:460–464.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu YJ, Neuwelt AJ, Muldoon LL and Neuwelt
EA: Acetaminophen enhances cisplatin- and paclitaxel-mediated
cytotoxicity to SKOV3 human ovarian carcinoma. Anticancer Res.
33:2391–2400. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Reszka KJ, Britigan LH, Rasmussen GT,
Wagner BA, Burns CP and Britigan BE: Acetaminophen stimulates the
peroxidative metabolism of anthracyclines. Arch Biochem Biophys.
427:16–29. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Manov I, Bashenko Y, Eliaz-Wolkowicz A,
Mizrahi M, Liran O and Iancu TC: High-dose acetaminophen inhibits
the lethal effect of doxorubicin in HepG2 cells: the role of
P-glycoprotein and mitogen-activated protein kinase p44/42 pathway.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 322:1013–1022. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kidokoro K, Satoh M, Nagasu H, et al:
Tacrolimus induces glomerular injury via endothelial dysfunction
caused by reactive oxygen species and inflammatory change. Kidney
Blood Press Res. 35:549–557. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Stacchiotti A, Li Volti G, Lavazza A, et
al: Different role of Schisandrin B on mercury-induced renal damage
in vivo and in vitro. Toxicology. 286:48–57. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Suddek GM: Sunitinib improves
chemotherapeutic efficacy and ameliorates cisplatin-induced
nephrotoxicity in experimental animals. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
67:1035–1044. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Neria F, Castilla MA, Sanchez RF, et al:
Inhibition of JAK2 protects renal endothelial and epithelial cells
from oxidative stress and cyclosporin A toxicity. Kidney Int.
75:227–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jang HS, Kim JI, Jung KJ, Kim J, Han KH
and Park KM: Bone marrow-derived cells play a major role in kidney
fibrosis via proliferation and differentiation in the infiltrated
site. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832.817–825. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Seikrit C, Henkel C, van Roeyen CR, et al:
Biological responses to PDGF-AA versus PDGF-CC in renal
fibroblasts. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 28:889–900. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim SH, Yu MA, Ryu ES, Jang YH and Kang
DH: Indoxyl sulfate-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
and apoptosis of renal tubular cells as novel mechanisms of
progression of renal disease. Lab Invest. 92:488–498. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Abdul Hamid Z, Budin SB, Wen Jie N, Hamid
A, Husain K and Mohamed J: Nephroprotective effects of Zingiber
zerumbet Smith ethyl acetate extract against
paracetamol-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. J
Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 13:176–185. 2012.
|
|
45
|
Chen N, Aleksa K, Woodland C, Rieder M and
Koren G: The effect of N-acetylcysteine on ifosfamide-induced
nephrotoxicity: in vitro studies in renal tubular cells. Transl
Res. 150:51–57. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Isik B, Bayrak R, Akcay A and Sogut S:
Erdosteine against acetaminophen induced renal toxicity. Mol Cell
Biochem. 287:185–191. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lorz C, Justo P, Sanz A, Subira D, Egido J
and Ortiz A: Paracetamol-induced renal tubular injury: a role for
ER stress. J Am Soc Nephrol. 15:380–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lorz C, Justo P, Sanz AB, Egido J and
Ortiz A: Role of Bcl-xL in paracetamol-induced tubular epithelial
cell death. Kidney Int. 67:592–601. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Boulares AH, Zoltoski AJ, Stoica BA,
Cuvillier O and Smulson ME: Acetaminophen induces a
caspase-dependent and Bcl-XL sensitive apoptosis in human hepatoma
cells and lymphocytes. Pharmacol Toxicol. 90:38–50. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Manov I, Hirsh M and Iancu TC:
N-acetylcysteine does not protect HepG2 cells against
acetaminophen-induced apoptosis. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
94:213–225. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Manov I, Hirsh M and Iancu TC:
Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and mechanisms of its protection by
N-acetylcysteine: a study of Hep3B cells. Exp Toxicol Pathol.
53:489–500. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu CS, Yen CJ, Chou RH, et al:
Cancer-associated carbohydrate antigens as potential biomarkers for
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e394662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yu YL, Su KJ, Chen CJ, et al: Synergistic
anti-tumor activity of isochaihulactone and paclitaxel on human
lung cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 227:213–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang L, Li J, Jiang Z, et al: Inhibition
of aquaporin-1 expression by RNAi protects against aristolochic
acid I-induced apoptosis in human proximal tubular epithelial
(HK-2) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 405:68–73. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yu YL, Chou RH, Wu CH, et al: Nuclear EGFR
suppresses ribonuclease activity of polynucleotide phosphorylase
through DNAPK-mediated phosphorylation at serine 776. J Biol Chem.
287:31015–31026. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen KH, Li PC, Lin WH, Chien CT and Low
BH: Depression by a green tea extract of alcohol-induced oxidative
stress and lipogenesis in rat liver. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
75:1668–1676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lin BR, Yu CJ, Chen WC, et al: Green tea
extract supplement reduces D-galactosamine-induced acute liver
injury by inhibition of apoptotic and proinflammatory signaling. J
Biomed Sci. 16:352009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yu YL, Yu SL, Su KJ, et al: Extended
O6-methylguanine methyltransferase promoter hypermethylation
following n-butylidenephthalide combined with
1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea (BCNU) on inhibition of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth. J Agric Food Chem.
58:1630–1638. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Yu YL, Wei CW, Chen YL, Chen MH and Yiang
GT: Immunotherapy of breast cancer by single delivery with
rAAV2-mediated interleukin-15 expression. Int J Oncol. 36:365–370.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yiang GT, Chen YH, Chou PL, Chang WJ, Wei
CW and Yu YL: The NS3 protease and helicase domains of Japanese
encephalitis virus trigger cell death via caspase-dependent and
-independent pathways. Mol Med Rep. 7:826–830. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yiang GT, Yu YL, Hu SC, Chen MH, Wang JJ
and Wei CW: PKC and MEK pathways inhibit caspase-9/-3-mediated
cytotoxicity in differentiated cells. FEBS Lett. 582:881–885. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wei CW, Lin CC, Yu YL, et al:
n-Butylidenephthalide induced apoptosis in the A549 human lung
adenocarcinoma cell line by coupled down-regulation of AP-2alpha
and telomerase activity. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:1297–1306. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hassane S, Leonhard WN, van der Wal A, et
al: Elevated TGFbeta-Smad signalling in experimental Pkd1 models
and human patients with polycystic kidney disease. J Pathol.
222:21–31. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Edward M, Quinn JA, Mukherjee S, et al:
Gadodiamide contrast agent ‘activates’ fibroblasts: a possible
cause of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. J Pathol. 214:584–593.
2008.
|
|
65
|
Kumari A and Kakkar P: Lupeol protects
against acetaminophen-induced oxidative stress and cell death in
rat primary hepatocytes. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:1781–1789. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Anoush M, Eghbal MA, Fathiazad F, Hamzeiy
H and Kouzehkonani NS: The protective effects of garlic extract
against acetaminophen-induced oxidative stress and glutathione
depletion. Pak J Biol Sci. 12:765–771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yao Y, Yang J, Wang D, et al: The aqueous
extract of Lycopus lucidus Turcz ameliorates
streptozotocin-induced diabetic renal damage via inhibiting
TGF-beta1 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 20:1160–1167. 2013.
|
|
68
|
Hsieh TJ, Hsieh PC, Tsai YH, et al:
Melamine induces human renal proximal tubular cell injury via
transforming growth factor-beta and oxidative stress. Toxicol Sci.
130:17–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hills CE, Siamantouras E, Smith SW,
Cockwell P, Liu KK and Squires PE: TGFβ modulates cell-to-cell
communication in early epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.
Diabetologia. 55:812–824. 2012.
|
|
70
|
Xu Y, Yang S, Huang J, Ruan S, Zheng Z and
Lin J: Tgf-β1 induces autophagy and promotes apoptosis in renal
tubular epithelial cells. Int J Mol Med. 29:781–790. 2012.
|
|
71
|
Yoshikawa M, Hishikawa K, Idei M and
Fujita T: Trichostatin a prevents TGF-beta1-induced apoptosis by
inhibiting ERK activation in human renal tubular epithelial cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 642:28–36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li R, Wang Y, Liu Y, et al: Curcumin
inhibits transforming growth factor-β1-induced EMT via PPARγ
pathway, not Smad pathway in renal tubular epithelial cells. PLoS
One. 8:e588482013.
|
|
73
|
Han WQ, Zhu Q, Hu J, Li PL, Zhang F and Li
N: Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl-hydroxylase-2 mediates
transforming growth factor beta 1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in renal tubular cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1833.1454–1462. 2013.
|
|
74
|
Yan HD, Li XZ, Xie JM and Li M: Effects of
advanced glycation end products on renal fibrosis and oxidative
stress in cultured NRK-49F cells. Chin Med J (Engl). 120:787–793.
2007.
|
|
75
|
Guo W, Xu H, Huang WY, et al: Prohibitin
suppresses renal interstitial fibroblasts proliferation and
phenotypic change induced by transforming growth factor-beta1.
Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 87:1660–1665. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
76
|
Levanon D, Manov I and Iancu TC:
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the effects of
acetaminophen and N-acetylcysteine on the surface morphology of
Hep3B hepatoma cells in vitro. Ultrastruct Pathol. 28:3–14.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Williamson K, Wahl MS and Mycyk MB: Direct
comparison of 20-hour IV, 36-hour oral, and 72-hour oral
acetylcysteine for treatment of acute acetaminophen poisoning. Am J
Ther. 20:37–40. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Saritas A, Kandis H, Baltaci D, et al:
N-Acetyl cysteine and erdosteine treatment in acetaminophen-induced
liver damage. Toxicol Ind Health. Oct 15–2012.(Epub ahead of
print).
|