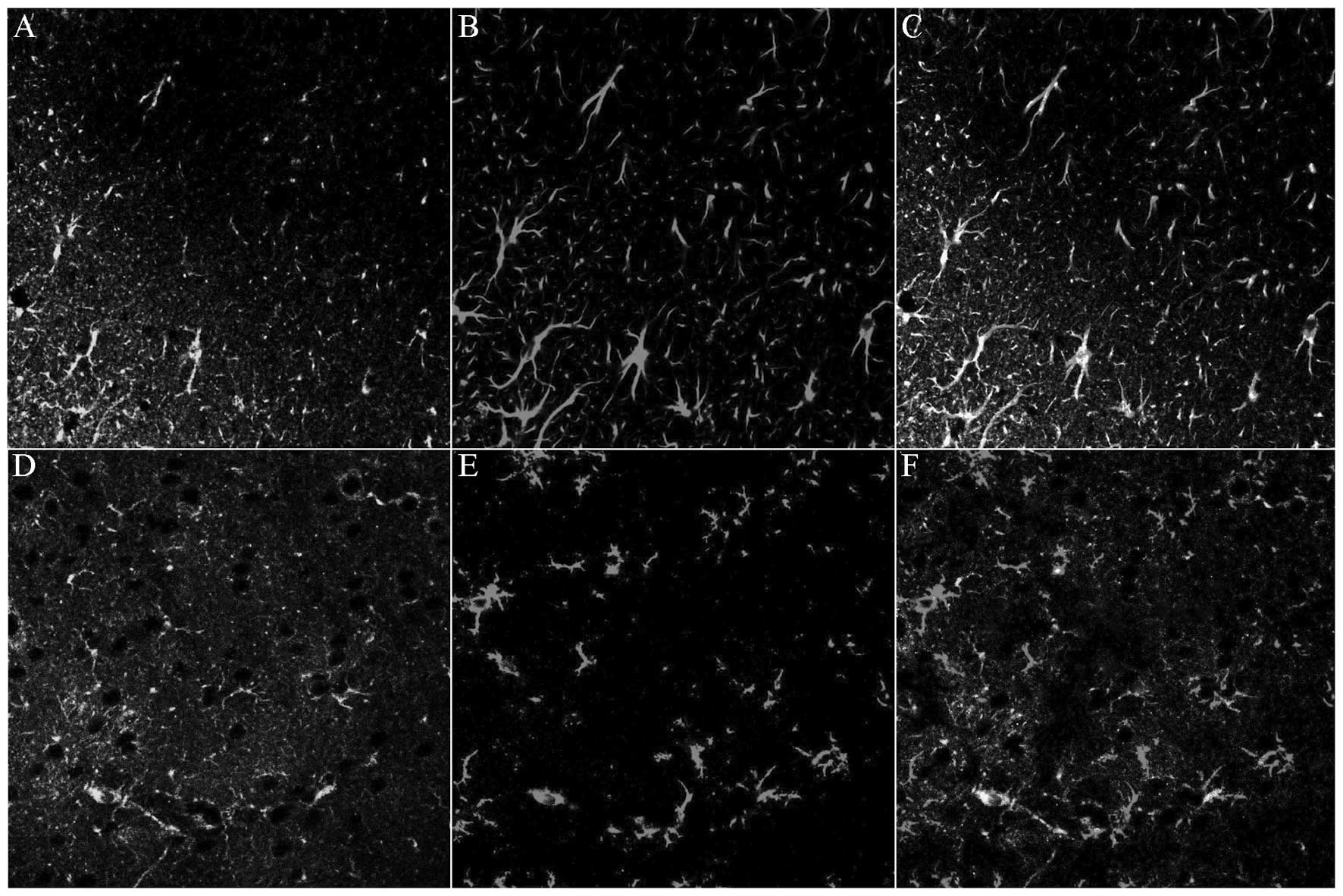
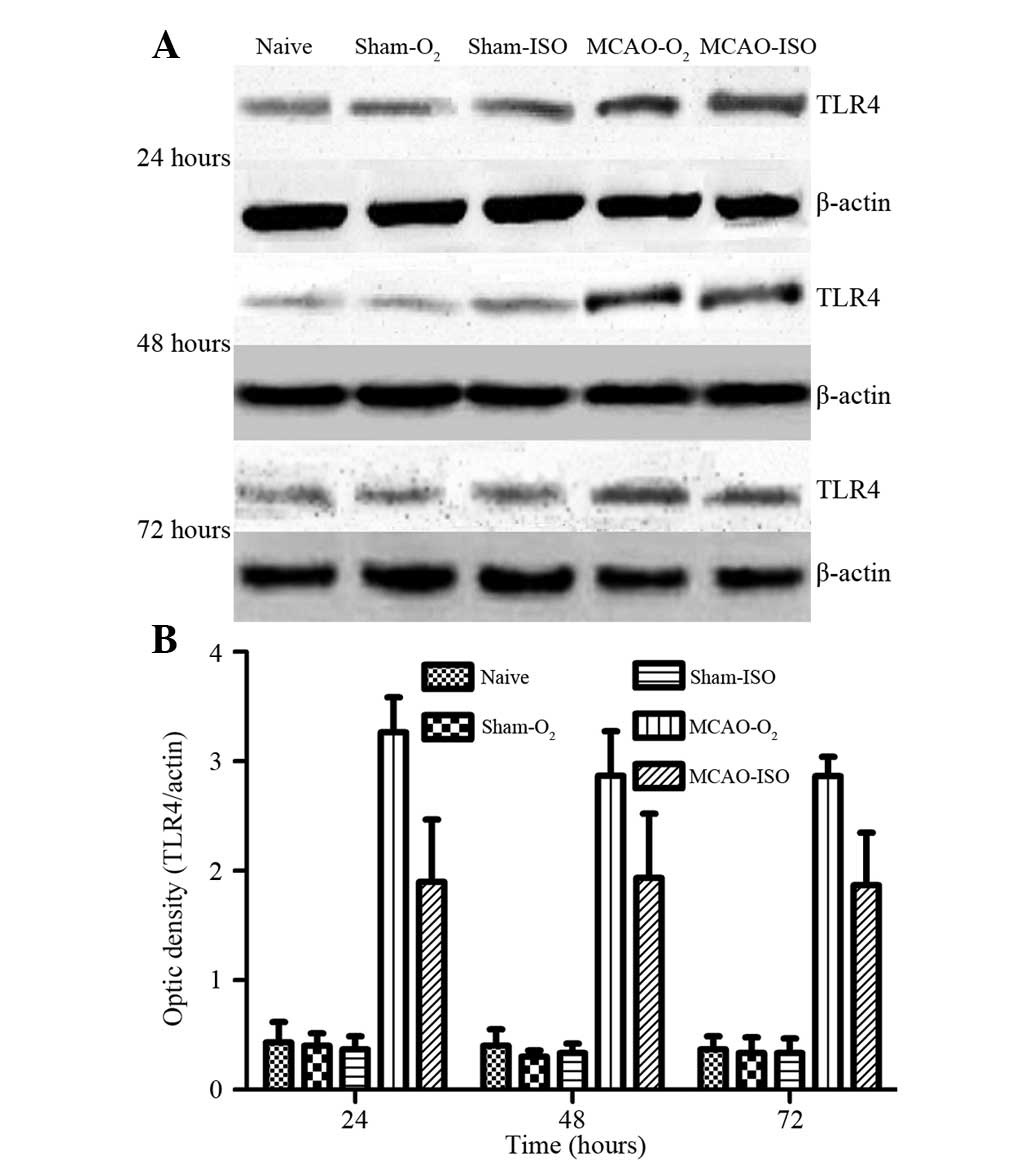
|
1
|
Fan H and Cook JA: Molecular mechanisms of
endotoxin tolerance. J Endotoxin Res. 10:71–84. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aderem A and Ulevitch RJ: Toll-like
receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature.
406:782–787. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chakravarty S and Herkenham M: Toll-like
receptor 4 on nonhematopoietic cells sustains CNS inflammation
during endotoxemia, independent of systemic cytokines. J Neurosci.
25:1788–1796. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kaisho T and Akira S: Toll-like receptors
as adjuvant receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1589:1–13. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kilic U, Kilic E, Matter CM, Bassetti CL
and Hermann DM: TLR-4 deficiency protects against focal cerebral
ischemia and axotomy-induced neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis.
31:33–40. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kitano H, Young JM, Cheng J, Wang L, Hurn
PD and Murphy SJ: Gender-specific response to isoflurane
preconditioning in focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 27:1377–1386. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang J, Yang ZJ, Klaus JA, Koehler RC and
Huang J: Delayed tolerance with repetitive transient focal ischemic
preconditioning in the mouse. Stroke. 39:967–974. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eilers H and Bickler PE: Hypothermia and
isoflurane similarly inhibit glutamate release evoked by chemical
anoxia in rat cortical brain slices. Anesthesiology. 85:600–607.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Becker K, Eder M, Ranft A, et al: Low dose
isoflurane exerts opposing effects on neuronal network excitability
in neocortex and hippocampus. PLoS One. 7:e393462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Puil E, El-Beheiry H and Baimbridge KG:
Anesthetic effects on glutamate-stimulated increase in
intraneuronal calcium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 255:955–961.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Puil E and El-Beheiry H: Anaesthetic
suppression of transmitter actions in neocortex. Br J Pharmacol.
101:61–66. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bickler PE, Buck LT and Hansen BM: Effects
of isoflurane and hypothermia on glutamate receptor-mediated
calcium influx in brain slices. Anesthesiology. 81:1461–1469. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dong Y and Benveniste EN: Immune function
of astrocytes. Glia. 36:180–190. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ladeby R, Wirenfeldt M, Garcia-Ovejero D,
et al: Microglial cell population dynamics in the injured adult
central nervous system. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 48:196–206. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song JH, Bellail A, Tse MC, Yong VW and
Hao C: Human astrocytes are resistant to Fas ligand and tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced
apoptosis. J Neurosci. 26:3299–3308. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li H, Yin J, Li L, Deng J, Feng C and Zuo
Z: Isoflurane post-conditioning reduces ischemia-induced nuclear
factor-kappaB activation and interleukin 1beta production to
provide neuroprotection in rats and mice. Neurobiol Dis.
54:216–224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bedirli N, Bagriacik EU, Emmez H, Yilmaz
G, Unal Y and Ozkose Z: Sevoflurane and isoflurane preconditioning
provides neuroprotection by inhibition of apoptosis-related mRNA
expression in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosurg
Anesthesiol. 24:336–344. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen J, Graham SH, Zhu RL and Simon RP:
Stress proteins and tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 16:566–577. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shimamura N, Matchett G, Solaroglu I,
Tsubokawa T, Ohkuma H and Zhang J: Inhibition of integrin
alphavbeta3 reduces blood-brain barrier breakdown in focal ischemia
in rats. J Neurosci Res. 84:1837–1847. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo W, Wang H, Watanabe M, et al:
Glial-cytokine neuronal interactions underlying the mechanisms of
persistent pain. J Neurosci. 27:6006–6018. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang SC, Arumugam TV, Xu X, et al: Pivotal
role for neuronal Toll-like receptors in ischemic brain injury and
functional deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:13798–13803. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hua F, Ma J, Ha T, et al: Activation of
Toll-like receptor 4 signaling contributes to hippocampal neuronal
death following global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. J
Neuroimmunol. 190:101–111. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiong L, Zheng Y, Wu M, et al:
Preconditioning with isoflurane produces dose-dependent
neuroprotection via activation of adenosine triphosphate-regulated
potassium channels after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Anesth
Analg. 96:233–237. 2003.
|
|
25
|
Kawaguchi M, Drummond JC, Cole DJ, Kelly
PJ, Spurlock MP and Patel PM: Effect of isoflurane on neuronal
apoptosis in rats subjected to focal cerebral ischemia. Anesth
Analg. 98:798–805. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hanisch UK and Kettenmann H: Microglia:
active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and
pathologic brain. Nat Neurosci. 10:1387–1394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kapinya KJ, Lowl D, Futterer C, et al:
Tolerance against ischemic neuronal injury can be induced by
volatile anesthetics and is inducible NO synthase dependent.
Stroke. 33:1889–1898. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee SJ and Lee S: Toll-like receptors and
inflammation in the CNS. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy.
1:181–191. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Beg AA: Endogenous ligands of Toll-like
receptors: implications for regulating inflammatory and immune
responses. Trends Immunol. 23:509–512. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Doyle SL and O’Neill LA: Toll-like
receptors: from the discovery of NFkappaB to new insights into
transcriptional regulations in innate immunity. Biochem Pharmacol.
72:1102–1113. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Baeuerle PA and Henkel T: Function and
activation of NF-kappaB in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol.
12:141–179. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Seki E, Tsutsui H, Iimuro Y, et al:
Contribution of Toll-like receptor/myeloid differentiation factor
88 signaling to murine liver regeneration. Hepatology. 41:443–450.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Farina C, Aloisi F and Meinl E: Astrocytes
are active players in cerebral innate immunity. Trends Immunol.
28:138–145. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Glezer I, Simard AR and Rivest S:
Neuroprotective role of the innate immune system by microglia.
Neuroscience. 147:867–883. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Aloisi F: Immune function of microglia.
Glia. 36:165–179. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Streit WJ, Conde JR, Fendrick SE, Flanary
BE and Mariani CL: Role of microglia in the central nervous
system’s immune response. Neurol Res. 27:685–691. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Akira S, Uematsu S and Takeuchi O:
Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 124:783–801. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bowman CC, Rasley A, Tranguch SL and
Marriott I: Cultured astrocytes express toll-like receptors for
bacterial products. Glia. 43:281–291. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hang CH, Shi JX, Li JS, Wu W and Yin HX:
Concomitant upregulation of nuclear factor-κB activity,
proinflammatory cytokines and ICAM-1 in the injured brain after
cortical contusion trauma in a rat model. Neurol India. 53:312–317.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|