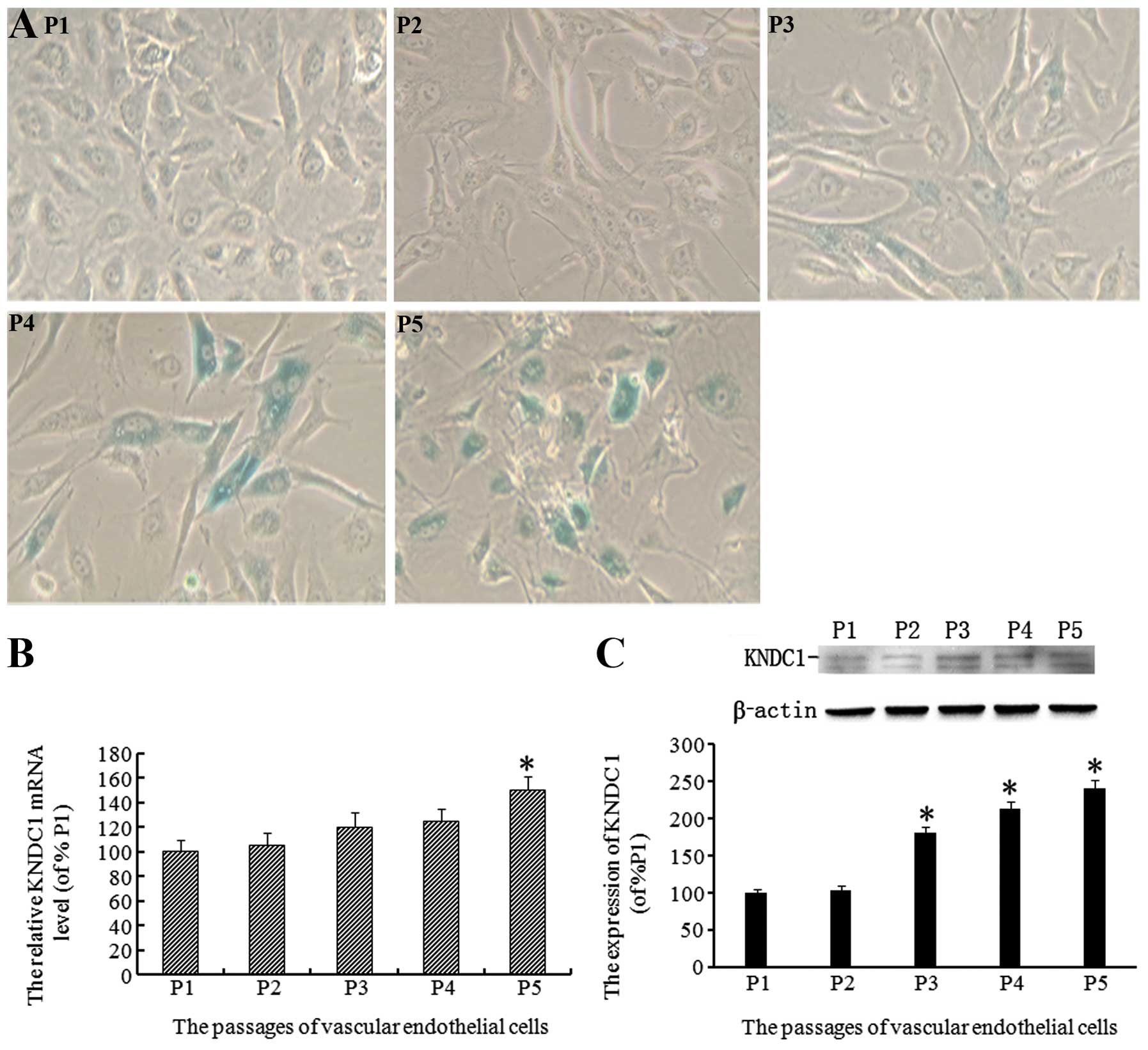
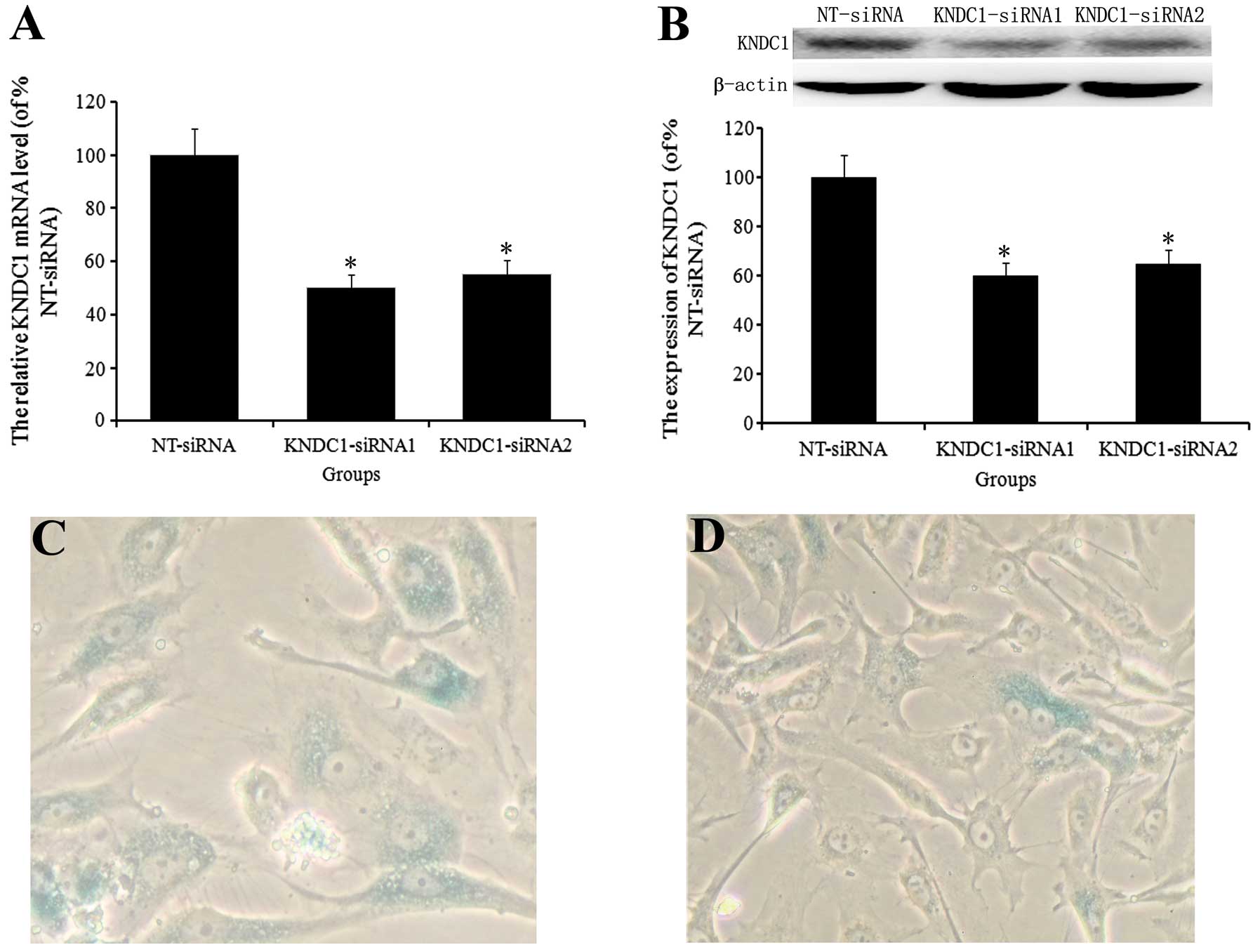
|
1
|
Huang J, Gan Q, Han L, et al: SIRT1
overexpression antagonizes cellular senescence with activated
ERK/S6k1 signaling in human diploid fibroblasts. PLoS One.
3:e17102008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Krouwer VJ, Hekking LH, Langelaar-Makkinje
M, Regan-Klapisz E and Post JA: Endothelial cell senescence is
associated with disrupted cell-cell junctions and increased
monolayer permeability. Vasc Cell. 4:122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang JC and Bennett M: Aging and
atherosclerosis: mechanisms, functional consequences, and potential
therapeutics for cellular senescence. Circ Res. 111:245–259. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Erusalimsky JD: Vascular endothelial
senescence: from mechanisms to pathophysiology. J Appl Physiol.
1985.106:326–332. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cardus A, Uryga AK, Walters G and
Erusalimsky JD: SIRT6 protects human endothelial cells from DNA
damage, telomere dysfunction, and senescence. Cardiovasc Res.
97:571–579. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang J, Furuya A, Hayashi K and Furuichi
T: Interaction between very-KIND Ras guanine exchange factor and
microtubule-associated protein 2, and its role in dendrite growth -
structure and function of the second kinase noncatalytic C-lobe
domain. FEBS J. 278:1651–1661. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pawson T and Nash P: Assembly of cell
regulatory systems through protein interaction domains. Science.
300:445–452. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ciccarelli FD, Bork P and Kerkhoff E: The
KIND module: a putative signalling domain evolved from the C lobe
of the protein kinase fold. Trends Biochem Sci. 28:349–352. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mees A, Rock R, Ciccarelli FD, et al:
Very-KIND is a novel nervous system specific guanine nucleotide
exchange factor for Ras GTPases. Gene Expr Patterns. 6:79–85. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zeth K, Pechlivanis M, Samol A, Pleiser S,
Vonrhein C and Kerkhoff E: Molecular basis of actin nucleation
factor cooperativity: crystal structure of the Spir-1 kinase
non-catalytic C-lobe domain (KIND)•formin-2 formin SPIR interaction
motif (FSI) complex. J Biol Chem. 286:30732–30739. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang J, Furuya A and Furuichi T:
Very-KIND, a KIND domain containing RasGEF, controls dendrite
growth by linking Ras small GTPases and MAP2. J Cell Biol.
179:539–552. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin YJ, Zhen YZ, Wei J, Liu B, Yu ZY and
Hu G: Effects of Rhein lysinate on H2O2-induced cellular senescence
of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
32:1246–1252. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim KS, Kim MS, Seu YB, Chung HY, Kim JH
and Kim JR: Regulation of replicative senescence by insulin-like
growth factor-binding protein 3 in human umbilical vein endothelial
cells. Aging Cell. 6:535–545. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jeyapalan JC and Sedivy JM: Cellular
senescence and organismal aging. Mech Ageing Dev. 129:467–474.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mao Z, Ke Z, Gorbunova V and Seluanov A:
Replicatively senescent cells are arrested in G1 and G2 phases.
Aging (Albany NY). 4:431–435. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Passos JF, Saretzki G, Ahmed S, et al:
Mitochondrial dysfunction accounts for the stochastic heterogeneity
in telomere-dependent senescence. PLoS Biol. 5:e1102007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tchkonia T, Morbeck DE, Von Zglinicki T,
et al: Fat tissue, aging, and cellular senescence. Aging Cell.
9:667–684. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fujikawa T, Shiraha H, Ueda N, et al:
Des-gamma-carboxyl prothrombin-promoted vascular endothelial cell
proliferation and migration. J Biol Chem. 282:8741–8748. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cho H, Balaji S, Sheikh AQ, et al:
Regulation of endothelial cell activation and angiogenesis by
injectable peptide nanofibers. Acta Biomater. 8:154–164. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miyauchi H, Minamino T, Tateno K, Kunieda
T, Toko H and Komuro I: Akt negatively regulates the in vitro
lifespan of human endothelial cells via a p53/p21-dependent
pathway. EMBO J. 23:212–220. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim KS, Kang KW, Seu YB, Baek SH and Kim
JR: Interferon-gamma induces cellular senescence through
p53-dependent DNA damage signaling in human endothelial cells. Mech
Ageing Dev. 130:179–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kida M, Sugiyama T, Yoshimoto T and Ogawa
Y: Hydrogen sulfide increases nitric oxide production with
calcium-dependent activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase
in endothelial cells. Eur J Pharm Sci. 48:211–215. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Murikipudi S, Methe H and Edelman ER: The
effect of substrate modulus on the growth and function of
matrix-embedded endothelial cells. Biomaterials. 34:677–684. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|