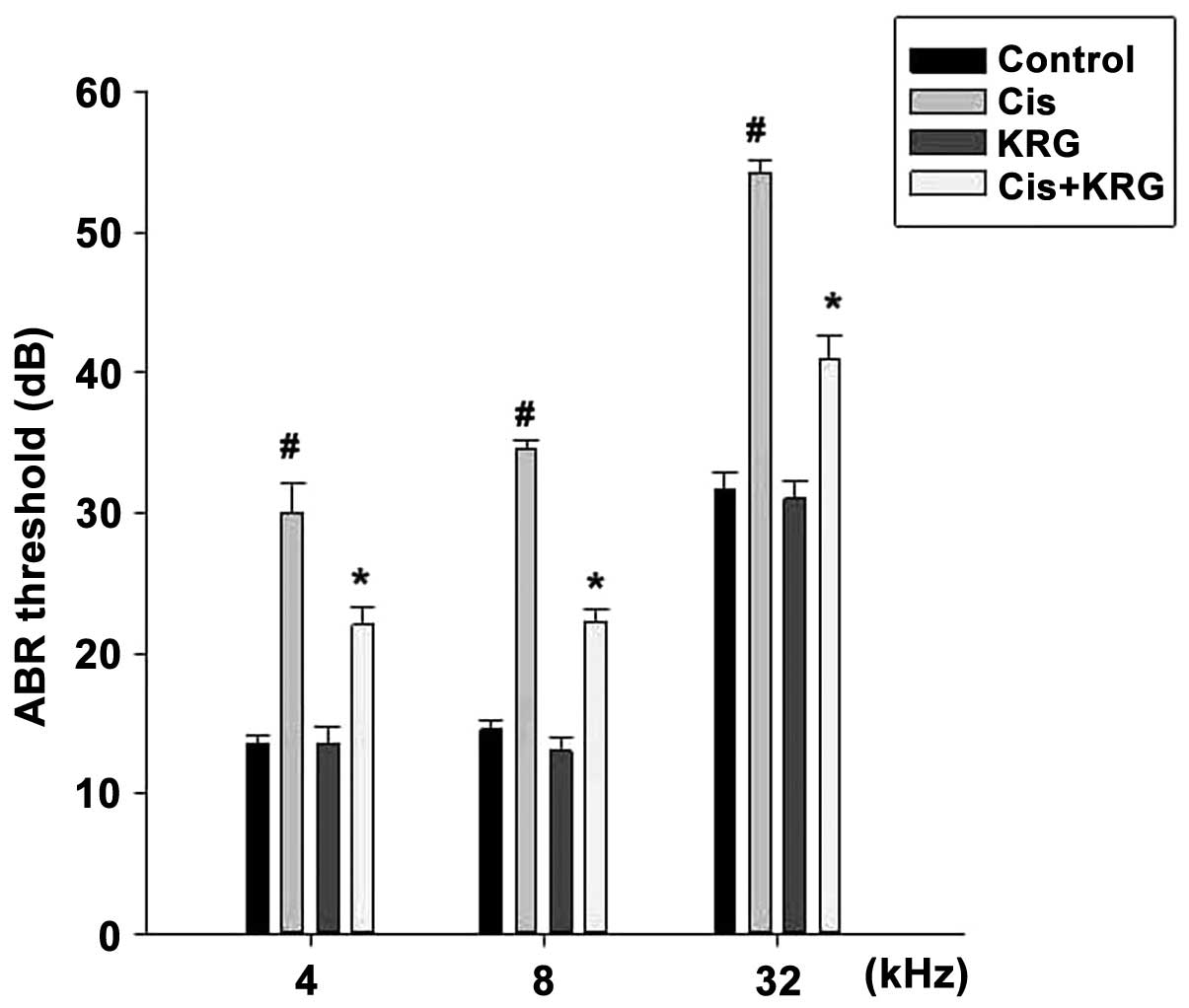
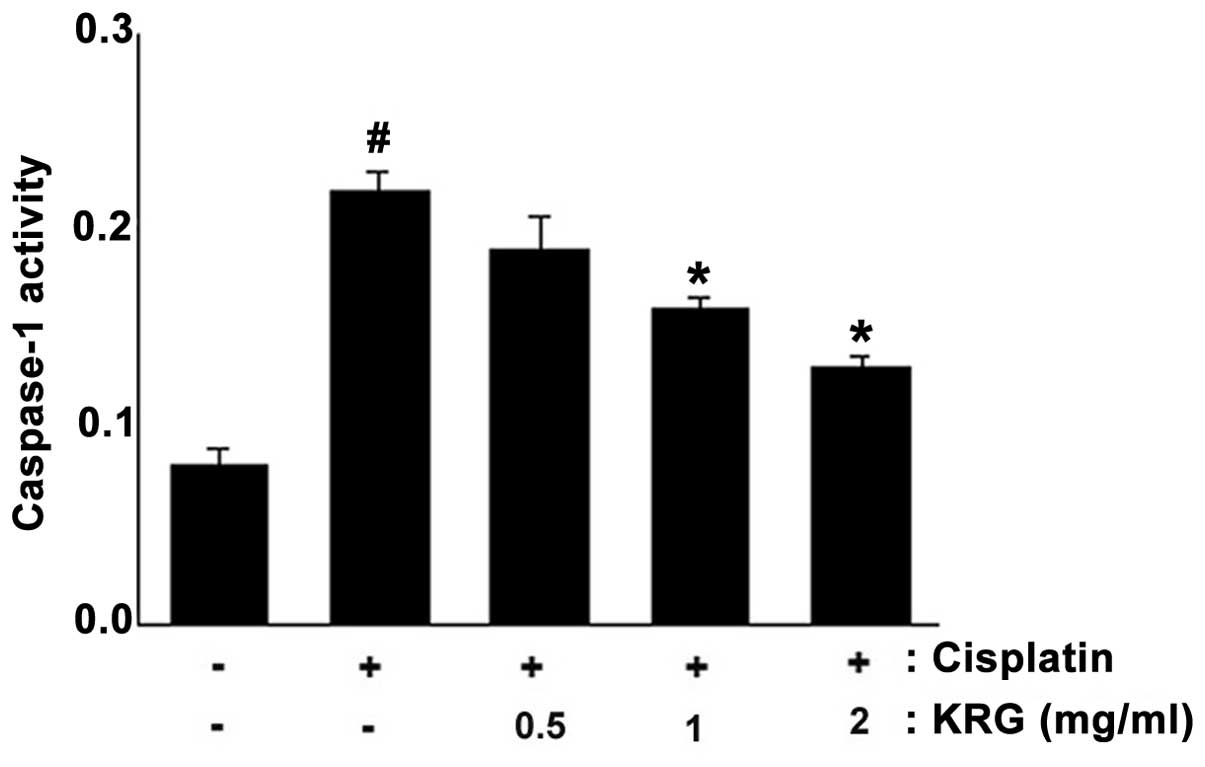
|
1
|
Cohen SM and Lippard SJ: Cisplatin: from
DNA damage to cancer chemotherapy. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol.
67:93–130. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Santos NA, Catão CS, Martins NM, Curti C,
Bianchi ML and Santos AC: Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity is
associated with oxidative stress, redox state unbalance, impairment
of energetic metabolism and apoptosis in rat kidney mitochondria.
Arch Toxicol. 81:495–504. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N and
Nugent K: Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Am J Med Sci.
334:115–124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu YN, Chen H and Li Yi: Protect effect of
bicyclol on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Arch Toxicol.
83:381–387. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jordan P and Carmo-Fonseca M: Molecular
mechanisms involved in cisplatin cytotoxicity. Cell Mol Life Sci.
57:1229–1235. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Satoh H, Firestein GS, Billings PB, Harris
JP and Keithley EM: Proinflammatory cytokine expression in the
endolymphatic sac during inner ear inflammation. J Assoc Res
Otolaryngol. 4:139–147. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Keithley EM, Wang X and Barkdull GC: Tumor
necrosis factor alpha can induce recruitment of inflammatory cells
to the cochlea. Otol Neurotol. 29:854–859. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wakabayashi K, Fujioka M, Kanzaki S, et
al: Blockade of interleukin-6 signaling suppressed cochlear
inflammatory response and improved hearing impairment in
noise-damaged mice cochlea. Neurosci Res. 66:345–352. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Oh GS, Kim HJ, Choi JH, et al: Activation
of lipopolysaccharide-TLR4 signaling accelerates the ototoxic
potential of cisplatin in mice. J Immunol. 186:1140–1150. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim HJ, Oh GS, Lee JH, et al: Cisplatin
ototoxicity involves cytokines and STAT6 signaling network. Cell
Res. 21:944–956. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
So H, Kim H, Lee JH, et al: Cisplatin
cytotoxicity of auditory cells requires secretions of
proinflammatory cytokines via activation of ERK and NF-kappaB. J
Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 8:338–355. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bharti AC, Donato N, Singh S and Aggarwal
BB: Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) down-regulates the constitutive
activation of nuclear factor-kappaB and IkappaBalpha kinase in
human multiple myeloma cells, leading to suppression of
proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Blood. 101:1053–1062.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Estrov Z, Shishodia S, Faderl S, et al:
Resveratrol blocks interleukin-1β-induced activation of the nuclear
transcription factor NF-κB, inhibits proliferation, causes S-phase
arrest and induces apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Blood. 102:987–995. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Christman JW, Sadikot RT and Blackwell TS:
The role of nuclear factor-κB in pulmonary diseases. Chest.
117:1482–1487. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Janssen-Heininger YM, Poynter ME and
Baeuerle PA: Recent advances towards understanding redox mechanisms
in the activation of nuclear factor kappaB. Free Radic Biol Med.
28:1317–1327. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang H, Sha SH and Schacht J: NF-κB
pathway protects cochlear hair cells from aminoglycoside-induced
ototoxicity. J Neurosci Res. 79:644–651. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nagashima R, Sugiyama C, Yoneyama M,
Kuramoto N, Kawada K and Ogita K: Acoustic overstimulation
facilitates the expression of glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic
subunit probably through enhanced DNA binding of activator
protein-1 and/or NF-κB in the murine cochlea. Neurochem Int.
51:209–215. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi X and Nuttall AL: Expression of
adhesion molecular proteins in the cochlear lateral wall of normal
and PARP-1 mutant mice. Hear Res. 224:1–14. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Masuda M, Nagashima R, Kanzaki S, Fujioka
M, Ogita K and Ogawa K: Nuclear factor-kappaB nuclear translocation
in the cochlea of mice following acoustic overstimulation. Brain
Res. 1068:237–247. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lee SH, Stehlik C and Reed JC: Cop, a
caspase recruitment domain-containing protein and inhibitor of
caspase-1 activation processing. J Biol Chem. 276:34495–34500.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang X, Wang H, Figueroa BE, et al:
Dysregulation of receptor interacting protein-2 and caspase
recruitment domain only protein mediates aberrant caspase-1
activation in Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci. 25:11645–11654.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Faubel S, Lewis EC, Reznikov L, et al:
Cisplatin-induced acute renal failure is associated with an
increase in the cytokines interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-18, IL-6 and
neutrophil infiltration in the kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
322:8–15. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sung J, Han KH, Zo JH, Park HJ, Kim CH and
Oh BH: Effects of red ginseng upon vascular endothelial function in
patients with essential hypertension. Am J Chin Med. 28:205–216.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ryu JK, Lee T, Kim DJ, et al: Free
radical-scavenging activity of Korean red ginseng for erectile
dysfunction in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus rats.
Urology. 65:611–615. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hong SH, Suk KT, Choi SH, et al:
Anti-oxidant and natural killer cell activity of Korean red ginseng
(Panax ginseng) and urushiol (Rhus vernicifera Stokes) on
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease of rat. Food Chem Toxicol.
55:586–591. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kalinec GM, Webster P, Lim DJ and Kalinec
F: A cochlear cell line as an in vitro system for drug ototoxicity
screening. Audiol Neurootol. 8:177–189. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zheng JL and Gao WQ: Differential damage
to auditory neurons and hair cells by ototoxins and neuroprotection
by specific neuro-trophins in rat cochlear organotypic cultures.
Eur J Neurosci. 8:1897–1905. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schoonbroodt S, Legrand-Poels S,
Best-Belpomme M and Piette J: Activation of the NF-kappaB
transcription factor in a T-lymphocytic cell line by hypochlorous
acid. Biochem J. 321:777–785. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Orrenius S: Reactive oxygen species in
mitochondria-mediated cell death. Drug Metab Rev. 39:443–455. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fujioka M, Kanzaki S, Okano HJ, Masuda M,
Ogawa K and Okano H: Proinflammatory cytokines expression in
noise-induced damaged cochlea. J Neurosci Res. 83:575–583. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ghaheri BA, Kempton JB, Pillers DA and
Trune DR: Cochlear cytokine gene expression in murine acute otitis
media. Laryngoscope. 117:22–29. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim HJ, So HS, Lee JH, et al: Role of
proinflammatory cytokines in cisplatin-induced vestibular hair cell
damage. Head Neck. 30:1445–1456. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ladrech S, Mathieu M, Puel JL and Lenoir
M: Supporting cells regulate the remodelling of
aminoglycoside-injured organ of Corti, through the release of high
mobility group box 1. Eur J Neurosci. 38:2962–2972. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gorman AM, Bonfoco E, Zhivotovsky B,
Orrenius S and Ceccatelli S: Cytochrome c release and caspase-3
activation during colchicine-induced apoptosis of cerebellar
granule cells. Eur J Neurosci. 11:1067–1072. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Abu-Qare AW and Abou-Donia MB: Biomarkers
of apoptosis: release of cytochrome c, activation of caspase-3,
induction of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine, increased
3-nitrotyrosine, and alteration of p53 gene. J Toxicol Environ
Health B Crit Rev. 4:313–332. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Brentnall M, Rodriguez-Menocal L, De
Guevara RL, Cepero E and Boise LH: Caspase-9, caspase-3 and
caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell
Biol. 14:322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lang H, Schulte BA, Zhou D, Smythe N,
Spicer SS and Schmiedt RA: Nuclear factor kappaB deficiency is
associated with auditory nerve degeneration and increased
noise-induced hearing loss. J Neurosci. 26:3541–3550. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yamamoto H, Omelchenko I, Shi X and
Nuttall AL: The influence of NF-κB signal-transduction pathways on
the murine inner ear by acoustic overstimulation. J Neurosci Res.
87:1832–1840. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Stark LA and Dunlop MG: Nucleolar
sequestration of RelA (p65) regulates NF-kappaB-driven
transcription and apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 25:5985–6004. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lamkanfi M, Kalai M, Saelens X, Declerq W
and Vandenabeele P: Caspase-1 activates nuclear factor of the
kappa-enhancer in B cells independently of its enzymatic activity.
J Biol Chem. 279:24785–24793. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Park K-S, Hwang D-S, Lee J-M, Jang J-B,
Lee K-S and Lee C-H: Inhibitory effect of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer
on gynecological cancer. Orient Pharm Exp Med. 13:217–223. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Rybak LP, Whitworth CA, Mukherjea D and
Ramkumar V: Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and
prevention. Hear Res. 226:157–167. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Devarajan P, Savoca M, Castaneda MP, et
al: Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in auditory cells: role of death
receptor and mitochondrial pathways. Hear Res. 174:45–54. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Roy S, Banerjee B and Vedasiromoni J:
Anti-tumor activity of Swietenia mahagoni (L.) Jacq. leaf extract
against Ehrlich’s ascites carcinoma in mice. Orient Pharm Exp Med.
13:205–216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
So HS, Park C, Kim HJ, et al: Protective
effect of T-type calcium channel blocker flunarizine on
cisplatin-induced death of auditory cells. Hear Res. 204:127–139.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee S, Moon SO, Kim W, et al: Protective
role of L-2-oxothiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid in cisplatin-induced
renal injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 21:2085–2095. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tahera Y, Meltser I, Johansson P, et al:
NF-kappaB mediated glucocorticoid response in the inner ear after
acoustic trauma. J Neurosci Res. 83:1066–1076. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Shishodia S and Aggarwal BB: Nuclear
factor-kappaB: a friend or a foe in cancer? Biochem Pharmacol.
68:1071–1080. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nagy I, Monge A, Albinger-Hegyi A, Schmid
S and Bodmer D: NF-kappaB is required for survival of immature
auditory hair cells in vitro. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 6:260–268.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kim SJ, Jeong HJ, Myung NY, et al: The
protective mechanism of antioxidants in cadmium-induced ototoxicity
in vitro and in vivo. Environ Health Perspect. 116:854–862. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Watanabe K, Inai S, Jinnouchi K, et al:
Nuclear-factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)-inducible nitric oxide synthase
(iNOS/NOS II) pathway damages the stria vascularis in
cisplatin-treated mice. Anticancer Res. 22:4081–4085. 2002.
|
|
53
|
Chu SH, Lim JW, Kim DG, Lee ES, Kim KH and
Kim H: Down-regulation of Bcl-2 is mediated by NF-κB activation in
Helicobacter pylori-induced apoptosis of gastric epithelial cells.
Scand J Gastroenterol. 46:148–155. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zhang WH, Wang X, Narayanan M, et al:
Fundamental role of the Rip2/caspase-1 pathway in hypoxia and
ischemia-induced neuronal cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:16012–16017. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu W, Staecker H, Stupak H, Malgrange B,
Lefebvre P and Van De Water TR: Caspase inhibitors prevent
cisplatin-induced apoptosis of auditory sensory cells. Neuroreport.
9:2609–2614. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|