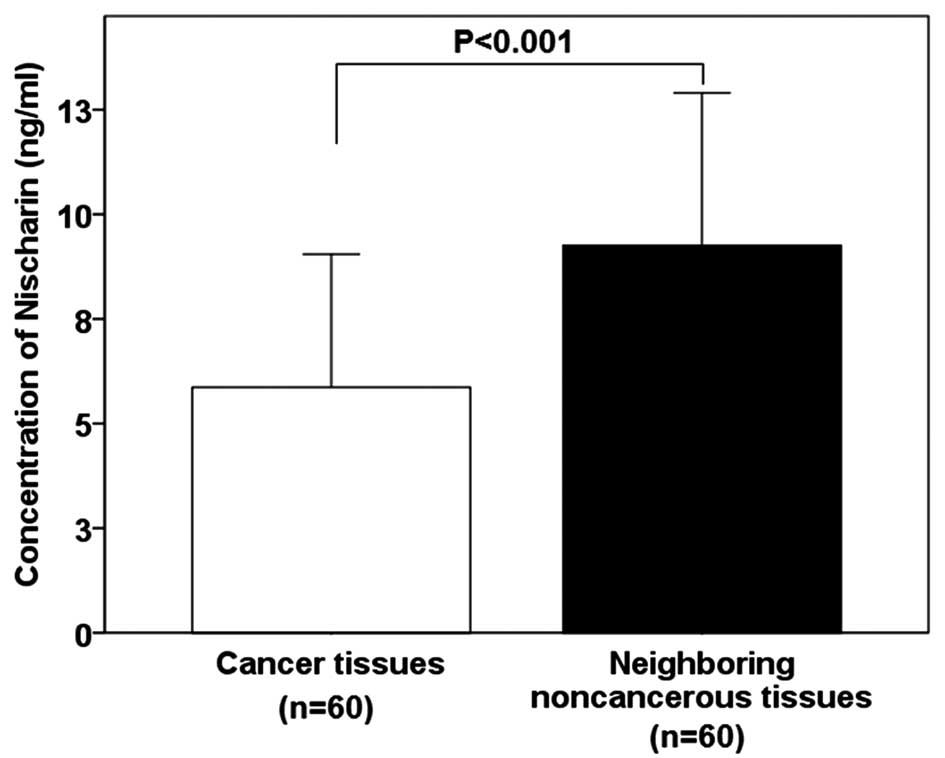
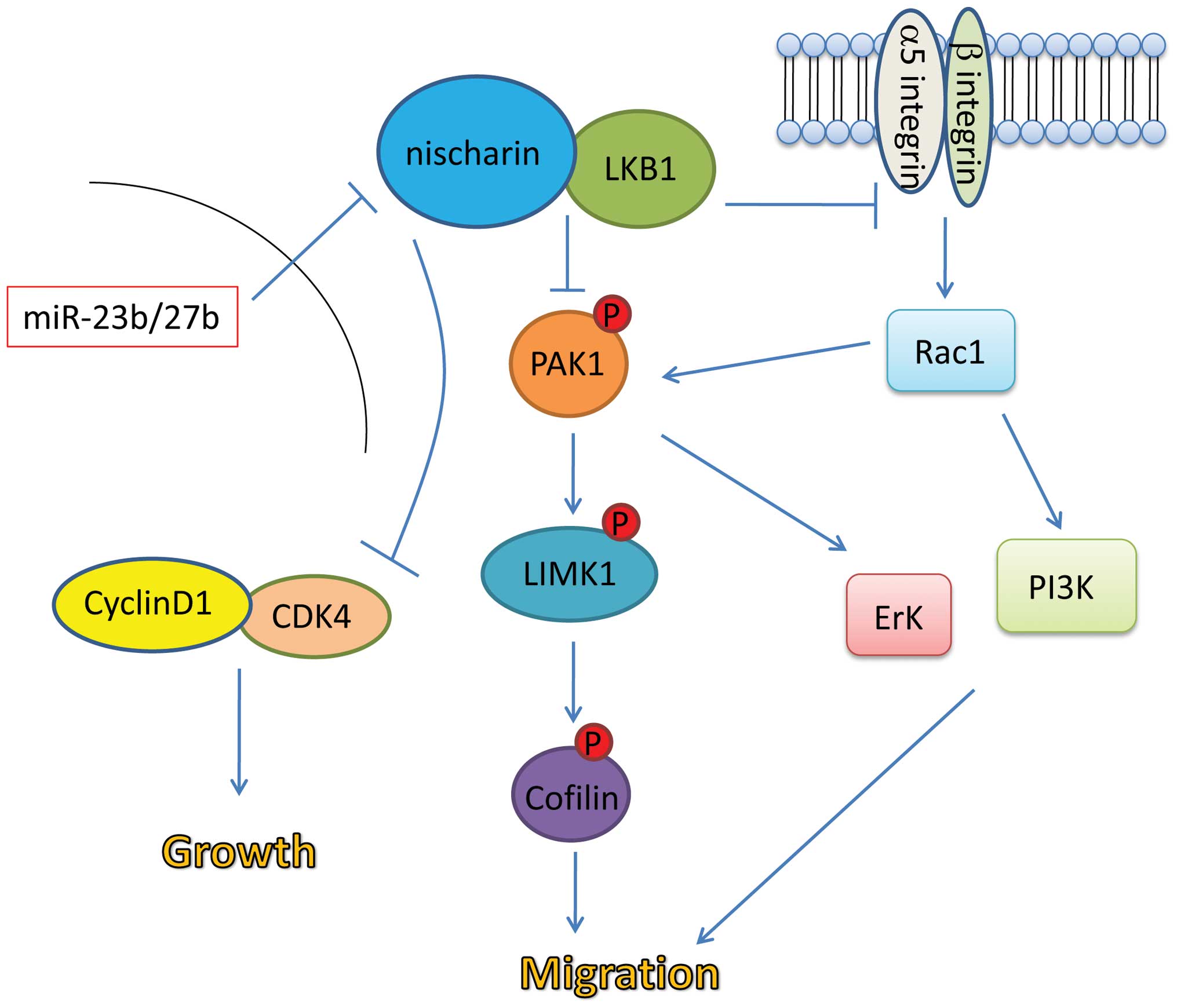
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’
Collaborative Group (EBCTCG): Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal
therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival:
an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 365:1687–1717. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Perez EA, Romond EH, Suman VJ, et al:
Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for human epidermal growth
factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer: planned joint analysis of
overall survival from NSABP B-31 and NCCTG N9831. J Clin Oncol.
32:3744–3752. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Albain KS, Barlow WE, Ravdin PM, et al:
Breast Cancer Intergroup of North America: Adjuvant chemotherapy
and timing of tamoxifen in postmenopausal patients with
endocrine-responsive, node-positive breast cancer: a phase 3,
open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 374:2055–2063
|
|
5
|
Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, et al: Early
Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group: Effects of
radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early
breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview
of the randomised trials. Lancet. 366:2087–2106. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aebi S, Davidson T and Gruber G: Primary
breast cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis,
treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 22(Suppl 6): vi12–vi24. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tazhibi M, Fayaz M and Mokarian F:
Detection of prognostic factors in metastatic breast cancer. J Res
Med Sci. 18:283–290. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cadoo KA, Fornier MN and Morris PG:
Biological subtypes of breast cancer: current concepts and
implications for recurrence patterns. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
57:312–321. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cristofanilli M, Budd GT, Ellis MJ, et al:
Circulating tumor cells, disease progression and survival in
metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 351:781–791. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Whale A, Hashim FN, Fram S, Jones GE and
Wells CM: Signalling to cancer cell invasion through PAK family
kinases. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:849–864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Redig AJ and McAllister SS: Breast cancer
as a systemic disease: a view of metastasis. J Intern Med.
274:113–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kjoller L and Hall A: Signaling to Rho
GTPases. Exp Cell Res. 253:166–179. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bagrodia S and Cerione RA: Pak to the
future. Trends Cell Biol. 9:350–355. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Szczepanowska J: Involvement of
Rac/Cdc42/PAK pathway in cytoskeletal rearrangements. Acta Biochim
Pol. 56:225–234. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Edwards DC, Sanders LC, Bokoch GM and Gill
GN: Activation of LIM-kinase by Pak1 couples Rac/Cdc42 GTPase
signalling to actin cytoskeletal dynamics. Nat Cell Biol.
1:253–259. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Martinez A, Walker RA, Shaw JA, Dearing
SJ, Maher ER and Latif F: Chromosome 3p allele loss in early
invasive breast cancer: detailed mapping and association with
clinicopathological features. Mol Pathol. 54:300–306. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Killary AM, Wolf ME, Giambernardi TA and
Naylor SL: Definition of a tumor suppressor locus within human
chromosome 3p21–p22. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:10877–10881. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ma H, Li W and Wu N: Advances in new
Nischarin protein. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin. 26:42010.In
Chinese.
|
|
19
|
Alahari SK, Lee JW and Juliano RL:
Nischarin, a novel protein that interacts with the integrin alpha5
subunit and inhibits cell migration. J Cell Biol. 151:1141–1154.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alahari SK: Nischarin inhibits Rac induced
migration and invasion of epithelial cells by affecting signaling
cascades involving PAK. Exp Cell Res. 288:415–424. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alahari SK and Nasrallah H: A membrane
proximal region of the integrin alpha5 subunit is important for its
interaction with nischarin. Biochem J. 377:449–457. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ivanov TR, Jones JC, Dontenwill M,
Bousquet P and Piletz JE: Characterization of a partial cDNA clone
detected by imidazoline receptor-selective antisera. J Auton Nerv
Syst. 72:98–110. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dontenwill M, Pascal G, Piletz JE, et al:
IRAS, the human homologue of Nischarin, prolongs survival of
transfected PC12 cells. Cell Death Differ. 10:933–935. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dontenwill M, Piletz JE, Chen M, et al:
IRAS is an anti-apoptotic protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1009:400–412.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ding Y, Zhang R, Zhang K, et al: Nischarin
is differentially expressed in rat brain and regulates neuronal
migration. PLoS One. 8:e545632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baranwal S, Wang Y, Rathinam R, et al:
Molecular characterization of the tumor-suppressive function of
nischarin in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 103:1513–1528.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jain P, Baranwal S, Dong S, Struckhoff AP,
Worthylake RA and Alahari SK: Integrin-binding protein nischarin
interacts with tumor suppressor liver kinase B1 (LKB1) to regulate
cell migration of breast epithelial cells. J Biol Chem.
288:15495–15509. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC, et al: AJCC
Cancer Staging Manual. 7th edition. Springer; New York, NY:
2010
|
|
29
|
Singletary SE, Allred C, Ashley P, et al:
Revision of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system
for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 20:3628–3636. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Harris L, Fritsche H, Mennel R, et al:
American Society of Clinical Oncology: American Society of Clinical
Oncology 2007 update of recommendations for the use of tumor
markers in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 25:5287–5312. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Assoian RK: Anchorage-dependent cell cycle
progression. J Cell Biol. 136:1–4. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Frisch SM and Ruoslahti E: Integrins and
anoikis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 9:701–706. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Varner JA, Emerson DA and Juliano RL:
Integrin alpha 5 beta 1 expression negatively regulates cell
growth: reversal by attachment to fibronectin. Mol Biol Cell.
6:725–740. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Z, Vuori K, Reed JC and Ruoslahti E:
The alpha 5 beta 1 integrin supports survival of cells on
fibronectin and up-regulates Bcl-2 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 92:6161–6165. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hu JJ, Lei HT, Hou and YM: A new
evaluation method for tumor cell migration process. Chinese
Pharmacological Bulletin. 1:128–131. 2010.
|
|
36
|
Alahari SK, Reddig PJ and Juliano RL: The
integrin-binding protein Nischarin regulates cell migration by
inhibiting PAK. EMBO J. 23:2777–2788. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Reddig PJ, Xu D and Juliano RL: Regulation
of p21-activated kinase-independent Rac1 signal transduction by
nischarin. J Biol Chem. 280:30994–31002. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Davila M, Frost AR, Grizzle WE and
Chakrabarti R: LIM kinase 1 is essential for the invasive growth of
prostate epithelial cells: implications in prostate cancer. J Biol
Chem. 278:36868–36875. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yoshioka K, Foletta V, Bernard O and Itoh
K: A role for LIM kinase in cancer invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 100:7247–7252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bagheri-Yarmand R, Mazumdar A, Sahin AA
and Kumar R: LIM kinase 1 increases tumor metastasis of human
breast cancer cells via regulation of the urokinase-type
plasminogen activator system. Int J Cancer. 118:2703–2710. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Nishita M, Tomizawa C, Yamamoto M, Horita
Y, Ohashi K and Mizuno K: Spatial and temporal regulation of
cofilin activity by LIM kinase and Slingshot is critical for
directional cell migration. J Cell Biol. 171:349–359. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Soosairajah J, Maiti S, Wiggan O, et al:
Interplay between components of a novel LIM kinase-slingshot
phosphatase complex regulates cofilin. EMBO J. 24:473–486. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ding Y, Milosavljevic T and Alahari SK:
Nischarin inhibits LIM kinase to regulate cofilin phosphorylation
and cell invasion. Mol Cell Biol. 28:3742–3756. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jackson RJ and Standart N: How do
microRNAs regulate gene expression? Sci STKE. 2007:re12007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jin L, Wessely O, Marcusson EG, Ivan C,
Calin GA and Alahari SK: Prooncogenic factors miR-23b and miR-27b
are regulated by Her2/Neu, EGF and TNF-α in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 73:2884–2896. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|