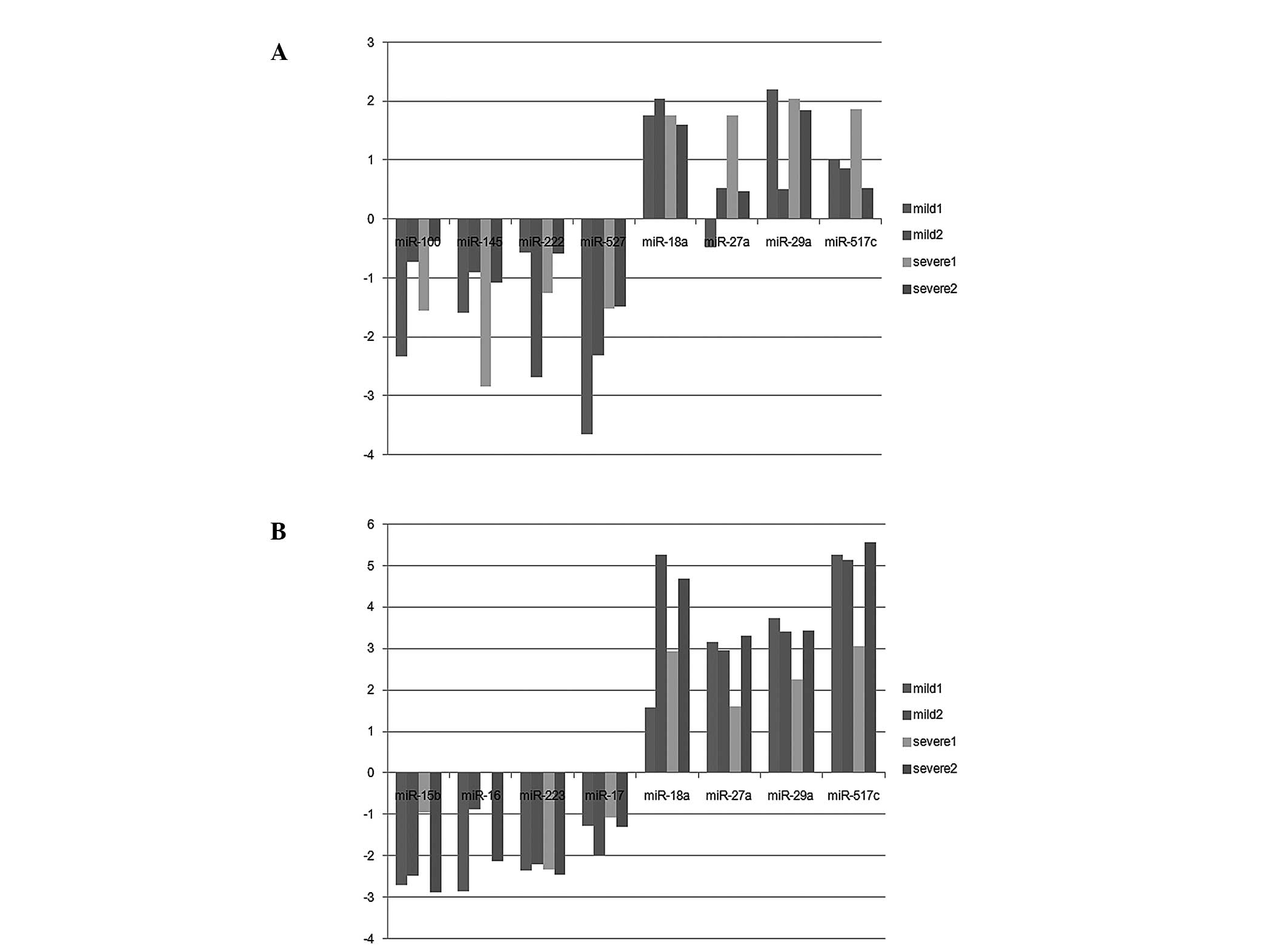
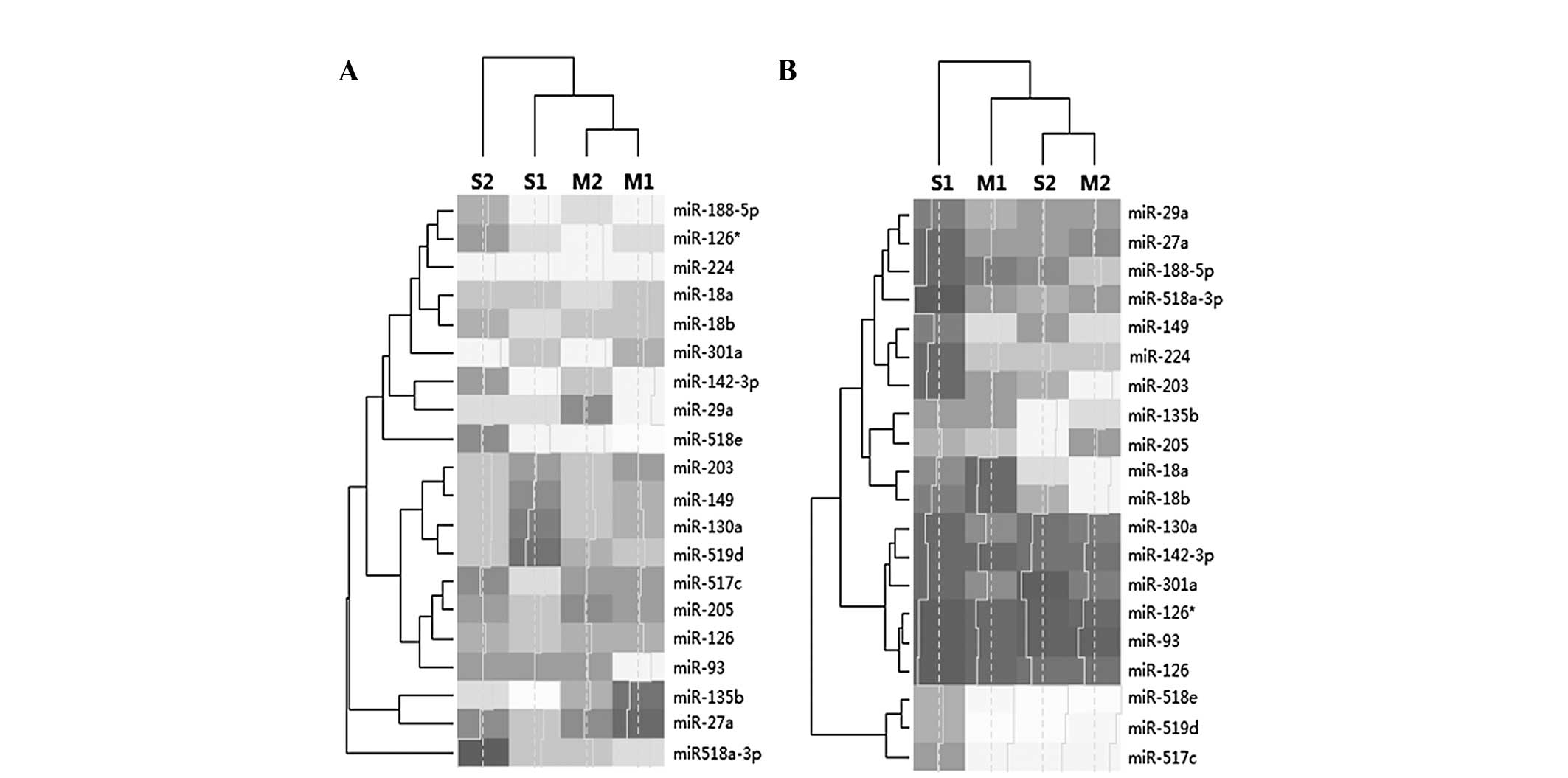
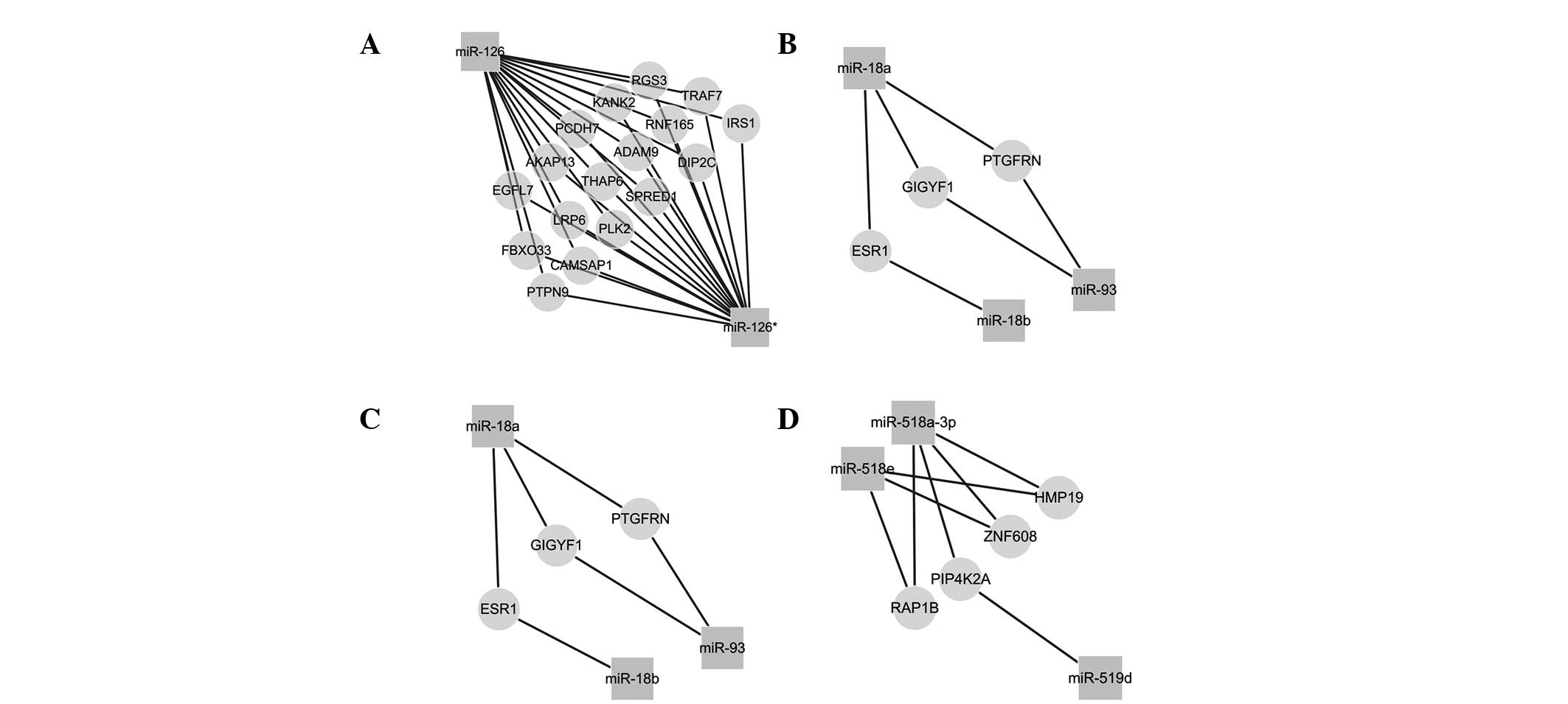
|
1
|
Enquobahrie DA, Abetew DF, Sorensen TK,
Willoughby D, Chidambaram K and Williams MA: Placental microRNA
expression in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 204:e12–e21. 2011.
|
|
2
|
Redman CW and Sargent IL: Latest advances
in understanding preeclampsia. Science. 308:1592–1594. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grill S, Rusterholz C, Zanetti-Dällenbach
R, et al: Potential markers of preeclampsia- a review. Reprod Biol
Endocrinol. 7:702009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Roberts JM and Cooper DW: Pathogenesis and
genetics of pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 357:53–56. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Broughton Pipkin F and Roberts JM:
Hypertension in pregnancy. J Hum Hypertens. 14:705–724. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huppertz B: Placental origins of
preeclampsia: challenging the current hypothesis. Hypertension.
51:970–975. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scioscia M, Gumaa K, Kunjara S, et al:
Insulin resistance in human preeclamptic placenta is mediated by
serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 and -2. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 91:709–717. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yi C, Wang Q, Wang L, et al: MiR-663, a
microRNA targeting p21(WAF1/CIP1), promotes the proliferation and
tumorigenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene. 31:4421–4433.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang Q, Lu J, Wang S, Li H, Ge Q and Lu Z:
Application of next-generation sequencing technology to profile the
circulating microRNAs in the serum of preeclampsia versus normal
pregnant women. Clin Chim Acta. 412:2167–2173. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Salim H, Akbar NS, Zong D, et al:
miRNA-214 modulates radiotherapy response of non-small cell lung
cancer cells through regulation of p38MAPK, apoptosis and
senescence. Br J Cancer. 107:1361–1373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo L, Yang Q, Lu J, et al: A
comprehensive survey of miRNA repertoire and 3′ addition events in
the placentas of patients with pre eclampsia from high throughput
sequencing. PLoS One. 6:e210722011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yi R, Qin Y, Macara IG and Cullen BR:
Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of pre-microRNAs and short
hairpin RNAs. Genes Dev. 17:3011–3016. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lund E, Güttinger S, Calado A, Dahlberg JE
and Kutay U: Nuclear export of microRNA precursors. Science.
303:95–98. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Schwarz DS, Tomari Y and Zamore PD: The
RNA-induced silencing complex is a Mg2+ dependent
endonuclease. Curr Biol. 14:787–791. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435:834–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, et al:
Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer
detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:10513–10518. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kotlabova K, Doucha J and Hromadnikova I:
Placental-specific microRNA in maternal circulation -
identification of appropriate pregnancy-associated microRNAs with
diagnostic potential. J Reprod Immunol. 89:185–191. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo L, Zhao Y, Yang S, Cai M, Wu Q and
Chen F: Genome-wide screen for aberrantly expressed miRNAs reveals
miRNA profile signature in breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep.
40:2175–2186. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang Y, Diao Z, Su L, et al: MicroRNA-155
contributes to preeclampsia by down-regulating CYR61. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 202:e1–e7. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu Y, Li P, Hao S, Liu L, Zhao J and Hou
Y: Differential expression of microRNAs in the placentae of Chinese
patients with severe pre-eclampsia. Clin Chem Lab Med. 47:923–929.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pineles BL, Romero R, Montenegro D, et al:
Distinct subsets of microRNAs are expressed differentially in the
human placentas of patients with preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
196:e1–e6. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu XM, Han T, Sargent IL, Yin GW and Yao
YQ: Differential expression profile of microRNAs in human placentas
from preeclamptic pregnancies vs normal pregnancies. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 200:e1–e7. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S
and Enright AJ: miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids
Res. 36:D154–D158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human microRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
2:e3632004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hsu SD, Lin FM, Wu WY, et al: miRTarBase:
a database curates experimentally validated microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:D163–D169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono
H and Kanehisa M: KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.
Nucleic Acids Res. 27:29–34. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, et al:
Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000.
|
|
29
|
Kosaka N, Iguchi H and Ochiya T:
Circulating microRNA in body fluid: a new potential biomarker for
cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 101:2087–2092. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mouillet JF, Chu T, Hubel CA, Nelson DM,
Parks WT and Sadovsky Y: The levels of hypoxia-regulated microRNAs
in plasma of pregnant women with fetal growth restriction.
Placenta. 31:781–784. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lázár L, Nagy B, Molvarec A, Szarka A and
Rigó J Jr: Role of hsa-miR-325 in the etiopathology of
preeclampsia. Mol Med Rep. 6:597–600. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fish JE, Santoro MM, Morton SU, et al:
miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev
Cell. 15:272–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang S, Aurora AB, Johnson BA, et al: The
endothelial-specific microRNA miR-126 governs vascular integrity
and angiogenesis. Dev Cell. 15:261–271. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gellhaus A, Schmidt M, Dunk C, Lye SJ and
Winterhager E: The circulating proangiogenic factors CYR61 (CCN1)
and NOV (CCN3) are significantly decreased in placentae and sera of
preeclamptic patients. Reprod Sci. 14(8 Suppl): 46–52. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Morales Prieto DM and Markert UR:
MicroRNAs in pregnancy. J Reprod Immunol. 88:106–111. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mouillet JF, Chu T, Nelson DM, Mishima T
and Sadovsky Y: MiR-205 silences MED1 in hypoxic primary human
trophoblasts. FASEB J. 24:2030–2039. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Maccani MA, Padbury JF and Marsit CJ:
miR-16 and miR-21 expression in the placenta is associated with
fetal growth. PLoS One. 6:e212102011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Muralimanoharan S, Maloyan A, Mele J, Guo
C, Myatt LG and Myatt L: MIR-210 modulates mitochondrial
respiration in placenta with preeclampsia. Placenta. 33:816–823.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Eremina V and Quaggin SE: The role of
VEGF-A in glomerular development and function. Curr Opin Nephrol
Hypertens. 13:9–15. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tsatsaris V, Goffin F, Munaut C, et al:
Overexpression of the soluble vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor in preeclamptic patients: pathophysiological consequences.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 88:5555–5563. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cudmore MJ, Ahmad S, Sissaoui S, et al:
Loss of Akt activity increases circulating soluble endoglin release
in preeclampsia: identification of inter-dependency between Akt-1
and heme oxygenase 1. Eur Heart J. 33:1150–1158. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|