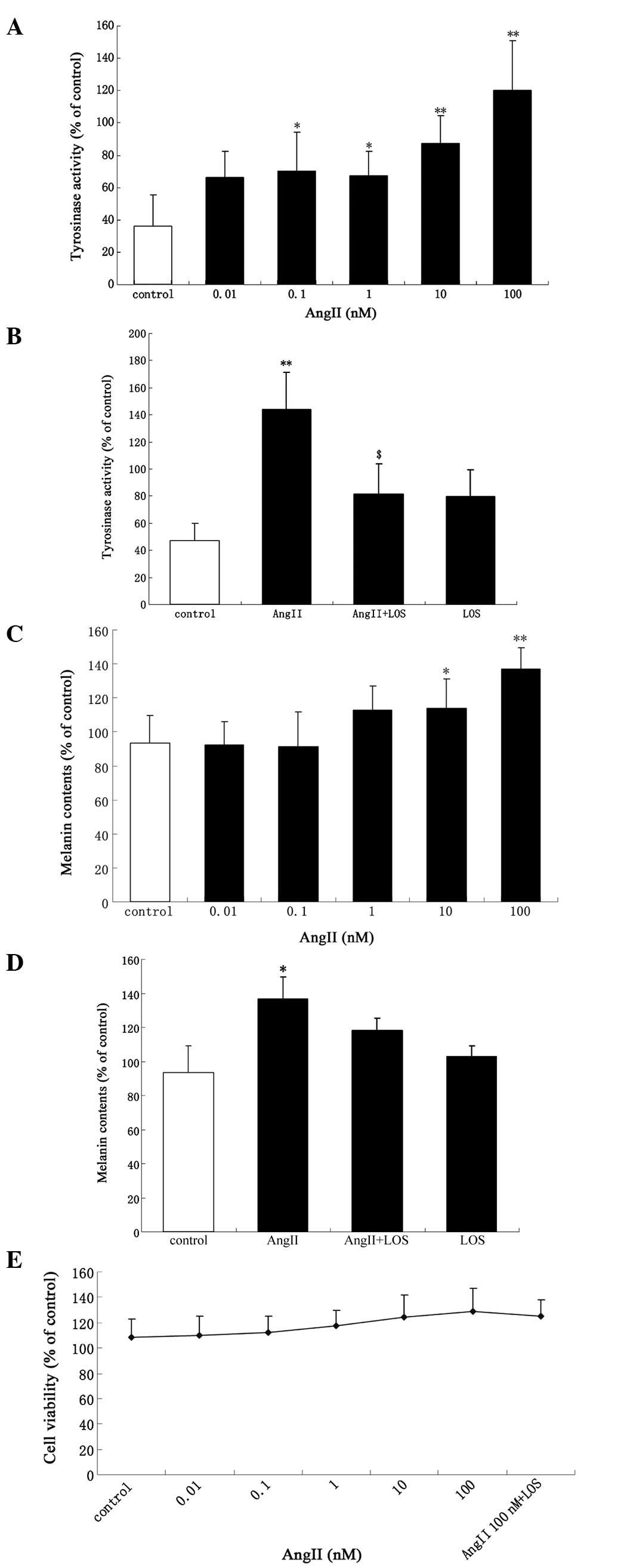
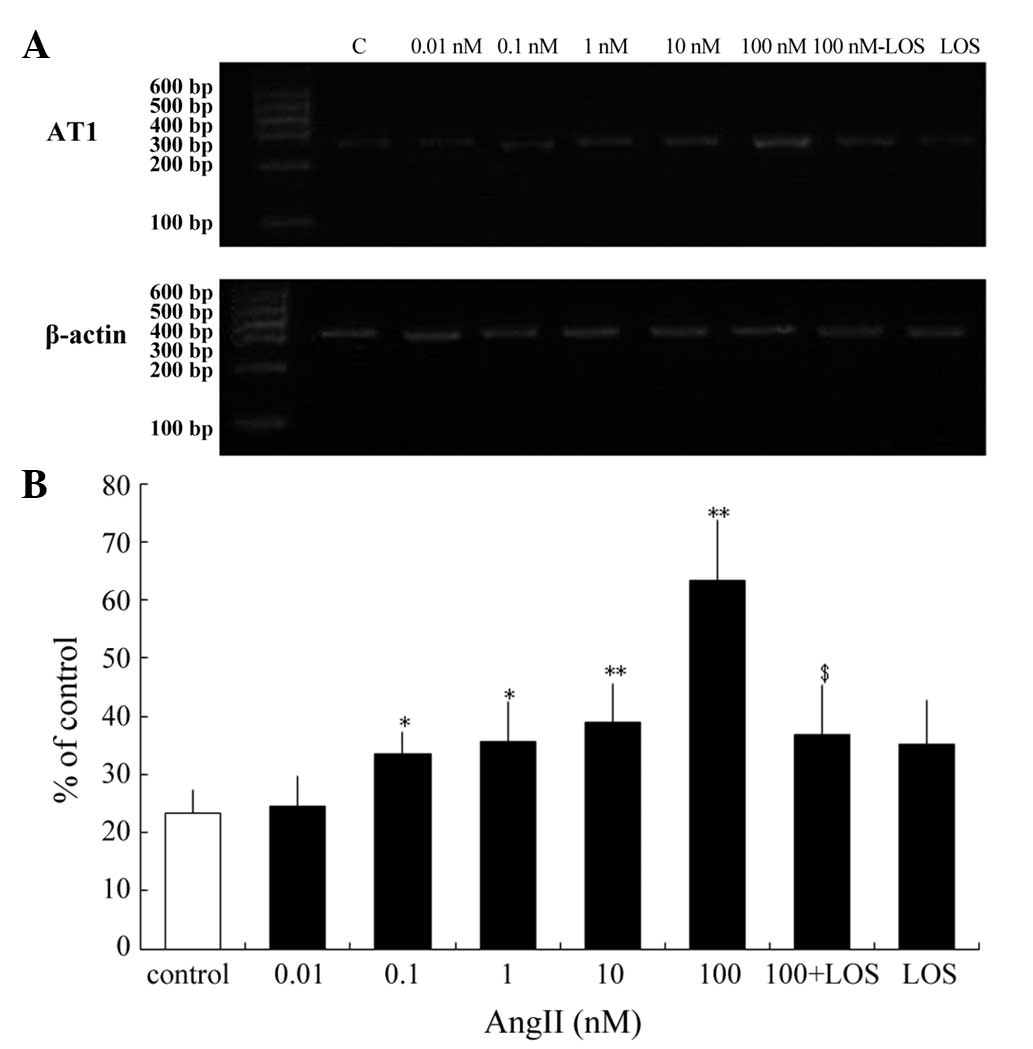
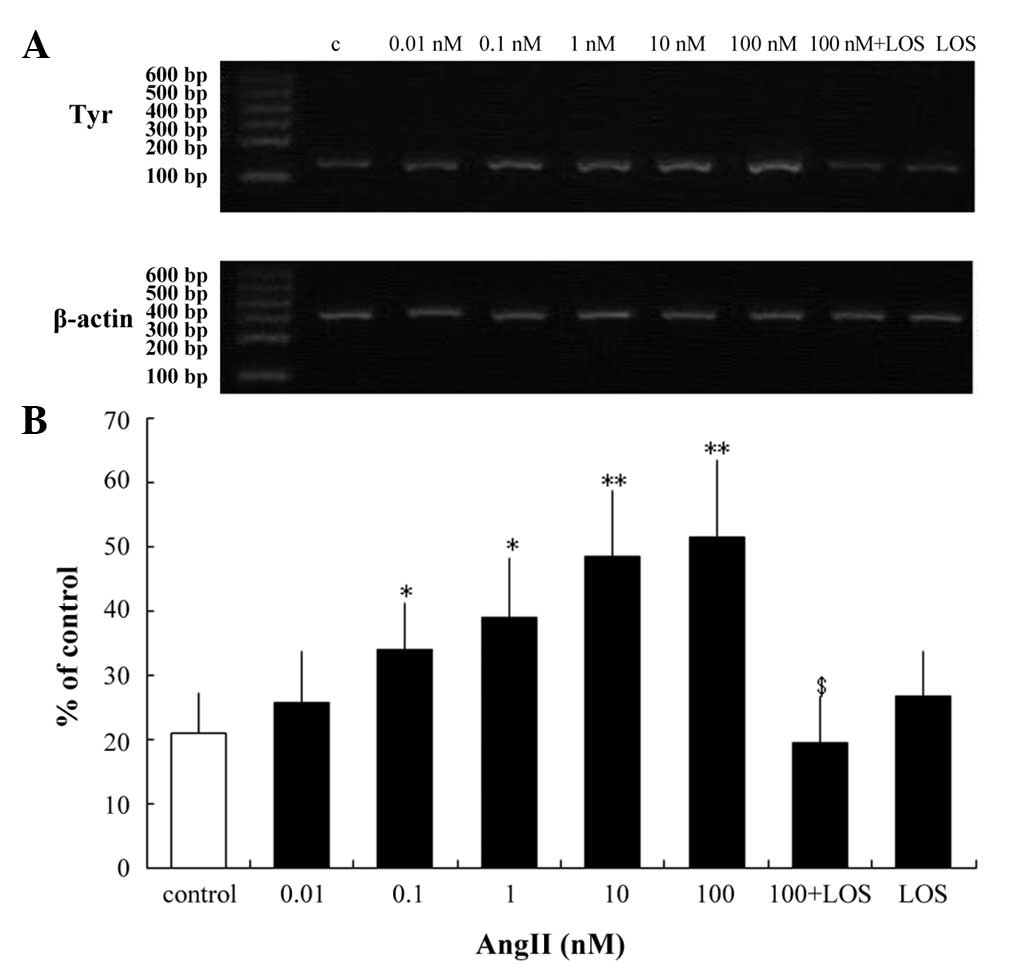
|
1
|
Wisely JA, Hoyle E, Tarrier N and Edwards
J: Where to start? Attempting to meet the psychological needs of
burned patients. Burns. 33:736–746. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zeitlin RE: Long-term psychosocial
sequelae of paediatric burns. Burns. 23:467–472. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Singer AJ and Clark RA: Cutaneous wound
healing. N Engl J Med. 341:738–746. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rodgers K, Xiong S, Felix J, Roda N,
Espinoza T, Maldonado S and Dizerega G: Development of angiotensin
(1–7) as an agent to accelerate dermal repair. Wound Repair Regen.
9:238–247. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim JA, Berliner JA and Nadler JL:
Angiotensin II increases monocyte binding to endothelial cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 226:862–868. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reddy HK, Sigusch H, Zhou G, Tyagi SC,
Janicki JS and Weber KT: Coronary vascular hyperpermeability and
angiotensin II. J Lab Clin Med. 126:307–315. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Steckelings UM, Artuc M, Paul M, Stoll M
and Henz BM: Angiotensin II stimulates proliferation of primary
human keratinocytes via a non-AT1, non-AT2 angiotensin receptor.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 229:329–333. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takeda H, Katagata Y, Hozumi Y and Kondo
S: Effects of angiotensin II receptor signaling during skin wound
healing. Am J Pathol. 165:1653–1662. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rodgers K, Abiko M, Girgis W, St Amand K,
Campeau J and diZerega G: Acceleration of dermal tissue repair by
angiotensin II. Wound Repair Regen. 5:175–183. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Steckelings UM, Wollschläger T, Peters J,
Henz BM, Hermes B and Artuc M: Human skin: source of and target
organ for angiotensin II. Exp Dermatol. 13:148–154. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nozawa Y, Matsuura N, Miyake H, Yamada S
and Kimura R: Effects of TH-142177 on angiotensin II-induced
proliferation, migration and intracellular signaling in vascular
smooth muscle cells and on neointimal thickening after balloon
injury. Life Sci. 64:2061–2070. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Steckelings UM, Henz BM, Wiehstutz S,
Unger T and Artuc M: Differential expression of angiotensin
receptors in human cutaneous wound healing. Br J Dermatol.
153:887–893. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Otake AH, Mattar AL, Freitas HC, et al:
Inhibition of angiotensin II receptor 1 limits tumor-associated
angiogenesis and attenuates growth of murine melanoma. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 66:79–87. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lei TC, Virador VM, Vieira WD and Hearing
VJ: A melanocyte-keratinocyte coculture model to assess regulators
of pigmentation in vitro. Anal Biochem. 305:260–268. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Virador VM, Kobayashi N, Matsunaga J and
Hearing VJ: A standardized protocol for assessing regulators of
pigmentation. Anal Biochem. 270:207–219. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marin-Castaño ME, Elliot SJ, Potier M, et
al: Regulation of estrogen receptors and MMP-2 expression by
estrogens in human retinal pigment epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 44:50–59. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Peng Y, Kang Q, Cheng H, et al:
Transcriptional characterization of bone morphogenetic proteins
(BMPs)-mediated osteogenic signaling. J Cell Biochem. 90:1149–1165.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright
JW and Unger T: International union of pharmacology. XXIII The
angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 52:415–472.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Striker GE, Praddaude F, Alcazar O,
Cousins SW and Marin-Castaño ME: Regulation of angiotensin II
receptors and extracellular matrix turnover in human retinal
pigment epithelium: roleof angiotensin II. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 295:C1633–C1646. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Olivares C and Solano F: New insights into
the active site structure and catalytic mechanism of tyrosinase and
its related proteins. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 22:750–760. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yahata Y, Shirakata Y, Tokumaru S, et al:
A novel function of angiotensin II in skin wound healing. Induction
of fibroblast and keratinocyte migration by angiotensin II via
heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like growth
factor-mediated EGF receptor transactivation. J Biol Chem.
281:13209–13216. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang W, Yu LF, Zhong J, et al:
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression in human gastric cancer
and induces MMP2 and MMP9 expression in MKN-28 cells. Dig Dis Sci.
53:163–168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sarlos S, Rizkalla B, Moravski CJ, Cao Z,
Cooper ME and Wilkinson-Berka JL: Retinal angiogenesis is mediated
by an interaction between the angiotensin type 2 receptor, VEGF and
angiopoietin. Am J Pathol. 163:879–887. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wolf G: Angiotensin II and tubular
development. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 17(Suppl 9): 48–51. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kaschina E and Unger T: Angiotensin
AT1/AT2 receptors: regulation, signalling and function. Blood
Press. 12:70–88. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iozumi K, Hoganson GE, Pennella R, Everett
MA and Fuller BB: Role of tyrosinase as the determinant of
pigmentation in cultured human melanocytes. J Invest Dermatol.
100:806–811. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yamaguchi Y and Hearing VJ: Physiological
factors that regulate skin pigmentation. Biofactors. 35:193–199.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|