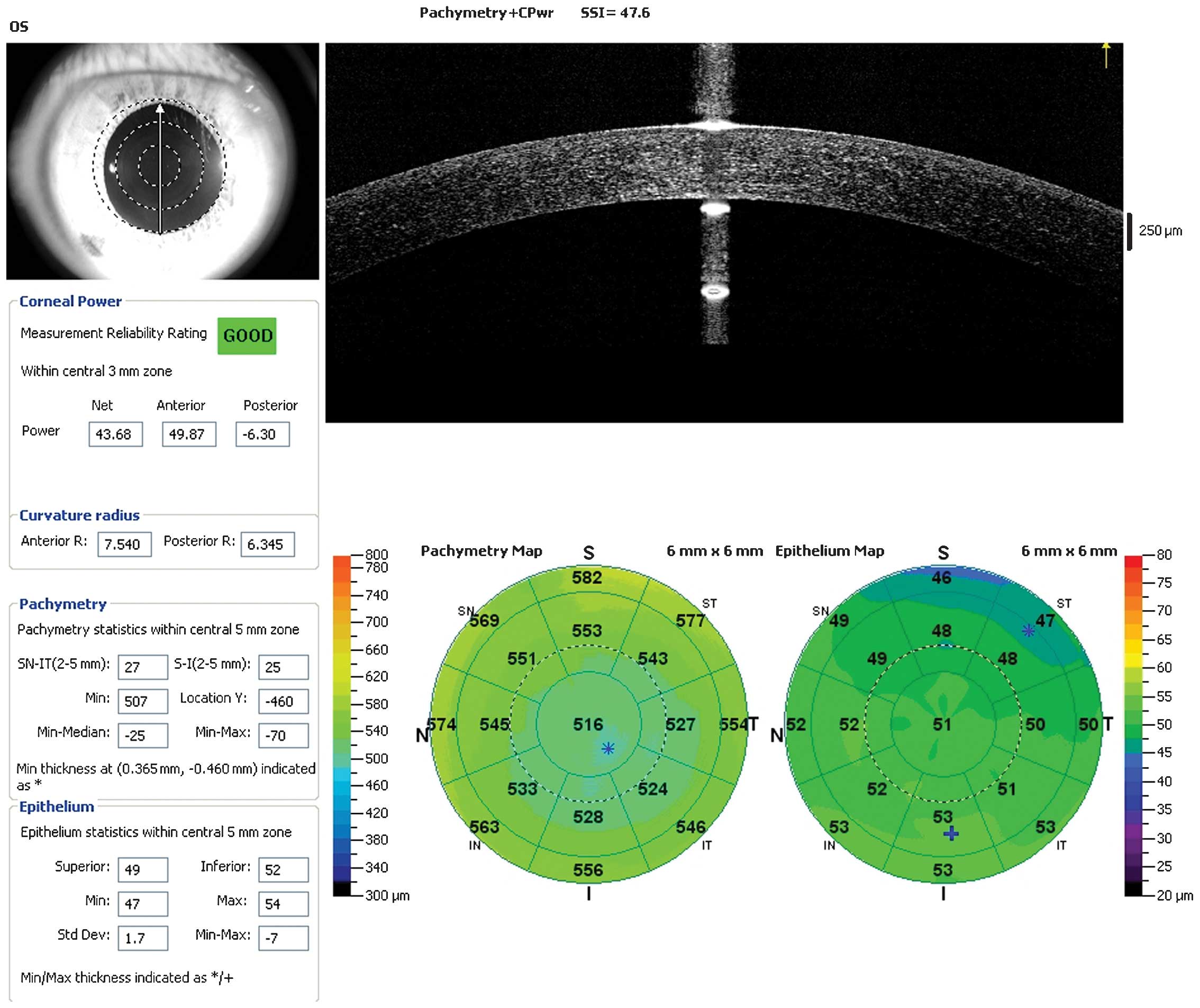
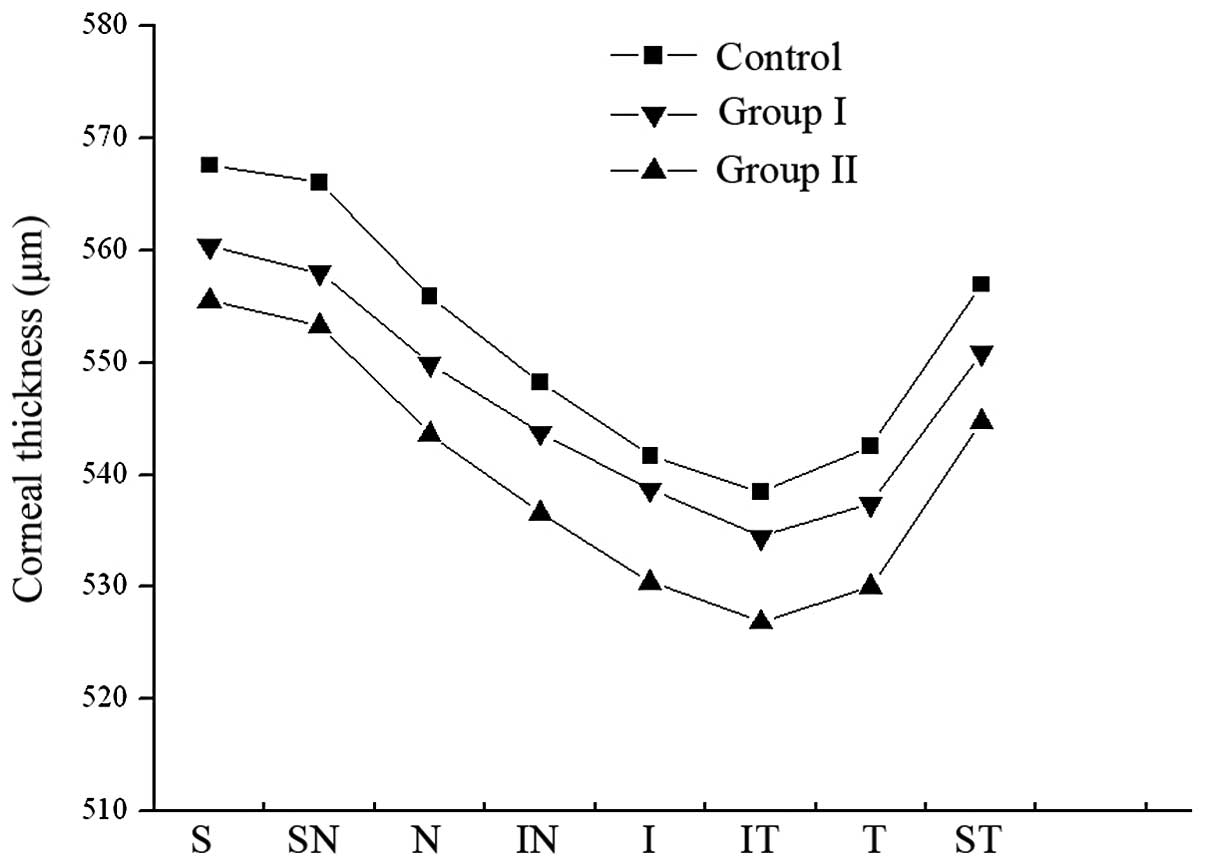
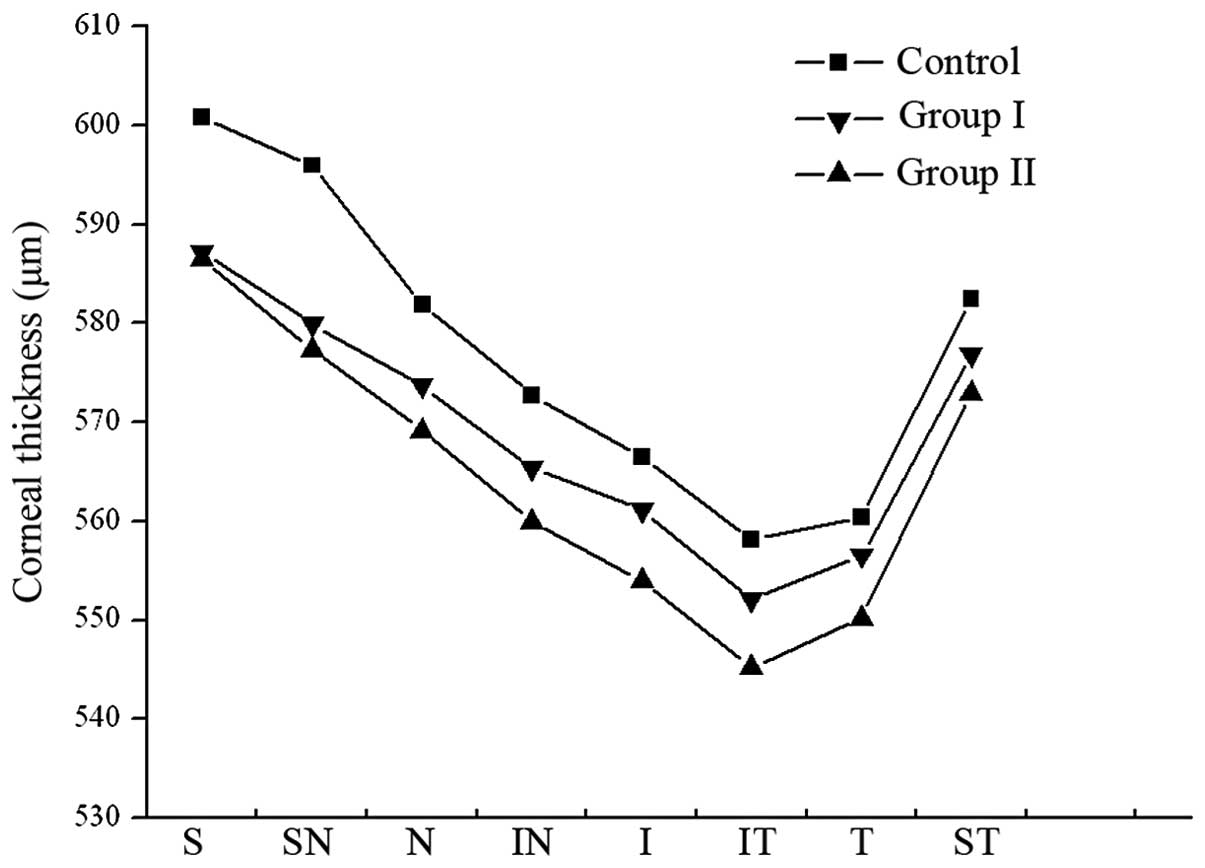
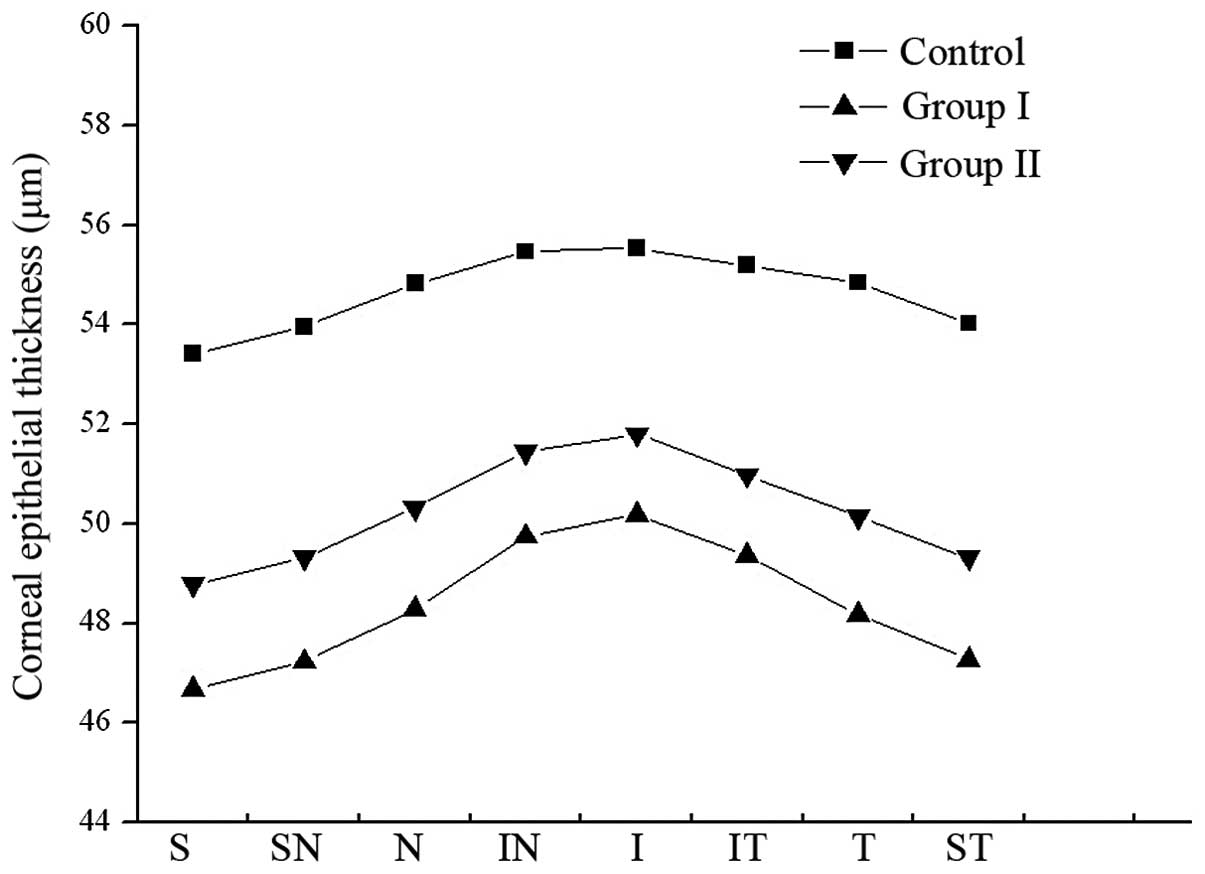
|
1
|
Reinstein DZ, Srivannaboon S, Archer TJ,
Silverman RH, Sutton H and Coleman DJ: Probability model of the
inaccuracy of residual stromal thickness prediction to reduce the
risk of ectasia after LASIK part I: quantifying individual risk. J
Refract Surg. 22:851–860. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Walline JJ, Gaume A, Jones LA, Rah MJ,
Manny RE, Berntsen DA, Chitkara M, Kim A and Quinn N: Benefits of
contact lens wear for children and teens. Eye Contact Lens.
33:317–321. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu Z and Pflugfelder SC: The effects of
long-term contact lens wear on corneal thickness, curvature, and
surface regularity. Ophthalmology. 107:105–111. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bonanno JA and Polse KA: Central and
peripheral corneal swelling accompanying soft lens extended wear.
Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 62:74–81. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fujimoto JG, Pitris C, Boppart SA and
Brezinski ME: Optical coherence tomography: an emerging technology
for biomedical imaging and optical biopsy. Neoplasia. 2:9–25. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stillitano I, Yamazaki E, Melo LA Jr,
Bottos J and Campos M: Wavefront-guided refractive surgery results
of training-surgeons. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 73:323–328. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sia RK, Coe CD, Edwards JD, Ryan DS and
Bower KS: Visual outcomes after Epi-LASIK and PRK for low and
moderate myopia. J Refract Surg. 28:65–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bergmanson JP: Histopathological analysis
of the corneal epithelium after contact lens wear. J Am Optom
Assoc. 58:812–818. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu L, Reinach PS and Kao WW: Corneal
epithelial wound healing. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 226:653–664.
2001.
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Tan O, Brass R, Weiss JL and Huang
D: Corneal epithelial thickness mapping by Fourier-domain optical
coherence tomography in normal and keratoconic eyes. Ophthalmology.
119:2425–2433. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Haque S, Jones L and Simpson T: Thickness
mapping of the cornea and epithelium using optical coherence
tomography. Optom Vis Sci. 85:E963–E976. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang D, Tang M and Shekhar R:
Mathematical model of corneal surface smoothing after laser
refractive surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 135:267–278. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Reinstein DZ, Archer TJ, Gobbe M,
Silverman RH and Coleman DJ: Epithelial thickness in the normal
cornea: three-dimensional display with Artemis very high-frequency
digital ultrasound. J Refract Surg. 24:571–581. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li HF, Petroll WM, Møller-Pedersen T,
Maurer JK, Cavanagh HD and Jester JV: Epithelial and corneal
thickness measurements by in vivo confocal microscopy through
focusing (CMTF). Curr Eye Res. 16:214–221. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ramos JL, Li Y and Huang D: Clinical and
research applications of anterior segment optical coherence
tomography - a review. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 37:81–89. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Ehsaei A, Chisholm CM, MacIsaac JC, Mallen
EA and Pacey IE: Central and peripheral visual performance in
myopes: contact lenses versus spectacles. Cont Lens Anterior Eye.
34:128–132. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lim L and Wei RH: Laser in situ
keratomileusis treatment for myopia in a patient with partial
limbal stem cell deficiency. Eye Contact Lens. 31:67–69. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Feng Y and Simpson TL: Comparison of human
central cornea and limbus in vivo using optical coherence
tomography. Optom Vis Sci. 82:416–419. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Fonn D, Simpson TL, Sorbara L,
Kort R and Jones L: Topographical thickness of the epithelium and
total cornea after overnight wear of reverse-geometry rigid contact
lenses for myopia reduction. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
44:4742–4746. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Patel SV, McLaren JW, Hodge DO and Bourne
WM: Confocal microscopy in vivo in corneas of long-term contact
lens wearers. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 43:995–1003.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hashemi H, Firoozabadi MR, Mehravaran S
and Gorouhi F: Corneal stability after discontinued soft contact
lens wear. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 31:122–125. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nourouzi H, Rajavi J and Okhovatpour MA:
Time to resolution of corneal edema after long-term contact lens
wear. Am J Ophthalmol. 142:671–673. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Y, Thompson DC, Koppaka V, Jester JV
and Vasiliou V: Ocular aldehyde dehydrogenases: protection against
ultraviolet damage and maintenance of transparency for vision. Prog
Retin Eye Res. 33:28–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Thiel HJ: Epithelium of the cornea and its
significance for transparency. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 99:1630–1635.
1974.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takatori SC, de la Jara PL, Holden B,
Ehrmann K, Ho A and Radke CJ: In vivo oxygen uptake into the human
cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:6331–6337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weissman BA, Fatt I and Rasson J:
Diffusion of oxygen in human corneas in vivo. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 20:123–125. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Efron N and Carney LG: Oxygen levels
beneath the closed eyelid. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 18:93–95.
1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ichijima H, Hayashi T, Mitsunaga S and
Hamano H: Determination of oxygen tension on rabbit corneas under
contact lenses. CLAO J. 24:220–226. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Braun DA and Anderson Penno EE: Effect of
contact lens wear on central corneal thickness measurements. J
Cataract Refract Surg. 29:1319–1322. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang J, Fonn D, Simpson TL and Jones L:
The measurement of corneal epithelial thickness in response to
hypoxia using optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol.
133:315–319. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hutchings N, Simpson TL, Hyun C, Moayed
AA, Hariri S, Sorbara L and Bizheva K: Swelling of the human cornea
revealed by high-speed, ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence
tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:4579–4584. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Efron N, Perez-Gomez I and Morgan PB:
Confocal microscopic observations of stromal keratocytes during
extended contact lens wear. Clin Exp Optom. 85:156–160. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cerretani C, Peng CC, Chauhan A and Radke
CJ: Aqueous salt transport through soft contact lenses: an
osmotic-withdrawal mechanism for prevention of adherence. Cont Lens
Anterior Eye. 35:260–265. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
McMonnies CW, Chapman-Davies A and Holden
BA: The vascular response to contact lens wear. Am J Optom Physiol
Opt. 59:795–799. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kanellopoulos AJ and Asimellis G: Anterior
segment optical coherence tomography: assisted topographic corneal
epithelial thickness distribution imaging of a keratoconus patient.
Case Rep Ophthalmol. 4:74–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou W and Stojanovic A: Comparison of
corneal epithelial and stromal thickness distributions between eyes
with keratoconus and healthy eyes with corneal astigmatism ≥ 2.0 D.
PLoS One. 9:e859942014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pérez JG, Méijome JM, Jalbert I, Sweeney
DF and Erickson P: Corneal epithelial thinning profile induced by
long-term wear of hydrogel lenses. Cornea. 22:304–307. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Simon G, Ren Q, Kervick GN and Parel JM:
Optics of the corneal epithelium. Refract Corneal Surg. 9:42–50.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liesegang TJ: Physiologic changes of the
cornea with contact lens wear. CLAO J. 28:12–27. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pearlman E, Sun Y, Roy S, Karmakar M, Hise
AG, Szczotka-Flynn L, Ghannoum M, Chinnery HR, McMenamin PG and
Rietsch A: Host defense at the ocular surface. Int Rev Immunol.
32:4–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Markoulli M, Papas E, Cole N and Holden B:
Corneal erosions in contact lens wear. Cont Lens Anterior Eye.
35:2–8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Brewitt H: Contact lenses. 2: Contact lens
associated infections. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 211:aA7–A10.
1997.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|