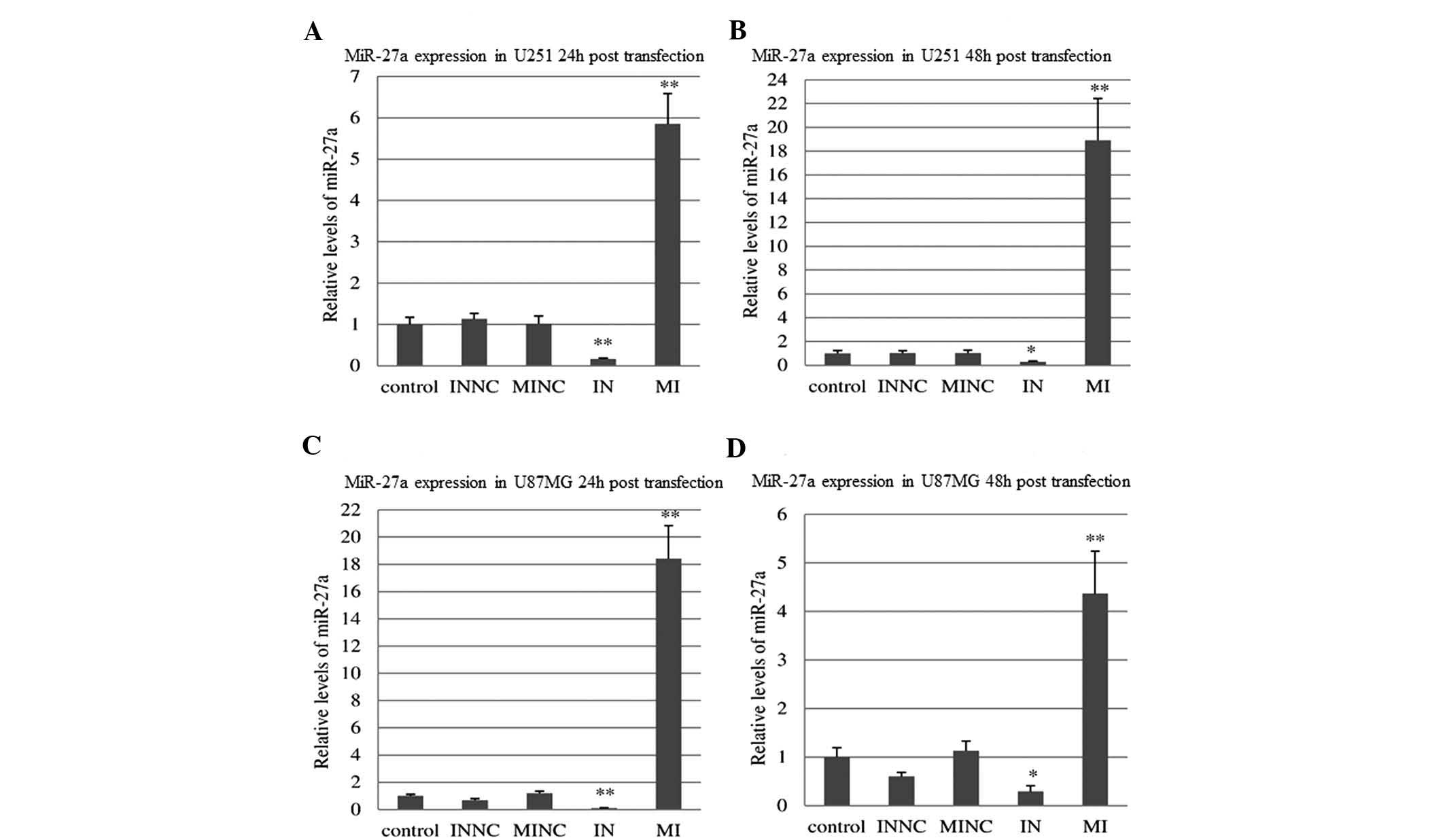
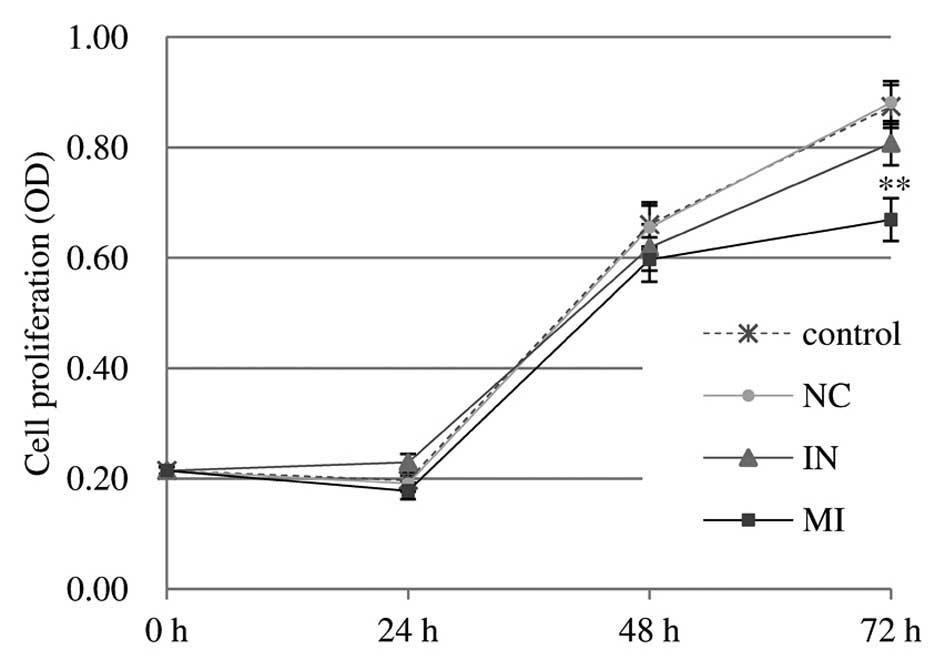
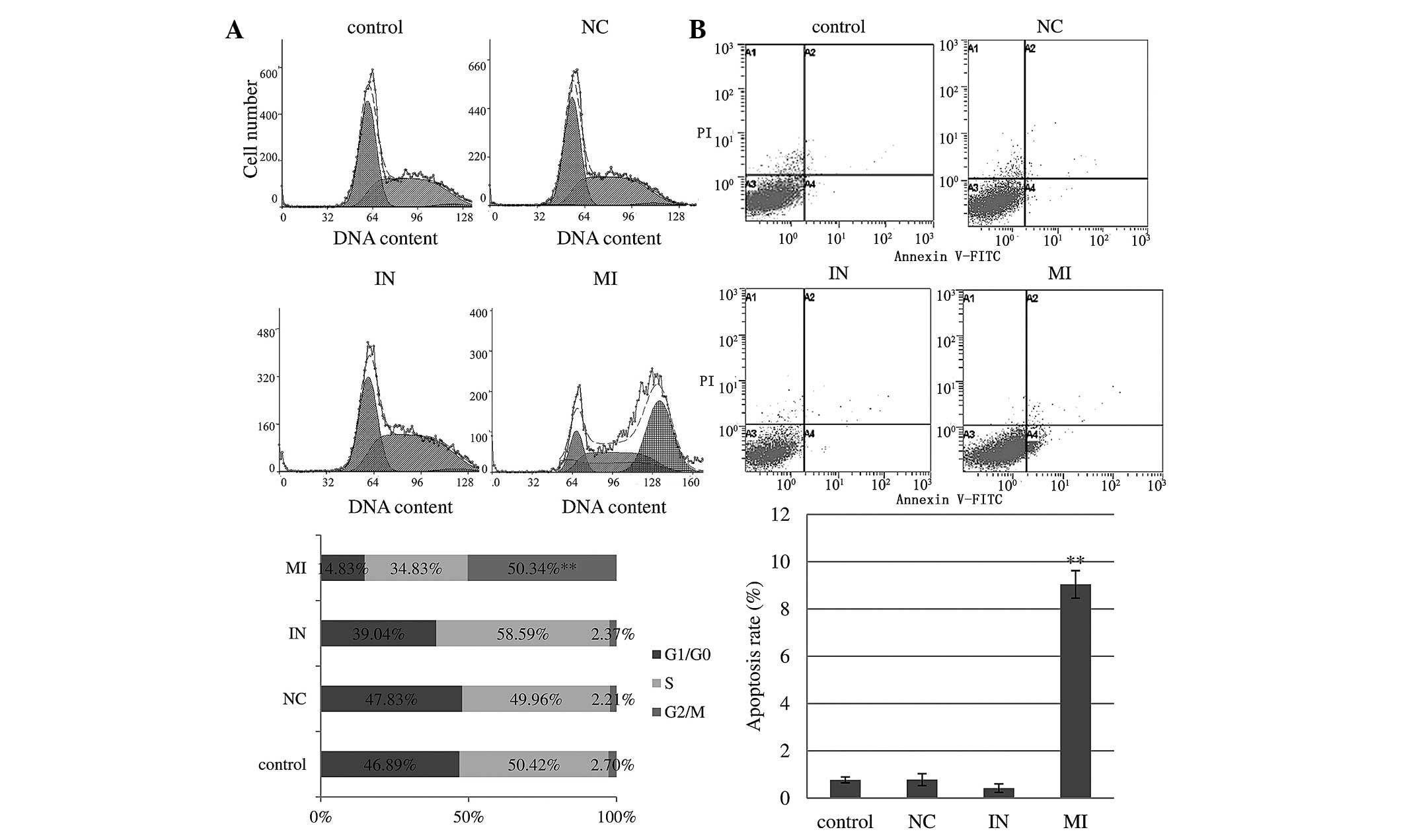
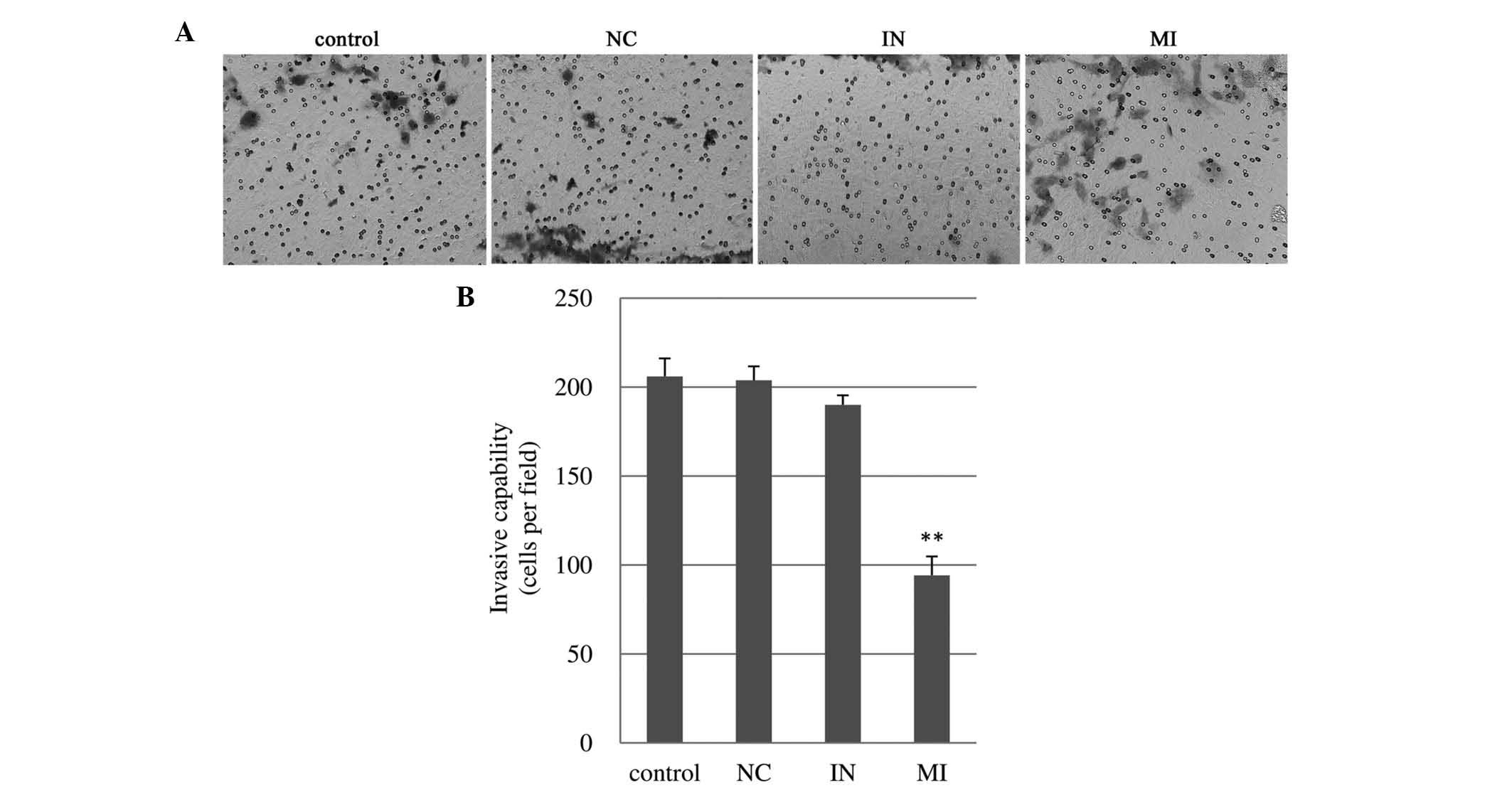
|
1
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gabayan AJ, Green SB, Sanan A, et al:
GliaSite brachytherapy for treatment of recurrent malignant
gliomas: a retrospective multi-institutional analysis.
Neurosurgery. 58:701–709. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cho WC: OncomiRs: the discovery and
progress of microRNAs in cancers. Mol Cancer. 6:602007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Anderson E, Grant R, Lewis SC and Whittle
IR: Randomized Phase III controlled trials of therapy in malignant
glioma: where are we after 40 years? Br J Neurosurg. 22:339–349.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Auffinger B, Thaci B, Ahmed A, et al:
MicroRNA targeting as a therapeutic strategy against glioma. Curr
Mol Med. 13:535–542. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chhabra R, Adlakha YK, Hariharan M, Scaria
V and Saini N: Upregulation of miR-23a-27a-24-2 cluster induces
caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis in human embryonic
kidney cells. PLoS One. 4:e58482009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chhabra R, Dubey R and Saini N:
Cooperative and individualistic functions of the microRNAs in the
miR-23a~27a~24-2 cluster and its implication in human diseases. Mol
Cancer. 9:2322010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Feng DD, Zhang H, Zhang P, et al:
Down-regulated miR-331-5p and miR-27a are associated with
chemotherapy resistance and relapse in leukaemia. J Cell Mol Med.
15:2164–2175. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ballabio E, Armesto M, Breeze CE, et al:
Bortezomib action in multiple myeloma: microRNA-mediated synergy
(and miR-27a/CDK5 driven sensitivity)? Blood Cancer J. 2:e832012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chow TF, Youssef YM, Lianidou E, et al:
Differential expression profiling of microRNAs and their potential
involvement in renal cell carcinoma pathogenesis. Clin Biochem.
43:150–158. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Guttilla IK and White BA: Coordinate
regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96 and miR-182 in breast cancer
cells. J Biol Chem. 284:23204–23216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang S, He X, Ding J, et al: Upregulation
of miR-23a approximately 27a approximately 24 decreases
transforming growth factor-beta-induced tumor-suppressive
activities in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer.
123:972–978. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Prueitt RL, Yi M, Hudson RS, et al:
Expression of microRNAs and protein-coding genes associated with
perineural invasion in prostate cancer. Prostate. 68:1152–1164.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saumet A, Vetter G, Bouttier M, et al:
Transcriptional repression of microRNA genes by PML-RARA increases
expression of key cancer proteins in acute promyelocytic leukemia.
Blood. 113:412–421. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xi Y, Shalgi R, Fodstad O, Pilpel Y and Ju
J: Differentially regulated micro-RNAs and actively translated
messenger RNA transcripts by tumor suppressor p53 in colon cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 12(7 Pt 1): 2014–2024. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang W, Cheng B, Miao L, Mei Y and Wu M:
Mutant p53-R273H gains new function in sustained activation of EGFR
signaling via suppressing miR-27a expression. Cell Death Dis.
4:e5742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Deighton RF, McGregor R, Kemp J, McCulloch
J and Whittle IR: Glioma pathophysiology: insights emerging from
proteomics. Brain Pathol. 20:691–703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chumbalkar VC, Subhashini C, Dhople VM, et
al: Differential protein expression in human gliomas and molecular
insights. Proteomics. 5:1167–1177. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hiratsuka M, Inoue T, Toda T, et al:
Proteomics-based identification of differentially expressed genes
in human gliomas: down-regulation of SIRT2 gene. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 309:558–566. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Iwadate Y, Sakaida T, Hiwasa T, et al:
Molecular classification and survival prediction in human gliomas
based on proteome analysis. Cancer Res. 64:2496–2501. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou JQ, Wang JT, Liu QH, Guo Xb, Zhou J
and Song LJ: Proteomic profiling and identification of malignant
grade related proteins in human brain astrocytoma. Chin J Neuromed.
11:780–783. 2012.
|
|
23
|
Mishra S, Murphy LC and Murphy LJ: The
Prohibitins: emerging roles in diverse functions. J Cell Mol Med.
10:353–363. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mishra S, Murphy LC, Nyomba BL and Murphy
LJ: Prohibitin: a potential target for new therapeutics. Trends Mol
Med. 11:192–197. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu T, Tang H, Lang Y, Liu M and Li X:
MicroRNA-27a functions as an oncogene in gastric adenocarcinoma by
targeting prohibitin. Cancer Lett. 273:233–242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mertens-Talcott SU, Chintharlapalli S, Li
X and Safe S: The oncogenic microRNA-27a targets genes that
regulate specificity protein transcription factors and the G2-M
checkpoint in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
67:11001–11011. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scott GK, Mattie MD, Berger CE, Benz SC
and Benz CC: Rapid alteration of microRNA levels by histone
deacetylase inhibition. Cancer Res. 66:1277–1281. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lerner M, Lundgren J, Akhoondi S, et al:
MiRNA-27a controls FBW7/hCDC4-dependent cyclin E degradation and
cell cycle progression. Cell Cycle. 10:2172–2183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Belair C, Darfeuille F and Staedel C:
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: possible role of microRNAs
in this intimate relationship. Clin Microbiol Infect. 15:806–812.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chintharlapalli S, Papineni S, Abdelrahim
M, et al: Oncogenic microRNA-27a is a target for anticancer agent
methyl 2-cyano-3,11-dioxo-18beta-olean-1,12-dien-30-oate in colon
cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 125:1965–1974. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, et al: A
microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer
gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schultz J, Lorenz P, Gross G, Ibrahim S
and Kunz M: MicroRNA let-7b targets important cell cycle molecules
in malignant melanoma cells and interferes with
anchorage-independent growth. Cell Res. 18:549–557. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kozaki K, Imoto I, Mogi S, Omura K and
Inazawa J: Exploration of tumor-suppressive microRNAs silenced by
DNA hypermethylation in oral cancer. Cancer Res. 68:2094–2105.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Scheibner KA, Teaboldt B, Hauer MC, et al:
MiR-27a functions as a tumor suppressor in acute leukemia by
regulating 14-3-3theta. PLoS One. 7:e508952012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhou TB and Qin YH: Signaling pathways of
prohibitin and its role in diseases. J Recept Signal Transduct Res.
33:28–36. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nijtmans LG, de Jong L, Artal Sanz M, et
al: Prohibitins act as a membrane-bound chaperone for the
stabilization of mitochondrial proteins. EMBO J. 19:2444–2451.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chowdhury I, Thompson WE, Welch C, Thomas
K and Matthews R: Prohibitin (PHB) inhibits apoptosis in rat
granulosa cells (GCs) through the extracellular signal-regulated
kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and the Bcl family of proteins. Apoptosis.
18:1513–1525. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kasashima K, Ohta E, Kagawa Y and Endo H:
Mitochondrial functions and estrogen receptor-dependent nuclear
translocation of pleiotropic human prohibitin 2. J Biol Chem.
281:36401–36410. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Merkwirth C, Dargazanli S, Tatsuta T, et
al: Prohibitins control cell proliferation and apoptosis by
regulating OPA1-dependent cristae morphogenesis in mitochondria.
Genes Dev. 22:476–488. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ross JA, Nagy ZS and Kirken RA: The PHB1/2
phosphocomplex is required for mitochondrial homeostasis and
survival of human T cells. J Biol Chem. 283:4699–4713. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Rajalingam K, Wunder C, Brinkmann V, et
al: Prohibitin is required for Ras-induced Raf-MEK-ERK activation
and epithelial cell migration. Nat Cell Biol. 7:837–843. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chiu CF, Ho MY, Peng JM, et al: Raf
activation by Ras and promotion of cellular metastasis require
phosphorylation of prohibitin in the raft domain of the plasma
membrane. Oncogene. 32:777–787. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Muraguchi T, Kawawa A and Kubota S:
Prohibitin protects against hypoxia-induced H9c2 cardiomyocyte cell
death. Biomed Res. 31:113–122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fusaro G, Wang S and Chellappan S:
Differential regulation of Rb family proteins and prohibitin during
camptothecin-induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 21:4539–4548. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Phillips AC and Vousden KH: E2F-1 induced
apoptosis. Apoptosis. 6:173–182. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fusaro G, Dasgupta P, Rastogi S, Joshi B
and Chellappan S: Prohibitin induces the transcriptional activity
of p53 and is exported from the nucleus upon apoptotic signaling. J
Biol Chem. 278:47853–47861. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Clark MJ, Homer N, O’Connor BD, et al:
U87MG decoded: the genomic sequence of a cytogenetically aberrant
human cancer cell line. PLoS Genet. 6:e10008322010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|