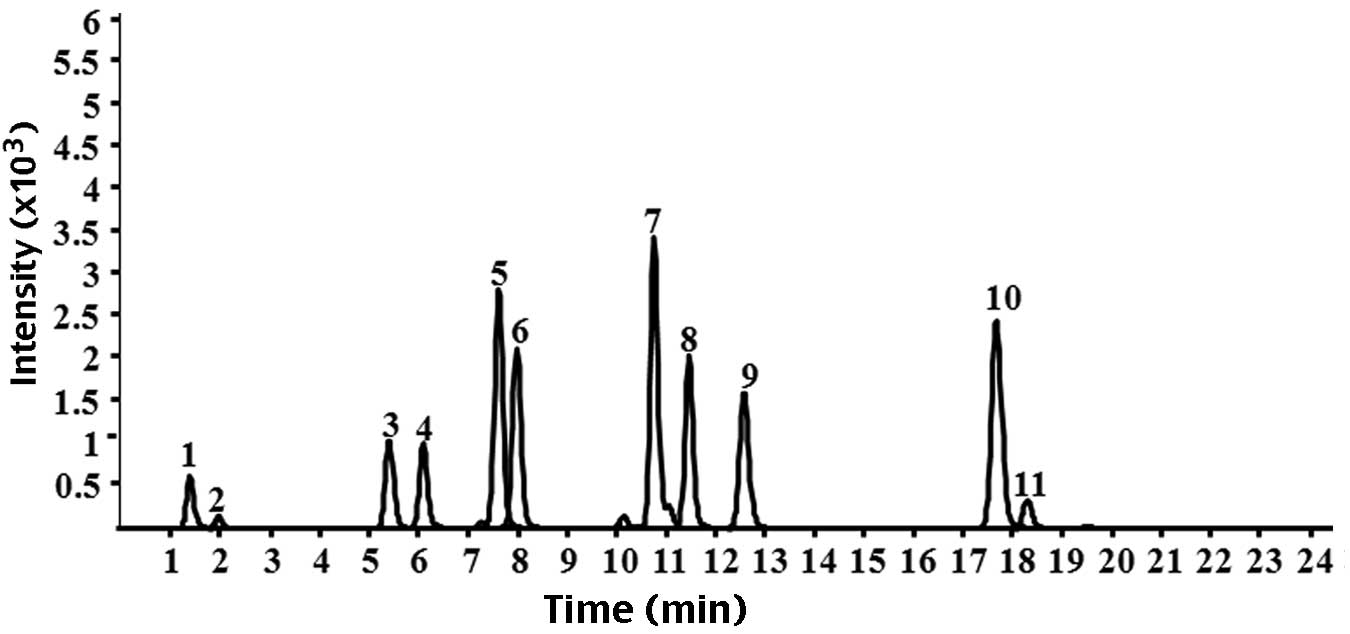
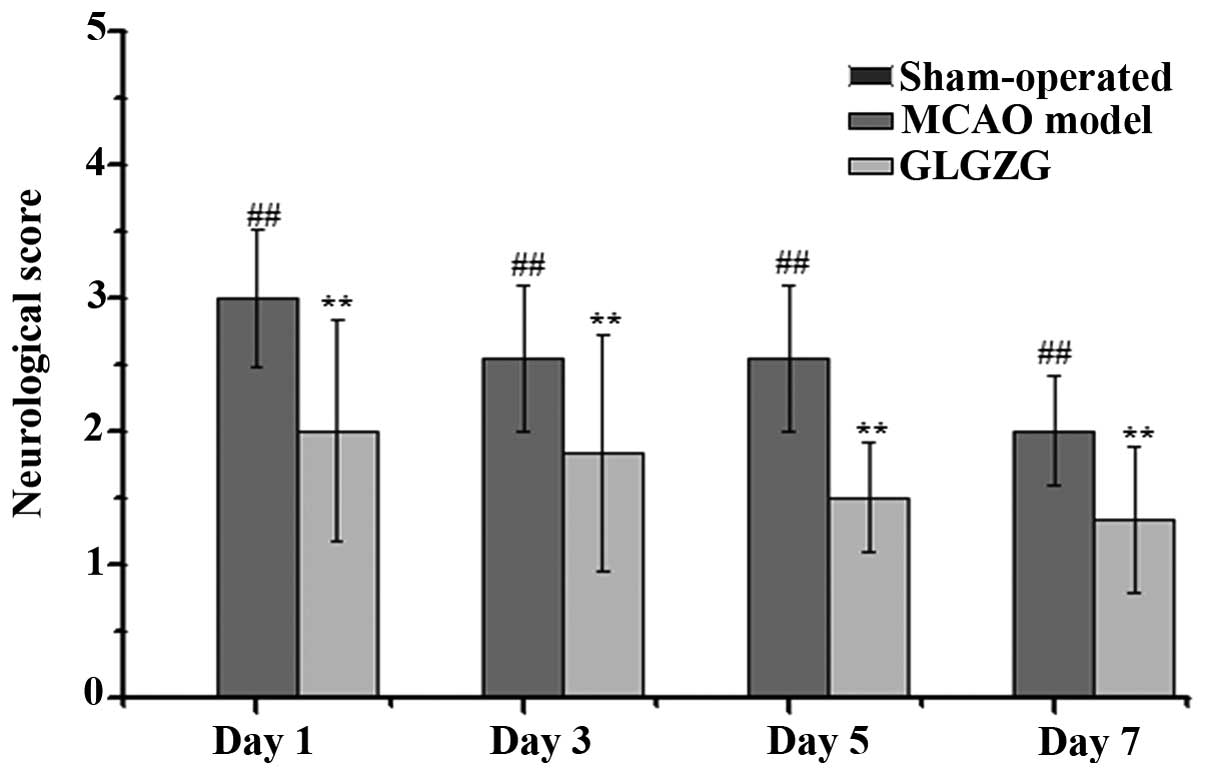
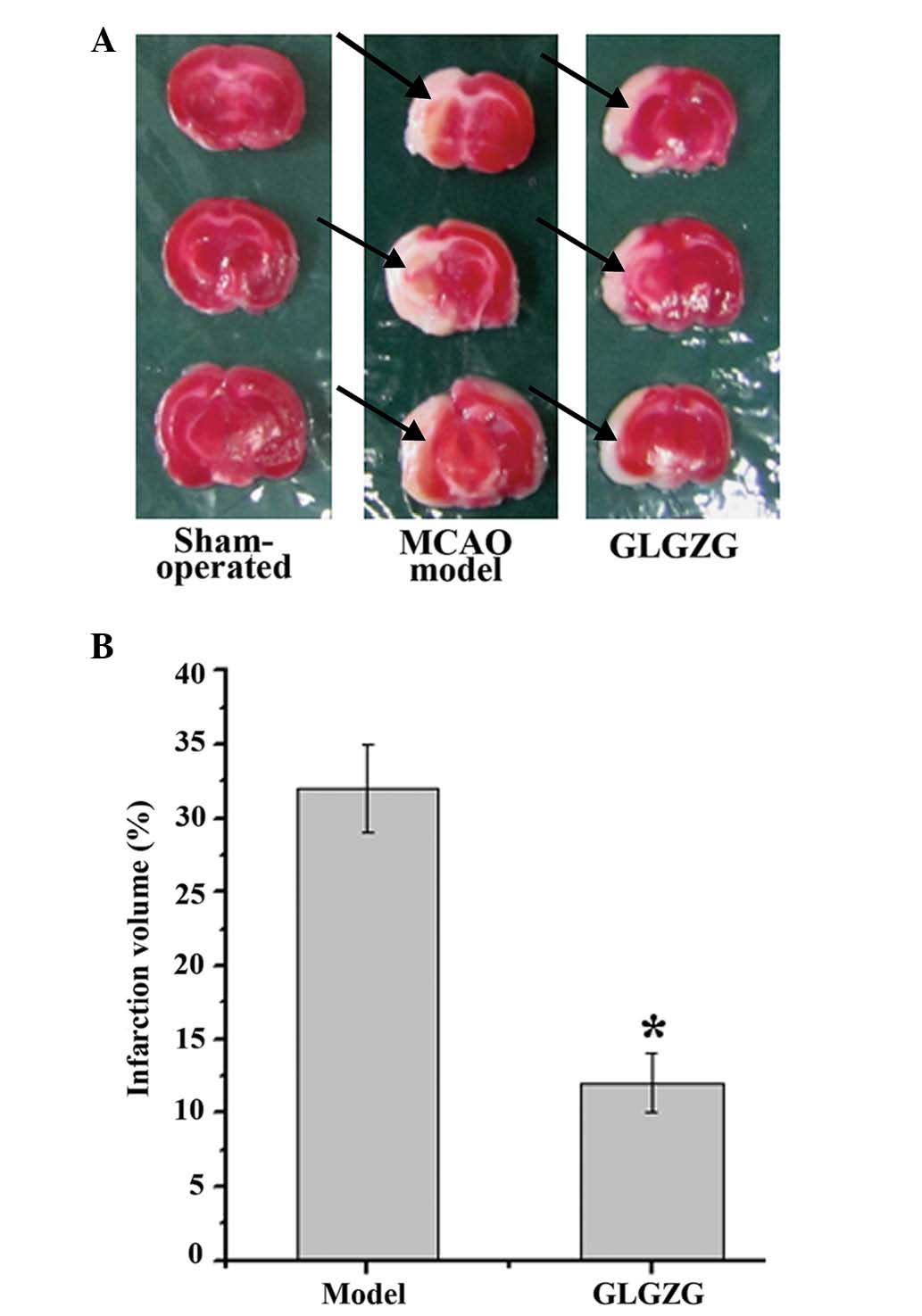
|
1
|
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, et al:
Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics - 2010
update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation.
121:948–954. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu M, Wu BO, Wang WZ, Lee LM, Zhang SH
and Kong LZ: Stroke in China: epidemiology, prevention, and
management strategies. Lancet Neurolo. 6:456–464. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
(CDC): Prevalence of disabilities and associated health conditions
among adults - United States, 1999. MMWR Morb Mortals Wkly Rep.
50:120–125. 2001.
|
|
4
|
The World Health Report 2002. World Health
Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2002
|
|
5
|
Del Zoppo GJ, Saver JL, Jauch EC and Adams
HP Jr; American Heart Association Stroke Council: Expansion of the
time window for treatment of acute ischemic stroke with intravenous
tissue plasminogen activator: a science advisory from the American
Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke.
40:2945–2948. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ballabh P, Braun A and Nedergaard M: The
blood-brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation, and
clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis. 16:1–13. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Begley DJ and Brightman MW: Structural and
functional aspects of the blood-brain barrier. Prog Drug Res.
61:39–78. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sandoval KE and Witt KA: Blood-brain
barrier tight junction permeability and ischemic stroke. Neurobiol
Dis. 32:200–219. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Strbian D, Durukan A, Pitkonen M,
Marinkovic I, Tatlisumak E, Pedrono E, et al: The blood-brain
barrier is continuously open for several weeks following transient
focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 153:175–181. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang ZJ, Jinkui YL, Lin Y, Yang PJ, Hou
XM and Yang YW: Synopsis of Golden Chamber. Macmillan Press;
Beijing, China: pp. 203–204. 2008, In Chinese.
|
|
11
|
Sun X: Research on formula treating
paralysis and spasticity from ‘treatise on febrile and
miscellaneous diseases’. Zhongguo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi.
8:644–645. 2010.In Chinese.
|
|
12
|
Yang C, Chen L and Tao J: New usage of a
classical formula-Gua Lou Gui Zhi decoction. Liaoning J Tradit Chin
Med. 8:166–167. 2010.
|
|
13
|
Zhang L and Ai H: Effects of Gua Lou Gui
Zhi decoction on c-fos and c-jun in epileptic rats. Sichuan Hua Xi
Zhong Yi Yao Yan Jiu Suo. 23:21–22. 2005.
|
|
14
|
Hu H, Li Z, Zhu X, Lin R, Lin J, Peng J,
Tao J and Chen L: Gua Lou Gui Zhi decoction suppresses LPS-induced
activation of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway in BV-2 murine microglial
cells. Int J Mol. 31:1327–1332. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Hu H, Li Z, Zhu X, Lin R, Lin J, Peng J,
Tao J and Chen L: GuaLou GuiZhi decoction inhibits LPS-induced
microglial cell motility through the MAPK signaling pathway. In J
Mol Med. 32:1281–1286. 2013.
|
|
16
|
Li ZF, Lin RH, Mao JJ, Hu HX, Zhu XQ, Chen
WL and Chen LD: Protective effect of Gualou Guizhi decoction on
BV-2 cells injured by glutamate. Journal of Fujian University of
Traditional Chinese Medicine. 23:14–17. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Huang J, Tao J, Xue XH, et al: Gua Lou Gui
Zhi decoction exerts neuroprotective effects on post-stroke
spasticity via the modulation of glutamate levels and AMPA receptor
expression. Int J Mol Med. 31:841–848. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen X, Li H, Huang M, Huang M, et al:
Effect of Gua Lou Gui Zhi decoction on focal cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury through regulating the expression of
excitatory amino acids and their receptors. Mol Med Rep.
10:248–254. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Germano SM,
Nishimura MC, Davis RL and Bartkowski HM: Evaluation of
2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium-chloride as a stain for detection and
quantification of experimental cerebralin farction in rats. Stroke.
17:1304–1308. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hou SZ, Li Y, Zhu XL, Wang ZY, Wang X and
Xu Y: Ameliorative effects of diammonium glycyrrhizinate on
inflammation in focal cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury. Brain
Res. 1447:20–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Weiss N, Miller F, Cazaubon S and Couraud
PO: The blood-brain barrier in brain homeostasis and neurological
diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1788:842–857. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhan C and Yang J: Protective effects of
isoliquiritigenin in transient middle cerebral artery
occlusion-induced focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Pharmacol Res.
53:303–309. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kape R, Parniske M, Brandt S and Werner D:
Isoliquiritigenin, a strong nod gene- and glyceollin
resistance-inducing flavonoid from soybean root exudate. Appl
Environ Microbiol. 58:1705–1710. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu DZ, Xie KQ, Ji XQ, Ye Y, Jiang CL, et
al: Neuroprotective effect of paeoniflorin on cerebral ischemic rat
by activating adenosine A1 receptor in a manner different from its
classical agonists. Br J Pharmacol. 146:604–611. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mao QQ, Zhong XM, Feng CR, Pan AJ, Li ZY,
et al: Protective effects of paeoniflorin against glutamate-induced
neurotoxicity in PC12 cells via antioxidant mechanisms and
Ca(2+) antagonism. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 30:1059–1066.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo RB, Wang GF, Zhao AP, Gu J, Sun XL and
Hu G: Paeoniflorin protects against ischemia-induced brain damages
in rats via inhibiting MAPKs/NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses.
PLoS ONE. 7:e497012012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kim SW, Lim CM, Lee HK and Lee JK: The use
of Stronger NeoMinophagen C, a glycyrrhizin-containing preparation,
in robust neuroprotection in the postischemic brain. Anat Cell
Biol. 44:304–313. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gong G, Xiang L, Yuan L, et al: Protective
effect of glycyrrhizin, a direct HMGB1 inhibitor, on focal cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, and
apoptosis in rats. PLoS One. 9:e894502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun YX, Tang Y, Wu AL, Liu T, Dai XL,
Zheng QS and Wang ZB: Neuroprotective effect of liquiritin against
focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in mice via its antioxidant and
antiapoptosis properties. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 12:1051–1060. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|