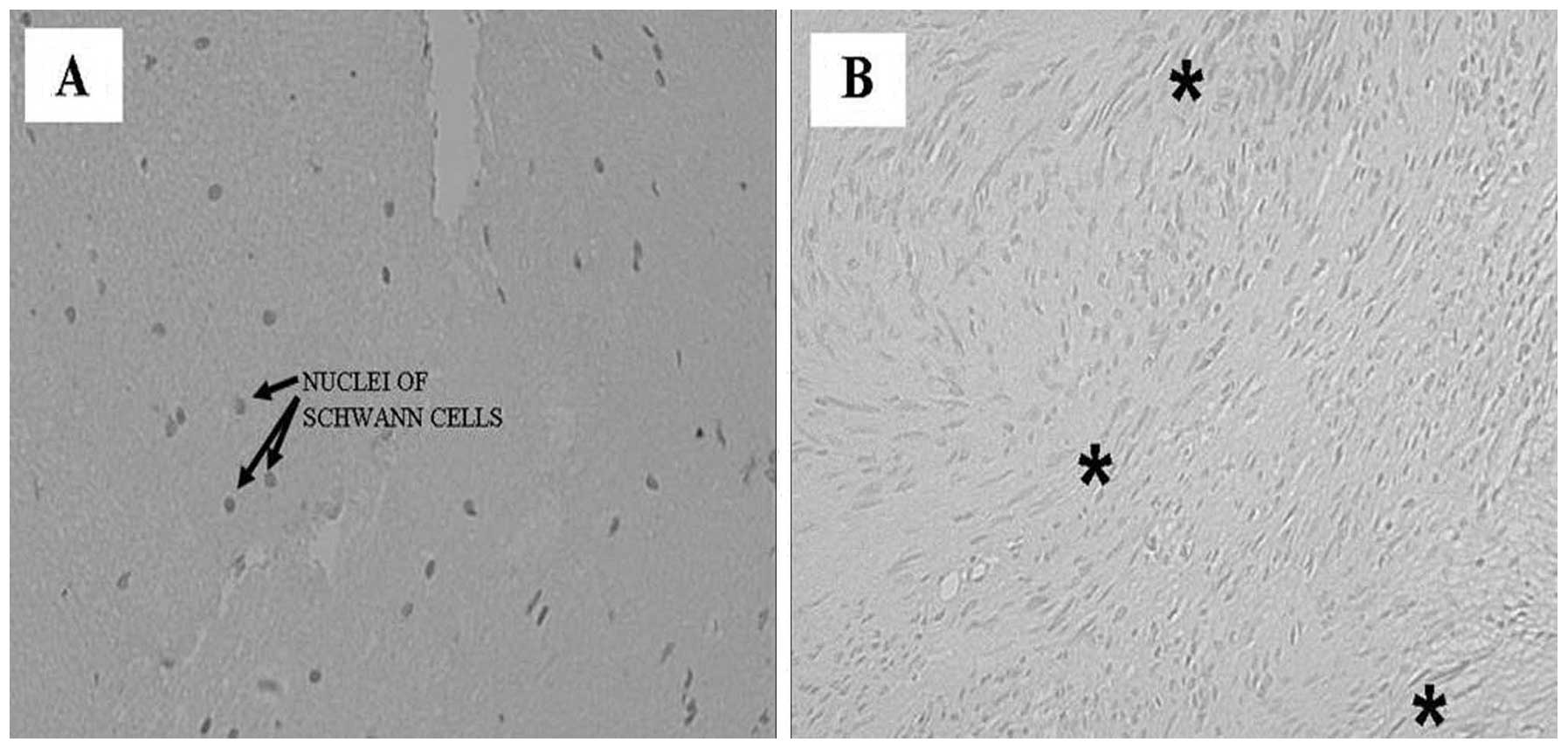
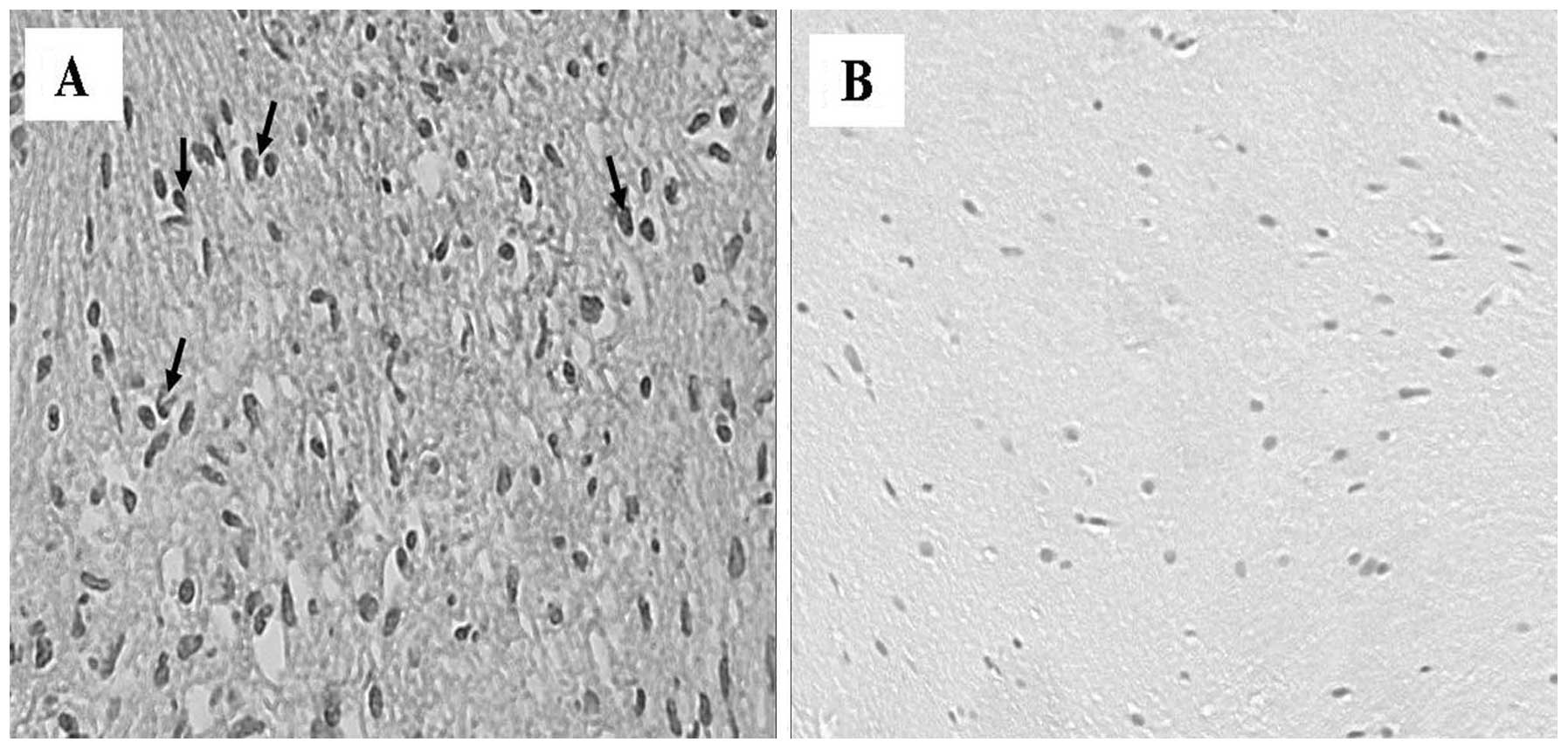
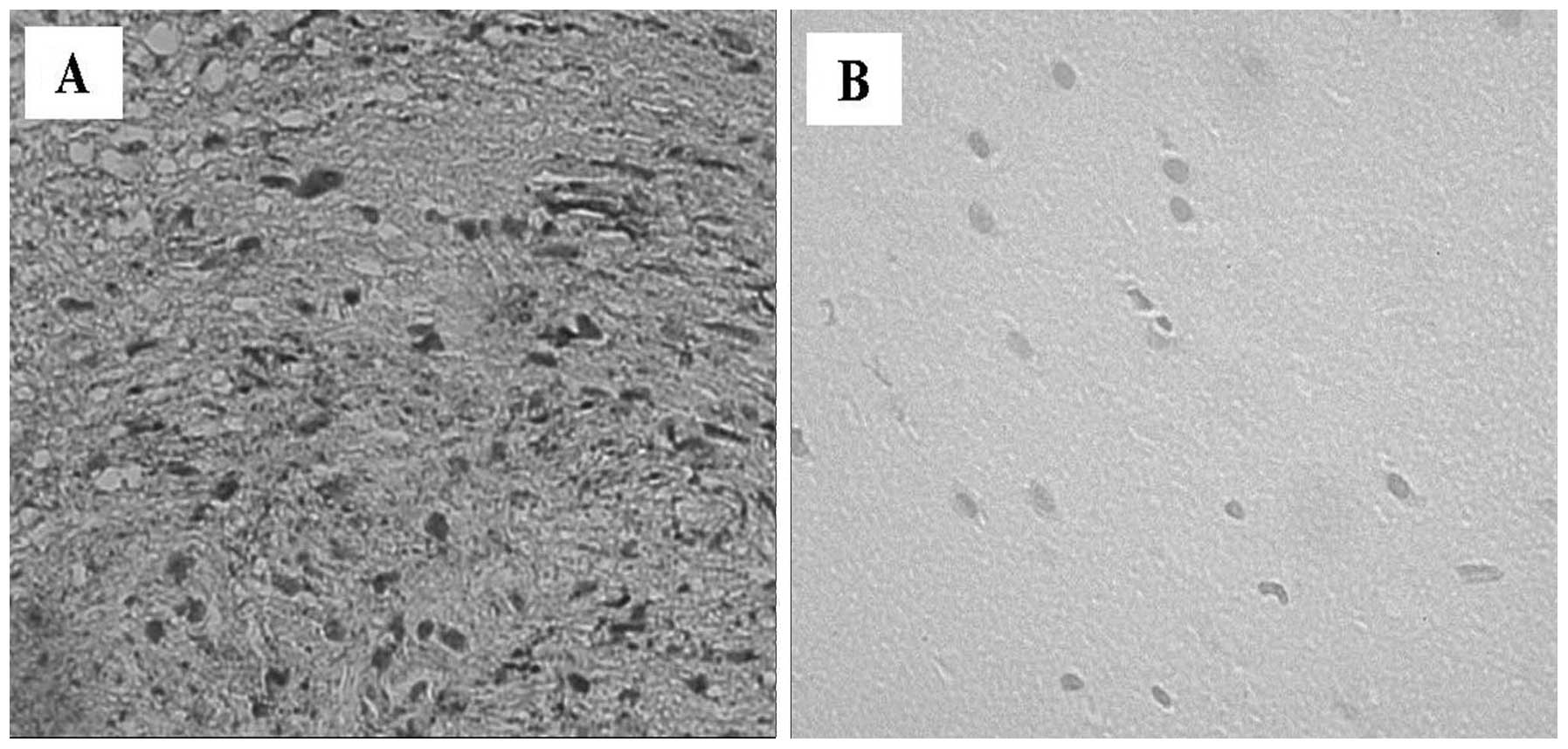
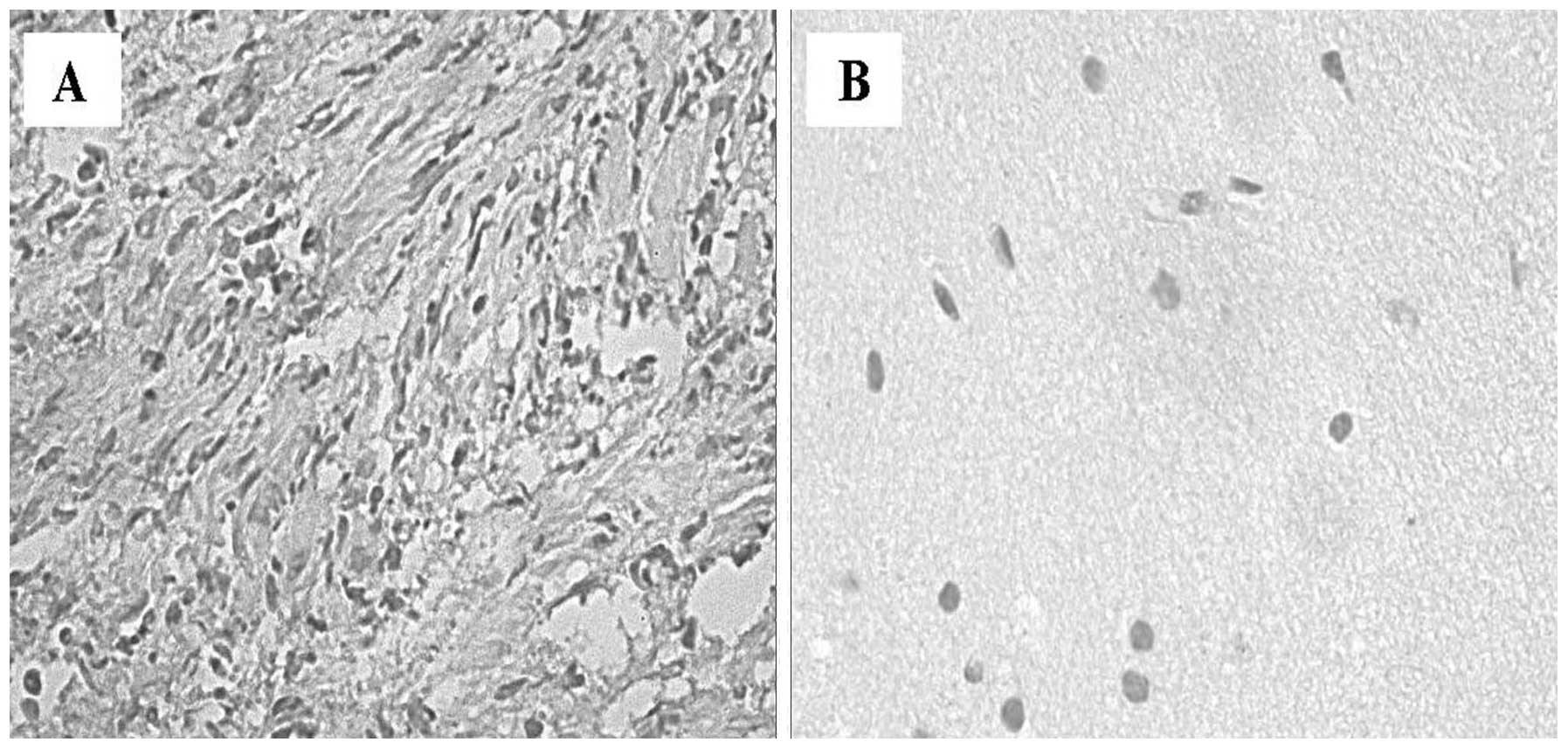
|
1
|
McDonald R: Acoustic neuroma: what the
evidence says about evaluation and treatment. J Fam Pract.
60:E1–E4. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Celis-Aguilar E, Lassalletta L, Torres
Martin M, Rodrigues FY, Nistal M, Castresana JS, et al: The
molecular biology of vestibular schwannomas and its association
with hearing loss: a review. Genet Res Int.
2012:8561572012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bondi S, Limardo P, Toma S and Bussi M:
Non-vestibular head and neck schwannomas: a 10-year experience. Eur
Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 270:2365–2369. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van Leeuwen JP, Cremers CW, Thewissen NP,
Harhangi BS and Meijer E: Acoustic neuroma: correlation among tumor
size, symptoms, and patient age. Laryngoscope. 105:701–707. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carroll SL: Molecular mechanisms promoting
the pathogenesis of Schwann cell neoplasms. Acta Neuropathol.
123:321–348. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Klenke C, Widera D, Sepehrnia A, Moffat
DA, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B, Ebmeyer J and Sudhoff H: Clinical
and biological behaviour of vestibular schwannomas: signalling
cascades involved in vestibular Schwannoma resemble molecular and
cellular mechanisms of injury-induced Schwann cell
dedifferentiation. Head Neck Oncol. 16:202013.
|
|
7
|
Mirsky R, Parmantier E, McMahon AP and
Jessen KR: Schwann cell-derived desert Hedgehog signals nerve
sheath formation. Ann NY Acad Sci. 883:196–202. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen ZL and Strickland S: Laminin gamma1
is critical for Schwann cell differentiation, axon myelination, and
regeneration in the peripheral nerve. J Cell Biol. 163:889–899.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Weerda H, Gamberger TI, Siegner A, Gjuric
M and Tamm ER: Effects of transforming growth factor-β1 and basic
fibroblast growth factor on proliferation of cell cultures derived
from human vestibular nerve schwannoma. Acta Otolaryngol.
118:337–343. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Diensthuber M, Brandis A, Lenarz T and
Stover T: Co-expression of transforming growth factor-β1 and glial
cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in vestibular schwannoma.
Otol Neurotol. 25:359–365. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Löttrich M, Mawrin C, Chamaon K, Kirches
E, Dietzmann K and Freigang B: Expression of transforming growth
factor-beta receptor type 1 and type 2 in human sporadic vestibular
Schwannoma. Pathol Res Pract. 203:245–249. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wagner R and Myers RR: Schwann cells
produce tumor necrosis factor alpha: expression in injured and
non-injured nerves. Neuroscience. 73:625–629. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Tang X, Yu B, Gu Y, Yuan Y, Yao D,
Ding F and Gu X: Gene network revealed involvements of Birc2, Birc3
and Tnfrsf1a in anti-apoptosis of injured peripheral nerves. PloS
One. 7:e434362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee HK, Seo IA, Suh DJ, Hong JI, Yoo YH
and Park HT: Interleukin-6 is required for the early induction of
glial fibrillary acidic protein in Schwann cells during Wallerian
degeneration. J Neurochem. 108:776–786. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bolin LM, Verity AN, Silver JE, Shooter EM
and Abrams JS: Interleukin-6 production by Schwann cells and
induction in sciatic nerve injury. J Neurochem. 64:850–858. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Constantin G, Piccio L, Bussini S, Pizzuti
A, Scarpini E, Baron P, Conti G, Pizzul S and Scarlato G: Induction
of adhesion molecules on human Schwann cells by proinflammatory
cytokines, an immunofluorescence study. J Neurol Sci. 170:124–130.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bevilacqua MP: Endothelial-leukocyte
adhesion molecules. Annu Rev Immunol. 11:767–804. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Møller MN, Werther K, Nalla A, Stangerup
SE, Thomsen J, Bøg-Hansen TC, Nielsen HJ and Cayé-Thomasen P:
Angiogenesis in vestibular schwannomas: expression of extracellular
matrix factors MMP-2, MMP-9 and TIMP-1. Laryngoscope. 120:657–662.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ferrara N, Gerber HP and LeCouter J: The
biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 9:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bancroft JD and Gamble M: Theory and
Practice of Histological Techniques. 6th. Churchill Livingstone;
Elsevier, London: 2008
|
|
21
|
Joshi R: Learning from eponyms: Jose
Verocay and Verocay bodies, Antoni A and B areas, Nils Antoni and
Schwannomas. Indian Dermatol Online J. 3:215–219. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Charabi S: Acoustic neuroma/vestibular
schwannoma in vivo and in vitro growth models. A clinical and
experimental study. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 530:1–27.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Namiecińska M, Marciniak K and Nowak JZ:
VEGF as an angiogenic neurotrophic, and neuroprotective factor.
Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 59:573–583. 2005.In Polish.
|
|
25
|
Kramer F, Stöver T, Wamecke A, Diensthuber
M, Lenarz T and Wissel K: BDNF mRNA expression is significantly
upregulated in vestibular schwannomas and correlates with
proliferative activity. J Neurooncol. 98:31–39. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Maehara Y, Kakeji Y, Kabashima A, Emi Y,
Watanabe A, Alkazawa K, Baba H, Kohnoe S and Sugimachi K: Role of
transforming growth factor-beta 1 in invasion and metastasis in
gastric carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 17:607–614. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ridley AJ, Davis JB, Stroobant P and Land
H: Transforming growth factors-beta 1 and beta 2 are mitogens for
rat Schwann cells. J Cell Biol. 109:3419–3424. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lemke GE and Brockes JP: Identification
and purification of glial growth factor. J Neurosci. 4:74–83.
1984.
|
|
29
|
Ratner N, Bunge RP and Glaser L: Schwann
cell proliferation in vitro. An overview. Ann NY Acad Sci.
486:170–181. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Candido J and Hagemann T: Cancer-related
inflammation. J Clin Immunol. 33:S79–S84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sethi G, Sung B and Aggaewal BB: TNF: a
master switch for inflammation to cancer. Front Biosci.
13:5094–5107. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lisak RP and Bealmear B: Upregulation of
intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) on rat Schwann cells in
vitro: comparison of interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha
and interleukin-1. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2:233–243. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mithen F, Colburn S and Birchem R: Human
alpha tumor necrosis factor does not damage cultures containing rat
Schwann cells and sensory neurons. Neurosci Res. 9:59–63. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chandross KJ, Spray DC, Cohen RI, Kumar
NM, Kremer M, Dermietzel R and Kessler JA: TNF-alpha inhibits
Schwann cell proliferation, connexin46 expression and gap
junctional communication. Mol Cell Neurosci. 7:479–500. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Uren AG and Vaux DL: Molecular and
clinical aspects of apoptosis. Pharmacol Ther. 72:37–50. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nagano K, Alles N, Mian AH, et al: The
tumor necrosis factor type 2 receptor plays a protective role in
tumor necrosis factor-α-induced bone resorption lacunae on mouse
calvariae. J Bone Miner Metab. 29:671–681. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tracey D, Klareskog L, Sasso EH, Salfeld
JG and Tak PP: Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanism of
action: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther. 117:244–279. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Baker SJ and Reddy EP: Transducers of life
and death: TNF receptor superfamily and associated proteins.
Oncogene. 12:1–9. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Beg AA and Baltimore D: An essential role
for NF-kappaB in preventing TNF-alpha-induced cell death. Science.
274:782–784. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C
and Mantovani A: Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark
of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis.
30:1073–1081. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhong J, Dietzel ID, Wahle P, Kopf M and
Heumann R: Sensory impairments and delayed regeneration of sensory
axons in interleukin-6-deficient mice. J Neurosci. 19:4305–4313.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee HK, Wang L, Shin YK, Lee KY, Suh DJ
and Park HT: Interleukin-6 induces proinflammatory signaling in
Schwann cells: a high-throughput analysis. Biochem Biophy Res
Commun. 382:410–414. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Haura EB, Turkson J and Jove R: Mechanisms
of disease: insights into the emerging role of signal transducers
and activators of transcription in cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol.
2:315–324. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Klampfer L: Cytokines, inflammation and
colon cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 11:451–464. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Artico M, Cervoni L, Celli P, Salvati M
and Palma L: Supratentorial glioblastoma in children a series of 27
surgically treated cases. Childs Nerv Syst. 9:7–9. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gobbi G, Mirandola P, Micheloni C, et al:
Expression of HLA class I antigen and proteasome subunits LMP-2 and
LMP-10 in primary vs. metastatic breast carcinoma lesions. Int J
Oncol. 25:1625–1629. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cayé-Thomasen P, Werther K, Nalla A, et
al: VEGF and VEGF receptor-1 concentration in vestibular schwannoma
homogenates correlates to tumor growth rate. Otol Neurotol.
26:98–101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Brieger J, Bedavanija A, Lehr HA, Maurer J
and Mann WJ: Expression of angiogenic growth factors in acoustic
neurinoma. Acta Otolaryngol. 123:1040–1045. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Koutsimpelas D, Bjelopavlovic M, Yetis R,
et al: The VEGF/VEGFR axis in sporadic vestibular schwannoma
correlates with irradiation and disease recurrence. ORL J
Otorinilaryngol Relat Spec. 74:330–338. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, et al: Inhibition
of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis
suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature. 362:841–844. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|