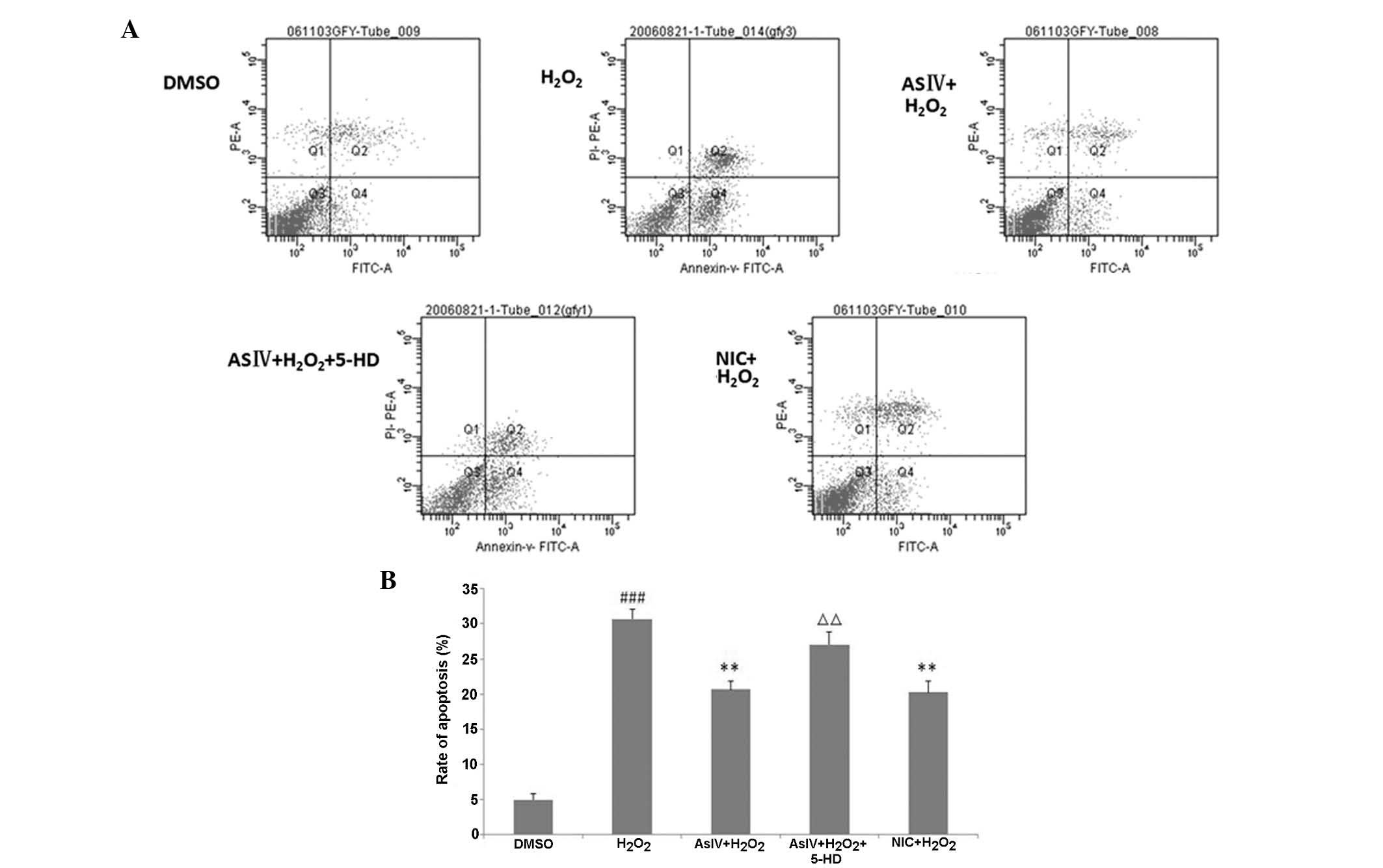
|
1
|
Murphy E and Steenbergen C: Mechanisms
underlying acute protection from cardiac ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Physiol Rev. 88:581–609. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paradies G, Petrosillo G, Pistolese M, Di
Venosa N, Federici A and Ruggiero FM: Decrease in mitochondrial
complex I activity in ischemic/reperfused rat heart: involvement of
reactive oxygen species and cardiolipin. Circ Res. 94:53–59. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lemasters JJ, Theruvath TP, Zhong Z and
Nieminen AL: Mitochondrial calcium and the permeability transition
in cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1787:1395–1401. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baines CP: The mitochondrial permeability
transition pore and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol.
104:181–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Weiss JN, Korge P, Honda HM and Ping P:
Role of the mitochondrial permeability transition in myocardial
disease. Circ Res. 93:292–301. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fryer RM, Eells JT, Hsu AK, Henry MM and
Gross GJ: Ischemic preconditioning in rats: role of mitochondrial
K(ATP) channel in preservation of mitochondrial function. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 278:H305–H312. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Garlid KD and Halestrap AP: The
mitochondrial K(ATP) channel-fact or fiction? J Mol Cell Cardiol.
52:578–583. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wakiyama H, Cowan DB, Toyoda Y, Federman
M, Levitsky S and McCully JD: Selective opening of mitochondrial
ATP-sensitive potassium channels during surgically induced
myocardial ischemia decreases necrosis and apoptosis. Eur J
Cardiothorac Surg. 21:424–433. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou JY, Fan Y, Kong JL, Wu DZ and Hu ZB:
Effects of components isolated from Astragalus membranaceus Bunge
on cardiac function injured by myocardial ischemia reperfusion in
rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 300–302. 2000.In Chinese.
|
|
10
|
Xu YC, Lan SL and Chen JY: Effects of
huangqi sijun decoction on thyroxin and cyclic nucleotide levels in
rat models with spleen deficiency syndrome. Chin Drug Res Clin
Pharm. 18:291–293. 2007.
|
|
11
|
Guan FY and Yu XX: The protective effect
of Astragalus membranaceus injection preconditioning on
experimental myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Chin J
Geront. 30:3126–3129. 2010.
|
|
12
|
Yang J, Li J, Lu J, Zhang Y, Zhu Z and Wan
H: Synergistic protective effect of astragaloside
IV-tetramethylpyrazine against cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury
induced by transient focal ischemia. J Ethnopharmacol. 140:64–72.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Meng LQ, Tang JW, Wang Y, et al:
Astragaloside IV synergizes with ferulic acid to inhibit renal
tubulointerstitial fibrosis in rats with obstructive nephropathy.
Br J Pharmacol. 162:1805–1818. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xie W and Du L: Diabetes is an
inflammatory disease: evidence from traditional Chinese medicines.
Diabetes Obes Metab. 13:289–301. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qiu LH, Xie XJ and Zhang BQ: Astragaloside
IV improves homocysteine-induced acute phase endothelial
dysfunction via antioxidation. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:641–646. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao Z, Wang W, Wang F, et al: Effects of
Astragaloside IV on heart failure in rats. Chin Med. 4:62009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guan FY, Li H, Sun W and Yang SJ:
Protective effects of Astragaloside IV on hydrogen peroxide-induced
injury of cultured neonatal rat myocardial cells. J Jilin Uni Med
Ed. 33:211–214. 2007.
|
|
18
|
Zhang WD, Chen H, Zhang C, Liu RH, Li HL
and Chen HZ: Astragaloside IV from Astragalus membranaceus shows
cardio-protection during myocardial ischemia in vivo and in vitro.
Planta Med. 72:4–8. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu XL, Chen XJ, Ji H, et al: Astragaloside
IV improved intracellular calcium handling in hypoxia-reoxygenated
cardiocytes via the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase. Pharmacology.
81:325–332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yu WP, Xu GL, Shen CX and Qian ZY: Effects
of crocetin on the apoptosis and the changes of its related
regulating proteins caspase-3 and Bcl-2 induced by
H2O2 in myocardial cell. Chin J Pathoph.
22:54–57. 2006.
|
|
21
|
Smith MA and Schnellmann RG: Calpains,
mitochondria and apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res. 96:32–37. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Grivicich I, Regner A, da Rocha AB, et al:
Irinotecan/5-fluorouracil combination induces alterations in
mitochondrial membrane potential and caspases on colon cancer cell
lines. Oncol Res. 15:385–392. 2005.
|
|
23
|
Kallio A, Zheng A, Dahllund J, Heiskanen
KM and Harkonen P: Role of mitochondria in tamoxifen-induced rapid
death of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Apoptosis. 10:1395–1410. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shrivastava A, Tiwari M, Sinha RA, et al:
Molecular iodine induces caspase-independent apoptosis in human
breast carcinoma cells involving the mitochondria-mediated pathway.
J Biol Chem. 281:19762–19771. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi LG, Zhang GP and Jin HM: Inhibition of
microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis by angiopoietin-1 and the
involvement of cytochrome C. Chin Med J (Engl). 119:725–730.
2006.
|
|
26
|
Murata M, Akao M, O’Rourke B and Marban E:
Mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels attenuate matrix
Ca(2+) overload during simulated ischemia and reperfusion: possible
mechanism of cardioprotection. Circ Res. 89:891–898. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shahid M, Tauseef M, Sharma KK and Fahim
M: Brief femoral artery ischaemia provides protection against
myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats: the possible
mechanisms. Exp Physiol. 93:954–968. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu Q, Bie P, Tang C and Zhang YJ: An
experiment study on the role of bcl-2 in attenuation
ischemia-reperfusion injury in liver graft in mice induced by
mitoKATP channel opener diazoxide. J Clin Med Practi. 12:35–40.
2008.
|
|
29
|
Tratsiakovich Y, Gonon AT, Krook A, et al:
Arginase inhibition reduces infarct size via nitric oxide, protein
kinase C epsilon and mitochondrial ATP-dependent K+
channels. Eur J Pharmacol. 712:16–21. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Soeding PF, Crack PJ, Wright CE, Angus JA
and Royse CF: Levosimendan preserves the contractile responsiveness
of hypoxic human myocardium via mitochondrial K(ATP) channel and
potential pERK 1/2 activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 655:59–66. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|