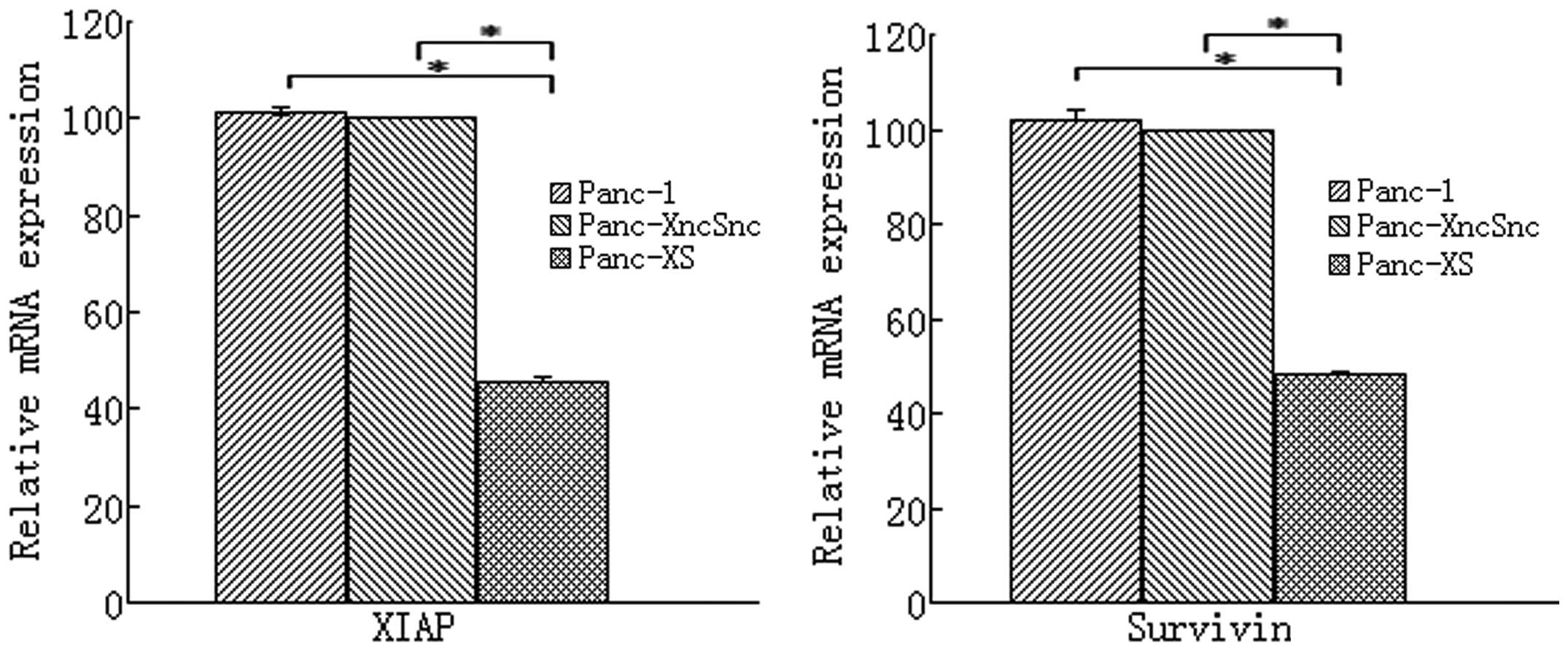
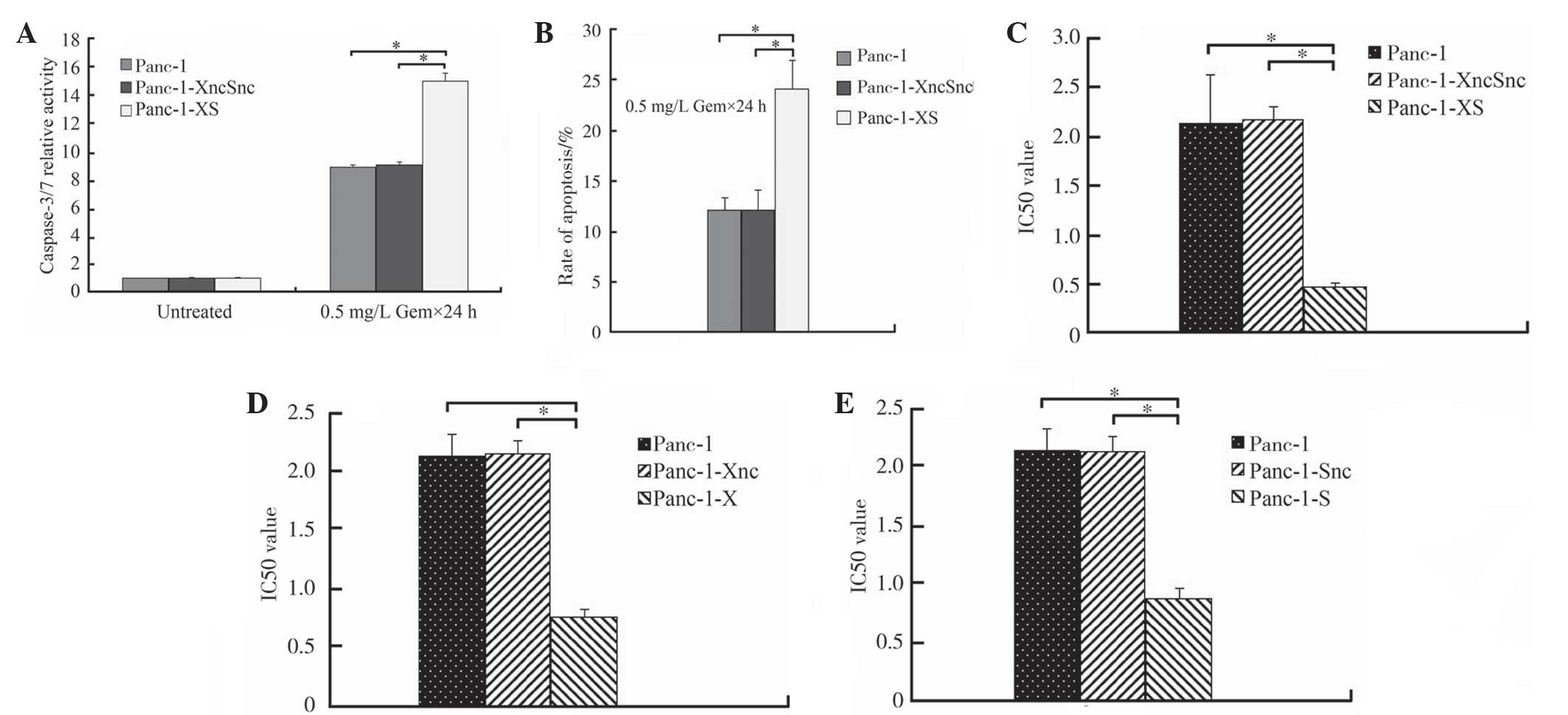
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1710. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Muniraj T, Jamidar PA and Aslanian HR:
Pancreatic cancer: a comprehensive review and update. Dis Mon.
59:368–402. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wei Y, Fan T and Yu M: Inhibitor of
apoptosis proteins and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 40:278–288. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Silke J and Meier P: Inhibitor of
apoptosis (IAP) proteins-modulators of cell death and inflammation.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mehrotra S, Languino LR, Raskett CM, et
al: IAP regulation of metastasis. Cancer Cell. 17:53–64. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang C, Tan T, Yi XP, et al:
Lentivirus-mediated shRNA targeting XIAP and survivin inhibit
SW1990 pancreatic cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo.
Mol Med Rep. 4:667–674. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Krepela E, Dankova P, Moravcikova E, et
al: Increased expression of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins,
survivin and XIAP, in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
35:1449–1462. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Arumugam T, Ramachandran V, Fournier KF,
et al: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition contributes to drug
resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5820–5828. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer development and its
clinical significance. Cancer Sci. 101:293–299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hannon GJ: RNA interference. Nature.
418:244–251. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tonomura H, Takahashi KA, Mazda O, et al:
Glutamine protects articular chondrocytes from heat stress and
NO-induced apoptosis with HSP70 expression. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 14:545–553. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
LaCasse EC, Mahoney DJ, Cheung HH, et al:
IAP-targeted therapies for cancer. Oncogene. 27:6252–6275. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Urrutia R: The IAP: more international
than ever. Pancreatology. 9:III–IV. 2009.
|
|
17
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RYJ and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Kong D, et al: Acquisition
of epithelial-mesen-chymal transition phenotype of
gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells is linked with
activation of the notch signaling pathway. Cancer Res.
69:2400–2407. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deng Y, Wang CC, Choy KW, et al:
Therapeutic potentials of gene silencing by RNA interference:
Principles, challenges, and new strategies. Gene. 538:217–227.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang G, Li J, Zeng Z and Xian L:
Lentivirus-mediated gene therapy by suppressing survivin in BALB/c
nude mice bearing oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther.
5:435–440. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kunze D, Kraemer K, Erdmann K, et al:
Simultaneous siRNA-mediated knockdown of antiapoptotic BCL2,
Bcl-xL, XIAP and survivin in bladder cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
41:1271–1277. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ravet E, Lulka H, Gross F, et al: Using
lentiviral vectors for efficient pancreatic cancer gene therapy.
Cancer Gene Ther. 17:315–324. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ruckert F, Samm N, Lehner AK, et al:
Simultaneous gene silencing of Bcl-2, XIAP and Survivin
re-sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells towards apoptosis. Bmc
Cancer. 10:3792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Min C, Eddy SF, Sherr DH, et al: NF-κB and
epithelial to mesenchymal transition of cancer. J Cell Biochem.
104:733–744. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Carnero A, Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, et
al: The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer, therapeutic
implications. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:187–198. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang BH and Liu LZ: PI3K/PTEN signaling
in angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 102:19–65.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hafsi S, Pezzino FM, Candido S, et al:
Gene alterations in the PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathway as a mechanism of
drug-resistance (review). Int J Oncol. 40:639–644. 2012.
|
|
28
|
Ma J, Sawai H, Ochi N, et al: PTEN
regulates angiogenesis through PI3K/Akt/VEGF signaling pathway in
human pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 331:161–171. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen X, Liao J, Lu Y, et al: Activation of
the PI3K/Akt pathway mediates bone morphogenetic protein 2-induced
invasion of pancreatic cancer cells Panc-1. Pathol Oncol Res.
17:257–261. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Parsons CM, Muilenburg D, Bowles TL, et
al: The role of Akt activation in the response to chemotherapy in
pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res. 30:3279–3289. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|