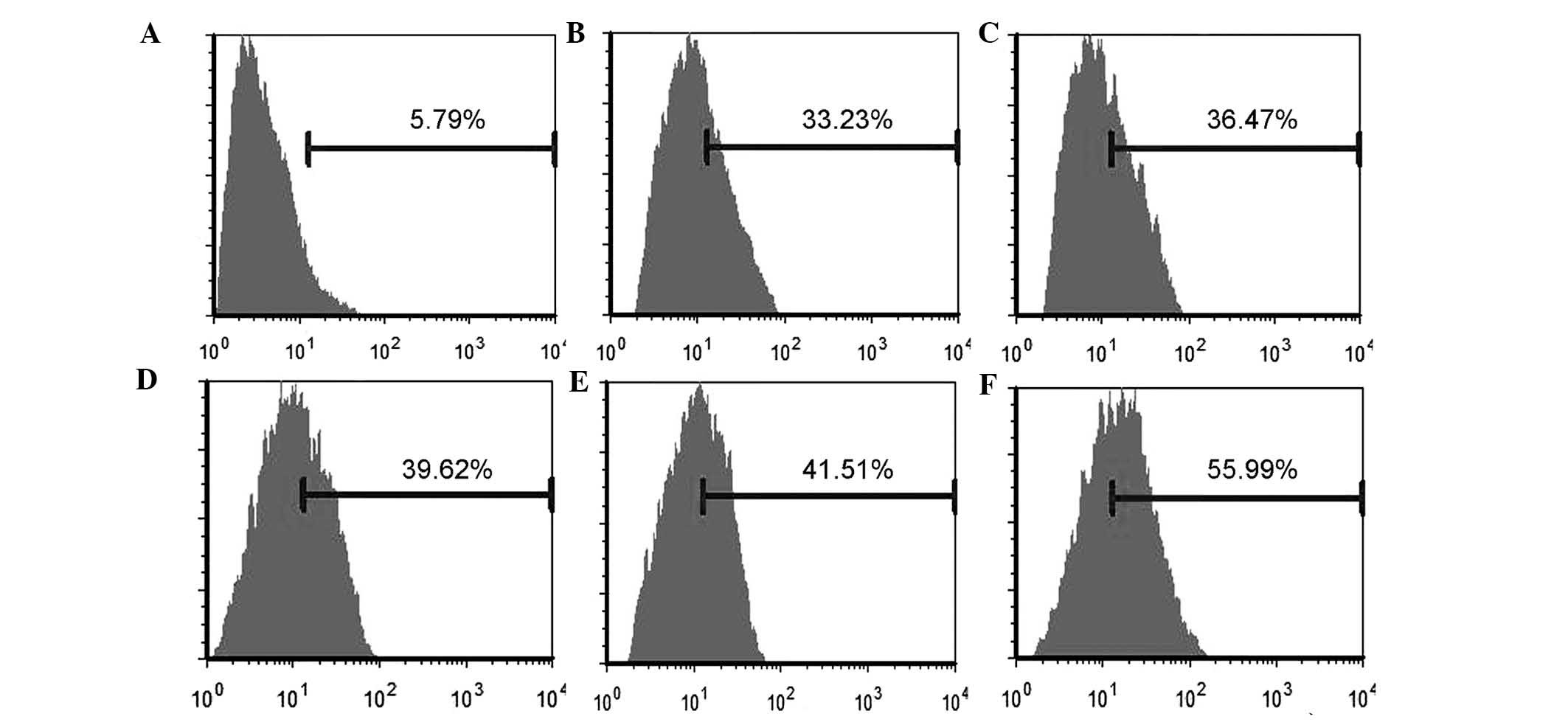
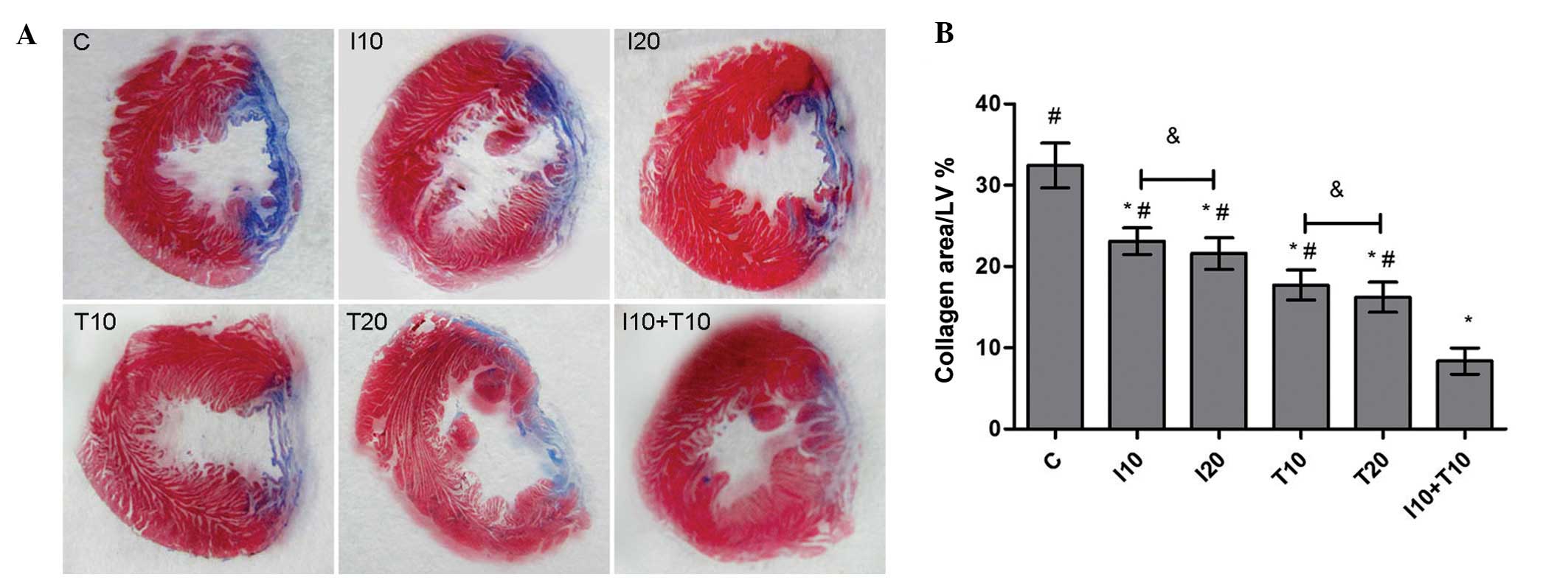
|
1
|
Schulman IH and Hare JM: Key developments
in stem cell therapy in cardiology. Regen Med. 7(6 Suppl): 17–24.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Luo Y, Wang Y, Poynter JA, et al:
Pretreating mesenchymal stem cells with interleukin-1β and
transforming growth factor-β synergistically increases vascular
endothelial growth factor production and improves mesenchymal stem
cell-mediated myocardial protection after acute ischemia. Surgery.
151:353–363. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zheng Z, Leng Y, Zhou C, Ma Z, Zhong Z,
Shi XM and Zhang W: Effects of matrix metalloproteinase-1 on the
myogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 428:309–314. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Herrmann JL, Weil BR, Abarbanell AM, Wang
Y, Poynter JA, Manukyan MC and Meldrum DR: IL-6 and TGF-α
costimulate mesenchymal stem cell vascular endothelial growth
factor production by ERK-, JNK-, and PI3K-mediated mechanisms.
Shock. 35:512–516. 2011.
|
|
5
|
Cui X, Wang H, Guo H, Wang C, Ao H, Liu X
and Tan YZ: Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells
preconditioned with diazoxide, a mitochondrial ATP-sensitive
potassium channel opener, promotes repair of myocardial infarction
in rats. Tohoku J Exp Med. 220:139–147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang M, Methot D, Poppa V, Fujio Y, Walsh
K and Murry CE: Cardiomyocyte grafting for cardiac repair: graft
cell death and anti-death strategies. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
33:907–921. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nian M, Lee P, Khaper N and Liu P:
Inflammatory cytokines and postmyocardial infarction remodeling.
Circ Res. 94:1543–1553. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carrero R, Cerrada I, Lledó E, et al: IL1β
induces mesenchymal stem cells migration and leucocyte chemotaxis
through NF-κB. Stem Cell Rev. 8:905–916. 2012.
|
|
9
|
Fan H, Zhao G, Liu L, et al: Pre-treatment
with IL-1β enhances the efficacy of MSC transplantation in
DSS-induced colitis. Cell Mol Immunol. 9:473–481. 2012.
|
|
10
|
Heo SC, Jeon ES, Lee IH, Kim HS, Kim MB
and Kim JH: Tumor necrosis factor-α-activated human adipose
tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerate cutaneous wound
healing through paracrine mechanisms. J Invest Dermatol.
131:1559–1567. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Kim YS, Park HJ, Hong MH, et al: TNF-alpha
enhances engraftment of mesenchymal stem cells into infarcted
myocardium. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 14:2845–2856. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Herrmann JL, Abarbanell AM, Weil BR, et
al: Postinfarct intramyocardial injection of mesenchymal stem cells
pretreated with TGF-alpha improves acute myocardial function. Am J
Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 299:R371–R378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Deten A, Volz HC, Briest W and Zimmer HG:
Cardiac cytokine expression is upregulated in the acute phase after
myocardial infarction. Experimental studies in rats. Cardiovasc
Res. 55:329–340. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chute JP: Stem cell homing. Curr Opin
Hematol. 13:399–406. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Segers VF, Van Riet I, Andries LJ, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cell adhesion to cardiac microvascular
endothelium: activators and mechanisms. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 290:H1370–H1377. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Balzer EM and Konstantopoulos K:
Intercellular adhesion: mechanisms for growth and metastasis of
epithelial cancers. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 4:171–181.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bonig H, Priestley GV and Papayannopoulou
T: Hierarchy of molecular-pathway usage in bone marrow homing and
its shift by cytokines. Blood. 107:79–86. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu Y, Cheng P, Xue YX and Liu YH: Glioma
cells promote the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
on bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a possible mechanism
for their tropism toward gliomas. J Mol Neurosci. 48:127–135. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Crisostomo PR, Wang M, Markel TA,
Novotny NM and Meldrum DR: TGF-alpha increases human mesenchymal
stem cell-secreted VEGF by MEK- and PI3-K- but not JNK- or
ERK-dependent mechanisms. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
295:R1115–R1123. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Herrmann JL, Abarbanell AM, Wang Y, Weil
BR, Poynter JA, Manukyan MC and Meldrum DR: Transforming growth
factor-α enhances stem cell-mediated postischemic myocardial
protection. Ann Thorac Surg. 92:1719–1725. 2011.
|
|
21
|
Böcker W, Docheva D, Prall WC, et al:
IKK-2 is required for TNF-alpha-induced invasion and proliferation
of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Mol Med (Berl). 86:1183–1192.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tropel P, Noël D, Platet N, Legrand P,
Benabid AL and Berger F: Isolation and characterisation of
mesenchymal stem cells from adult mouse bone marrow. Exp Cell Res.
295:395–406. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang A, Shen F, Lang Y and Wang J:
Marrow-derived MSCs and atorvastatin improve cardiac function in
rat model of AMI. Int J Cardiol. 150:28–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ren G, Roberts AI and Shi Y: Adhesion
molecules: key players in mesenchymal stem cell-mediated
immunosuppression. Cell Adh Migr. 5:20–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim HJ, Lee SI, Lee DH, Smith D, Jo H,
Schellhorn HE and Boo YC: Ascorbic acid synthesis due to
L-gulono-1,4-lactone oxidase expression enhances NO production in
endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 345:1657–1662. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Niagara MI, Haider HKh, Jiang S and Ashraf
M: Pharmacologically preconditioned skeletal myoblasts are
resistant to oxidative stress and promote angiomyogenesis via
release of paracrine factors in the infarcted heart. Circ Res.
100:545–555. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mias C, Lairez O, Trouche E, et al:
Mensenchymal stem cells promote matrix metalloproteinase secretion
by cardiac fibroblasts and reduce cardiacventricular fibrosis after
myocardial infarction. Stem Cells. 27:2734–2743. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xiao Q, Wang SK, Tian H, et al: TNF-α
increases bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell migration to ischemic
tissues. Cell Biochem Biophys. 62:409–414. 2012.
|
|
29
|
Thankamony SP and Sackstein R: Enforced
hematopoietic cell E- and L-selectin ligand (HCELL) expression
primes transendothelial migration of human mesenchymal stem cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:2258–2263. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hyun YM, Chung HL, McGrath JL, Waugh RE
and Kim M: Activated integrin VLA-4 localizes to the lamellipodia
and mediates T cell migration on VCAM-1. J Immunol. 183:359–369.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yilmaz G and Granger DN: Leukocyte
recruitment and ischemic brain injury. Neuromolecular Med.
12:193–204. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Armiñán A, Gandía C, García-Verdugo JM, et
al: Mesenchymal stem cells provide better results than
hematopoietic precursors for the treatment of myocardial
infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 55:2244–2253. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kawada H, Fujita J, Kinjo K, et al:
Nonhematopoietic mesenchymal stem cells can be mobilized and
differentiate into cardiomyocytes after myocardial infarction.
Blood. 104:3581–3587. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Horwitz EM and Prather WR: Cytokines as
the major mechanism of mesenchymal stem cell clinical activity:
expanding the spectrum of cell therapy. Isr Med Assoc J.
11:209–211. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shake JG, Gruber PJ, Baumgartner WA, et
al: Mesenchymal stem cell implantation in a swine myocardial
infarct model: engraftment and functional effects. Ann Thorac Surg.
73:1919–1925. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mangi AA, Noiseux N, Kong D, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells modified with Akt prevent remodeling and
restore performance of infarcted hearts. Nat Med. 9:1195–1201.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tsoyi K, Jang HJ, Nizamutdinova IT, et al:
PTEN differentially regulates expressions of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1
through PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/GATA-6 signaling pathways in
TNF-α-activated human endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis.
213:115–121. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ward SG, Westwick J and Harris S: Sat-Nav
for T cells: role of PI3K isoforms and lipid phosphatases in
migration of T lymphocytes. Immunol Lett. 138:15–18. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|