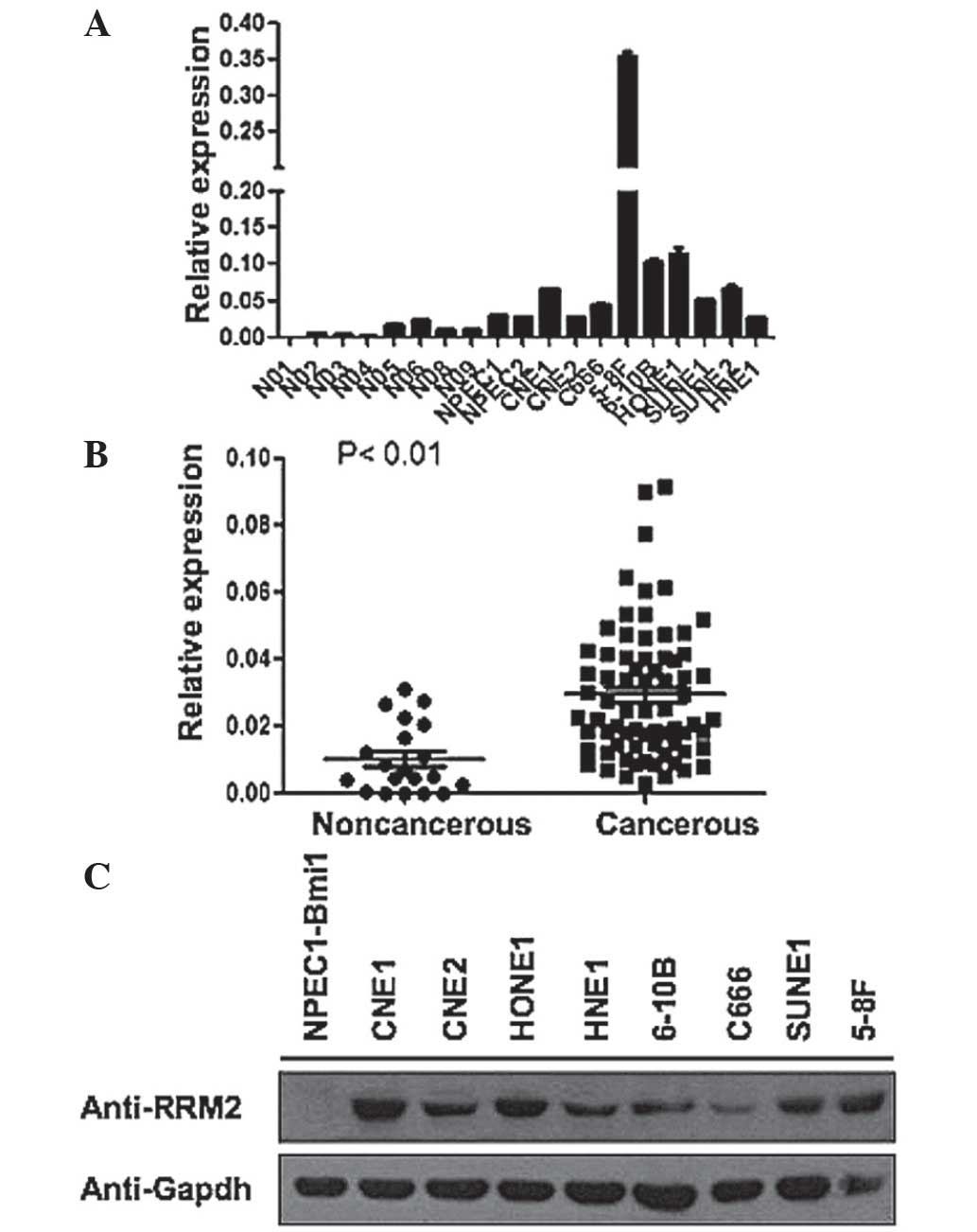
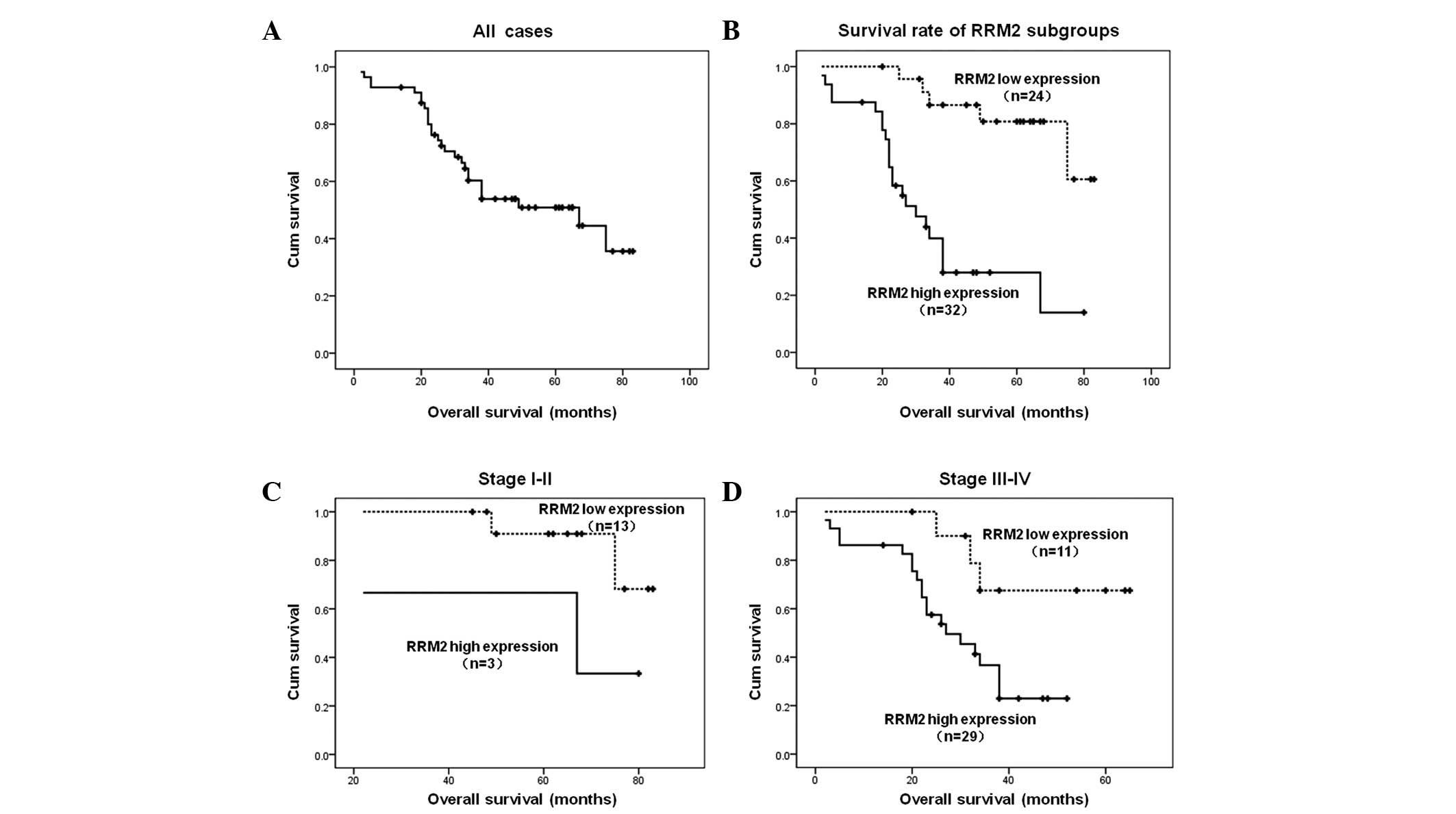
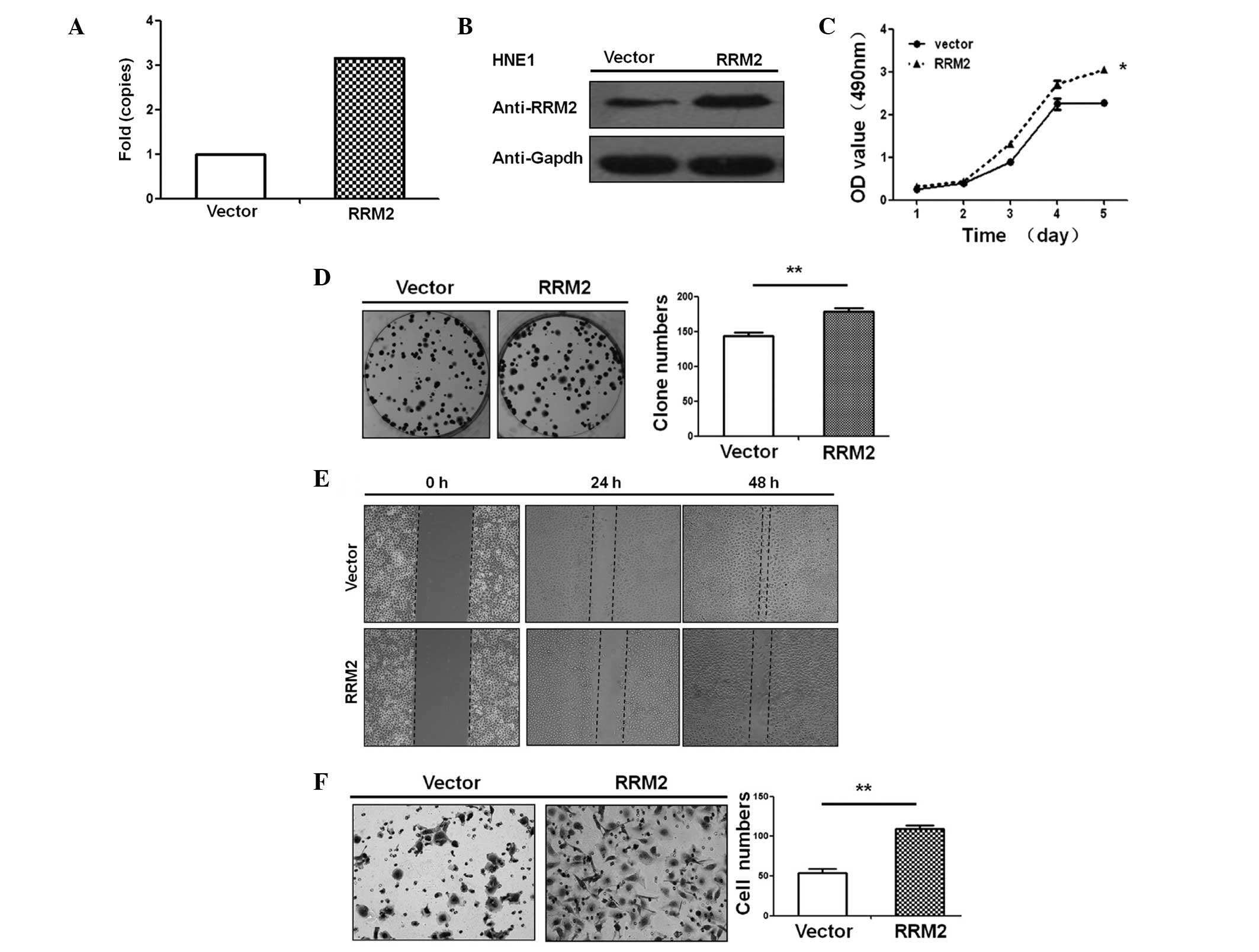
|
1
|
Yu MC and Yuan JM: Epidemiology of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 12:421–429. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC, et al: AJCC
Cancer Staging Manual. 7th. Lippincott-Raven; Philidelphia, PA:
2009
|
|
3
|
Chua DT, Ma J, Sham JS, et al: Improvement
of survival after addition of induction chemotherapy to
radiotherapy in patients with early-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
Subgroup analysis of two Phase III trials. Int J Radia Oncol Biol
Phys. 65:1300–1306. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tao Q and Chan AT: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic developments.
Exper Rev Mol Med. 9:1–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tatsumi-Tamori A, Yoshizaki T, Miwa T and
Furukawa M: Clinical evaluation of staging system for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma: comparison of fourth and fifth editions
of UICC TNM classification. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol.
109:1125–1129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Patel SG and Shah JP: TNM staging of
cancers of the head and neck: striving for uniformity among
diversity. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:242–258; quiz. 261–242. 2642005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liang FY, Sun W, Han P, Lu X, Lian YN and
Huang XM: Detecting plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA to diagnose
postradiation nasopharyngeal skull base lesions in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma patients: a prospective study. Chin J Cancer. 31:142–149.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang LQ, Chen QY, Fan W, et al:
Prospective study of tailoring whole-body dual-modality
[18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed
tomography with plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA for detecting distant
metastasis in endemic nasopharyngeal carcinoma at initial staging.
J Clin Oncol. 31:2861–2869. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cory JG and Sato A: Regulation of
ribonucleotide reductase activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 53–54:257–266. 1983.
|
|
10
|
Thelander M, Gräslund A and Thelander L:
Subunit M2 of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase. Characterization
of a homogeneous protein isolated from M2-overproducing mouse
cells. J Bio Chem. 260:2737–2741. 1985.
|
|
11
|
Eriksson S and Martin DW Jr:
Ribonucleotide reductase in cultured mouse lymphoma cells. Cell
cycle-dependent variation in the activity of subunit protein M2. J
Biol Chem. 256:9436–9440. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Morikawa T, Maeda D, Kume H, Homma Y and
Fukayama M: Ribonucleotide reductase M2 subunit is a novel
diagnostic marker and a potential therapeutic target in bladder
cancer. Histopathology. 57:885–892. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kolesar J, Huang W, Eickhoff J, et al:
Evaluation of mRNA by Q-RTPCR and protein expression by AQUA of the
M2 subunit of ribonucleotide reductase (RRM2) in human tumors.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 64:79–86. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zuckerman JE, Hsueh T, Koya RC, Davis ME
and Ribas A: siRNA knockdown of ribonucleotide reductase inhibits
melanoma cell line proliferation alone or synergistically with
temozolomide. J Invest Dermatol. 131:453–460. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Morikawa T, Hino R, Uozaki H, et al:
Expression of ribonucleotide reductase M2 subunit in gastric cancer
and effects of RRM2 inhibition in vitro. Hum Pathol. 41:1742–1748.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Burton TR, Kashour T, Wright JA and Amara
FM: Cellular signaling pathways affect the function of
ribonucleotide reductase mRNA binding proteins: mRNA stabilization,
drug resistance, and malignancy (Review). Int J Oncol. 22:21–31.
2003.
|
|
17
|
Song LB, Zeng MS, Liao WT, et al: Bmi-1 is
a novel molecular marker of nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression
and immortalizes primary human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells.
Cancer Res. 66:6225–6232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Song LB, Li J, Liao WT, et al: The
polycomb group protein Bmi-1 represses the tumor suppressor PTEN
and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human
nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 119:3626–3636.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liao WT, Song LB, Zhang HZ, et al:
Centromere protein H is a novel prognostic marker for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and overall patient survival.
Clin Cancer Res. 13:508–514. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun W, Guo MM, Han P, et al: Id-1 and the
p65 subunit of NF-κB promote migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cells and are correlated with poor prognosis. Carcinogenesis.
33:810–817. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang HY, Sun BY, Zhu ZH, et al:
Eight-signature classifier for prediction of nasopharyngeal
[corrected] carcinoma survival. J Clin Oncol. 29:4516–4525. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang YL, Li J, Mo HY, et al: Different
subsets of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes correlate with NPC
progression in different ways. Mol Cancer. 9:42010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guigay J, Temam S, Bourhis J, Pignon JP
and Armand JP: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma and therapeutic management:
the place of chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 17(Suppl 10): x304–x307.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma BB and Chan AT: Recent perspectives in
the role of chemotherapy in the management of advanced
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. 103:22–31. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen QY, Wen YF, Guo L, et al: Concurrent
chemoradiotherapy vs radiotherapy alone in stage II nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: phase III randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst.
103:1761–1770. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Au JS, Law CK, Foo W and Lau WH: In-depth
evaluation of the AJCC/UICC 1997 staging system of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: prognostic homogeneity and proposed refinements. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 56:413–426. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mao YP, Xie FY, Liu LZ, et al:
Re-evaluation of 6th edition of AJCC staging system for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma and proposed improvement based on magnetic
resonance imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 73:1326–1334.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gautam A, Li ZR and Bepler G: RRM1-induced
metastasis suppression through PTEN-regulated pathways. Oncogene.
22:2135–2142. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cao MY, Lee Y, Feng NP, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated ribonucleotide reductase R1 gene therapy of
human colon adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 9:4553–4561.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu X, Zhou B, Xue L, et al:
Metastasis-suppressing potential of ribonucleotide reductase small
subunit p53R2 in human cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6337–6344.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Filatov D, Björklund S, Johansson E and
Thelander L: Induction of the mouse ribonucleotide reductase R1 and
R2 genes in response to DNA damage by UV light. J Biol Chem.
271:23698–23704. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Engström Y, Eriksson S, Jildevik I, Skog
S, Thelander L and Tribukait B: Cell cycle-dependent expression of
mammalian ribonucleotide reductase. Differential regulation of the
two subunits. J Biol Chem. 260:9114–9116. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yoshida Y, Tsunoda T, Doi K, et al:
KRAS-mediated upregulation of RRM2 expression is essential for the
proliferation of colorectal cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res.
31:2535–2539. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang K, Hu S, Wu J, et al: Overexpression
of RRM2 decreases thrombspondin-1 and increases VEGF production in
human cancer cells in vitro and in vivo: implication of RRM2 in
angiogenesis. Mol Cancer. 8:112009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Duxbury MS and Whang EE: RRM2 i nduc es
NF-kappaB-dependent MMP-9 activation and enhances cellular
invasiveness. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 354:190–196. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu X, Zhou B, Xue L, et al:
Ribonucleotide reductase subunits M2 and p53R2 are potential
biomarkers for metastasis of colon cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer.
6:374–381. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW
and Whang EE: RNA interference targeting the M2 subunit of
ribonucleotide reductase enhances pancreatic adenocarcinoma
chemosensitivity to gemcitabine. Oncogene. 23:1539–1548. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Rahman MA, Amin AR, Wang X, et al:
Systemic delivery of siRNA nanoparticles targeting RRM2 suppresses
head and neck tumor growth. J Control Release. 159:384–392. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|