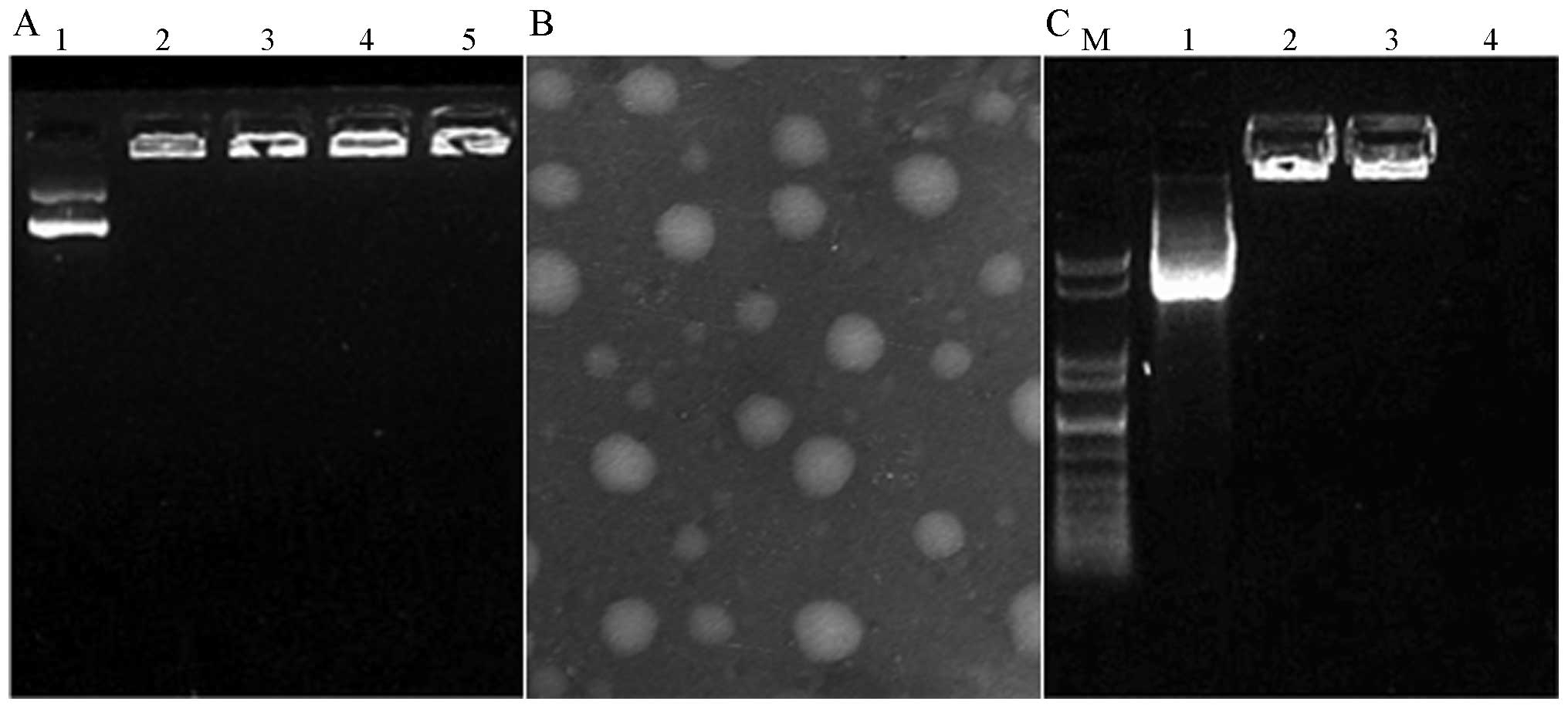
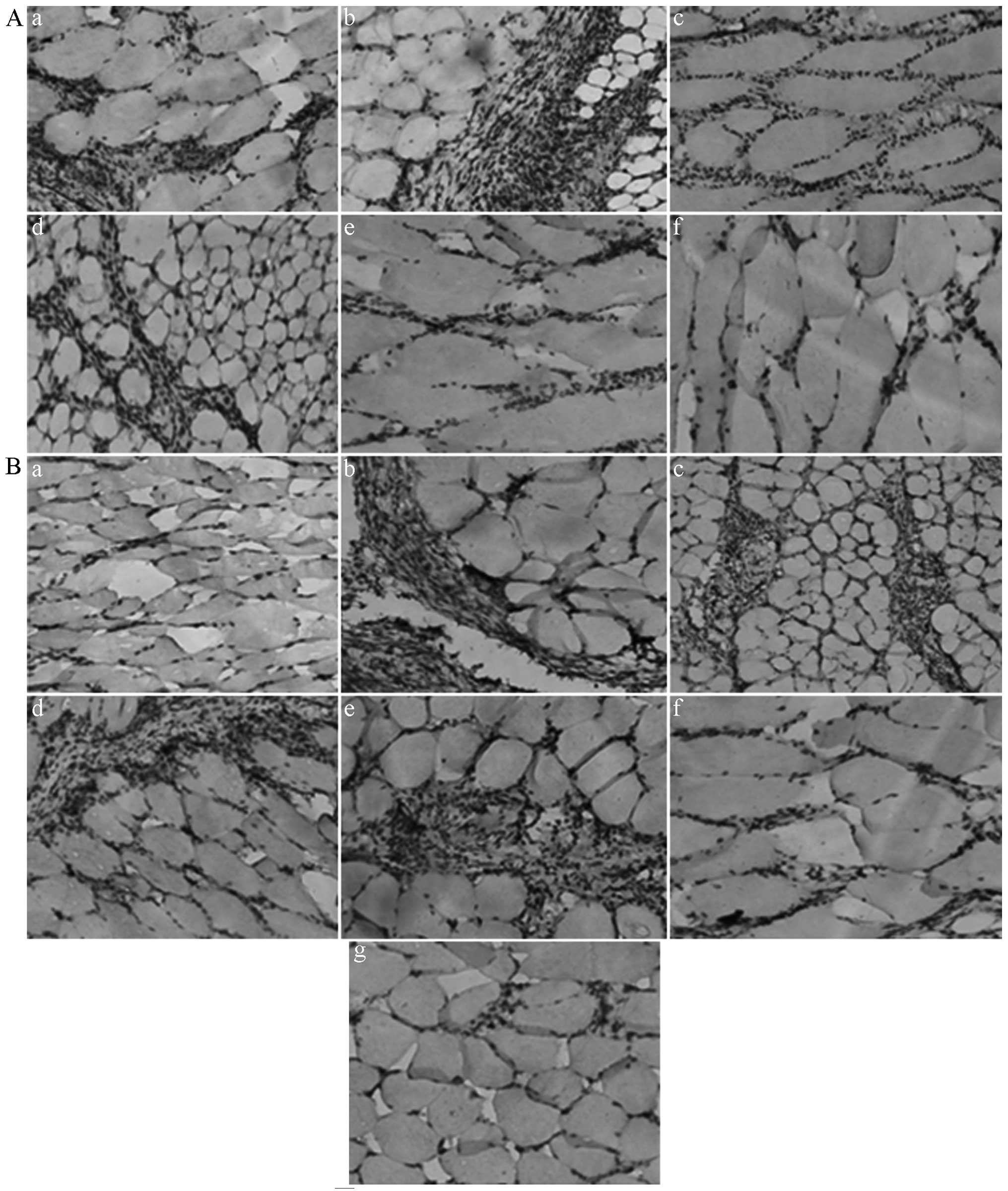
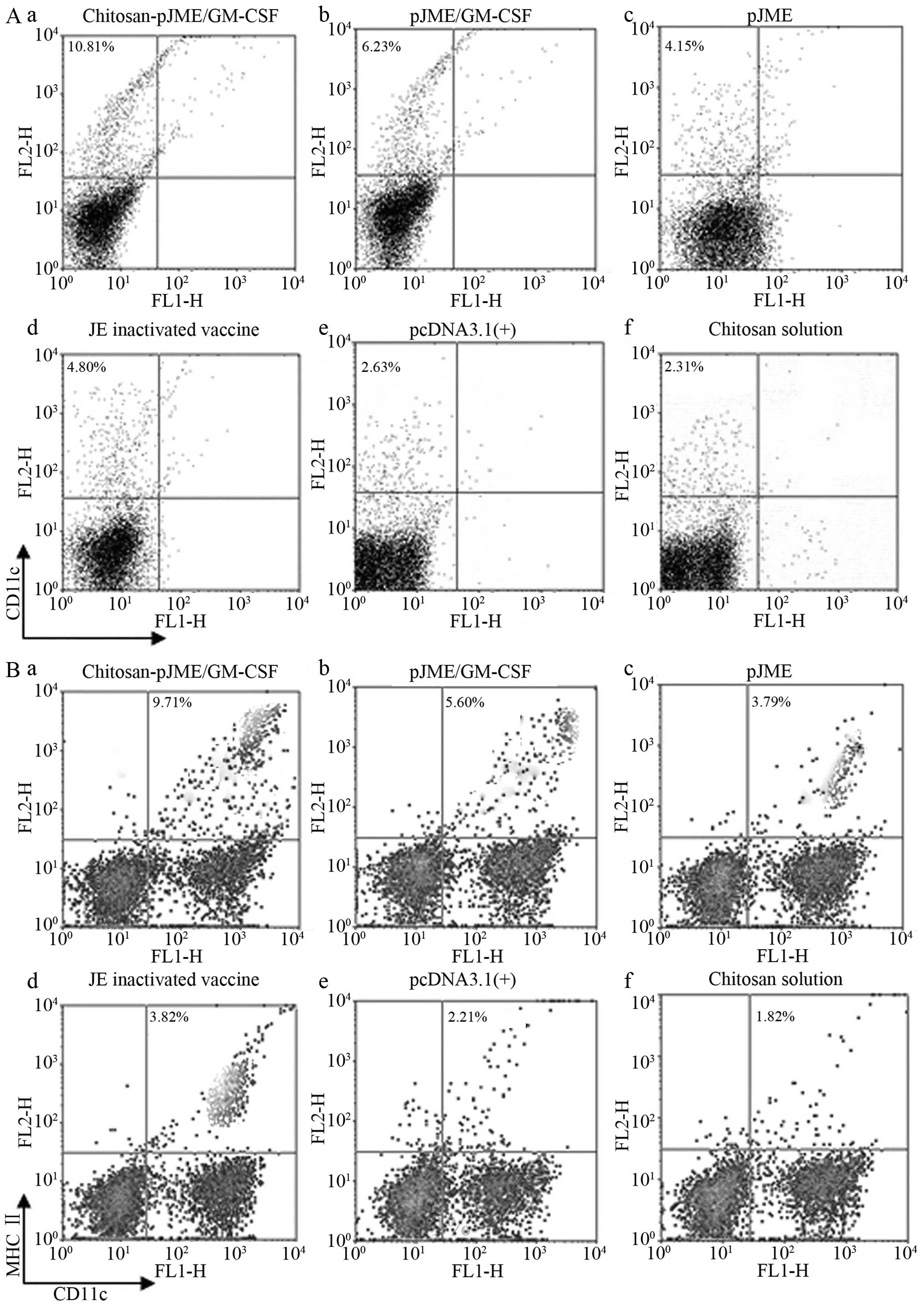
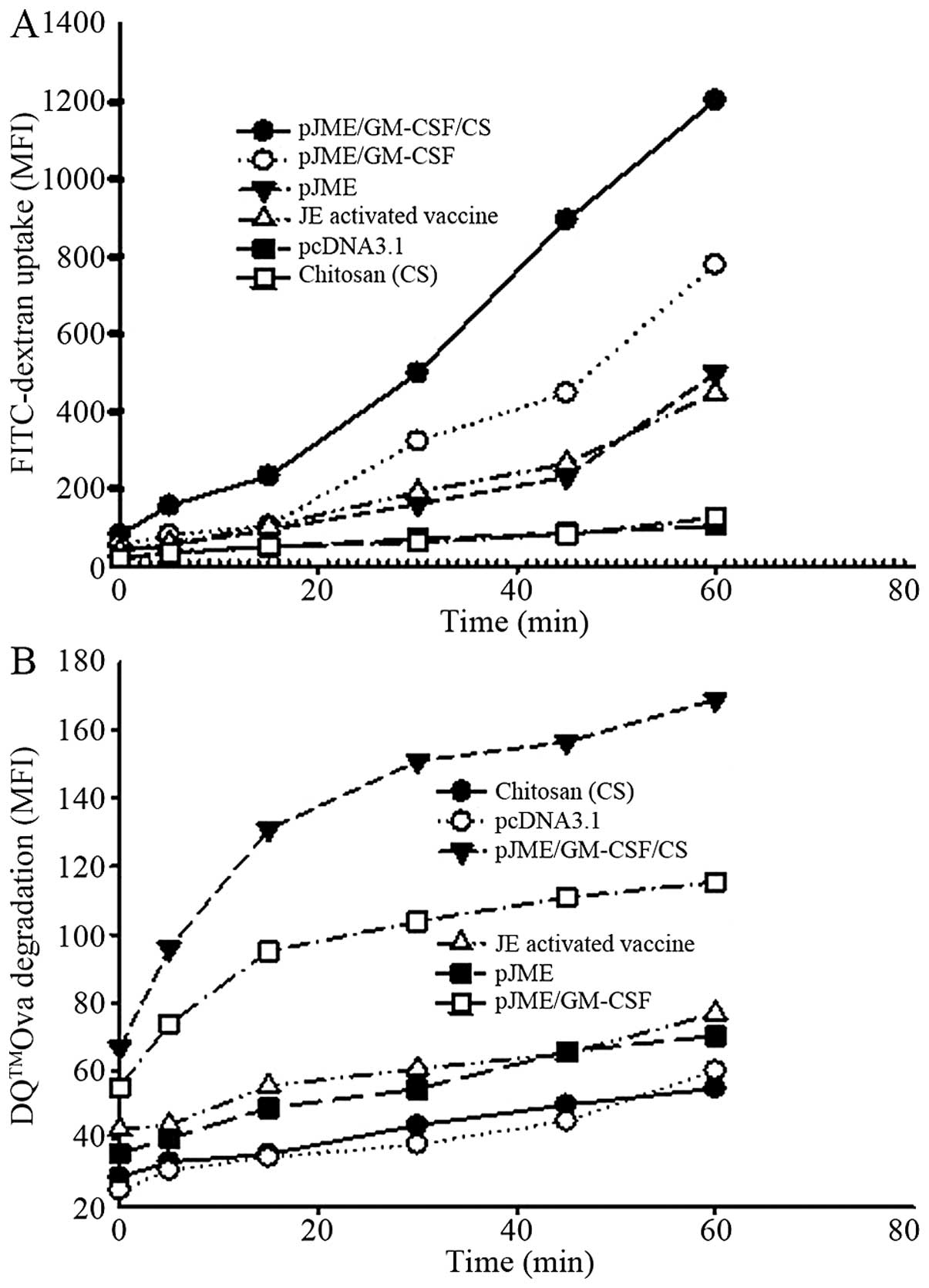
|
1
|
Yamamoto A, Nakayama M, Kurosawa Y, et al:
Development of a particle agglutination assay system for detecting
Japanese encephalitis virus-specific human IgM, using
hydroxyapatite-coated nylon beads. J Virol Methods. 104:195–201.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Solomon T and Vaughn DW: Pathogenesis and
clinical features of Japanese encephalitis and West Nile virus
infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 267:171–194.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hoke CH, Nisalak A, Sangawhipa N, et al:
Protection against Japanese encephalitis by inactivated vaccines. N
Engl J Med. 319:608–614. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ueba N, Kimura T, Nakajima S, Kurimura T
and Kitaura T: Field experiments on live attenuated Japanese
encephalitis virus vaccine for swine. Biken J. 21:95–103.
1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xin YY, Ming ZG, Peng GY, Jian A and Min
LH: Safety of a live-attenuated Japanese encephalitis virus vaccine
(SA14-14-2) for children. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 39:214–217.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Plesner AM and Ronne T: Allergic
mucocutaneous reactions to Japanese encephalitis vaccine. Vaccine.
15:1239–1243. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Andersen MM and Rønne T: Side-effects with
Japanese encephalitis vaccine. Lancet. 337:10441991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ruff TA, Eisen D, Fuller A and Kass R:
Adverse reactions to Japanese encephalitis vaccine. Lancet.
338:881–882. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sakaguchi M, Yoshida M, Kuroda W, Harayama
O, Matsunaga Y and Inouye S: Systemic immediate-type reactions to
gelatin included in Japanese encephalitis vaccines. Vaccine.
15:121–122. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu MA: DNA vaccines: a review. J
InternMed. 253:402–410. 2003.
|
|
11
|
Putnak R, Porter K and Schmaljohn C: DNA
vaccines for flavi-viruses. Adv Virus Res. 61:445–468. 2003.
|
|
12
|
Konishi E, Yamaoka M, Khin-Sane-Win,
Kurane I, Takada K and Mason PW: The anamnestic neutralizing
antibody response is critical for protection of mice from challenge
following vaccination with a plasmid encoding the Japanese
encephalitis virus premembrane and envelope genes. J Virol.
73:5527–5534. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Konishi E, Ajiro N, Nukuzuma C, Mason PW
and Kurane I: Comparison of protective efficacies of plasmid DNAs
encoding Japanese encephalitis virus proteins that induce
neutralizing antibody or cytotoxic T lymphocytes in mice. Vaccine.
21:3675–3683. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu CJ, Li TL, Huang HW, Tao MH and Chan
YL: Development of an effective Japanese encephalitis
virus-specific DNA vaccine. Microbes Infect. 8:2578–2586. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kaur R, Sachdeva G and Vrati S: Plasmid
DNA immunization against Japanese encephalitis virus:
immunogenicity of membrane-anchored and secretory envelope protein.
J Infect Dis. 185:1–12. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bharati K, Appaiahgari MB and Vrati S:
Effect of cytokine-encoding plasmid delivery on immune response to
Japanese encephalitis virus DNA vaccine in mice. Microbiol Immunol.
49:349–353. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kutzler MA and Weiner DB: Developing DNA
vaccines that call to dendritic cells. J Clin Invest.
114:1241–1244. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Daro E, Pulendran B, Brasel K, et al:
Polyethylene glycol-modified GM-CSF expands CD11b(high)CD11c(high)
but not CD11b(low) CD11c(high) murine dendritic cells in vivo: a
comparative analysis with Flt3 ligand. J Immunol. 165:49–58. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Daro E, Butz E, Smith J, Teepe M,
Maliszewski CR and McKenna HJ: Comparison of the functional
properties of murine dendritic cells generated in vivo with Flt3
ligand, GM-CSF and Flt3 ligand plus GM-SCF. Cytokine. 17:119–130.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hanada K, Tsunoda R and Hamada H:
GM-CSF-induced in vivo expansion of splenic dendritic cells and
their strong costimulation activity. J Leukoc Biol. 60:181–190.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mach N, Gillessen S, Wilson SB, Sheehan C,
Mihm M and Dranoff G: Differences in dendritic cells stimulated in
vivo by tumors engineered to secrete granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor or Flt3-ligand. Cancer Res. 60:3239–3246.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dranoff G, Jaffee E, Lazenby A, et al:
Vaccination with irradiated tumor cells engineered to secrete
murine granu-locyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulates
potent, specific, and long-lasting anti-tumor immunity. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 90:3539–3543. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chiodoni C, Paglia P, Stoppacciaro A,
Rodolfo M, Parenza M and Colombo MP: Dendritic cells infiltrating
tumors cotransduced with granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating
factor (GM-CSF) and CD40 ligand genes take up and present
endogenous tumor-associated antigens, and prime naive mice for a
cytotoxic T lymphocyte response. J Exp Med. 190:125–133. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zaharoff DA, Rogers CJ, Hance KW, Schlom J
and Greiner JW: Chitosan solution enhances the immunoadjuvant
properties of GM-CSF. Vaccine. 25:8673–8686. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pouton CW and Seymour LW: Key issues in
non-viral gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 46:187–203. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Crystal RG: The gene as the drug. Nat Med.
1:15–17. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Garnett MC: Gene-delivery systems using
cationic polymers. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 16:147–207.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Read RC, Naylor SC, Potter CW, et al:
Effective nasal influenza vaccine delivery using chitosan. Vaccine.
23:4367–4374. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vila A, Sánchez A, Janes K, Behrens I,
Kissel T, Vila Jato JL and Alonso MJ: Low molecular weight chitosan
nanoparticles as new carriers for nasal vaccine delivery in mice.
Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 57:123–131. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Van der Lubben IM, Kersten G, Fretz MM,
Beuvery C, Coos Verhoef J and Junginger HE: Chitosan microparticles
for mucosal vaccination against diphtheria: oral and nasal efficacy
studies in mice. Vaccine. 21:1400–1408. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mao HQ, Roy K, Troung-Le VL, et al:
Chitosan-DNA nanopar-ticles as gene carriers: synthesis,
characterization and transfection efficiency. J Control Release.
70:399–421. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Haddad D, Ramprakash J, Sedegah M, et al:
Plasmid vaccine expressing granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor attracts infiltrates including immature
dendritic cells into injected muscles. J Immunol. 165:3772–3781.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhai YZ, Zhou Y, Ma L and Feng GH: The
dominant roles of ICAM-1-encoding gene in DNA vaccination against
Japanese encephalitis virus are the activation of dendritic cells
and enhancement of cellular immunity. Cell Immunol. 281:1–10. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhai YZ, Li XM, Zhou Y and Feng GH:
Intramuscular immunization with a plasmid DNA vaccine encoding
prM-E protein from Japanese encephalitis virus: Enhanced
immunogenicity by co-administration of GM-CSF gene and genetic
fusions of prM-E protein and GM-CSF. Intervirology. 52:152–163.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gordon S, Teichmann E, Young K, Finnie K,
Rades T and Hook S: In vitro and in vivo investigation of
thermosensitive chitosan hydrogels containing silica nanoparticles
for vaccine delivery. Eur J Pharm Sci. 41:360–368. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McKay PF, Barouch DH, Santra S, et al:
Recruitment of different subsets of antigen-presenting cells
selectively modulates DNA vaccine-elicited CD4+ and CD8+T
lymphocyte responses. Eur J Immunol. 34:1011–1020. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Oka Y, Akbar SM, Horiike N, Joko K and
Onji M: Mechanism and therapeutic potential of DNA-based
immunization against the envelope proteins of hepatitis B virus in
normal and transgenic mice. Immunology. 103:90–97. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cella M, Sallusto F and Lanzavecchia A:
Origin, maturation and antigen presenting function of dendritic
cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 9:10–16. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Banchereau J and Steinman RM: Dendritic
cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 392:245–252. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mellman I, Turley SJ and Steinman RM:
Antigen processing for amateurs and professionals. Trends Cell
Biol. 8:231–237. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Steinman RM: Dendritic cells and the
control of immunity: enhancing the efficiency of antigen
presentation. Mt Sinai J Med. 68:160–166. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Seferian PG and Martinez ML: Imune
stimulating activity of two new chitosan containing adjuvant
formulations. Vaccine. 19:661–668. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|