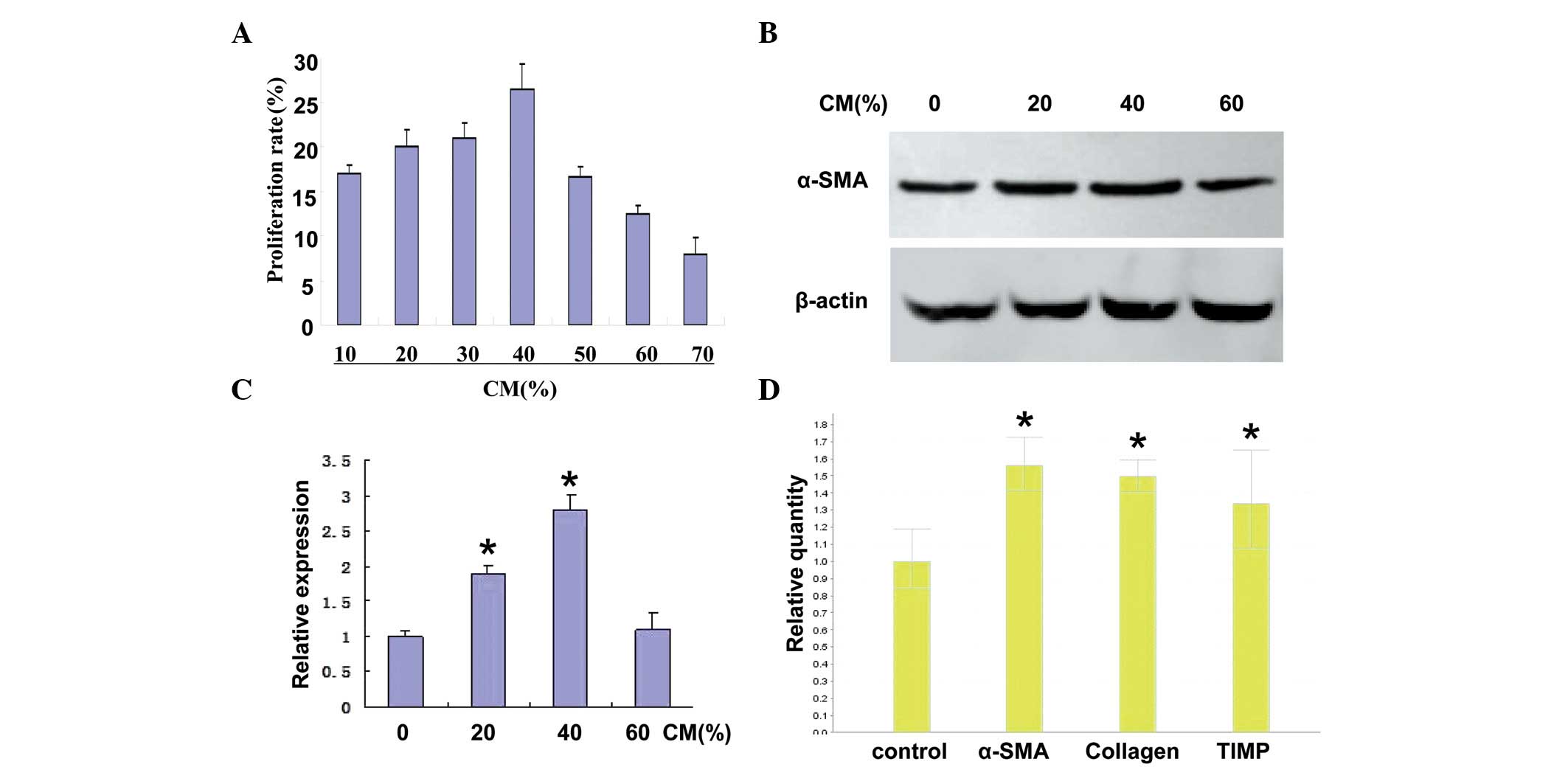
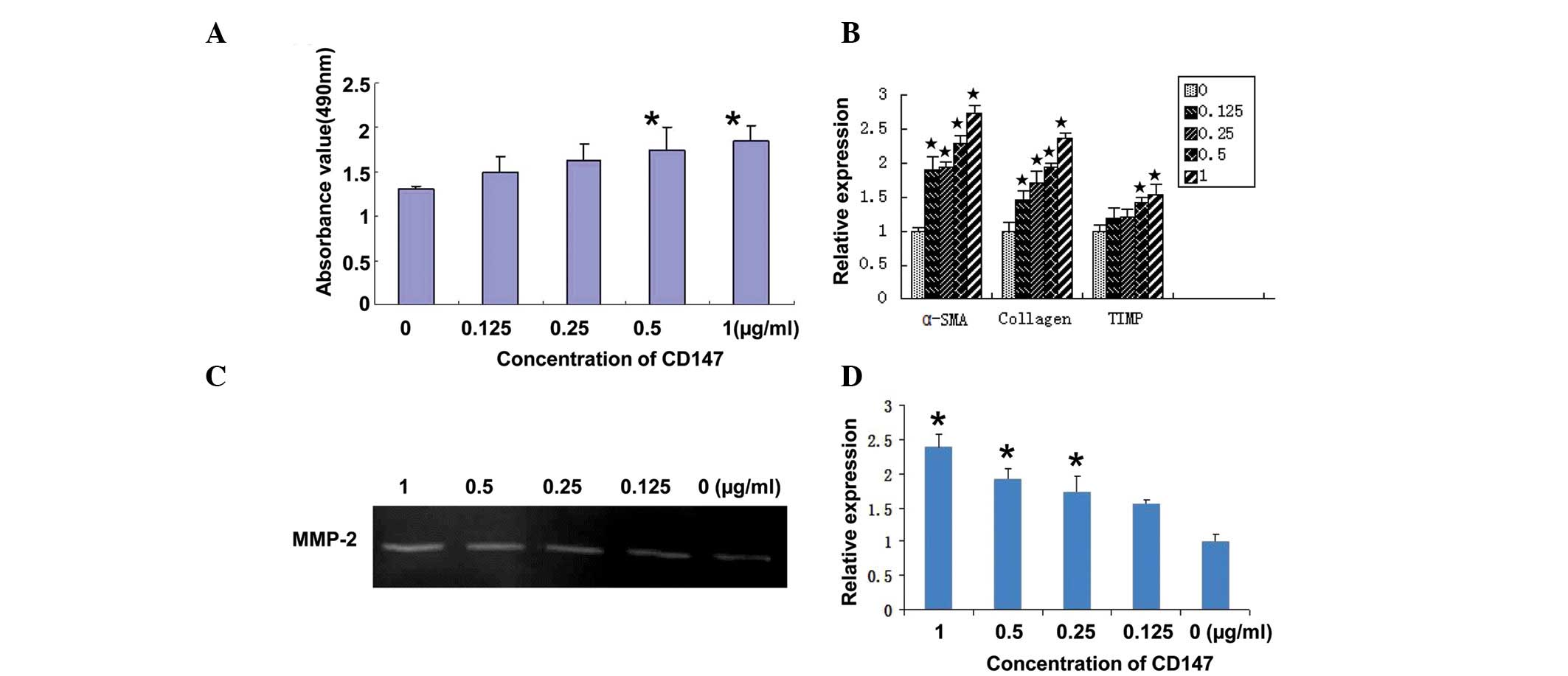
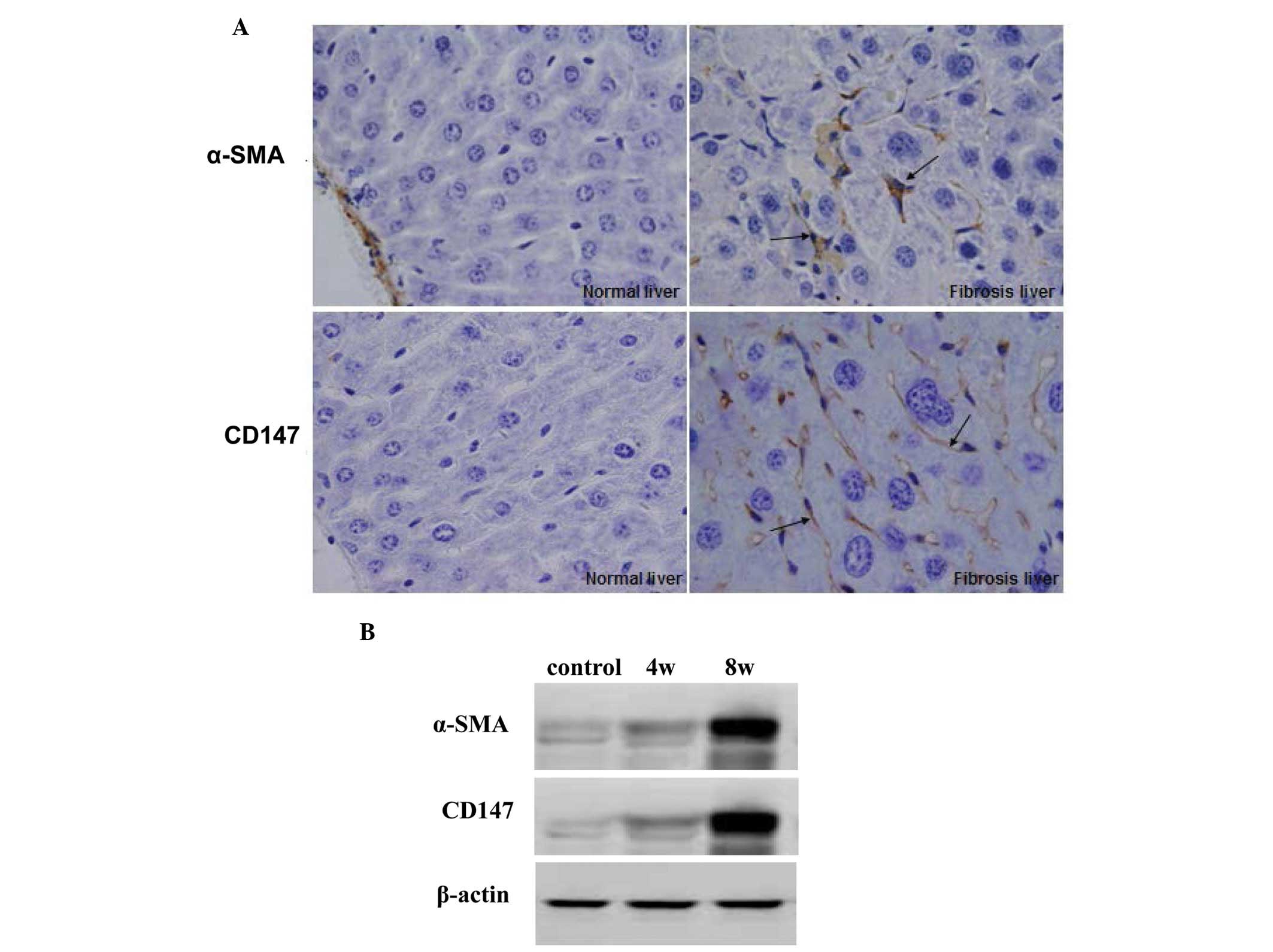
|
1
|
Mikula M, Proell V, Fischer AM and
Mikulits W: Activated hepatic stellate cells induce tumor
progression of neoplastic hepatocytes in a TGF-beta dependent
fashion. J Cell Physiol. 209:560–567. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Liver fibrosis.
J Clin Invest. 115:209–218. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Friedman SL: Mechanisms of hepatic
fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 134:1655–1669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guyot C, Lepreux S, Combe C, et al:
Hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis: The (myo)fibroblastic cell
subpopulations involved. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:135–151.
2006.
|
|
5
|
Friedman SL: Hepatic stellate cells:
Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol
Rev. 88:125–172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Novo E, di Bonzo LV, Cannito S, et al:
Hepatic myofibroblasts: a heterogeneous population of
multifunctional cells in liver fibrogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 41:2089–2093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Coulouarn C, Corlu A, Glaise D, et al:
Hepatocyte-stellate cell cross-talk in the liver engenders a
permissive inflammatory microenvironment that drives progression in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 72:2533–2542. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang BB, Cheng JY, Gao HH, et al: Hepatic
stellate cells in inflammation-fibrosis-carcinoma axis. Anat Rec
(Hoboken). 293:1492–1496. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhao W, Zhang L, Yin Z, et al: Activated
hepatic stellate cells promote hepatocellular carcinoma development
in immunocompetent mice. Int J Cancer. 129:2651–2661. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Amann T, Bataille F, Spruss T, et al:
Activated hepatic stellate cells promote tumorigenicity of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 100:646–653. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jung JO, Gwak GY, Lim YS, et al: Role of
hepatic stellate cells in the angiogenesis of hepatoma. Korean J
Gastroenterol. 42:142–148. 2003.In Korean. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xia Y, Chen R, Song Z, et al: Gene
expression profiles during activation of cultured rat hepatic
stellate cells by tumoral hepatocytes and fetal bovine serum. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:309–321. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sancho-Bru P, Juez E, Moreno M, et al:
Hepatocarcinoma cells stimulate the growth, migration and
expression of pro-angiogenic genes in human hepatic stellate cells.
Liver Int. 30:31–41. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Xia YH, Song ZJ, Chen RX, et al: Analysis
of differential gene expression in rat hepatic stellate cells
activated by culture or hepatocellular carcinoma cell induction.
Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 31:164–169. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nagoshi S: Liver diseases. Nihon Rinsho.
72:726–729. 2014.In Japanese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tahashi Y, Matsuzaki K, Date M, et al:
Differential regulation of TGF-beta signal in hepatic stellate
cells between acute and chronic liver injury. Hepatology. 35:49–61.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang J, Zohar R and McCulloch CA: Multiple
roles of alpha-smooth muscle actin in mechanotransduction. Exp Cell
Res. 312:205–214. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ooi LL, Bay BH, Ng RT, et al: An animal
model for the study of hepatic stellate cell and hepatocellular
carcinoma interaction. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 28:95–98.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kurogi M, Nakashima O, Miyaaki H, et al:
Clinicopathological study of scirrhous hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:1470–1477. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao W, Zhang L, Xu Y, et al: Hepatic
stellate cells promote tumor progression by enhancement of
immunosuppressive cells in an orthotopic liver tumor mouse model.
Lab Invest. 94:182–191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Han S, Han L, Yao Y, et al: Activated
hepatic stellate cells promote hepatocellular carcinoma cell
migration and invasion via the activation of FAK-MMP9 signaling.
Oncol Rep. 31:641–648. 2014.
|
|
22
|
Nevzorova YA, Hu W, Cubero FJ, et al:
Overexpression of c-myc in hepatocytes promotes activation of
hepatic stellate cells and facilitates the onset of liver fibrosis.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832:1765–1775. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang DW, Zhao YX, Wei D, et al: H
Ab18G/CD147 promotes activation of hepatic stellate cells and is a
target for antibody therapy of liver fibrosis. J Hepatol.
57:1283–1291. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Muramatsu T and Miyauchi T: Basigin
(CD147): a multifunctional transmembrane protein involved in
reproduction, neural function, inflammation and tumor invasion.
Histol Histopathol. 18:981–987. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weidle UH, Scheuer W, Eggle D, et al:
Cancer-related issues of CD147. Cancer Genomics Proteomics.
7:157–169. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hao JL, Cozzi PJ, Khatri A, et al: C
D147/EMMPRIN and CD44 are potential therapeutic targets for
metastatic prostate cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 10:287–306.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu S, Li Y, Zhang Y, et al: Expression
and clinical implications of H Ab18G/CD147 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 45:97–106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Faouzi S, Lepreux S, Bedin C, et al:
Activation of cultured rat hepatic stellate cells by tumoral
hepatocytes. Lab Invest. 79:485–493. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|