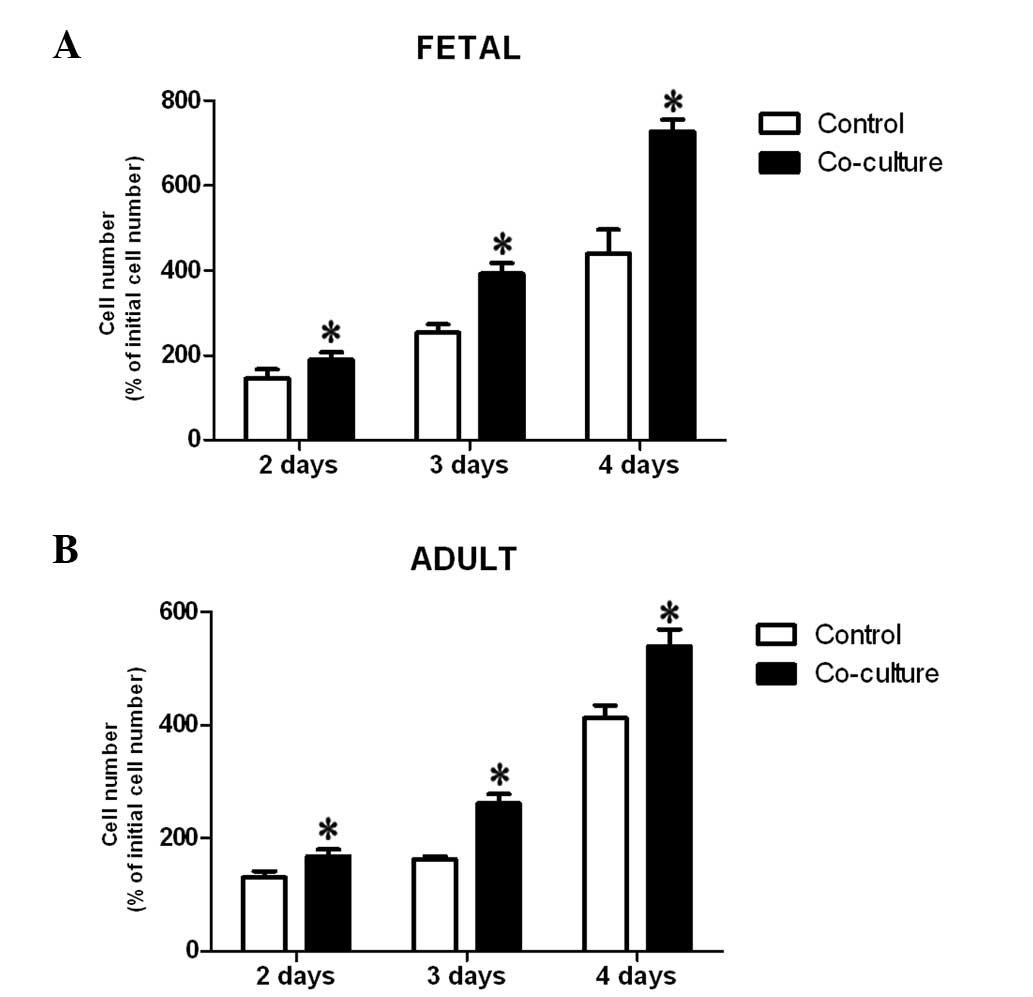
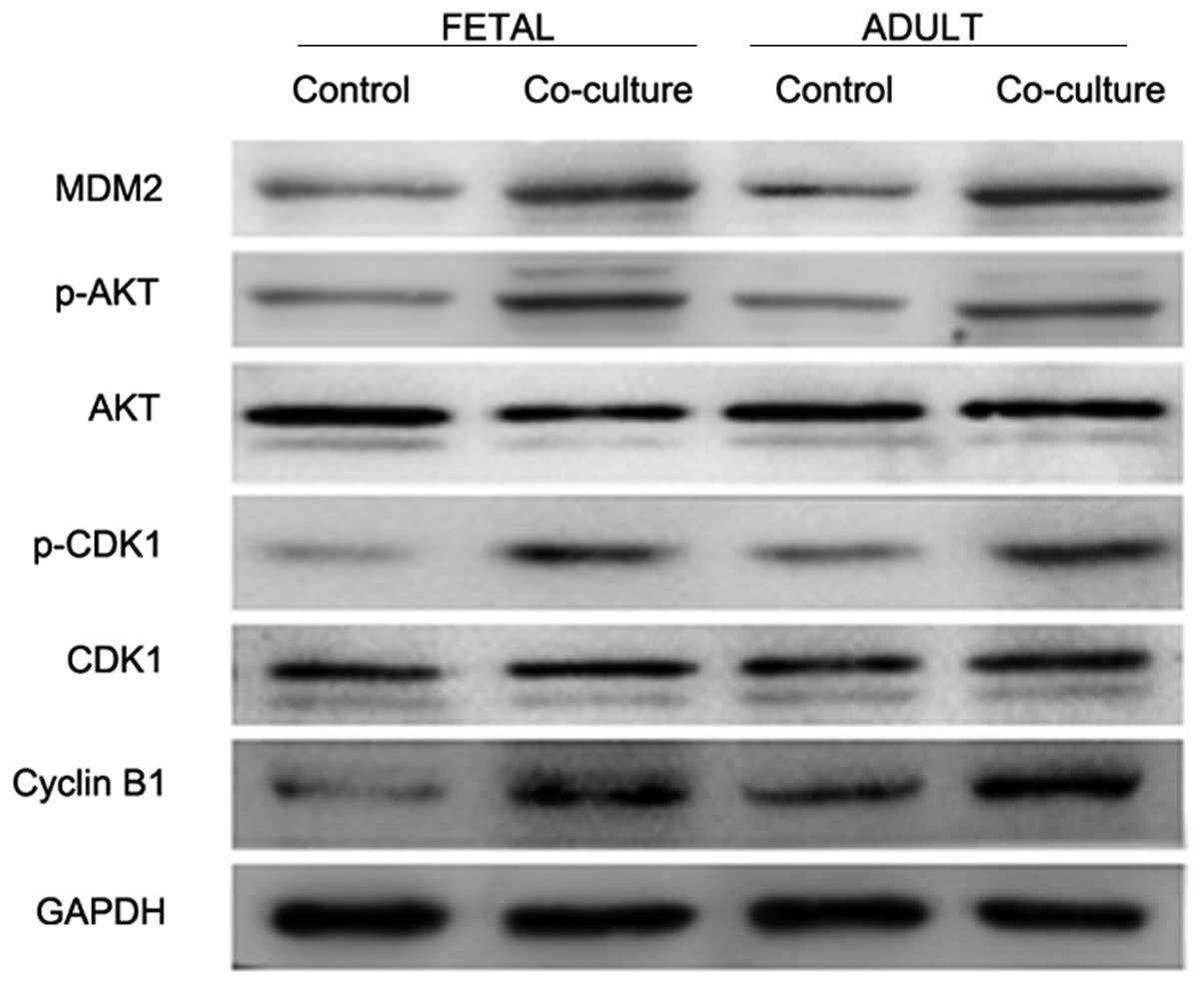
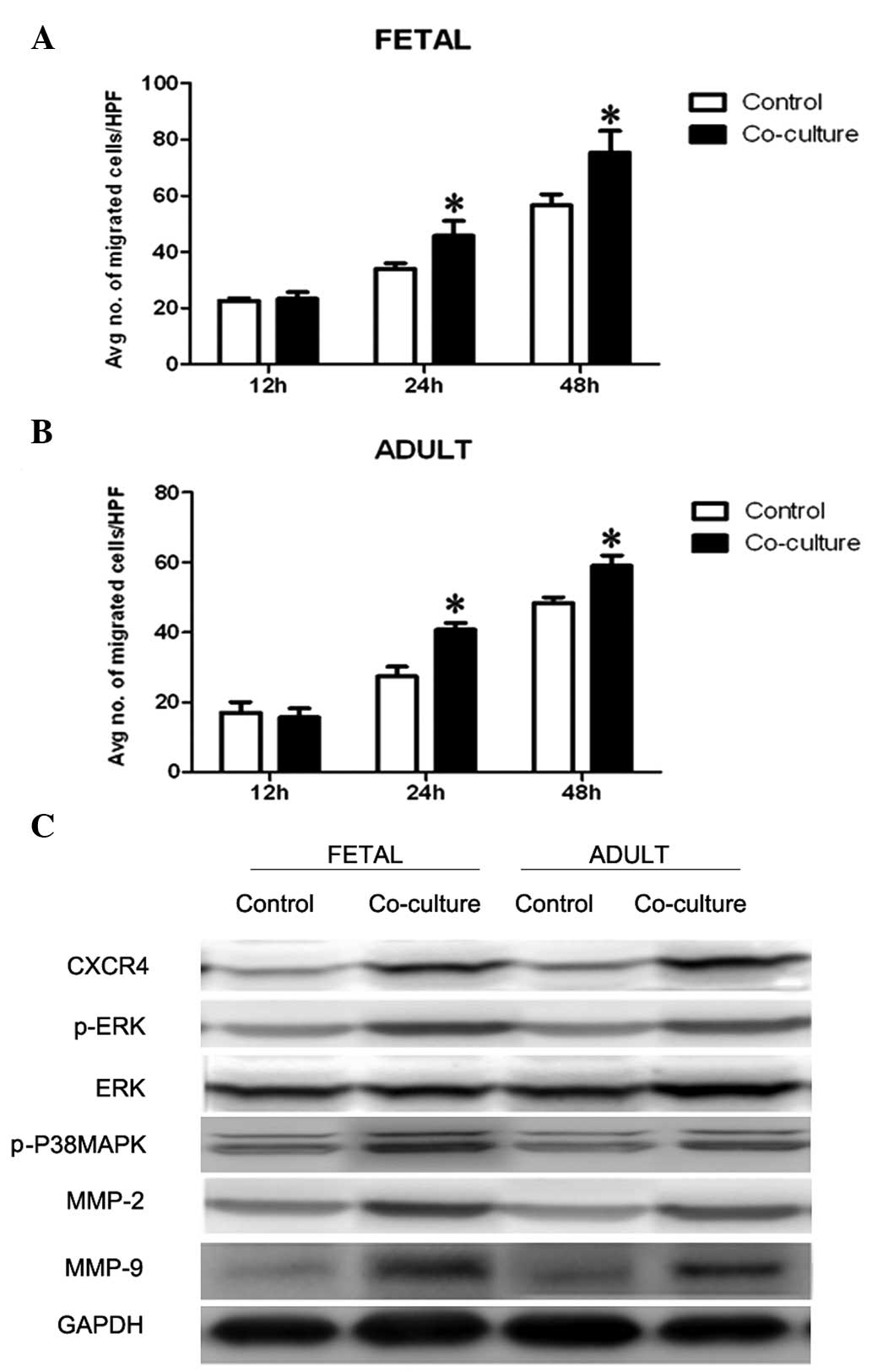
|
1
|
Wulff BC, Yu L, Parent AE and Wilgus TA:
Novel differences in the expression of inflammation-associated
genes between mid- and late-gestational dermal fibroblasts. Wound
Repair Regen. 21:103–112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Namazi MR, Fallahzadeh MK and Schwartz RA:
Strategies for prevention of scars: what can we learn from fetal
skin? Int J Dermatol. 50:85–93. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Pouyani T, Papp S and Schaffer L:
Tissue-engineered fetal dermal matrices. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol
Anim. 48:493–506. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng J, Yu H, Deng S and Shen G: MicroRNA
profiling in mid- and late-gestational fetal skin: implication for
scarless wound healing. Tohoku J Exp Med. 221:203–209. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nowinski D, Höijer P, Engstrand T, et al:
Keratinocytes inhibit expression of connective tissue growth factor
in fibroblasts in vitro by an interleukin-1alpha-dependent
mechanism. J Invest Dermatol. 119:449–455. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fusenig NE, Limat A, Stark HJ and
Breitkreutz D: Modulation of the differentiated phenotype of
keratinocytes of the hair follicle and from epidermis. J Dermatol
Sci. 7:S142–S151. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Haverstock BD: Hypertrophic scars and
keloids. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 18:147–159. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Maas-Szabowski N, Stark HJ and Fusenig NE:
Keratinocyte growth regulation in defined organotypic cultures
through IL-1-induced keratinocyte growth factor expression in
resting fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 114:1075–1084. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Naik-Mathuria B, Gay AN, Yu L, et al:
Fetal wound healing using a genetically modified murine model: the
contribution of P-selectin. J Pediatr Surg. 43:675–682. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Colwell AS, Yun R, Krummel TM, Longaker MT
and Lorenz HP: Keratinocytes modulate fetal and postnatal
fibroblast transforming growth factor-beta and Smad expression in
co-culture. Plast Reconstr Surg. 119:1440–1445. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gangnuss S, Cowin AJ, Daehn IS, et al:
Regulation of MAPK activation, AP-1 transcription factor expression
and keratinocyte differentiation in wounded fetal skin. J Invest
Dermatol. 122:791–804. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hahn JM, Glaser K, McFarland KL, et al:
Keloid-derived keratinocytes exhibit an abnormal gene expression
profile consistent with a distinct causal role in keloid pathology.
Wound Repair Regen. 21:530–544. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yeh J, Green LM, Jiang TX, et al:
Accelerated closure of skin wounds in mice deficient in the
homeobox gene Msx2. Wound Repair Regen. 17:639–648. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu X, Wang Z, Wang R, et al: Direct
comparison of the potency of human mesenchymal stem cells derived
from amnion tissue, bone marrow and adipose tissue at inducing
dermal fibroblast responses to cutaneous wounds. Int J Mol Med.
31:407–415. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Zhang L, Aerziguli T and Guzalnur A:
Establishment and characterization of a new carcinoma cell line
from uterine cervix of Uyghur women. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi.
41:248–253. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Z, Wang Y, Farhangfar F, Zimmer M and
Zhang Y: Enhanced keratinocyte proliferation and migration in
co-culture with fibroblasts. PLoS One. 7:e409512012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Laeeq S and Faust R: Modeling the
cholesteatoma microenvironment: coculture of HaCaT keratinocytes
with WS1 fibroblasts induces MMP-2 activation, invasive phenotype,
and proteolysis of the extracellular matrix. Laryngoscope.
117:313–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bernerd F: Human skin reconstructed in
vitro as a model to study the keratinocyte, the fibroblast and
their interactions: photodamage and repair processes. J Soc Biol.
199:313–320. 2005.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kratz G, Haegerstrand A and Dalsgaard CJ:
Conditioned medium from cultured human keratinocytes has growth
stimulatory properties on different human cell types. J Invest
Dermatol. 97:1039–1043. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, et al: Akt
promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead
transcription factor. Cell. 96:857–868. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li N, Bu X, Tian X, et al: Fatty acid
synthase regulates proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer
cells via HER2-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Nutr Cancer. 64:864–870.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Srivastava VK, Gara RK, Bhatt ML, Sahu DP
and Mishra DP: Centchroman inhibits proliferation of head and neck
cancer cells through the modulation of PI3K/mTOR pathway. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 404:40–45. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ivarsson M, McWhirter A, Borg TK and Rubin
K: Type I collagen synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts:
regulation by cell spreading, platelet-derived growth factor and
interactions with collagen fibers. Matrix Biol. 16:409–425. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu M, Breyssens H, Salter V, et al:
Restoring p53 function in human melanoma cells by inhibiting MDM2
and cyclin B1/CDK1-phosphorylated nuclear iASPP. Cancer Cell.
23:618–633. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Polager S and Ginsberg D: p53 and E2f:
partners in life and death. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:738–748. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hipfner DR and Cohen SM: Connecting
proliferation and apoptosis in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 5:805–815. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iwakuma T and Agarwal N: MDM2 binding
protein, a novel metastasis suppressor. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
31:633–640. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nowack MK, Harashima H, Dissmeyer N, et
al: Genetic framework of cyclin-dependent kinase function in
Arabidopsis. Dev Cell. 22:1030–1040. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dissmeyer N, Weimer AK, Pusch S, et al:
Control of cell proliferation, organ growth, and DNA damage
response operate independently of dephosphorylation of the
Arabidopsis Cdk1 homolog CDKA;1. Plant Cell. 21:3641–3654. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Makino T, Jinnin M, Muchemwa FC, et al:
Basic fibroblast growth factor stimulates the proliferation of
human dermal fibroblasts via the ERK1/2 and JNK pathways. Br J
Dermatol. 162:717–723. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu Y, Liang C, Liu X, et al: AGEs
increased migration and inflammatory responses of adventitial
fibroblasts via RAGE, MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. Atherosclerosis.
208:34–42. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tarnowski M, Grymula K, Liu R, et al:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is secreted by
rhabdomyosarcoma cells, modulates tumor metastasis by binding to
CXCR4 and CXCR7 receptors and inhibits recruitment of
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Mol Cancer Res. 8:1328–1343. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang D, Shao S, Shuai H, et al: SDF-1α
reduces fibronectin expression in rat mesangial cells induced by
TGF-β1 and high glucose through PI3K/Akt pathway. Exp Cell Res.
319:1796–1803. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Blanc A, Pandey NR and Srivastava AK:
Synchronous activation of ERK 1/2, p38mapk and PKB/Akt signaling by
H2O2 in vascular smooth muscle cells:
potential involvement in vascular disease (review). Int J Mol Med.
11:229–234. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Song J, Xu H, Lu Q, et al: Madecassoside
suppresses migration of fibroblasts from keloids: involvement of
p38 kinase and PI3K signaling pathways. Burns. 38:677–684. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Park G, Yoon BS, Moon JH, et al: Green tea
polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses collagen
production and proliferation in keloid fibroblasts via inhibition
of the STAT3-signaling pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 128:2429–2441.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li L, Zhu DL, Shen WL and Gao PJ:
Increased migration of vascular adventitial fibroblasts from
spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res. 29:95–103. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jeffery TK, Upton PD, Trembath RC and
Morrell NW: BMP4 inhibits proliferation and promotes myocyte
differentiation of lung fibroblasts via Smad1 and JNK pathways. Am
J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 288:L370–L378. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Stawowy P, Goetze S, Margeta C, Fleck E
and Graf K: LPS regulate ERK1/2-dependent signaling in cardiac
fibroblasts via PKC-mediated MKP-1 induction. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 303:74–80. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yijing L, Liu H, Yuan C, et al: The
effects of qindan-capsule-containing serum on the TGF-β1/ERK
signaling pathway, matrix metalloproteinase synthesis and cell
function in adventitial fibroblasts. Pharm Biol. 51:712–721. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|